Signed-off-by: Glenn Jocher <glenn.jocher@ultralytics.com> Co-authored-by: UltralyticsAssistant <web@ultralytics.com>
159 lines
9.7 KiB
Markdown
159 lines
9.7 KiB
Markdown
---
|
|
comments: true
|
|
description: Explore Meituan YOLOv6, a top-tier object detector balancing speed and accuracy. Learn about its unique features and performance metrics on Ultralytics Docs.
|
|
keywords: Meituan YOLOv6, object detection, real-time applications, BiC module, Anchor-Aided Training, COCO dataset, high-performance models, Ultralytics Docs
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
# Meituan YOLOv6
|
|
|
|
## Overview
|
|
|
|
[Meituan](https://about.meituan.com/) YOLOv6 is a cutting-edge object detector that offers remarkable balance between speed and accuracy, making it a popular choice for real-time applications. This model introduces several notable enhancements on its architecture and training scheme, including the implementation of a Bi-directional Concatenation (BiC) module, an anchor-aided training (AAT) strategy, and an improved backbone and neck design for state-of-the-art accuracy on the COCO dataset.
|
|
|
|

|
|
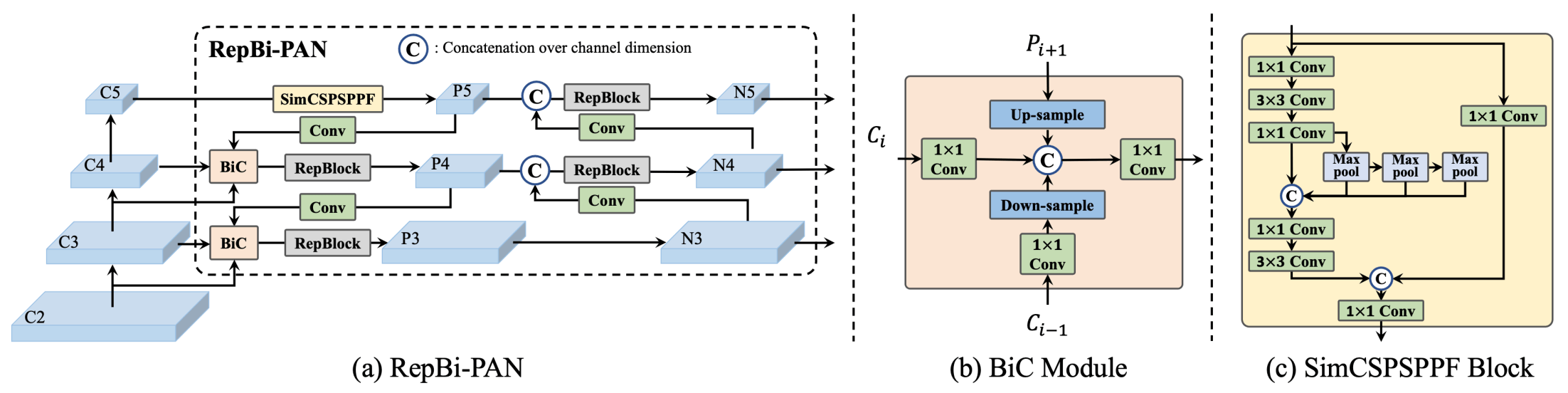 **Overview of YOLOv6.** Model architecture diagram showing the redesigned network components and training strategies that have led to significant performance improvements. (a) The neck of YOLOv6 (N and S are shown). Note for M/L, RepBlocks is replaced with CSPStackRep. (b) The structure of a BiC module. (c) A SimCSPSPPF block. ([source](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.05586.pdf)).
|
|
|
|
### Key Features
|
|
|
|
- **Bidirectional Concatenation (BiC) Module:** YOLOv6 introduces a BiC module in the neck of the detector, enhancing localization signals and delivering performance gains with negligible speed degradation.
|
|
- **Anchor-Aided Training (AAT) Strategy:** This model proposes AAT to enjoy the benefits of both anchor-based and anchor-free paradigms without compromising inference efficiency.
