Signed-off-by: Glenn Jocher <glenn.jocher@ultralytics.com> Co-authored-by: UltralyticsAssistant <web@ultralytics.com>
9.8 KiB
| comments | description | keywords |
|---|---|---|
| true | Explore Baidu's RT-DETR, a Vision Transformer-based real-time object detector offering high accuracy and adaptable inference speed. Learn more with Ultralytics. | RT-DETR, Baidu, Vision Transformer, real-time object detection, PaddlePaddle, Ultralytics, pre-trained models, AI, machine learning, computer vision |
Baidu's RT-DETR: A Vision Transformer-Based Real-Time Object Detector
Overview
Real-Time Detection Transformer (RT-DETR), developed by Baidu, is a cutting-edge end-to-end object detector that provides real-time performance while maintaining high accuracy. It is based on the idea of DETR (the NMS-free framework), meanwhile introducing conv-based backbone and an efficient hybrid encoder to gain real-time speed. RT-DETR efficiently processes multiscale features by decoupling intra-scale interaction and cross-scale fusion. The model is highly adaptable, supporting flexible adjustment of inference speed using different decoder layers without retraining. RT-DETR excels on accelerated backends like CUDA with TensorRT, outperforming many other real-time object detectors.
Watch: Real-Time Detection Transformer (RT-DETR)
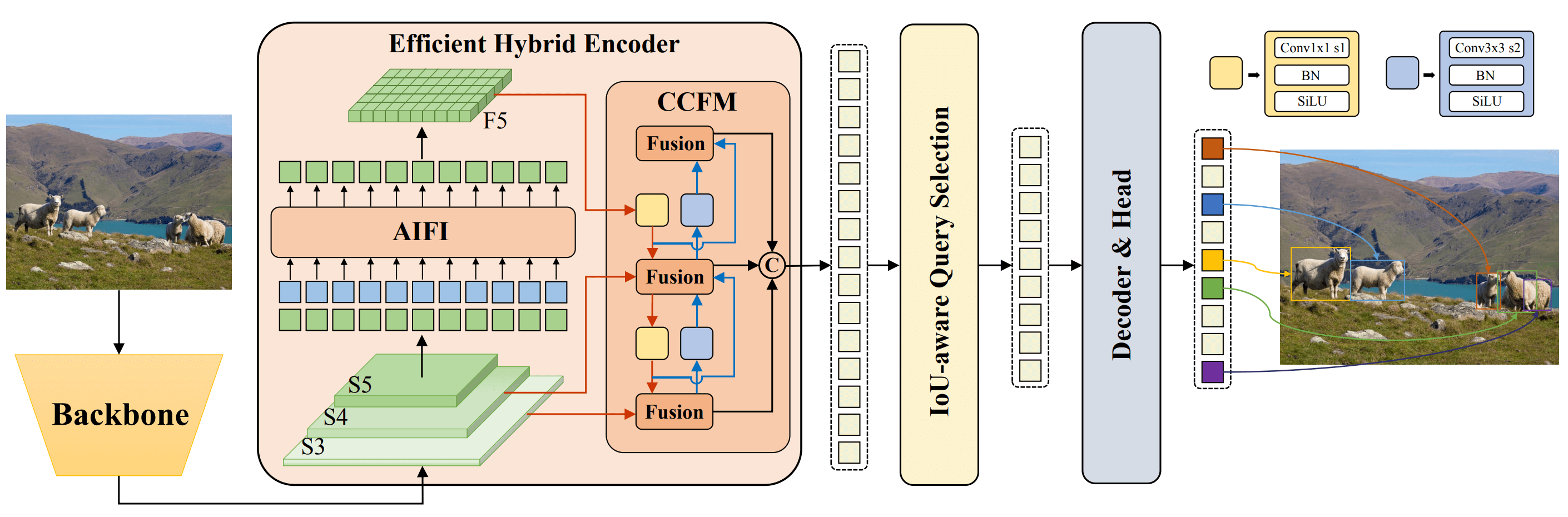 Overview of Baidu's RT-DETR. The RT-DETR model architecture diagram shows the last three stages of the backbone {S3, S4, S5} as the input to the encoder. The efficient hybrid encoder transforms multiscale features into a sequence of image features through intrascale feature interaction (AIFI) and cross-scale feature-fusion module (CCFM). The IoU-aware query selection is employed to select a fixed number of image features to serve as initial object queries for the decoder. Finally, the decoder with auxiliary prediction heads iteratively optimizes object queries to generate boxes and confidence scores (source).
Overview of Baidu's RT-DETR. The RT-DETR model architecture diagram shows the last three stages of the backbone {S3, S4, S5} as the input to the encoder. The efficient hybrid encoder transforms multiscale features into a sequence of image features through intrascale feature interaction (AIFI) and cross-scale feature-fusion module (CCFM). The IoU-aware query selection is employed to select a fixed number of image features to serve as initial object queries for the decoder. Finally, the decoder with auxiliary prediction heads iteratively optimizes object queries to generate boxes and confidence scores (source).
Key Features
- Efficient Hybrid Encoder: Baidu's RT-DETR uses an efficient hybrid encoder that processes multiscale features by decoupling intra-scale interaction and cross-scale fusion. This unique Vision Transformers-based design reduces computational costs and allows for real-time object detection.
- IoU-aware Query Selection: Baidu's RT-DETR improves object query initialization by utilizing IoU-aware query selection. This allows the model to focus on the most relevant objects in the scene, enhancing the detection accuracy.
