Optimize Docs images (#15900)
Signed-off-by: UltralyticsAssistant <web@ultralytics.com> Co-authored-by: UltralyticsAssistant <web@ultralytics.com> Co-authored-by: Glenn Jocher <glenn.jocher@ultralytics.com>
This commit is contained in:
parent
0f9f7b806c
commit
cfebb5f26b
174 changed files with 537 additions and 537 deletions
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ This guide will take you through the process of deploying YOLOv8 PyTorch models
|
|||
## Amazon SageMaker
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://d1.awsstatic.com/sagemaker/Amazon-SageMaker-Studio%402x.aa0572ebf4ea9237571644c7f853c914c1d0c985.png" alt="Amazon SageMaker Overview">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/amazon-sagemaker-overview.avif" alt="Amazon SageMaker Overview">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
[Amazon SageMaker](https://aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/) is a machine learning service from Amazon Web Services (AWS) that simplifies the process of building, training, and deploying machine learning models. It provides a broad range of tools for handling various aspects of machine learning workflows. This includes automated features for tuning models, options for training models at scale, and straightforward methods for deploying models into production. SageMaker supports popular machine learning frameworks, offering the flexibility needed for diverse projects. Its features also cover data labeling, workflow management, and performance analysis.
|
||||
|
|
@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ This guide will take you through the process of deploying YOLOv8 PyTorch models
|
|||
Deploying YOLOv8 on Amazon SageMaker lets you use its managed environment for real-time inference and take advantage of features like autoscaling. Take a look at the AWS architecture below.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://d2908q01vomqb2.cloudfront.net/f1f836cb4ea6efb2a0b1b99f41ad8b103eff4b59/2023/02/28/ML13353_AWSArchitecture-1024x605.png" alt="AWS Architecture">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/aws-architecture.avif" alt="AWS Architecture">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Setup Your AWS Environment
|
||||
|
|
@ -147,7 +147,7 @@ Now that your YOLOv8 model is deployed, it's important to test its performance a
|
|||
- Run the Test Notebook: Follow the instructions within the notebook to test the deployed SageMaker endpoint. This includes sending an image to the endpoint and running inferences. Then, you'll plot the output to visualize the model's performance and accuracy, as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://d2908q01vomqb2.cloudfront.net/f1f836cb4ea6efb2a0b1b99f41ad8b103eff4b59/2023/02/28/ML13353_InferenceOutput.png" alt="Testing Results YOLOv8">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/testing-results-yolov8.avif" alt="Testing Results YOLOv8">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
- Clean-Up Resources: The test notebook will also guide you through the process of cleaning up the endpoint and the hosted model. This is an important step to manage costs and resources effectively, especially if you do not plan to use the deployed model immediately.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ MLOps bridges the gap between creating and deploying machine learning models in
|
|||
## ClearML
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://clear.ml/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/DataOps@2x-1.png" alt="ClearML Overview">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/clearml-overview.avif" alt="ClearML Overview">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
[ClearML](https://clear.ml/) is an innovative open-source MLOps platform that is skillfully designed to automate, monitor, and orchestrate machine learning workflows. Its key features include automated logging of all training and inference data for full experiment reproducibility, an intuitive web UI for easy data visualization and analysis, advanced hyperparameter optimization algorithms, and robust model management for efficient deployment across various platforms.
|
||||
|
|
@ -175,7 +175,7 @@ This setup is applicable to cloud VMs, local GPUs, or laptops. ClearML Autoscale
|
|||
ClearML's user-friendly interface allows easy cloning, editing, and enqueuing of tasks. Users can clone an existing experiment, adjust parameters or other details through the UI, and enqueue the task for execution. This streamlined process ensures that the ClearML Agent executing the task uses updated configurations, making it ideal for iterative experimentation and model fine-tuning.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center"><br>
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://clear.ml/docs/latest/assets/images/integrations_yolov5-2483adea91df4d41bfdf1a37d28864d4.gif" alt="Cloning, Editing, and Enqueuing with ClearML">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/cloning-editing-enqueuing-clearml.avif" alt="Cloning, Editing, and Enqueuing with ClearML">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
## Summary
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -96,7 +96,7 @@ Let's dive into what you'll see on the Comet ML dashboard once your YOLOv8 model
|
|||
The experiment panels section of the Comet ML dashboard organize and present the different runs and their metrics, such as segment mask loss, class loss, precision, and mean average precision.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://www.comet.com/site/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/1_I20ts7j995-D86-BvtWYaw.png" alt="Comet ML Overview">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/comet-ml-dashboard-overview.avif" alt="Comet ML Overview">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
**Metrics**
|
||||
|
|
@ -104,7 +104,7 @@ The experiment panels section of the Comet ML dashboard organize and present the
|
|||
In the metrics section, you have the option to examine the metrics in a tabular format as well, which is displayed in a dedicated pane as illustrated here.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://www.comet.com/site/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/1_FNAkQKq9o02wRRSCJh4gDw.png" alt="Comet ML Overview">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/comet-ml-metrics-tabular.avif" alt="Comet ML Overview">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
**Interactive Confusion Matrix**
|
||||
|
|
@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ In the metrics section, you have the option to examine the metrics in a tabular
|
|||
The confusion matrix, found in the Confusion Matrix tab, provides an interactive way to assess the model's classification accuracy. It details the correct and incorrect predictions, allowing you to understand the model's strengths and weaknesses.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://www.comet.com/site/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/1_h-Nf-tCm8HbsvVK0d6rTng-1500x768.png" alt="Comet ML Overview">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/comet-ml-interactive-confusion-matrix.avif" alt="Comet ML Overview">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
**System Metrics**
|
||||
|
|
@ -120,7 +120,7 @@ The confusion matrix, found in the Confusion Matrix tab, provides an interactive
|
|||
Comet ML logs system metrics to help identify any bottlenecks in the training process. It includes metrics such as GPU utilization, GPU memory usage, CPU utilization, and RAM usage. These are essential for monitoring the efficiency of resource usage during model training.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://www.comet.com/site/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/1_B7dmqqUMyOtyH9XsVMr58Q.png" alt="Comet ML Overview">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/comet-ml-system-metrics.avif" alt="Comet ML Overview">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
## Customizing Comet ML Logging
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ The CoreML export format allows you to optimize your [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https:
|
|||
## CoreML
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://github.com/RizwanMunawar/ultralytics/assets/62513924/0c757e32-3a9f-422e-9526-efde5f663ccd" alt="CoreML Overview">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/coreml-overview.avif" alt="CoreML Overview">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
[CoreML](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/coreml) is Apple's foundational machine learning framework that builds upon Accelerate, BNNS, and Metal Performance Shaders. It provides a machine-learning model format that seamlessly integrates into iOS applications and supports tasks such as image analysis, natural language processing, audio-to-text conversion, and sound analysis.
|
||||
|
|
@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ Apple's CoreML framework offers robust features for on-device machine learning.
|
|||
- **Comprehensive Model Support**: Converts and runs models from popular frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, scikit-learn, XGBoost, and LibSVM.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://apple.github.io/coremltools/docs-guides/_images/introduction-coremltools.png" alt="CoreML Supported Models">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/coreml-supported-models.avif" alt="CoreML Supported Models">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
- **On-device Machine Learning**: Ensures data privacy and swift processing by executing models directly on the user's device, eliminating the need for network connectivity.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ Integrating DVCLive with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://ultralytics.com) transform
|
|||
## DVCLive
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://dvc.org/static/6daeb07124bab895bea3f4930e3116e9/aa619/dvclive-studio.webp" alt="DVCLive Overview">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/dvclive-overview.avif" alt="DVCLive Overview">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
[DVCLive](https://dvc.org/doc/dvclive), developed by DVC, is an innovative open-source tool for experiment tracking in machine learning. Integrating seamlessly with Git and DVC, it automates the logging of crucial experiment data like model parameters and training metrics. Designed for simplicity, DVCLive enables effortless comparison and analysis of multiple runs, enhancing the efficiency of machine learning projects with intuitive data visualization and analysis tools.