|
|
- **Enhanced Backbone and Neck Design:** By deepening YOLOv6 to include another stage in the backbone and neck, this model achieves state-of-the-art performance on the COCO dataset at high-resolution input.
|
|
- **Self-Distillation Strategy:** A new self-distillation strategy is implemented to boost the performance of smaller models of YOLOv6, enhancing the auxiliary regression branch during training and removing it at inference to avoid a marked speed decline.
|
|
|
|
## Performance Metrics
|
|
|
|
YOLOv6 provides various pre-trained models with different scales:
|
|
|
|
- YOLOv6-N: 37.5% AP on COCO val2017 at 1187 FPS with NVIDIA Tesla T4 GPU.
|
|
- YOLOv6-S: 45.0% AP at 484 FPS.
|
|
- YOLOv6-M: 50.0% AP at 226 FPS.
|
|
- YOLOv6-L: 52.8% AP at 116 FPS.
|
|
- YOLOv6-L6: State-of-the-art accuracy in real-time.
|
|
|
|
YOLOv6 also provides quantized models for different precisions and models optimized for mobile platforms.
|
|
|
|
## Usage Examples
|
|
|
|
This example provides simple YOLOv6 training and inference examples. For full documentation on these and other [modes](../modes/index.md) see the [Predict](../modes/predict.md), [Train](../modes/train.md), [Val](../modes/val.md) and [Export](../modes/export.md) docs pages.
|
|
|
|
!!! Example
|
|
|
|
=== "Python"
|
|
|
|
PyTorch pretrained `*.pt` models as well as configuration `*.yaml` files can be passed to the `YOLO()` class to create a model instance in python:
|
|
|
|
```python
|
|
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
|
|
|
# Build a YOLOv6n model from scratch
|
|
model = YOLO("yolov6n.yaml")
|
|
|
|
# Display model information (optional)
|
|
model.info()
|
|
|
|
# Train the model on the COCO8 example dataset for 100 epochs
|
|
results = model.train(data="coco8.yaml", epochs=100, imgsz=640)
|
|
|
|
# Run inference with the YOLOv6n model on the 'bus.jpg' image
|
|
results = model("path/to/bus.jpg")
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
=== "CLI"
|
|
|
|
CLI commands are available to directly run the models:
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
# Build a YOLOv6n model from scratch and train it on the COCO8 example dataset for 100 epochs
|
|
yolo train model=yolov6n.yaml data=coco8.yaml epochs=100 imgsz=640
|
|
|
|
# Build a YOLOv6n model from scratch and run inference on the 'bus.jpg' image
|
|
yolo predict model=yolov6n.yaml source=path/to/bus.jpg
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
## Supported Tasks and Modes
|
|
|
|
The YOLOv6 series offers a range of models, each optimized for high-performance [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md). These models cater to varying computational needs and accuracy requirements, making them versatile for a wide array of applications.
|
|
|
|
| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
|
|
| ---------- | ------------------- | -------------------------------------- | --------- | ---------- | -------- | ------ |
|
|
| YOLOv6-N | `yolov6-n.pt` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
|
| YOLOv6-S | `yolov6-s.pt` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
|
| YOLOv6-M | `yolov6-m.pt` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
|
| YOLOv6-L | `yolov6-l.pt` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
|
| YOLOv6-L6 | `yolov6-l6.pt` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
|
|
|
This table provides a detailed overview of the YOLOv6 model variants, highlighting their capabilities in object detection tasks and their compatibility with various operational modes such as [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md). This comprehensive support ensures that users can fully leverage the capabilities of YOLOv6 models in a broad range of object detection scenarios.