- Adaptable Inference Speed: Baidu's RT-DETR supports flexible adjustments of inference speed by using different decoder layers without the need for retraining. This adaptability facilitates practical application in various real-time object detection scenarios.
Pre-trained Models
The Ultralytics Python API provides pre-trained PaddlePaddle RT-DETR models with different scales:
- RT-DETR-L: 53.0% AP on COCO val2017, 114 FPS on T4 GPU
- RT-DETR-X: 54.8% AP on COCO val2017, 74 FPS on T4 GPU
Usage Examples
This example provides simple RT-DETR training and inference examples. For full documentation on these and other modes see the Predict, Train, Val and Export docs pages.
!!! Example
=== "Python"
```python
from ultralytics import RTDETR
# Load a COCO-pretrained RT-DETR-l model
model = RTDETR("rtdetr-l.pt")
# Display model information (optional)
model.info()
# Train the model on the COCO8 example dataset for 100 epochs
results = model.train(data="coco8.yaml", epochs=100, imgsz=640)
# Run inference with the RT-DETR-l model on the 'bus.jpg' image
results = model("path/to/bus.jpg")
```
=== "CLI"
```bash
# Load a COCO-pretrained RT-DETR-l model and train it on the COCO8 example dataset for 100 epochs
yolo train model=rtdetr-l.pt data=coco8.yaml epochs=100 imgsz=640
# Load a COCO-pretrained RT-DETR-l model and run inference on the 'bus.jpg' image
yolo predict model=rtdetr-l.pt source=path/to/bus.jpg
```
Supported Tasks and Modes
This table presents the model types, the specific pre-trained weights, the tasks supported by each model, and the various modes (Train , Val, Predict, Export) that are supported, indicated by ✅ emojis.
| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT-DETR Large | rtdetr-l.pt | Object Detection | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| RT-DETR Extra-Large | rtdetr-x.pt | Object Detection | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
Citations and Acknowledgements
If you use Baidu's RT-DETR in your research or development work, please cite the original paper:
!!! Quote ""
=== "BibTeX"
```bibtex
@misc{lv2023detrs,
title={DETRs Beat YOLOs on Real-time Object Detection},
author={Wenyu Lv and Shangliang Xu and Yian Zhao and Guanzhong Wang and Jinman Wei and Cheng Cui and Yuning Du and Qingqing Dang and Yi Liu},
year={2023},
eprint={2304.08069},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}
```
We would like to acknowledge Baidu and the PaddlePaddle team for creating and maintaining this valuable resource for the computer vision community. Their contribution to the field with the development of the Vision Transformers-based real-time object detector, RT-DETR, is greatly appreciated.
FAQ
What is Baidu's RT-DETR and how does it work?
Baidu's RT-DETR (Real-Time Detection Transformer) is an end-to-end vision transformer-based object detector designed for real-time performance without compromising accuracy. Unlike traditional object detectors, it employs a convolutional backbone with an efficient hybrid encoder that handles multiscale feature processing by decoupling intra-scale interaction and cross-scale fusion. The model also utilizes IoU-aware query selection for initializing object queries, which improves detection accuracy. For flexible applications, the inference speed can be adjusted using different decoder layers without retraining. For more details, you can check out the original paper.
How can I use a pre-trained RT-DETR model with Ultralytics?
Using a pre-trained RT-DETR model with the Ultralytics Python API is straightforward. Here's an example:
from ultralytics import RTDETR
# Load a COCO-pretrained RT-DETR-l model
model = RTDETR("rtdetr-l.pt")
# Display model information (optional)
model.info()
# Train the model on the COCO8 example dataset for 100 epochs
results = model.train(data="coco8.yaml", epochs=100, imgsz=640)
# Run inference with the RT-DETR-l model on the 'bus.jpg' image
results = model("path/to/bus.jpg")
You can find more details on specific modes like Predict, Train, and Export.
What are the key features of RT-DETR that make it unique?
The RT-DETR model has several key features that set it apart:
- Efficient Hybrid Encoder: This design processes multiscale features by decoupling intra-scale interaction and cross-scale fusion, reducing computational costs.
- IoU-aware Query Selection: Enhances object query initialization, focusing on the most relevant objects for higher detection accuracy.
- Adaptable Inference Speed: The model supports flexible adjustments of inference speed by using different decoder layers without retraining, making it highly adaptable for various real-time object detection scenarios.
What performance can I expect from RT-DETR on different scales?
The Ultralytics Python API provides pre-trained PaddlePaddle RT-DETR models in different scales, offering notable performance metrics:
- RT-DETR-L: Achieves 53.0% AP on COCO val2017 and runs at 114 FPS on a T4 GPU.
- RT-DETR-X: Achieves 54.8% AP on COCO val2017 and runs at 74 FPS on a T4 GPU.
This makes the RT-DETR models highly efficient for real-time applications requiring both speed and accuracy.
How can I acknowledge Baidu's contribution if I use RT-DETR in my research?
If you use Baidu's RT-DETR in your research or development work, you should cite the original paper. Here is the BibTeX entry for your reference:
@misc{lv2023detrs,
title={DETRs Beat YOLOs on Real-time Object Detection},
author={Wenyu Lv and Shangliang Xu and Yian Zhao and Guanzhong Wang and Jinman Wei and Cheng Cui and Yuning Du and Qingqing Dang and Yi Liu},
year={2023},
eprint={2304.08069},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}
Additionally, acknowledge Baidu and the PaddlePaddle team for creating and maintaining this valuable resource for the computer vision community.