|
||||
|
|
@ -138,7 +138,7 @@ dvc plots diff $(dvc exp list --names-only)
|
|||
After executing this command, DVC generates plots comparing the metrics across different experiments, which are saved as HTML files. Below is an example image illustrating typical plots generated by this process. The image showcases various graphs, including those representing mAP, recall, precision, loss values, and more, providing a visual overview of key performance metrics:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://dvc.org/yolo-studio-plots-0f1243f5a0c5ea940a080478de267cba.gif" alt="DVCLive Plots">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/dvclive-comparative-plots.avif" alt="DVCLive Plots">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
### Displaying DVC Plots
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ The export to TFLite Edge TPU format feature allows you to optimize your [Ultral
|
|||
Exporting models to TensorFlow Edge TPU makes machine learning tasks fast and efficient. This technology suits applications with limited power, computing resources, and connectivity. The Edge TPU is a hardware accelerator by Google. It speeds up TensorFlow Lite models on edge devices. The image below shows an example of the process involved.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://coral.ai/static/docs/images/edgetpu/compile-workflow.png" alt="TFLite Edge TPU">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/tflite-edge-tpu-compile-workflow.avif" alt="TFLite Edge TPU">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
The Edge TPU works with quantized models. Quantization makes models smaller and faster without losing much accuracy. It is ideal for the limited resources of edge computing, allowing applications to respond quickly by reducing latency and allowing for quick data processing locally, without cloud dependency. Local processing also keeps user data private and secure since it's not sent to a remote server.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ Training YOLOv8 models on Google Colab is pretty straightforward. Thanks to the
|
|||
|
||||
Sign in to your Google account and run the notebook's cells to train your model.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Learn how to train a YOLOv8 model with custom data on YouTube with Nicolai. Check out the guide below.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -67,7 +67,7 @@ Now, let's look at some of the standout features that make Google Colab a go-to
|
|||
|
||||
- **Hardware Resources:** Users also switch between different hardware options by modifying the runtime settings as shown below. Google Colab provides access to advanced hardware like Tesla K80 GPUs and TPUs, which are specialized circuits designed specifically for machine learning tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- **Collaboration:** Google Colab makes collaborating and working with other developers easy. You can easily share your notebooks with others and perform edits in real-time.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ This Gradio interface provides an easy and interactive way to perform object det
|
|||
- **Broad Accessibility:** The Gradio web interface can be accessed by anyone, making it an excellent tool for demonstrations, educational purposes, and quick experiments.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="800" alt="Gradio example screenshot" src="https://github.com/RizwanMunawar/ultralytics/assets/26833433/52ee3cd2-ac59-4c27-9084-0fd05c6c33be">
|
||||
<img width="800" alt="Gradio example screenshot" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/gradio-example-screenshot.avif">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
## How to Install the Gradio
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ You can train [Ultralytics YOLOv8 models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly
|
|||
[Watsonx](https://www.ibm.com/watsonx) is IBM's cloud-based platform designed for commercial generative AI and scientific data. IBM Watsonx's three components - watsonx.ai, watsonx.data, and watsonx.governance - come together to create an end-to-end, trustworthy AI platform that can accelerate AI projects aimed at solving business problems. It provides powerful tools for building, training, and [deploying machine learning models](../guides/model-deployment-options.md) and makes it easy to connect with various data sources.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="800" src="https://cdn.stackoverflow.co/images/jo7n4k8s/production/48b67e6aec41f89031a3426cbd1f78322e6776cb-8800x4950.jpg" alt="Overview of IBM Watsonx">
|
||||
<img width="800" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/overview-of-ibm-watsonx.avif" alt="Overview of IBM Watsonx">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Its user-friendly interface and collaborative capabilities streamline the development process and help with efficient model management and deployment. Whether for computer vision, predictive analytics, natural language processing, or other AI applications, IBM Watsonx provides the tools and support needed to drive innovation.
|
||||
|
|
@ -136,7 +136,7 @@ If you see "trash_ICRA19" among the directory's contents, then it has loaded suc
|
|||
We will use the config.yaml file and the contents of the dataset directory to train our object detection model. Here is a sample image from our marine litter data set.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="400" src="https://cf-courses-data.s3.us.cloud-object-storage.appdomain.cloud/sQy6asArOJ2weUuQ_POiVA.jpg" alt="Marine Litter with Bounding Box">
|
||||
<img width="400" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/marine-litter-bounding-box.avif" alt="Marine Litter with Bounding Box">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4: Preprocess the Data
|
||||
|
|
@ -144,13 +144,13 @@ We will use the config.yaml file and the contents of the dataset directory to tr
|
|||
Fortunately, all labels in the marine litter data set are already formatted as YOLO .txt files. However, we need to rearrange the structure of the image and label directories in order to help our model process the image and labels. Right now, our loaded data set directory follows this structure:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="400" src="https://cf-courses-data.s3.us.cloud-object-storage.appdomain.cloud/VfgvRT7vdgkeTQNqVMs_CQ.png" alt="Loaded Dataset Directory">
|
||||
<img width="400" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/marine-litter-bounding-box-1.avif" alt="Loaded Dataset Directory">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
But, YOLO models by default require separate images and labels in subdirectories within the train/val/test split. We need to reorganize the directory into the following structure:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="400" src="https://cf-courses-data.s3.us.cloud-object-storage.appdomain.cloud/uUk1YopS94mytGaCav3ZaQ.png" alt="Yolo Directory Structure">
|
||||
<img width="400" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/yolo-directory-structure.avif" alt="Yolo Directory Structure">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
To reorganize the data set directory, we can run the following script:
|
||||
|
|
@ -297,7 +297,7 @@ The code above displays ten images from the test set with their predicted boundi
|
|||
We can produce visualizations of the model's precision and recall for each class. These visualizations are saved in the home directory, under the train folder. The precision score is displayed in the P_curve.png:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="800" src="https://cf-courses-data.s3.us.cloud-object-storage.appdomain.cloud/EvQpqt4D6VI2And1T86Fww.png" alt="Precision Confidence Curve">
|
||||
<img width="800" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/precision-confidence-curve.avif" alt="Precision Confidence Curve">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
The graph shows an exponential increase in precision as the model's confidence level for predictions increases. However, the model precision has not yet leveled out at a certain confidence level after two epochs.
|
||||
|
|
@ -305,7 +305,7 @@ The graph shows an exponential increase in precision as the model's confidence l
|
|||
The recall graph (R_curve.png) displays an inverse trend:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="800" src="https://cf-courses-data.s3.us.cloud-object-storage.appdomain.cloud/NS0pQDHuEWM-WlpBpxTydw.png" alt="Recall Confidence Curve">
|
||||
<img width="800" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/recall-confidence-curve.avif" alt="Recall Confidence Curve">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike precision, recall moves in the opposite direction, showing greater recall with lower confidence instances and lower recall with higher confidence instances. This is an apt example of the trade-off in precision and recall for classification models.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, machine learning, ML workflows, dataset management, model
|
|||
|
||||
Welcome to the Ultralytics Integrations page! This page provides an overview of our partnerships with various tools and platforms, designed to streamline your machine learning workflows, enhance dataset management, simplify model training, and facilitate efficient deployment.
|
||||
|
||||
<img width="1024" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/raw/main/yolov8/banner-integrations.png" alt="Ultralytics YOLO ecosystem and integrations">
|
||||
<img width="1024" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/ultralytics-yolov8-ecosystem-integrations.avif" alt="Ultralytics YOLO ecosystem and integrations">
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -81,13 +81,13 @@ Navigate to the directory where you saved the notebook file using your terminal.
|
|||
|
||||
Once you've run this command, it will open JupyterLab in your default web browser, as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4: Start Experimenting
|
||||
|
||||
In JupyterLab, open the tutorial.ipynb notebook. You can now start running the cells to explore and experiment with YOLOv8.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
JupyterLab's interactive environment allows you to modify code, visualize outputs, and document your findings all in one place. You can try out different configurations and understand how YOLOv8 works.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -22,15 +22,15 @@ Training YOLOv8 models on Kaggle is simple and efficient, thanks to the platform
|
|||
|
||||
To get started, access the [Kaggle YOLOv8 Notebook](https://www.kaggle.com/code/ultralytics/yolov8). Kaggle's environment comes with pre-installed libraries like TensorFlow and PyTorch, making the setup process hassle-free.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once you sign in to your Kaggle account, you can click on the option to copy and edit the code, select a GPU under the accelerator settings, and run the notebook's cells to begin training your model. For a detailed understanding of the model training process and best practices, refer to our [YOLOv8 Model Training guide](../modes/train.md).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
On the [official YOLOv8 Kaggle notebook page](https://www.kaggle.com/code/ultralytics/yolov8), if you click on the three dots in the upper right-hand corner, you'll notice more options will pop up.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
These options include:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: MLflow, Ultralytics YOLO, machine learning, experiment tracking, metri
|
|||
|
||||
# MLflow Integration for Ultralytics YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
<img width="1024" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26833433/274929143-05e37e72-c355-44be-a842-b358592340b7.png" alt="MLflow ecosystem">
|
||||
<img width="1024" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/mlflow-integration-ultralytics-yolo.avif" alt="MLflow ecosystem">
|
||||
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -102,9 +102,9 @@ The logging is taken care of by the `on_pretrain_routine_end`, `on_fit_epoch_end
|
|||
|
||||
1. **Logging Custom Metrics**: You can add custom metrics to be logged by modifying the `trainer.metrics` dictionary before `on_fit_epoch_end` is called.