|
|
|
|
## Citations and Acknowledgements
|
|
|
|
We would like to acknowledge the authors for their significant contributions in the field of real-time object detection:
|
|
|
|
!!! Quote ""
|
|
|
|
=== "BibTeX"
|
|
|
|
```bibtex
|
|
@misc{li2023yolov6,
|
|
title={YOLOv6 v3.0: A Full-Scale Reloading},
|
|
author={Chuyi Li and Lulu Li and Yifei Geng and Hongliang Jiang and Meng Cheng and Bo Zhang and Zaidan Ke and Xiaoming Xu and Xiangxiang Chu},
|
|
year={2023},
|
|
eprint={2301.05586},
|
|
archivePrefix={arXiv},
|
|
primaryClass={cs.CV}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The original YOLOv6 paper can be found on [arXiv](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.05586). The authors have made their work publicly available, and the codebase can be accessed on [GitHub](https://github.com/meituan/YOLOv6). We appreciate their efforts in advancing the field and making their work accessible to the broader community.
|
|
|
|
## FAQ
|
|
|
|
### What is Meituan YOLOv6 and how does it differ from other YOLO models?
|
|
|
|
Meituan YOLOv6 is a highly advanced object detection model that balances speed and accuracy, making it ideal for real-time applications. This model features unique enhancements such as the Bidirectional Concatenation (BiC) module, Anchor-Aided Training (AAT) strategy, and an improved backbone and neck design, providing state-of-the-art performance on the COCO dataset. Unlike prior YOLO models, YOLOv6 incorporates these innovative strategies to enhance both inference speed and detection accuracy.
|
|
|
|
### How do I use the YOLOv6 model in a Python script?
|
|
|
|
Using the YOLOv6 model in a Python script is straightforward. Here is a sample code snippet to get you started:
|
|
|
|
```python
|
|
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
|
|
|
# Build a YOLOv6n model from scratch
|
|
model = YOLO("yolov6n.yaml")
|
|
|
|
# Display model information (optional)
|
|
model.info()
|
|
|
|
# Train the model on the COCO8 example dataset for 100 epochs
|
|
results = model.train(data="coco8.yaml", epochs=100, imgsz=640)
|
|
|
|
# Run inference with the YOLOv6n model on the 'bus.jpg' image
|
|
results = model("path/to/bus.jpg")
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
For more detailed examples and documentation, visit the [Train](../modes/train.md) and [Predict](../modes/predict.md) pages.
|
|
|
|
### What are the performance metrics for different scales of YOLOv6 models?
|
|
|
|
YOLOv6 offers pretrained models in various scales with the following performance metrics on the COCO val2017 dataset:
|
|
|
|
- **YOLOv6-N**: 37.5% AP at 1187 FPS using an NVIDIA Tesla T4 GPU
|
|
- **YOLOv6-S**: 45.0% AP at 484 FPS
|
|
- **YOLOv6-M**: 50.0% AP at 226 FPS
|
|
- **YOLOv6-L**: 52.8% AP at 116 FPS
|
|
- **YOLOv6-L6**: State-of-the-art accuracy for real-time
|
|
|
|
These metrics make YOLOv6 a versatile choice for both high-accuracy and high-speed applications.
|
|
|
|
### What are the unique features of YOLOv6 that improve its performance?
|
|
|
|
YOLOv6 introduces several key features that enhance its performance:
|
|
|
|
- **Bidirectional Concatenation (BiC) Module**: Improves localization signals and offers performance gains with minimal speed degradation.
|
|
- **Anchor-Aided Training (AAT) Strategy**: Combines the benefits of anchor-based and anchor-free methods for better efficiency without sacrificing inference speed.
|
|
- **Enhanced Backbone and Neck Design**: Adds additional stages to the backbone and neck, achieving state-of-the-art results on high-resolution inputs.
|
|
- **Self-Distillation Strategy**: Boosts smaller model performance by refining the auxiliary regression branch during training and removing it during inference to maintain speed.
|
|
|
|
### How can YOLOv6 be used for mobile and embedded applications?
|
|
|
|
YOLOv6 supports quantized models for different precisions and models optimized for mobile platforms, making it suitable for applications requiring low-latency and energy-efficient computations. For deployment on mobile and edge devices, you can explore conversion to formats like TFLite and ONNX, as detailed in the [Export](../modes/export.md) documentation. Quantized models ensure high performance even on resource-constrained devices, enabling real-time object detection in mobile and IoT applications.
|