|
||||
|
||||
2. **View Experiment**: To view your logs, navigate to your MLflow server (usually http://127.0.0.1:5000) and select your experiment and run. <img width="1024" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26833433/274933329-3127aa8c-4491-48ea-81df-ed09a5837f2a.png" alt="YOLO MLflow Experiment">
|
||||
2. **View Experiment**: To view your logs, navigate to your MLflow server (usually http://127.0.0.1:5000) and select your experiment and run. <img width="1024" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/yolo-mlflow-experiment.avif" alt="YOLO MLflow Experiment">
|
||||
|
||||
3. **View Run**: Runs are individual models inside an experiment. Click on a Run and see the Run details, including uploaded artifacts and model weights. <img width="1024" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26833433/274933337-ac61371c-2867-4099-a733-147a2583b3de.png" alt="YOLO MLflow Run">
|
||||
3. **View Run**: Runs are individual models inside an experiment. Click on a Run and see the Run details, including uploaded artifacts and model weights. <img width="1024" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/yolo-mlflow-run.avif" alt="YOLO MLflow Run">
|
||||
|
||||
## Disabling MLflow
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ The export to NCNN format feature allows you to optimize your [Ultralytics YOLOv
|
|||
## Why should you export to NCNN?
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://repository-images.githubusercontent.com/494294418/207a2e12-dc16-41a6-a39e-eae26e662638" alt="NCNN overview">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/ncnn-overview.avif" alt="NCNN overview">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
The [NCNN](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) framework, developed by Tencent, is a high-performance neural network inference computing framework optimized specifically for mobile platforms, including mobile phones, embedded devices, and IoT devices. NCNN is compatible with a wide range of platforms, including Linux, Android, iOS, and macOS.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ This guide shows you how to deploy YOLOv8 using Neural Magic's DeepSparse, how t
|
|||
## Neural Magic's DeepSparse
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://docs.neuralmagic.com/assets/images/nm-flows-55d56c0695a30bf9ecb716ea98977a95.png" alt="Neural Magic's DeepSparse Overview">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/neural-magic-deepsparse-overview.avif" alt="Neural Magic's DeepSparse Overview">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
[Neural Magic's DeepSparse](https://neuralmagic.com/deepsparse/) is an inference run-time designed to optimize the execution of neural networks on CPUs. It applies advanced techniques like sparsity, pruning, and quantization to dramatically reduce computational demands while maintaining accuracy. DeepSparse offers an agile solution for efficient and scalable neural network execution across various devices.
|
||||
|
|
@ -25,13 +25,13 @@ Before diving into how to deploy YOLOV8 using DeepSparse, let's understand the b
|
|||
- **Enhanced Inference Speed**: Achieves up to 525 FPS (on YOLOv8n), significantly speeding up YOLOv8's inference capabilities compared to traditional methods.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://neuralmagic.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/image1.png" alt="Enhanced Inference Speed">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/enhanced-inference-speed.avif" alt="Enhanced Inference Speed">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
- **Optimized Model Efficiency**: Uses pruning and quantization to enhance YOLOv8's efficiency, reducing model size and computational requirements while maintaining accuracy.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://neuralmagic.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/YOLOv8-charts-Page-1.drawio.png" alt="Optimized Model Efficiency">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/optimized-model-efficiency.avif" alt="Optimized Model Efficiency">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
- **High Performance on Standard CPUs**: Delivers GPU-like performance on CPUs, providing a more accessible and cost-effective option for various applications.
|
||||
|
|
@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ Neural Magic's Deep Sparse technology is inspired by the human brain's efficienc
|
|||
- **Locality of Reference**: DeepSparse uses a unique execution method, breaking the network into Tensor Columns. These columns are executed depth-wise, fitting entirely within the CPU's cache. This approach mimics the brain's efficiency, minimizing data movement and maximizing the CPU's cache use.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://neuralmagic.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/03/Screen-Shot-2021-03-16-at-11.09.45-AM.png" alt="How Neural Magic's DeepSparse Technology Works ">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/neural-magic-deepsparse-technology.avif" alt="How Neural Magic's DeepSparse Technology Works ">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
For more details on how Neural Magic's DeepSparse technology work, check out [their blog post](https://neuralmagic.com/blog/how-neural-magics-deep-sparse-technology-works/).
|
||||
|
|
@ -148,7 +148,7 @@ DeepSparse provides additional features for practical integration of YOLOv8 in a
|
|||
Running the annotate command processes your specified image, detecting objects, and saving the annotated image with bounding boxes and classifications. The annotated image will be stored in an annotation-results folder. This helps provide a visual representation of the model's detection capabilities.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/3195154/211942937-1d32193a-6dda-473d-a7ad-e2162bbb42e9.png" alt="Image Annotation Feature">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/image-annotation-feature.avif" alt="Image Annotation Feature">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
After running the eval command, you will receive detailed output metrics such as precision, recall, and mAP (mean Average Precision). This provides a comprehensive view of your model's performance on the dataset. This functionality is particularly useful for fine-tuning and optimizing your YOLOv8 models for specific use cases, ensuring high accuracy and efficiency.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: YOLOv8, OpenVINO, model export, Intel, AI inference, CPU speedup, GPU
|
|||
|
||||
# Intel OpenVINO Export
|
||||
|
||||
<img width="1024" src="https://github.com/RizwanMunawar/RizwanMunawar/assets/62513924/2b181f68-aa91-4514-ba09-497cc3c83b00" alt="OpenVINO Ecosystem">
|
||||
<img width="1024" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/openvino-ecosystem.avif" alt="OpenVINO Ecosystem">
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, we cover exporting YOLOv8 models to the [OpenVINO](https://docs.openvino.ai/) format, which can provide up to 3x [CPU](https://docs.openvino.ai/2024/openvino-workflow/running-inference/inference-devices-and-modes/cpu-device.html) speedup, as well as accelerating YOLO inference on Intel [GPU](https://docs.openvino.ai/2024/openvino-workflow/running-inference/inference-devices-and-modes/gpu-device.html) and [NPU](https://docs.openvino.ai/2024/openvino-workflow/running-inference/inference-devices-and-modes/npu-device.html) hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -118,7 +118,7 @@ The Intel® Data Center GPU Flex Series is a versatile and robust solution desig
|
|||
Benchmarks below run on Intel® Data Center GPU Flex 170 at FP32 precision.
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img width="800" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26833433/253741543-62659bf8-1765-4d0b-b71c-8a4f9885506a.jpg" alt="Flex GPU benchmarks">
|
||||
<img width="800" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/flex-gpu-benchmarks.avif" alt="Flex GPU benchmarks">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
| Model | Format | Status | Size (MB) | mAP50-95(B) | Inference time (ms/im) |
|
||||
|
|
@ -157,7 +157,7 @@ Early reviews have praised the Arc™ series, particularly the integrated A770M
|
|||
Benchmarks below run on Intel® Arc 770 GPU at FP32 precision.
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img width="800" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26833433/253741545-8530388f-8fd1-44f7-a4ae-f875d59dc282.jpg" alt="Arc GPU benchmarks">
|
||||
<img width="800" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/arc-gpu-benchmarks.avif" alt="Arc GPU benchmarks">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
| Model | Format | Status | Size (MB) | metrics/mAP50-95(B) | Inference time (ms/im) |
|
||||
|
|
@ -192,7 +192,7 @@ Notably, Xeon® CPUs deliver high compute density and scalability, making them i
|
|||
Benchmarks below run on 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable CPU at FP32 precision.
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img width="800" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26833433/253741546-dcd8e52a-fc38-424f-b87e-c8365b6f28dc.jpg" alt="Xeon CPU benchmarks">
|
||||
<img width="800" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/xeon-cpu-benchmarks.avif" alt="Xeon CPU benchmarks">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
| Model | Format | Status | Size (MB) | metrics/mAP50-95(B) | Inference time (ms/im) |
|
||||
|
|
@ -225,7 +225,7 @@ The Intel® Core® series is a range of high-performance processors by Intel. Th
|
|||
Benchmarks below run on 13th Gen Intel® Core® i7-13700H CPU at FP32 precision.
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<img width="800" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26833433/254559985-727bfa43-93fa-4fec-a417-800f869f3f9e.jpg" alt="Core CPU benchmarks">
|
||||
<img width="800" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/core-cpu-benchmarks.avif" alt="Core CPU benchmarks">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
| Model | Format | Status | Size (MB) | metrics/mAP50-95(B) | Inference time (ms/im) |
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ This is where a platform like Paperspace Gradient can make things simpler. Paper
|
|||
## Paperspace
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://assets-global.website-files.com/5db99670374d1d829291af4f/62dde8621ae3452ade8096e7_workflows-gallery-1.png" alt="Paperspace Overview">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/paperspace-overview.avif" alt="Paperspace Overview">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
[Paperspace](https://www.paperspace.com/), launched in 2014 by University of Michigan graduates and acquired by DigitalOcean in 2023, is a cloud platform specifically designed for machine learning. It provides users with powerful GPUs, collaborative Jupyter notebooks, a container service for deployments, automated workflows for machine learning tasks, and high-performance virtual machines. These features aim to streamline the entire machine learning development process, from coding to deployment.
|
||||
|
|
@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ This is where a platform like Paperspace Gradient can make things simpler. Paper
|
|||
## Paperspace Gradient
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://assets-global.website-files.com/5db99670374d1d829291af4f/62e0184d19e4ff1f63801150_Layers-Diagram.jpg" alt="PaperSpace Gradient Overview">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/paperspace-gradient-overview.avif" alt="PaperSpace Gradient Overview">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Paperspace Gradient is a suite of tools designed to make working with AI and machine learning in the cloud much faster and easier. Gradient addresses the entire machine learning development process, from building and training models to deploying them.
|
||||
|
|
@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ Paperspace Gradient makes training a YOLOv8 model possible with a few clicks. Th
|
|||
|
||||
Sign in and then click on the “Start Machine” button shown in the image below. In a few seconds, a managed GPU environment will start up, and then you can run the notebook's cells.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Explore more capabilities of YOLOv8 and Paperspace Gradient in a discussion with Glenn Jocher, Ultralytics founder, and James Skelton from Paperspace. Watch the discussion below.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ Hyperparameter tuning is vital in achieving peak model performance by discoverin
|
|||
### Ray Tune
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/_images/tune_overview.png" alt="Ray Tune Overview">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/ray-tune-overview.avif" alt="Ray Tune Overview">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
[Ray Tune](https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/tune/index.html) is a hyperparameter tuning library designed for efficiency and flexibility. It supports various search strategies, parallelism, and early stopping strategies, and seamlessly integrates with popular machine learning frameworks, including Ultralytics YOLOv8.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -32,19 +32,19 @@ Roboflow provides two services that can help you collect data for YOLOv8 models:
|
|||
Universe is an online repository with over 250,000 vision datasets totalling over 100 million images.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_universe.png" alt="Roboflow Universe" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/roboflow-universe.avif" alt="Roboflow Universe" width="800">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
With a [free Roboflow account](https://app.roboflow.com/?ref=ultralytics), you can export any dataset available on Universe. To export a dataset, click the "Download this Dataset" button on any dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_dataset.png" alt="Roboflow Universe dataset export" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/roboflow-universe-dataset-export.avif" alt="Roboflow Universe dataset export" width="800">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
For YOLOv8, select "YOLOv8" as the export format:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_data_format.png" alt="Roboflow Universe dataset export" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/roboflow-universe-dataset-export-1.avif" alt="Roboflow Universe dataset export" width="800">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Universe also has a page that aggregates all [public fine-tuned YOLOv8 models uploaded to Roboflow](https://universe.roboflow.com/search?q=model:yolov8). You can use this page to explore pre-trained models you can use for testing or [for automated data labeling](https://docs.roboflow.com/annotate/use-roboflow-annotate/model-assisted-labeling) or to prototype with [Roboflow inference](https://roboflow.com/inference?ref=ultralytics).
|
||||
|
|
@ -58,13 +58,13 @@ If you want to gather images yourself, try [Collect](https://github.com/roboflow
|
|||
To label data for a YOLOv8 object detection, instance segmentation, or classification model, first create a project in Roboflow.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_create_project.png" alt="Create a Roboflow project" width="400">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/create-roboflow-project.avif" alt="Create a Roboflow project" width="400">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Next, upload your images, and any pre-existing annotations you have from other tools ([using one of the 40+ supported import formats](https://roboflow.com/formats?ref=ultralytics)), into Roboflow.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_upload_data.png" alt="Upload images to Roboflow" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/upload-images-to-roboflow.avif" alt="Upload images to Roboflow" width="800">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Select the batch of images you have uploaded on the Annotate page to which you are taken after uploading images. Then, click "Start Annotating" to label images.
|
||||
|
|
@ -72,7 +72,7 @@ Select the batch of images you have uploaded on the Annotate page to which you a
|
|||
To label with bounding boxes, press the `B` key on your keyboard or click the box icon in the sidebar. Click on a point where you want to start your bounding box, then drag to create the box:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_annotate.png" alt="Annotating an image in Roboflow" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/annotating-an-image-in-roboflow.avif" alt="Annotating an image in Roboflow" width="800">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
A pop-up will appear asking you to select a class for your annotation once you have created an annotation.
|
||||
|
|
@ -84,7 +84,7 @@ Roboflow offers a SAM-based label assistant with which you can label images fast
|
|||
To use the label assistant, click the cursor icon in the sidebar, SAM will be loaded for use in your project.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_annotate_interactive.png" alt="Annotating an image in Roboflow with SAM-powered label assist" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/annotating-image-roboflow-sam-powered-label-assist.avif" alt="Annotating an image in Roboflow with SAM-powered label assist" width="800">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Hover over any object in the image and SAM will recommend an annotation. You can hover to find the right place to annotate, then click to create your annotation. To amend your annotation to be more or less specific, you can click inside or outside the annotation SAM has created on the document.
|
||||
|
|
@ -92,7 +92,7 @@ Hover over any object in the image and SAM will recommend an annotation. You can
|
|||
You can also add tags to images from the Tags panel in the sidebar. You can apply tags to data from a particular area, taken from a specific camera, and more. You can then use these tags to search through data for images matching a tag and generate versions of a dataset with images that contain a particular tag or set of tags.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_tags.png" alt="Adding tags to an image in Roboflow" width="300">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/adding-tags-to-image.avif" alt="Adding tags to an image in Roboflow" width="300">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Models hosted on Roboflow can be used with Label Assist, an automated annotation tool that uses your YOLOv8 model to recommend annotations. To use Label Assist, first upload a YOLOv8 model to Roboflow (see instructions later in the guide). Then, click the magic wand icon in the left sidebar and select your model for use in Label Assist.
|
||||
|
|
@ -100,13 +100,13 @@ Models hosted on Roboflow can be used with Label Assist, an automated annotation
|
|||
Choose a model, then click "Continue" to enable Label Assist:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_label_assist.png" alt="Enabling Label Assist" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/rf-label-assist.avif" alt="Enabling Label Assist" width="800">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
When you open new images for annotation, Label Assist will trigger and recommend annotations.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_label_assist.png" alt="ALabel Assist recommending an annotation" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/rf-label-assist.avif" alt="ALabel Assist recommending an annotation" width="800">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
## Dataset Management for YOLOv8
|
||||
|
|
@ -118,13 +118,13 @@ First, you can use dataset search to find images that meet a semantic text descr
|
|||
For example, the following text query finds images that contain people in a dataset:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_dataset_management.png" alt="Searching for an image" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/searching-for-an-image.avif" alt="Searching for an image" width="800">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
You can narrow your search to images with a particular tag using the "Tags" selector:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_filter_by_tag.png" alt="Filter images by tag" width="350">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/filter-images-by-tag.avif" alt="Filter images by tag" width="350">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Before you start training a model with your dataset, we recommend using Roboflow [Health Check](https://docs.roboflow.com/datasets/dataset-health-check), a web tool that provides an insight into your dataset and how you can improve the dataset prior to training a vision model.
|
||||
|
|
@ -132,7 +132,7 @@ Before you start training a model with your dataset, we recommend using Roboflow
|
|||
To use Health Check, click the "Health Check" sidebar link. A list of statistics will appear that show the average size of images in your dataset, class balance, a heatmap of where annotations are in your images, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_dataset_health_check.png" alt="Roboflow Health Check analysis" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/rf-dataset-health-check.avif" alt="Roboflow Health Check analysis" width="800">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Health Check may recommend changes to help enhance dataset performance. For example, the class balance feature may show that there is an imbalance in labels that, if solved, may boost performance or your model.
|
||||
|
|
@ -142,19 +142,19 @@ Health Check may recommend changes to help enhance dataset performance. For exam
|
|||
To export your data, you will need a dataset version. A version is a state of your dataset frozen-in-time. To create a version, first click "Versions" in the sidebar. Then, click the "Create New Version" button. On this page, you will be able to choose augmentations and preprocessing steps to apply to your dataset:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_generate_dataset.png" alt="Creating a dataset version on Roboflow" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/creating-dataset-version-on-roboflow.avif" alt="Creating a dataset version on Roboflow" width="800">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
For each augmentation you select, a pop-up will appear allowing you to tune the augmentation to your needs. Here is an example of tuning a brightness augmentation within specified parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_augmentations.png" alt="Applying augmentations to a dataset" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/applying-augmentations-to-dataset.avif" alt="Applying augmentations to a dataset" width="800">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
When your dataset version has been generated, you can export your data into a range of formats. Click the "Export Dataset" button on your dataset version page to export your data:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_export_data.png" alt="Exporting a dataset" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/exporting-dataset.avif" alt="Exporting a dataset" width="800">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
You are now ready to train YOLOv8 on a custom dataset. Follow this [written guide](https://blog.roboflow.com/how-to-train-yolov8-on-a-custom-dataset/) and [YouTube video](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wuZtUMEiKWY) for step-by-step instructions or refer to the [Ultralytics documentation](../modes/train.md).
|
||||
|
|
@ -185,7 +185,7 @@ When you run the code above, you will be asked to authenticate. Then, your model
|
|||
To test your model and find deployment instructions for supported SDKs, go to the "Deploy" tab in the Roboflow sidebar. At the top of this page, a widget will appear with which you can test your model. You can use your webcam for live testing or upload images or videos.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_test_project.png" alt="Running inference on an example image" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/running-inference-example-image.avif" alt="Running inference on an example image" width="800">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use your uploaded model as a [labeling assistant](https://docs.roboflow.com/annotate/use-roboflow-annotate/model-assisted-labeling). This feature uses your trained model to recommend annotations on images uploaded to Roboflow.
|
||||
|
|
@ -199,13 +199,13 @@ Once you have uploaded a model to Roboflow, you can access our model evaluation
|
|||
To access a confusion matrix, go to your model page on the Roboflow dashboard, then click "View Detailed Evaluation":
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_model_eval.png" alt="Start a Roboflow model evaluation" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/roboflow-model-evaluation.avif" alt="Start a Roboflow model evaluation" width="800">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
A pop-up will appear showing a confusion matrix:
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_confusion_matrix.png" alt="A confusion matrix" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/confusion-matrix.avif" alt="A confusion matrix" width="800">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Hover over a box on the confusion matrix to see the value associated with the box. Click on a box to see images in the respective category. Click on an image to view the model predictions and ground truth data associated with that image.
|
||||
|
|
@ -213,7 +213,7 @@ Hover over a box on the confusion matrix to see the value associated with the bo
|
|||
For more insights, click Vector Analysis. This will show a scatter plot of the images in your dataset, calculated using CLIP. The closer images are in the plot, the more similar they are, semantically. Each image is represented as a dot with a color between white and red. The more red the dot, the worse the model performed.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_vector_analysis.png" alt="A vector analysis plot" width="800">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/vector-analysis-plot.avif" alt="A vector analysis plot" width="800">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
You can use Vector Analysis to:
|
||||
|
|
@ -237,9 +237,9 @@ Want to learn more about using Roboflow for creating YOLOv8 models? The followin
|
|||
Below are a few of the many pieces of feedback we have received for using YOLOv8 and Roboflow together to create computer vision models.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_showcase_1.png" alt="Showcase image" width="500">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_showcase_2.png" alt="Showcase image" width="500">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_showcase_3.png" alt="Showcase image" width="500">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/rf-showcase-1.avif" alt="Showcase image" width="500">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/rf-showcase-2.avif" alt="Showcase image" width="500">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/rf-showcase-3.avif" alt="Showcase image" width="500">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ This guide covers how to use TensorBoard with YOLOv8. You'll learn about various
|
|||
## TensorBoard
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://www.tensorflow.org/static/tensorboard/images/tensorboard.gif" alt="Tensorboard Overview">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/tensorboard-overview.avif" alt="Tensorboard Overview">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
[TensorBoard](https://www.tensorflow.org/tensorboard), TensorFlow's visualization toolkit, is essential for machine learning experimentation. TensorBoard features a range of visualization tools, crucial for monitoring machine learning models. These tools include tracking key metrics like loss and accuracy, visualizing model graphs, and viewing histograms of weights and biases over time. It also provides capabilities for projecting embeddings to lower-dimensional spaces and displaying multimedia data.
|
||||
|
|
@ -88,7 +88,7 @@ Now, let's focus on understanding the various features and components of TensorB
|
|||
|
||||
The Time Series feature in the TensorBoard offers a dynamic and detailed perspective of various training metrics over time for YOLOv8 models. It focuses on the progression and trends of metrics across training epochs. Here's an example of what you can expect to see.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Key Features of Time Series in TensorBoard
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -108,7 +108,7 @@ The Time Series section is essential for a thorough analysis of the YOLOv8 model
|
|||
|
||||
Scalars in the TensorBoard are crucial for plotting and analyzing simple metrics like loss and accuracy during the training of YOLOv8 models. They offer a clear and concise view of how these metrics evolve with each training epoch, providing insights into the model's learning effectiveness and stability. Here's an example of what you can expect to see.
|
||||
|
||||
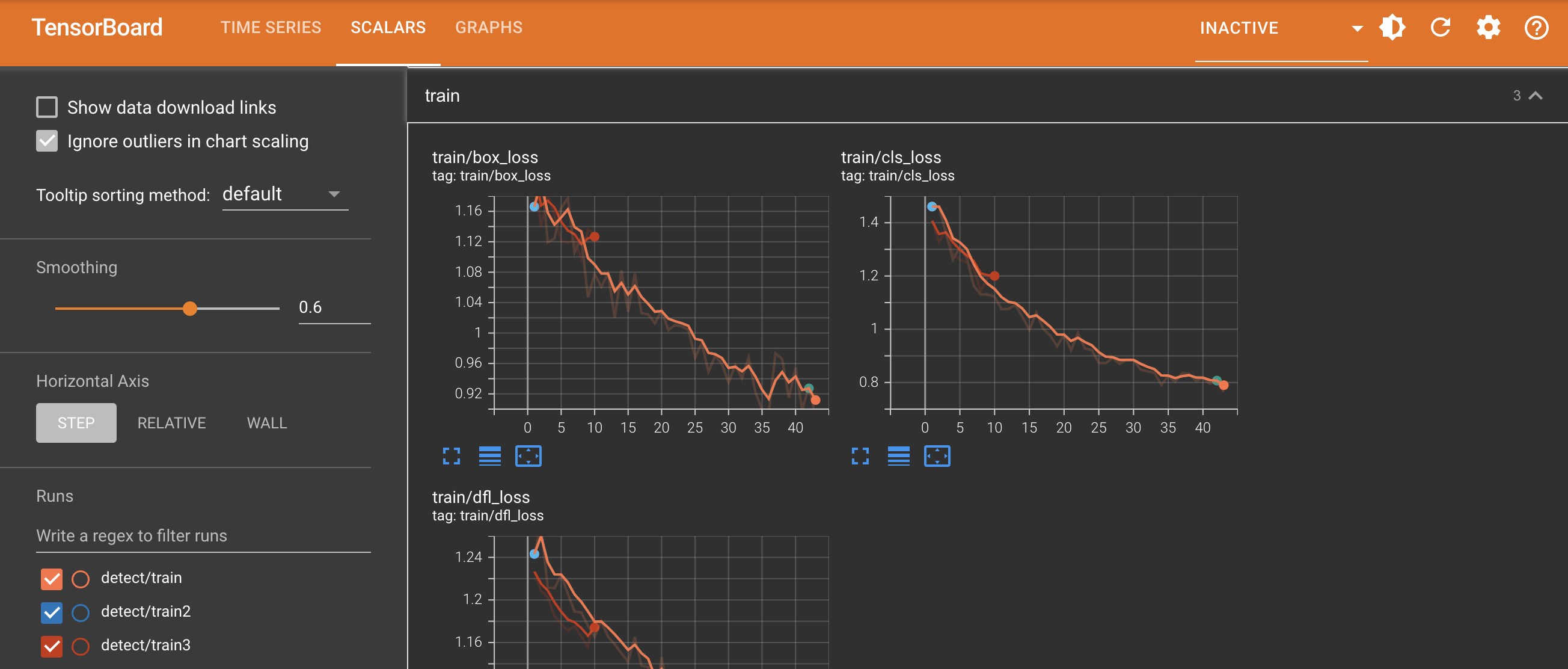
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Key Features of Scalars in TensorBoard
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -140,7 +140,7 @@ While both Scalars and Time Series in TensorBoard are used for tracking metrics,
|
|||
|
||||
The Graphs section of the TensorBoard visualizes the computational graph of the YOLOv8 model, showing how operations and data flow within the model. It's a powerful tool for understanding the model's structure, ensuring that all layers are connected correctly, and for identifying any potential bottlenecks in data flow. Here's an example of what you can expect to see.
|
||||
|
||||
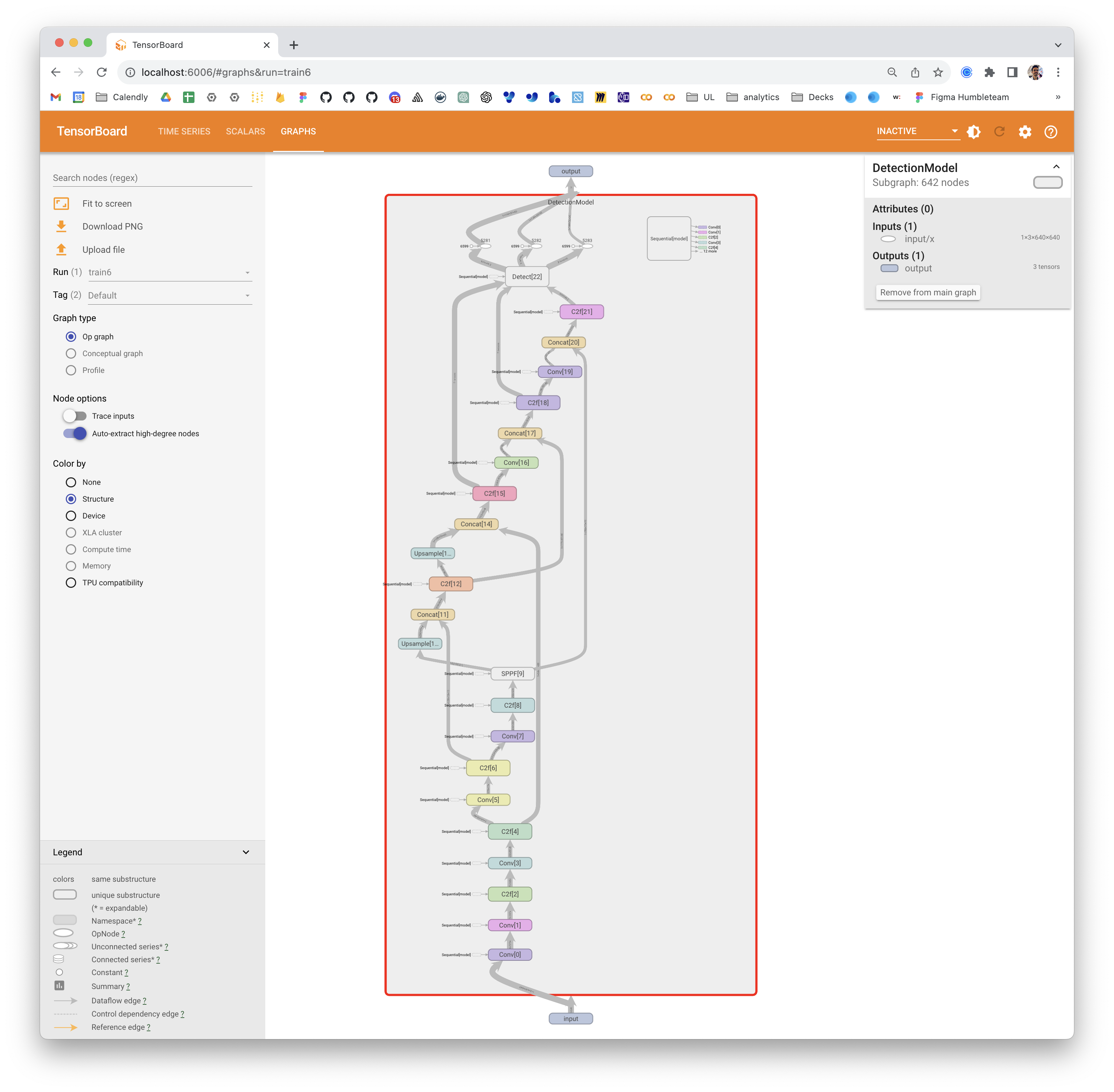
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Graphs are particularly useful for debugging the model, especially in complex architectures typical in deep learning models like YOLOv8. They help in verifying layer connections and the overall design of the model.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ By using the TensorRT export format, you can enhance your [Ultralytics YOLOv8](h
|
|||
## TensorRT
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/assets/26833433/7fea48c2-9709-4deb-8d04-eaf95d12a91d" alt="TensorRT Overview">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/tensorrt-overview.avif" alt="TensorRT Overview">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
[TensorRT](https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt), developed by NVIDIA, is an advanced software development kit (SDK) designed for high-speed deep learning inference. It's well-suited for real-time applications like object detection.
|
||||
|
|
@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ TensorRT models offer a range of key features that contribute to their efficienc
|
|||
- **Layer Fusion**: The TensorRT optimization process includes layer fusion, where multiple layers of a neural network are combined into a single operation. This reduces computational overhead and improves inference speed by minimizing memory access and computation.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://developer-blogs.nvidia.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/pasted-image-0-3.png" alt="TensorRT Layer Fusion">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/tensorrt-layer-fusion.avif" alt="TensorRT Layer Fusion">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
- **Dynamic Tensor Memory Management**: TensorRT efficiently manages tensor memory usage during inference, reducing memory overhead and optimizing memory allocation. This results in more efficient GPU memory utilization.
|
||||
|
|
@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ TensorRT offers several deployment options, and each option balances ease of int
|
|||
- **Deploying within TensorFlow**: This method integrates TensorRT into TensorFlow, allowing optimized models to run in a familiar TensorFlow environment. It's useful for models with a mix of supported and unsupported layers, as TF-TRT can handle these efficiently.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/tensorrt/quick-start-guide/graphics/tf-trt-workflow.png" alt="TensorRT Overview">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/tf-trt-workflow.avif" alt="TensorRT Overview">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
- **Standalone TensorRT Runtime API**: Offers granular control, ideal for performance-critical applications. It's more complex but allows for custom implementation of unsupported operators.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ When you are deploying cutting-edge computer vision models, like YOLOv8, in diff
|
|||
In this guide, we'll walk you step by step through how to export your [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) models to the TF GraphDef model format. By converting your model, you can streamline deployment and use YOLOv8's computer vision capabilities in a broader range of applications and platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://github.com/RizwanMunawar/RizwanMunawar/assets/62513924/2d793b51-19f2-49e0-bf4b-5208f2eb5993" alt="TensorFlow GraphDef">
|
||||
<img width="640" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/tensorflow-graphdef.avif" alt="TensorFlow GraphDef">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
## Why Should You Export to TF GraphDef?
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ Learning how to export to TF SavedModel from [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github
|
|||
The TensorFlow SavedModel format is a part of the TensorFlow ecosystem developed by Google as shown below. It is designed to save and serialize TensorFlow models seamlessly. It encapsulates the complete details of models like the architecture, weights, and even compilation information. This makes it straightforward to share, deploy, and continue training across different environments.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://sdtimes.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/0_C7GCWYlsMrhUYRYi.png" alt="TF SavedModel">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/tf-savedmodel-overview.avif" alt="TF SavedModel">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
The TF SavedModel has a key advantage: its compatibility. It works well with TensorFlow Serving, TensorFlow Lite, and TensorFlow.js. This compatibility makes it easier to share and deploy models across various platforms, including web and mobile applications. The TF SavedModel format is useful both for research and production. It provides a unified way to manage your models, ensuring they are ready for any application.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ The 'export to TF.js model format' feature allows you to optimize your [Ultralyt
|
|||
Exporting your machine learning models to TensorFlow.js, developed by the TensorFlow team as part of the broader TensorFlow ecosystem, offers numerous advantages for deploying machine learning applications. It helps enhance user privacy and security by keeping sensitive data on the device. The image below shows the TensorFlow.js architecture, and how machine learning models are converted and deployed on both web browsers and Node.js.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://res.cloudinary.com/practicaldev/image/fetch/s--oepXBlvm--/c_limit%2Cf_auto%2Cfl_progressive%2Cq_auto%2Cw_880/https://dev-to-uploads.s3.amazonaws.com/uploads/articles/m7r4grt0zkrgyx62xxx3.png" alt="TF.js Architecture">
|
||||
<img width="100%" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/tfjs-architecture.avif" alt="TF.js Architecture">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Running models locally also reduces latency and provides a more responsive user experience. TensorFlow.js also comes with offline capabilities, allowing users to use your application even without an internet connection. TF.js is designed for efficient execution of complex models on devices with limited resources as it is engineered for scalability, with GPU acceleration support.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ keywords: YOLOv8, TFLite, model export, TensorFlow Lite, edge devices, deploymen
|
|||
# A Guide on YOLOv8 Model Export to TFLite for Deployment
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="75%" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/assets/26833433/6ecf34b9-9187-4d6f-815c-72394290a4d3" alt="TFLite Logo">
|
||||
<img width="75%" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/tflite-logo.avif" alt="TFLite Logo">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
Deploying computer vision models on edge devices or embedded devices requires a format that can ensure seamless performance.
|
||||
|
|
@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ TFLite offers various on-device deployment options for machine learning models,
|
|||
- **Deploying with Android and iOS**: Both Android and iOS applications with TFLite can analyze edge-based camera feeds and sensors to detect and identify objects. TFLite also offers native iOS libraries written in [Swift](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/tree/master/tensorflow/lite/swift) and [Objective-C](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/tree/master/tensorflow/lite/objc). The architecture diagram below shows the process of deploying a trained model onto Android and iOS platforms using TensorFlow Lite.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="75%" src="https://1.bp.blogspot.com/-6fS9FD8KD7g/XhJ1l8y2S4I/AAAAAAAACKw/MW9MQZ8gtiYmUe0naRdN0n2FwkT1l4trACLcBGAsYHQ/s1600/architecture.png" alt="Architecture">
|
||||
<img width="75%" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/architecture-diagram-tflite-deployment.avif" alt="Architecture">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
- **Implementing with Embedded Linux**: If running inferences on a [Raspberry Pi](https://www.raspberrypi.org/) using the [Ultralytics Guide](../guides/raspberry-pi.md) does not meet the speed requirements for your use case, you can use an exported TFLite model to accelerate inference times. Additionally, it's possible to further improve performance by utilizing a [Coral Edge TPU device](https://coral.withgoogle.com/).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -12,13 +12,13 @@ Export to Torchscript to serialize your [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/
|
|||
|
||||
## Why should you export to TorchScript?
|
||||
|
||||
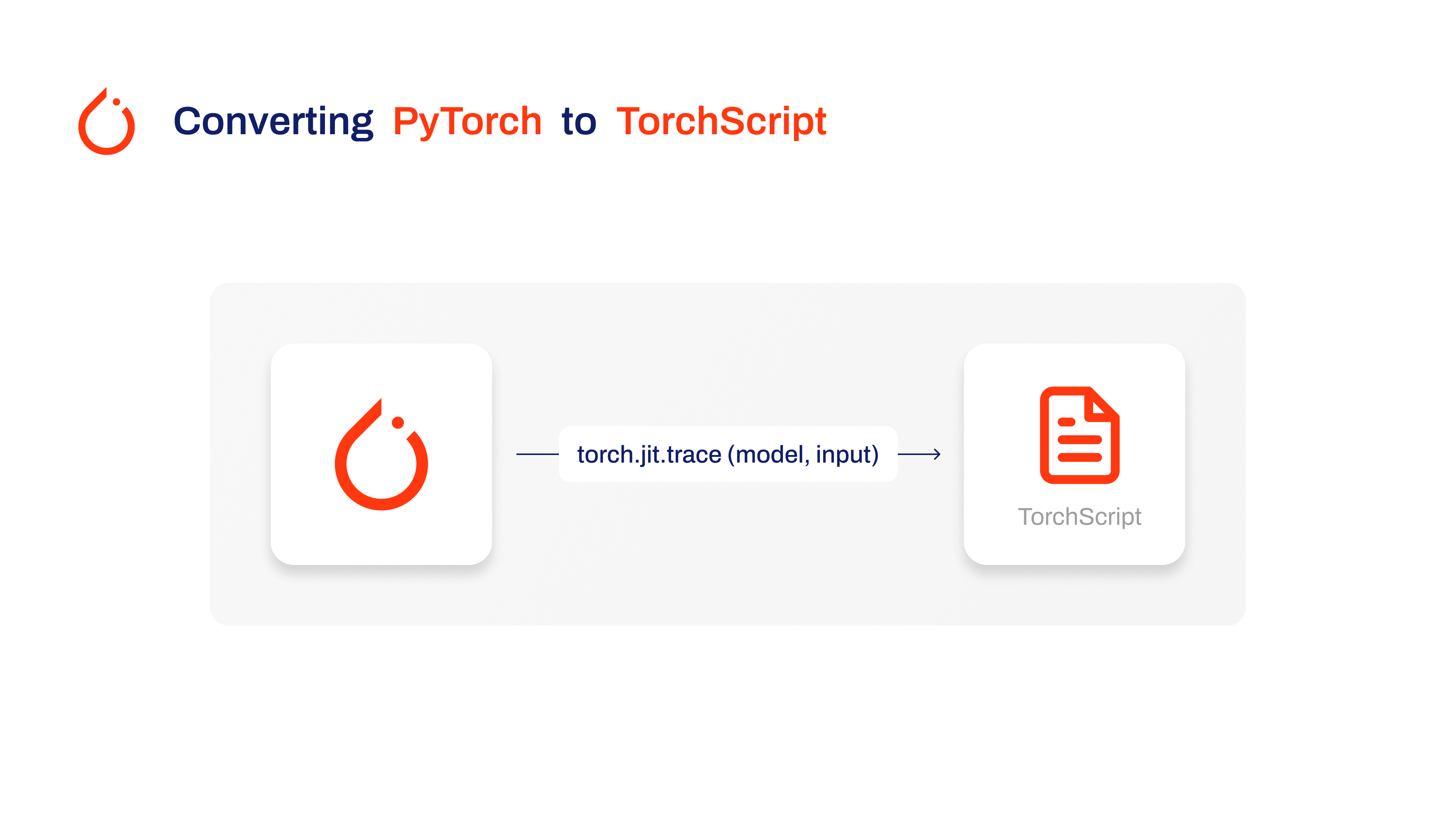
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Developed by the creators of PyTorch, TorchScript is a powerful tool for optimizing and deploying PyTorch models across a variety of platforms. Exporting YOLOv8 models to [TorchScript](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/jit.html) is crucial for moving from research to real-world applications. TorchScript, part of the PyTorch framework, helps make this transition smoother by allowing PyTorch models to be used in environments that don't support Python.
|
||||
|
||||
The process involves two techniques: tracing and scripting. Tracing records operations during model execution, while scripting allows for the definition of models using a subset of Python. These techniques ensure that models like YOLOv8 can still work their magic even outside their usual Python environment.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
TorchScript models can also be optimized through techniques such as operator fusion and refinements in memory usage, ensuring efficient execution. Another advantage of exporting to TorchScript is its potential to accelerate model execution across various hardware platforms. It creates a standalone, production-ready representation of your PyTorch model that can be integrated into C++ environments, embedded systems, or deployed in web or mobile applications.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ TorchScript models can also be optimized through techniques such as operator fus
|
|||
|
||||
TorchScript, a key part of the PyTorch ecosystem, provides powerful features for optimizing and deploying deep learning models.
|
||||
|
||||
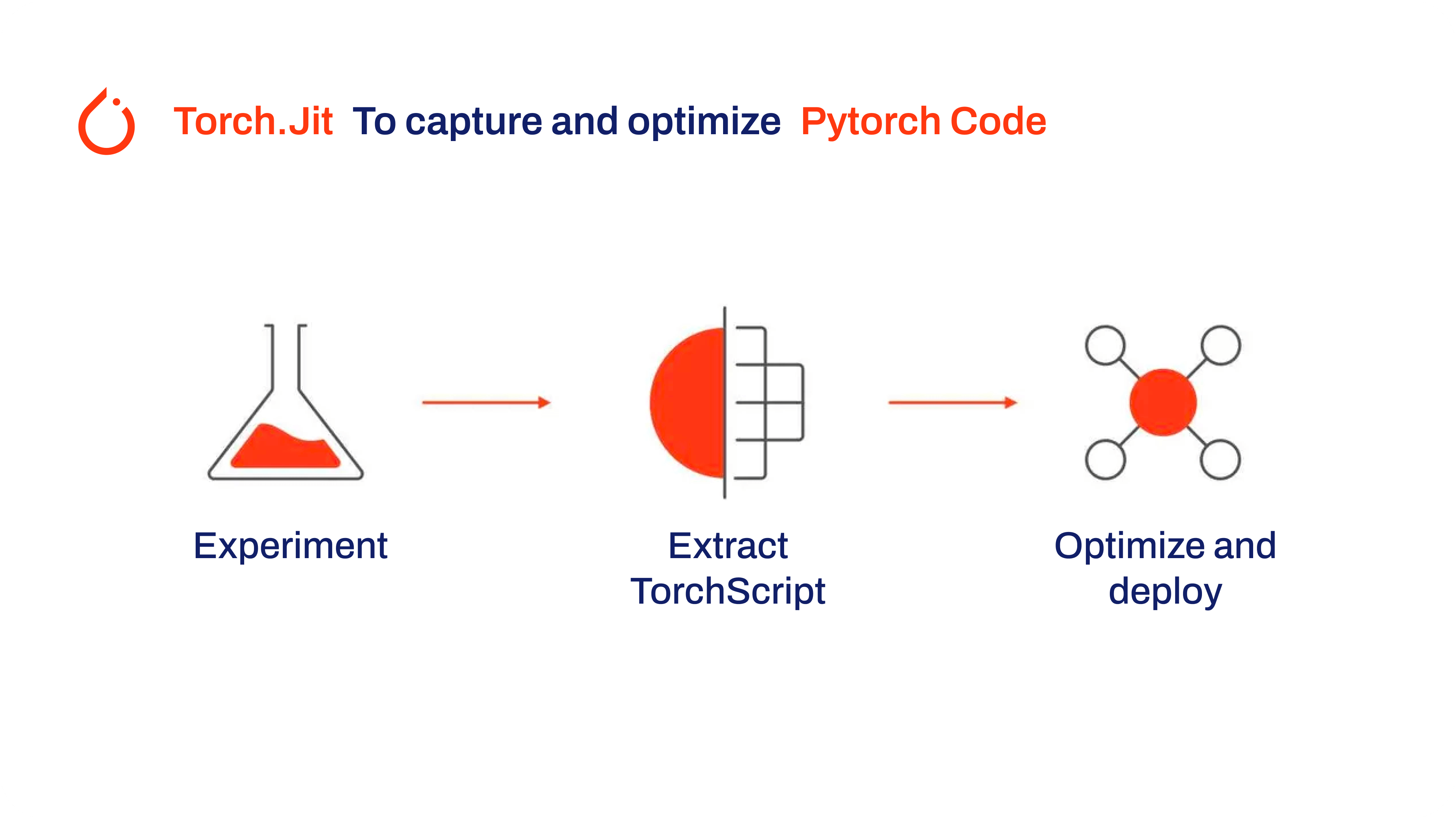
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Here are the key features that make TorchScript a valuable tool for developers:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ keywords: Visual Studio Code, VS Code, deep learning, convolutional neural netwo
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/Burhan-Q/ultralytics-snippets/assets/62214284/42ad0b17-e752-479c-9c6c-e451fffbe8b3" alt="Snippet Prediction Preview">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/snippet-prediction-preview.avif" alt="Snippet Prediction Preview">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
Run example code using Ultralytics YOLO in under 20 seconds! 🚀
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
|
@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ Want to let us know what you use for developing code? Head over to our Discourse
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/9de46d22-ef7b-4765-ba2c-d0459cafa4dc" alt="VS Code extension menu">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/vs-code-extension-menu.avif" alt="VS Code extension menu">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -65,7 +65,7 @@ Want to let us know what you use for developing code? Head over to our Discourse
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/b40cc8e2-2353-4165-859a-c84eec070db6" alt="VS Code marketplace extension install">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/vscode-marketplace-extension-install.avif" alt="VS Code marketplace extension install">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
Visual Studio Code Extension Marketplace page for <a href="https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=Ultralytics.ultralytics-snippets">Ultralytics-Snippets</a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
|
@ -90,7 +90,7 @@ Many snippets have "fields" with default placeholder values or names. For instan
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/661c1b85-39a5-48ec-9faa-89d44e49aa37" alt="Multi-update field and options">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/multi-update-field-and-options.avif" alt="Multi-update field and options">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
After inserting snippet, renaming <code>model</code> as <code>world_model</code> updates all instances. Pressing <kbd>Tab ⇥</kbd> moves to the next field, which opens a dropdown menu and allows for selection of a model scale, and moving to the next field provides another dropdown to choose either <code>world</code> or <code>worldv2</code> model variant.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
|
@ -105,7 +105,7 @@ The snippets are named in the most descriptive way possible, but this means ther
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/bdd9aada-de8a-4d73-b714-04f8a48c0436" alt="Incomplete Snippet Example">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/incomplete-snippet-example.avif" alt="Incomplete Snippet Example">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
Typing <code>ex-yolo-p</code> will <em>still</em> arrive at the correct snippet.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
|
@ -161,7 +161,7 @@ However, since Ultralytics supports numerous [tasks], when [working with inferen
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/16cc72eb-4390-4380-bfaa-a0e84e5251db" alt="Results Loop Options">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/results-loop-options.avif" alt="Results Loop Options">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
Once tabbed to the <code>boxes</code> field, a dropdown menu appears to allow selection of another attribute as required.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
|
@ -241,7 +241,7 @@ Like any other VS Code extension, you can uninstall it by navigating to the Exte
|
|||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/3d154bb1-a184-4c01-9537-341692fdcabf" alt="VS Code extension menu">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/vscode-extension-menu.avif" alt="VS Code extension menu">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ This guide showcases Ultralytics YOLOv8 integration with Weights & Biases' for e
|
|||
## Weights & Biases
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<img width="800" src="https://docs.wandb.ai/assets/images/wandb_demo_experiments-4797af7fe7236d6c5c42adbdc93deb4c.gif" alt="Weights & Biases Overview">
|
||||
<img width="800" src="https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/releases/download/0/wandb-demo-experiments.avif" alt="Weights & Biases Overview">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
[Weights & Biases](https://wandb.ai/site) is a cutting-edge MLOps platform designed for tracking, visualizing, and managing machine learning experiments. It features automatic logging of training metrics for full experiment reproducibility, an interactive UI for streamlined data analysis, and efficient model management tools for deploying across various environments.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue