
 +
+ - **Mosaiced Image**: This image demonstrates a training batch composed of mosaiced dataset images. Mosaicing is a technique used during training that combines multiple images into a single image to increase the variety of objects and scenes within each training batch. This helps improve the model's ability to generalize to different object sizes, aspect ratios, and contexts.
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/detect/globalwheat2020.md b/docs/en/datasets/detect/globalwheat2020.md
index 28c95c10..a8e255b5 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/detect/globalwheat2020.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/detect/globalwheat2020.md
@@ -65,7 +65,7 @@ To train a YOLOv8n model on the Global Wheat Head Dataset for 100 epochs with an
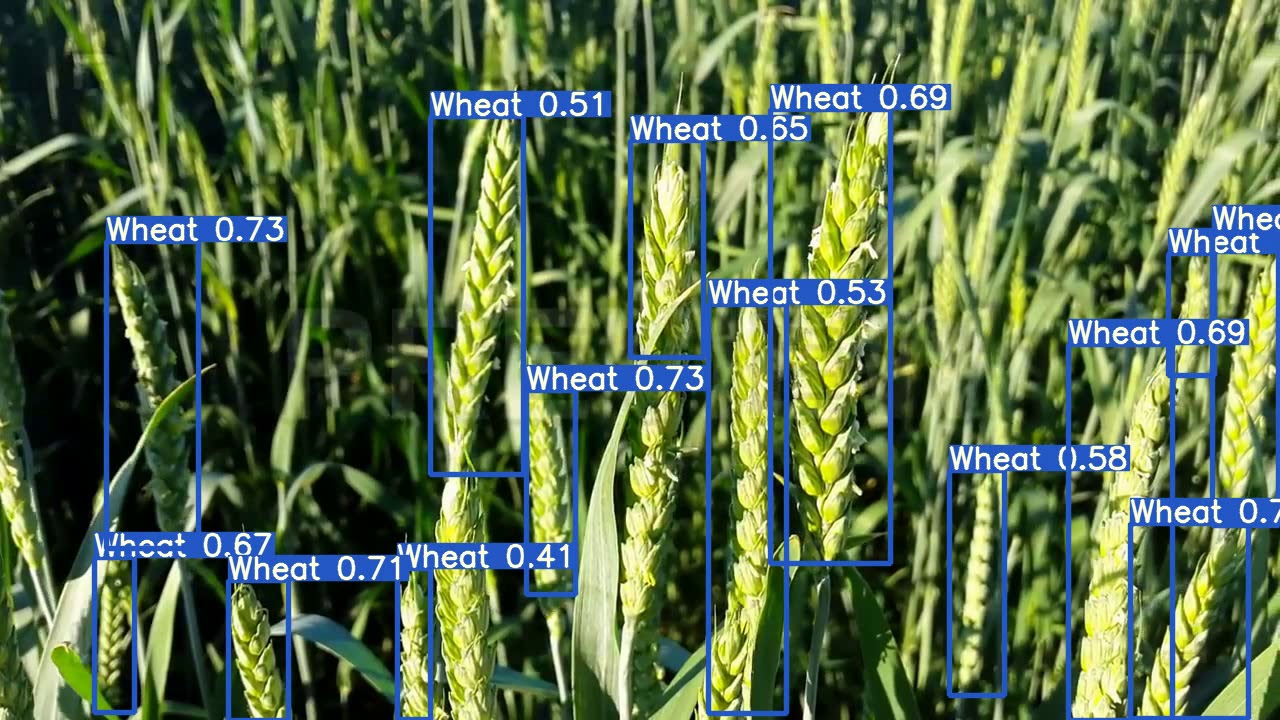
The Global Wheat Head Dataset contains a diverse set of outdoor field images, capturing the natural variability in wheat head appearances, environments, and conditions. Here are some examples of data from the dataset, along with their corresponding annotations:
-
+
- **Wheat Head Detection**: This image demonstrates an example of wheat head detection, where wheat heads are annotated with bounding boxes. The dataset provides a variety of images to facilitate the development of models for this task.
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/detect/index.md b/docs/en/datasets/detect/index.md
index 97806cb0..934fe385 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/detect/index.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/detect/index.md
@@ -34,15 +34,15 @@ names:
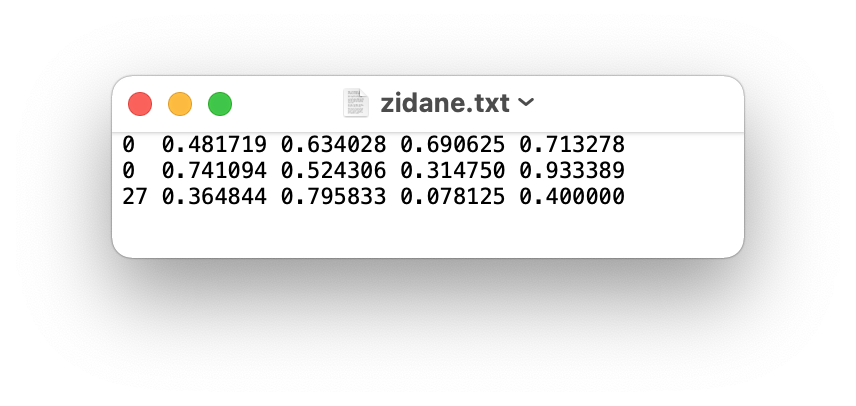
Labels for this format should be exported to YOLO format with one `*.txt` file per image. If there are no objects in an image, no `*.txt` file is required. The `*.txt` file should be formatted with one row per object in `class x_center y_center width height` format. Box coordinates must be in **normalized xywh** format (from 0 to 1). If your boxes are in pixels, you should divide `x_center` and `width` by image width, and `y_center` and `height` by image height. Class numbers should be zero-indexed (start with 0).
-
- **Mosaiced Image**: This image demonstrates a training batch composed of mosaiced dataset images. Mosaicing is a technique used during training that combines multiple images into a single image to increase the variety of objects and scenes within each training batch. This helps improve the model's ability to generalize to different object sizes, aspect ratios, and contexts.
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/detect/globalwheat2020.md b/docs/en/datasets/detect/globalwheat2020.md
index 28c95c10..a8e255b5 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/detect/globalwheat2020.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/detect/globalwheat2020.md
@@ -65,7 +65,7 @@ To train a YOLOv8n model on the Global Wheat Head Dataset for 100 epochs with an
The Global Wheat Head Dataset contains a diverse set of outdoor field images, capturing the natural variability in wheat head appearances, environments, and conditions. Here are some examples of data from the dataset, along with their corresponding annotations:
-
+
- **Wheat Head Detection**: This image demonstrates an example of wheat head detection, where wheat heads are annotated with bounding boxes. The dataset provides a variety of images to facilitate the development of models for this task.
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/detect/index.md b/docs/en/datasets/detect/index.md
index 97806cb0..934fe385 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/detect/index.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/detect/index.md
@@ -34,15 +34,15 @@ names:
Labels for this format should be exported to YOLO format with one `*.txt` file per image. If there are no objects in an image, no `*.txt` file is required. The `*.txt` file should be formatted with one row per object in `class x_center y_center width height` format. Box coordinates must be in **normalized xywh** format (from 0 to 1). If your boxes are in pixels, you should divide `x_center` and `width` by image width, and `y_center` and `height` by image height. Class numbers should be zero-indexed (start with 0).
-



-
+

-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-
+

@@ -41,19 +41,19 @@ Semantic search is a technique for finding similar images to a given image. It i For example: In this VOC Exploration dashboard, user selects a couple airplane images like this:
-
+

-
+

-
+

-
+

-
+

-
+

-
+

 - **Mosaiced Image**: This image demonstrates a training batch composed of mosaiced dataset images. Mosaicing is a technique used during training that combines multiple images into a single image to increase the variety of objects and scenes within each training batch. This helps improve the model's ability to generalize to different object sizes, aspect ratios, and contexts.
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/obb/index.md b/docs/en/datasets/obb/index.md
index f7708a10..10631703 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/obb/index.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/obb/index.md
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ class_index x1 y1 x2 y2 x3 y3 x4 y4
Internally, YOLO processes losses and outputs in the `xywhr` format, which represents the bounding box's center point (xy), width, height, and rotation.
-
- **Mosaiced Image**: This image demonstrates a training batch composed of mosaiced dataset images. Mosaicing is a technique used during training that combines multiple images into a single image to increase the variety of objects and scenes within each training batch. This helps improve the model's ability to generalize to different object sizes, aspect ratios, and contexts.
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/obb/index.md b/docs/en/datasets/obb/index.md
index f7708a10..10631703 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/obb/index.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/obb/index.md
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ class_index x1 y1 x2 y2 x3 y3 x4 y4
Internally, YOLO processes losses and outputs in the `xywhr` format, which represents the bounding box's center point (xy), width, height, and rotation.
-

 +
+ - **Mosaiced Image**: This image demonstrates a training batch composed of mosaiced dataset images. Mosaicing is a technique used during training that combines multiple images into a single image to increase the variety of objects and scenes within each training batch. This helps improve the model's ability to generalize to different object sizes, aspect ratios, and contexts.
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/pose/tiger-pose.md b/docs/en/datasets/pose/tiger-pose.md
index d1e338cc..457e8fef 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/pose/tiger-pose.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/pose/tiger-pose.md
@@ -64,7 +64,7 @@ To train a YOLOv8n-pose model on the Tiger-Pose dataset for 100 epochs with an i
Here are some examples of images from the Tiger-Pose dataset, along with their corresponding annotations:
-
- **Mosaiced Image**: This image demonstrates a training batch composed of mosaiced dataset images. Mosaicing is a technique used during training that combines multiple images into a single image to increase the variety of objects and scenes within each training batch. This helps improve the model's ability to generalize to different object sizes, aspect ratios, and contexts.
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/pose/tiger-pose.md b/docs/en/datasets/pose/tiger-pose.md
index d1e338cc..457e8fef 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/pose/tiger-pose.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/pose/tiger-pose.md
@@ -64,7 +64,7 @@ To train a YOLOv8n-pose model on the Tiger-Pose dataset for 100 epochs with an i
Here are some examples of images from the Tiger-Pose dataset, along with their corresponding annotations:
- +
+ - **Mosaiced Image**: This image demonstrates a training batch composed of mosaiced dataset images. Mosaicing is a technique used during training that combines multiple images into a single image to increase the variety of objects and scenes within each training batch. This helps improve the model's ability to generalize to different object sizes, aspect ratios, and contexts.
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/segment/carparts-seg.md b/docs/en/datasets/segment/carparts-seg.md
index 60890e06..d5799954 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/segment/carparts-seg.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/segment/carparts-seg.md
@@ -72,7 +72,7 @@ To train Ultralytics YOLOv8n model on the Carparts Segmentation dataset for 100
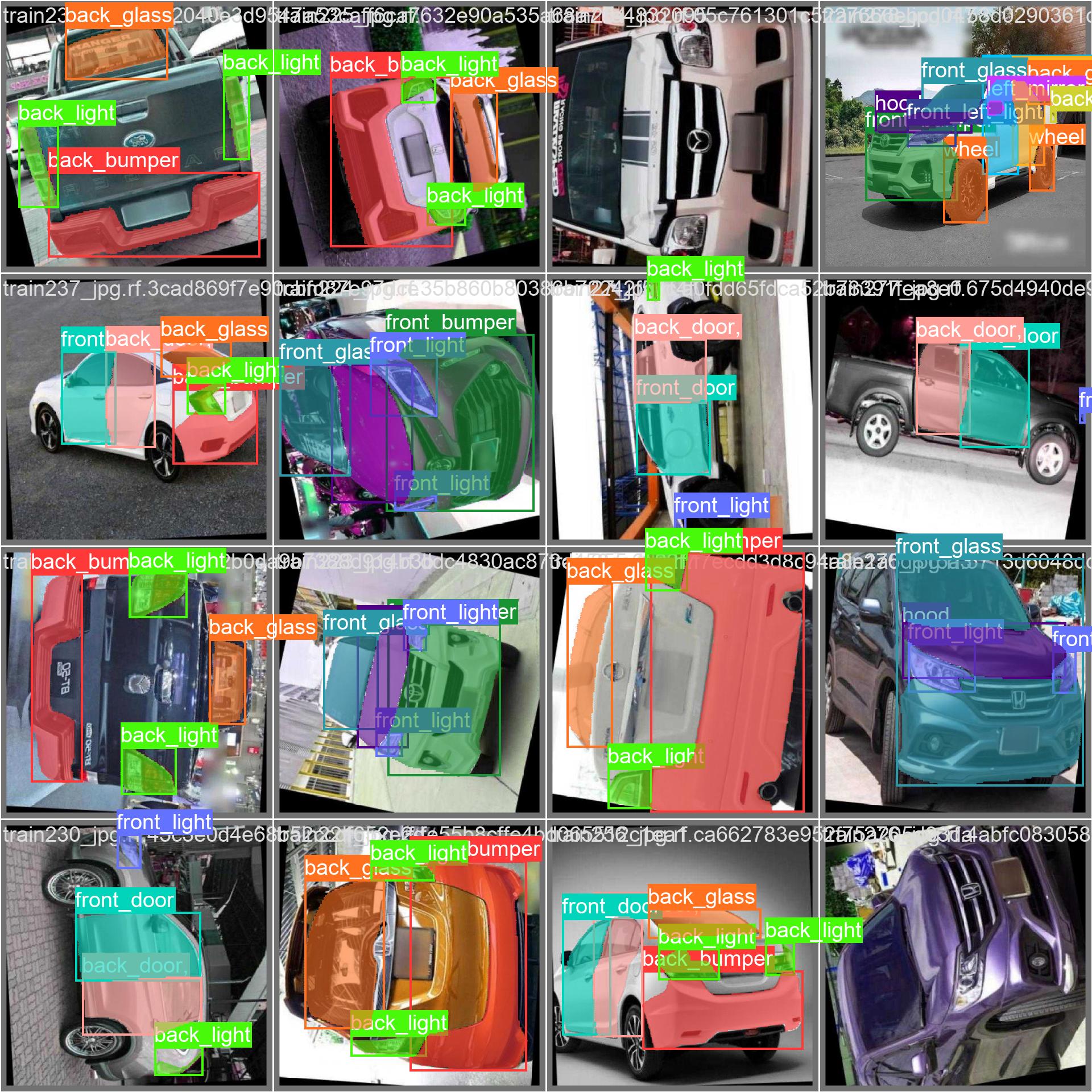
The Carparts Segmentation dataset includes a diverse array of images and videos taken from various perspectives. Below, you'll find examples of data from the dataset along with their corresponding annotations:
-
+
- This image illustrates object segmentation within a sample, featuring annotated bounding boxes with masks surrounding identified objects. The dataset consists of a varied set of images captured in various locations, environments, and densities, serving as a comprehensive resource for crafting models specific to this task.
- This instance highlights the diversity and complexity inherent in the dataset, emphasizing the crucial role of high-quality data in computer vision tasks, particularly in the realm of car parts segmentation.
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/segment/coco.md b/docs/en/datasets/segment/coco.md
index e02b6771..bb88a232 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/segment/coco.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/segment/coco.md
@@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ To train a YOLOv8n-seg model on the COCO-Seg dataset for 100 epochs with an imag
COCO-Seg, like its predecessor COCO, contains a diverse set of images with various object categories and complex scenes. However, COCO-Seg introduces more detailed instance segmentation masks for each object in the images. Here are some examples of images from the dataset, along with their corresponding instance segmentation masks:
-
+
- **Mosaiced Image**: This image demonstrates a training batch composed of mosaiced dataset images. Mosaicing is a technique used during training that combines multiple images into a single image to increase the variety of objects and scenes within each training batch. This aids the model's ability to generalize to different object sizes, aspect ratios, and contexts.
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/segment/coco8-seg.md b/docs/en/datasets/segment/coco8-seg.md
index bcca4a26..f22d6a68 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/segment/coco8-seg.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/segment/coco8-seg.md
@@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ To train a YOLOv8n-seg model on the COCO8-Seg dataset for 100 epochs with an ima
Here are some examples of images from the COCO8-Seg dataset, along with their corresponding annotations:
-
- **Mosaiced Image**: This image demonstrates a training batch composed of mosaiced dataset images. Mosaicing is a technique used during training that combines multiple images into a single image to increase the variety of objects and scenes within each training batch. This helps improve the model's ability to generalize to different object sizes, aspect ratios, and contexts.
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/segment/carparts-seg.md b/docs/en/datasets/segment/carparts-seg.md
index 60890e06..d5799954 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/segment/carparts-seg.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/segment/carparts-seg.md
@@ -72,7 +72,7 @@ To train Ultralytics YOLOv8n model on the Carparts Segmentation dataset for 100
The Carparts Segmentation dataset includes a diverse array of images and videos taken from various perspectives. Below, you'll find examples of data from the dataset along with their corresponding annotations:
-
+
- This image illustrates object segmentation within a sample, featuring annotated bounding boxes with masks surrounding identified objects. The dataset consists of a varied set of images captured in various locations, environments, and densities, serving as a comprehensive resource for crafting models specific to this task.
- This instance highlights the diversity and complexity inherent in the dataset, emphasizing the crucial role of high-quality data in computer vision tasks, particularly in the realm of car parts segmentation.
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/segment/coco.md b/docs/en/datasets/segment/coco.md
index e02b6771..bb88a232 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/segment/coco.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/segment/coco.md
@@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ To train a YOLOv8n-seg model on the COCO-Seg dataset for 100 epochs with an imag
COCO-Seg, like its predecessor COCO, contains a diverse set of images with various object categories and complex scenes. However, COCO-Seg introduces more detailed instance segmentation masks for each object in the images. Here are some examples of images from the dataset, along with their corresponding instance segmentation masks:
-
+
- **Mosaiced Image**: This image demonstrates a training batch composed of mosaiced dataset images. Mosaicing is a technique used during training that combines multiple images into a single image to increase the variety of objects and scenes within each training batch. This aids the model's ability to generalize to different object sizes, aspect ratios, and contexts.
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/segment/coco8-seg.md b/docs/en/datasets/segment/coco8-seg.md
index bcca4a26..f22d6a68 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/segment/coco8-seg.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/segment/coco8-seg.md
@@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ To train a YOLOv8n-seg model on the COCO8-Seg dataset for 100 epochs with an ima
Here are some examples of images from the COCO8-Seg dataset, along with their corresponding annotations:
- +
+ - **Mosaiced Image**: This image demonstrates a training batch composed of mosaiced dataset images. Mosaicing is a technique used during training that combines multiple images into a single image to increase the variety of objects and scenes within each training batch. This helps improve the model's ability to generalize to different object sizes, aspect ratios, and contexts.
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/segment/crack-seg.md b/docs/en/datasets/segment/crack-seg.md
index 83f01987..5fa99dfb 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/segment/crack-seg.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/segment/crack-seg.md
@@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ To train Ultralytics YOLOv8n model on the Crack Segmentation dataset for 100 epo
The Crack Segmentation dataset comprises a varied collection of images and videos captured from multiple perspectives. Below are instances of data from the dataset, accompanied by their respective annotations:
-
+
- This image presents an example of image object segmentation, featuring annotated bounding boxes with masks outlining identified objects. The dataset includes a diverse array of images taken in different locations, environments, and densities, making it a comprehensive resource for developing models designed for this particular task.
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/segment/package-seg.md b/docs/en/datasets/segment/package-seg.md
index 86fad9e9..bf88410f 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/segment/package-seg.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/segment/package-seg.md
@@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ To train Ultralytics YOLOv8n model on the Package Segmentation dataset for 100 e
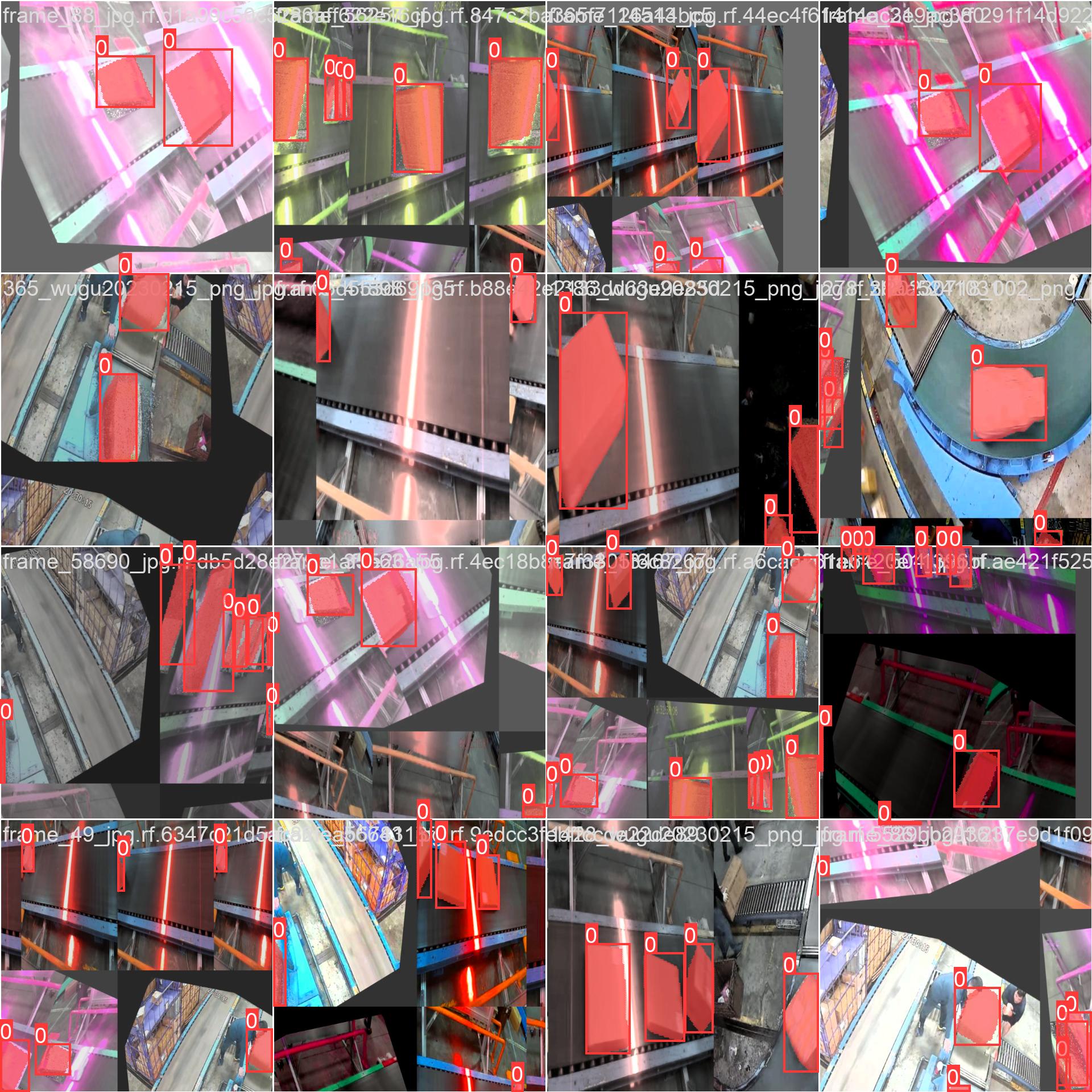
The Package Segmentation dataset comprises a varied collection of images and videos captured from multiple perspectives. Below are instances of data from the dataset, accompanied by their respective annotations:
-
+
- This image displays an instance of image object detection, featuring annotated bounding boxes with masks outlining recognized objects. The dataset incorporates a diverse collection of images taken in different locations, environments, and densities. It serves as a comprehensive resource for developing models specific to this task.
- The example emphasizes the diversity and complexity present in the VisDrone dataset, underscoring the significance of high-quality sensor data for computer vision tasks involving drones.
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/analytics.md b/docs/en/guides/analytics.md
index 96cadb86..a29e6abe 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/analytics.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/analytics.md
@@ -12,9 +12,9 @@ This guide provides a comprehensive overview of three fundamental types of data
### Visual Samples
-| Line Graph | Bar Plot | Pie Chart |
-| :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
-|  |  |  |
+| Line Graph | Bar Plot | Pie Chart |
+| :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
+|  |  |  |
### Why Graphs are Important
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/azureml-quickstart.md b/docs/en/guides/azureml-quickstart.md
index 0ffaa45d..92e3d837 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/azureml-quickstart.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/azureml-quickstart.md
@@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ Before you can get started, make sure you have access to an AzureML workspace. I
From your AzureML workspace, select Compute > Compute instances > New, select the instance with the resources you need.
- **Mosaiced Image**: This image demonstrates a training batch composed of mosaiced dataset images. Mosaicing is a technique used during training that combines multiple images into a single image to increase the variety of objects and scenes within each training batch. This helps improve the model's ability to generalize to different object sizes, aspect ratios, and contexts.
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/segment/crack-seg.md b/docs/en/datasets/segment/crack-seg.md
index 83f01987..5fa99dfb 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/segment/crack-seg.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/segment/crack-seg.md
@@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ To train Ultralytics YOLOv8n model on the Crack Segmentation dataset for 100 epo
The Crack Segmentation dataset comprises a varied collection of images and videos captured from multiple perspectives. Below are instances of data from the dataset, accompanied by their respective annotations:
-
+
- This image presents an example of image object segmentation, featuring annotated bounding boxes with masks outlining identified objects. The dataset includes a diverse array of images taken in different locations, environments, and densities, making it a comprehensive resource for developing models designed for this particular task.
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/segment/package-seg.md b/docs/en/datasets/segment/package-seg.md
index 86fad9e9..bf88410f 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/segment/package-seg.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/segment/package-seg.md
@@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ To train Ultralytics YOLOv8n model on the Package Segmentation dataset for 100 e
The Package Segmentation dataset comprises a varied collection of images and videos captured from multiple perspectives. Below are instances of data from the dataset, accompanied by their respective annotations:
-
+
- This image displays an instance of image object detection, featuring annotated bounding boxes with masks outlining recognized objects. The dataset incorporates a diverse collection of images taken in different locations, environments, and densities. It serves as a comprehensive resource for developing models specific to this task.
- The example emphasizes the diversity and complexity present in the VisDrone dataset, underscoring the significance of high-quality sensor data for computer vision tasks involving drones.
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/analytics.md b/docs/en/guides/analytics.md
index 96cadb86..a29e6abe 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/analytics.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/analytics.md
@@ -12,9 +12,9 @@ This guide provides a comprehensive overview of three fundamental types of data
### Visual Samples
-| Line Graph | Bar Plot | Pie Chart |
-| :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
-|  |  |  |
+| Line Graph | Bar Plot | Pie Chart |
+| :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
+|  |  |  |
### Why Graphs are Important
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/azureml-quickstart.md b/docs/en/guides/azureml-quickstart.md
index 0ffaa45d..92e3d837 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/azureml-quickstart.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/azureml-quickstart.md
@@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ Before you can get started, make sure you have access to an AzureML workspace. I
From your AzureML workspace, select Compute > Compute instances > New, select the instance with the resources you need.
-
+

-
+

-
+

-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
 !!! Note
@@ -168,7 +168,7 @@ deepstream-app -c deepstream_app_config.txt
It will take a long time to generate the TensorRT engine file before starting the inference. So please be patient.
-
!!! Note
@@ -168,7 +168,7 @@ deepstream-app -c deepstream_app_config.txt
It will take a long time to generate the TensorRT engine file before starting the inference. So please be patient.
-

-  +
+ 
-  +
+ ![]()
-  +
+ 
- 

-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-
+

-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
 !!! Note
@@ -287,7 +287,7 @@ YOLOv8 benchmarks were run by the Ultralytics team on 10 different model formats
Even though all model exports are working with NVIDIA Jetson, we have only included **PyTorch, TorchScript, TensorRT** for the comparison chart below because, they make use of the GPU on the Jetson and are guaranteed to produce the best results. All the other exports only utilize the CPU and the performance is not as good as the above three. You can find benchmarks for all exports in the section after this chart.
!!! Note
@@ -287,7 +287,7 @@ YOLOv8 benchmarks were run by the Ultralytics team on 10 different model formats
Even though all model exports are working with NVIDIA Jetson, we have only included **PyTorch, TorchScript, TensorRT** for the comparison chart below because, they make use of the GPU on the Jetson and are guaranteed to produce the best results. All the other exports only utilize the CPU and the performance is not as good as the above three. You can find benchmarks for all exports in the section after this chart.

 ## Next Steps
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md b/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md
index 033b845f..00aa9174 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md
@@ -41,10 +41,10 @@ Object counting with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly
## Real World Applications
-| Logistics | Aquaculture |
-| :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
-|  | 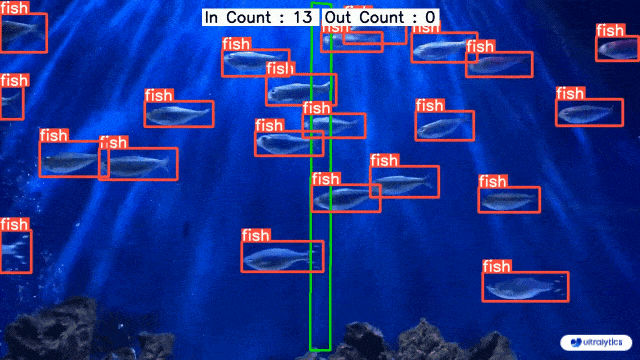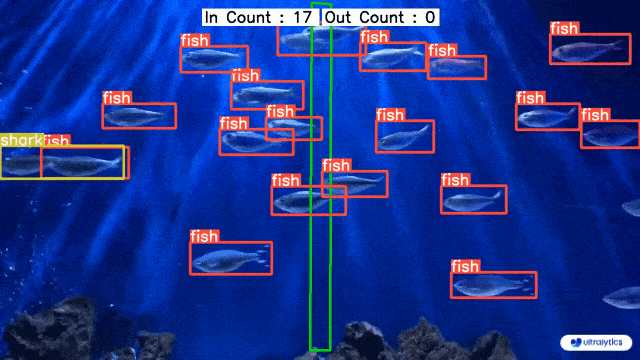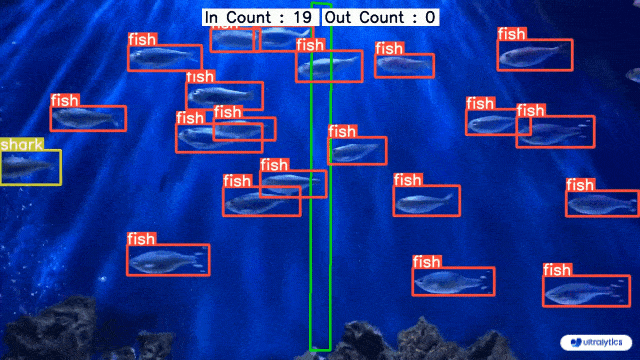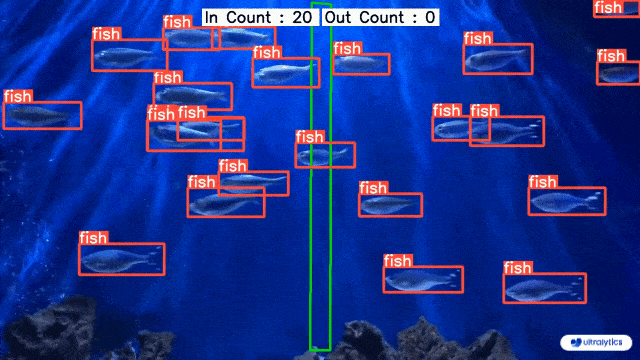 |
-| Conveyor Belt Packets Counting Using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Fish Counting in Sea using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
+| Logistics | Aquaculture |
+| :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
+|  |  |
+| Conveyor Belt Packets Counting Using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Fish Counting in Sea using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
!!! Example "Object Counting using YOLOv8 Example"
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md b/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md
index d314cee0..3efaba93 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md
@@ -29,10 +29,10 @@ Object cropping with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly
## Visuals
-| Airport Luggage |
-| :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
-| 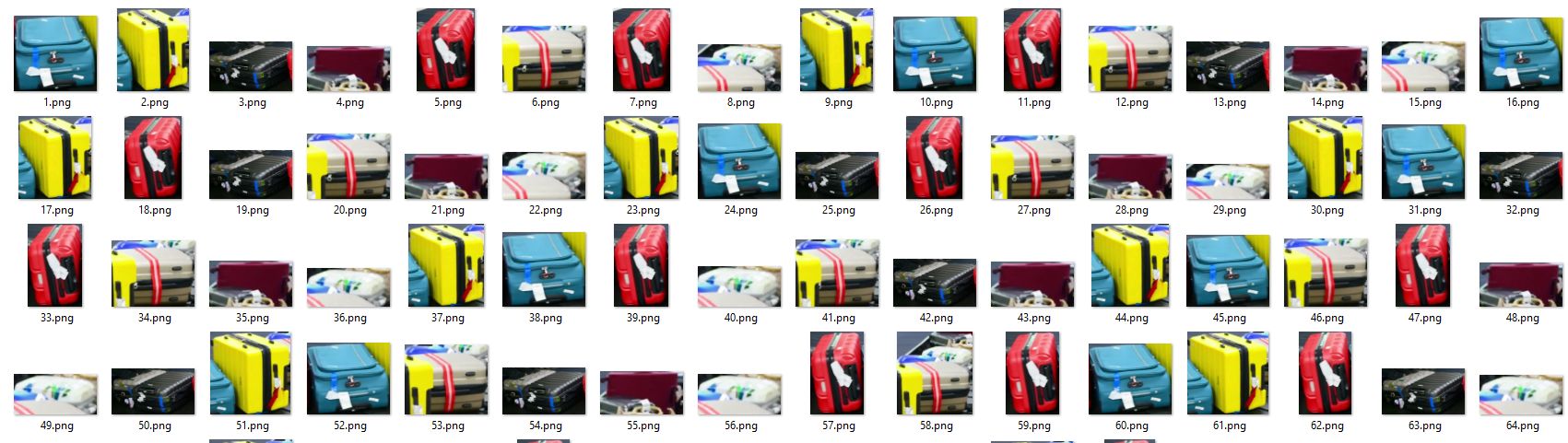 |
-| Suitcases Cropping at airport conveyor belt using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
+| Airport Luggage |
+| :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
+|  |
+| Suitcases Cropping at airport conveyor belt using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
!!! Example "Object Cropping using YOLOv8 Example"
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/optimizing-openvino-latency-vs-throughput-modes.md b/docs/en/guides/optimizing-openvino-latency-vs-throughput-modes.md
index b6886d5d..a9acfb12 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/optimizing-openvino-latency-vs-throughput-modes.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/optimizing-openvino-latency-vs-throughput-modes.md
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics YOLO, OpenVINO optimization, deep learning, model inferenc
# Optimizing OpenVINO Inference for Ultralytics YOLO Models: A Comprehensive Guide
-
## Next Steps
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md b/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md
index 033b845f..00aa9174 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md
@@ -41,10 +41,10 @@ Object counting with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly
## Real World Applications
-| Logistics | Aquaculture |
-| :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
-|  |  |
-| Conveyor Belt Packets Counting Using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Fish Counting in Sea using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
+| Logistics | Aquaculture |
+| :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
+|  |  |
+| Conveyor Belt Packets Counting Using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Fish Counting in Sea using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
!!! Example "Object Counting using YOLOv8 Example"
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md b/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md
index d314cee0..3efaba93 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md
@@ -29,10 +29,10 @@ Object cropping with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly
## Visuals
-| Airport Luggage |
-| :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
-|  |
-| Suitcases Cropping at airport conveyor belt using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
+| Airport Luggage |
+| :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
+|  |
+| Suitcases Cropping at airport conveyor belt using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
!!! Example "Object Cropping using YOLOv8 Example"
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/optimizing-openvino-latency-vs-throughput-modes.md b/docs/en/guides/optimizing-openvino-latency-vs-throughput-modes.md
index b6886d5d..a9acfb12 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/optimizing-openvino-latency-vs-throughput-modes.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/optimizing-openvino-latency-vs-throughput-modes.md
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics YOLO, OpenVINO optimization, deep learning, model inferenc
# Optimizing OpenVINO Inference for Ultralytics YOLO Models: A Comprehensive Guide
- ## Introduction
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/parking-management.md b/docs/en/guides/parking-management.md
index cc42fb9b..e25936fb 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/parking-management.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/parking-management.md
@@ -29,10 +29,10 @@ Parking management with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultr
## Real World Applications
-| Parking Management System | Parking Management System |
-| :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
-|  |  |
-| Parking management Aerial View using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Parking management Top View using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
+| Parking Management System | Parking Management System |
+| :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
+|  |  |
+| Parking management Aerial View using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Parking management Top View using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
## Parking Management System Code Workflow
@@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ Parking management with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultr
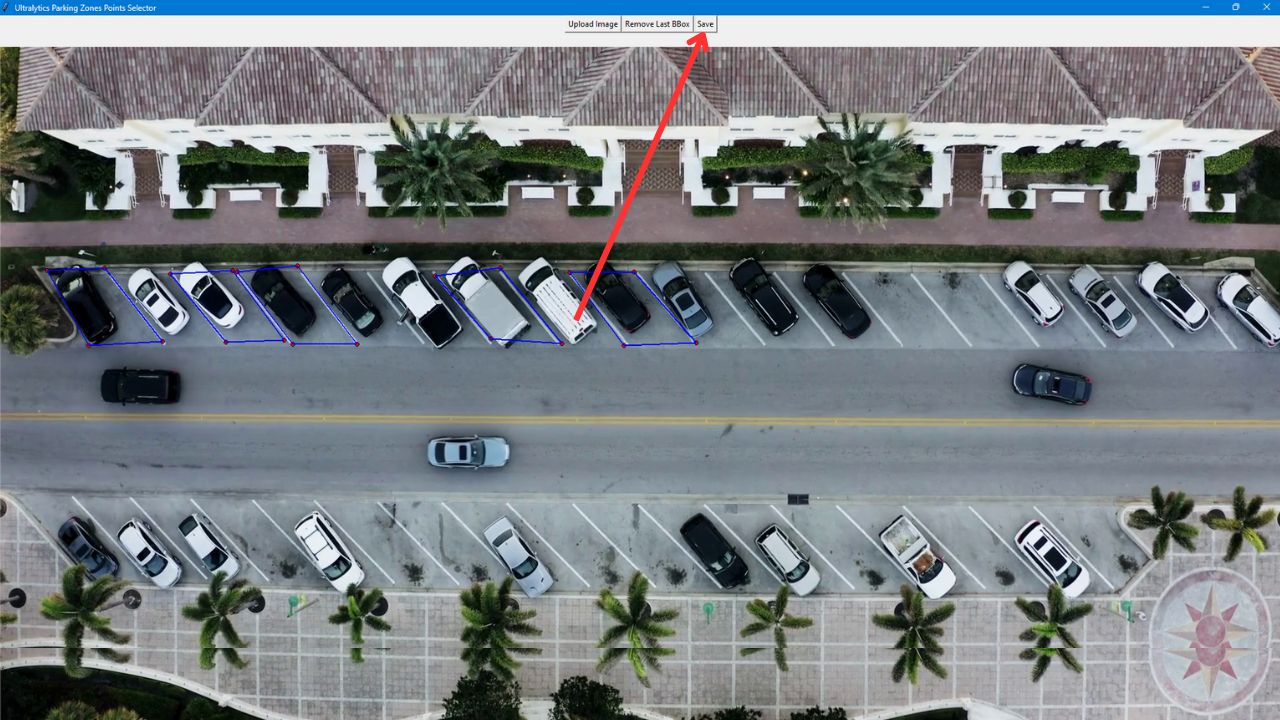
- After defining the parking areas with polygons, click `save` to store a JSON file with the data in your working directory.
-
+
### Python Code for Parking Management
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/preprocessing_annotated_data.md b/docs/en/guides/preprocessing_annotated_data.md
index 8935d7d8..ef771a28 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/preprocessing_annotated_data.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/preprocessing_annotated_data.md
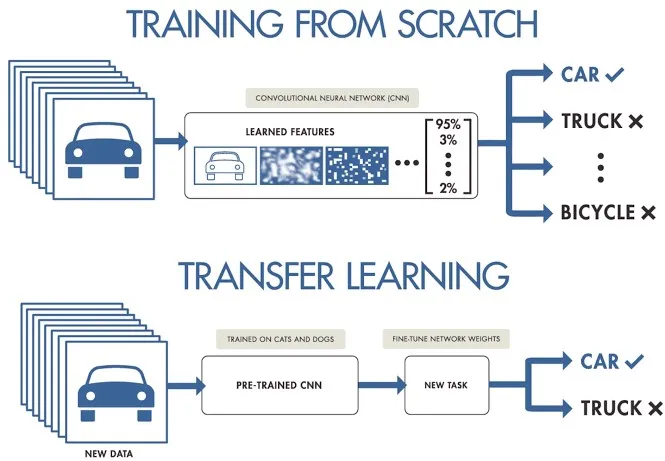
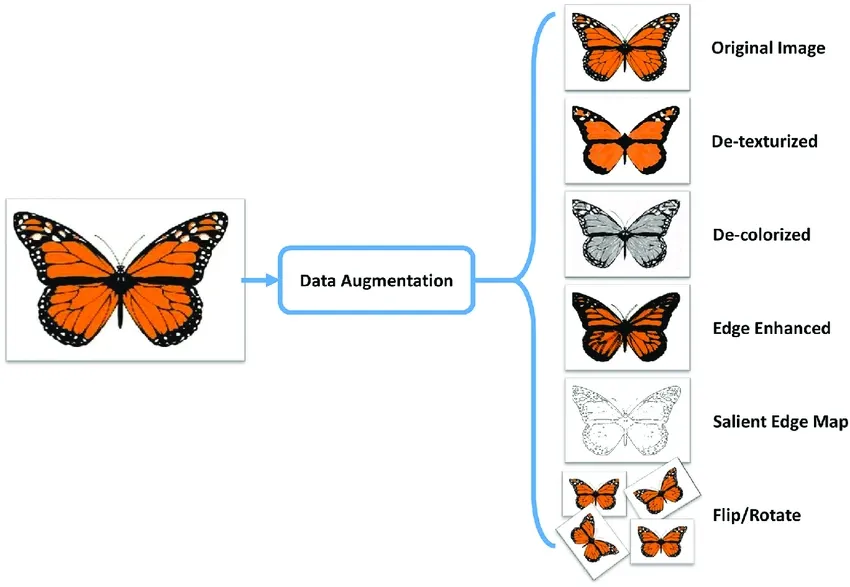
@@ -73,7 +73,7 @@ Here are some other benefits of data augmentation:
Common augmentation techniques include flipping, rotation, scaling, and color adjustments. Several libraries, such as Albumentations, Imgaug, and TensorFlow's ImageDataGenerator, can generate these augmentations.
## Introduction
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/parking-management.md b/docs/en/guides/parking-management.md
index cc42fb9b..e25936fb 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/parking-management.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/parking-management.md
@@ -29,10 +29,10 @@ Parking management with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultr
## Real World Applications
-| Parking Management System | Parking Management System |
-| :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
-|  |  |
-| Parking management Aerial View using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Parking management Top View using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
+| Parking Management System | Parking Management System |
+| :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
+|  |  |
+| Parking management Aerial View using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Parking management Top View using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
## Parking Management System Code Workflow
@@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ Parking management with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultr
- After defining the parking areas with polygons, click `save` to store a JSON file with the data in your working directory.
-
+
### Python Code for Parking Management
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/preprocessing_annotated_data.md b/docs/en/guides/preprocessing_annotated_data.md
index 8935d7d8..ef771a28 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/preprocessing_annotated_data.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/preprocessing_annotated_data.md
@@ -73,7 +73,7 @@ Here are some other benefits of data augmentation:
Common augmentation techniques include flipping, rotation, scaling, and color adjustments. Several libraries, such as Albumentations, Imgaug, and TensorFlow's ImageDataGenerator, can generate these augmentations.
-  +
+ 
-
+



-
+

-
+

-
+

-
+

-  +
+ 




 The Security Alarm System Project utilizing Ultralytics YOLOv8 integrates advanced computer vision capabilities to enhance security measures. YOLOv8, developed by Ultralytics, provides real-time object detection, allowing the system to identify and respond to potential security threats promptly. This project offers several advantages:
@@ -175,7 +175,7 @@ That's it! When you execute the code, you'll receive a single notification on yo
#### Email Received Sample
-
The Security Alarm System Project utilizing Ultralytics YOLOv8 integrates advanced computer vision capabilities to enhance security measures. YOLOv8, developed by Ultralytics, provides real-time object detection, allowing the system to identify and respond to potential security threats promptly. This project offers several advantages:
@@ -175,7 +175,7 @@ That's it! When you execute the code, you'll receive a single notification on yo
#### Email Received Sample
- ## FAQ
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/speed-estimation.md b/docs/en/guides/speed-estimation.md
index ee42bfe6..9e9ddce5 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/speed-estimation.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/speed-estimation.md
@@ -33,10 +33,10 @@ keywords: Ultralytics YOLOv8, speed estimation, object tracking, computer vision
## Real World Applications
-| Transportation | Transportation |
-| :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
-|  | 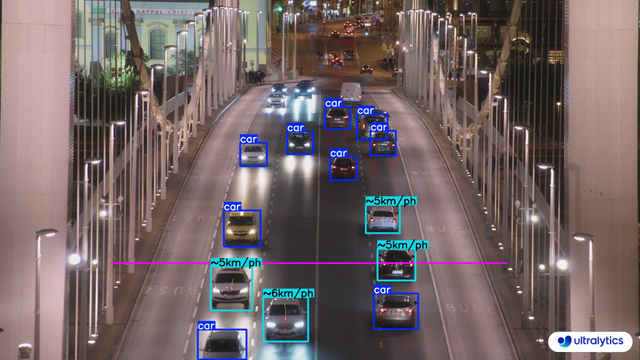 |
-| Speed Estimation on Road using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Speed Estimation on Bridge using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
+| Transportation | Transportation |
+| :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
+|  |  |
+| Speed Estimation on Road using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Speed Estimation on Bridge using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
!!! Example "Speed Estimation using YOLOv8 Example"
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/steps-of-a-cv-project.md b/docs/en/guides/steps-of-a-cv-project.md
index a1fbdb5e..3b98171d 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/steps-of-a-cv-project.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/steps-of-a-cv-project.md
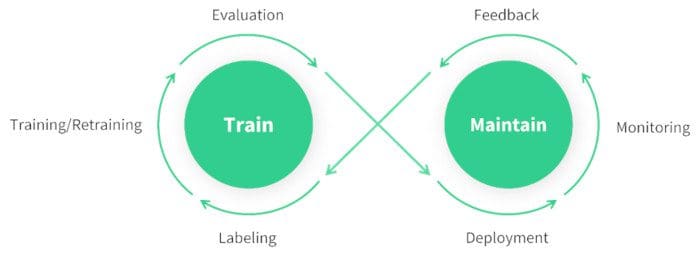
@@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ Before discussing the details of each step involved in a computer vision project
- Finally, you'd deploy your model into the real world and update it based on new insights and feedback.
## FAQ
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/speed-estimation.md b/docs/en/guides/speed-estimation.md
index ee42bfe6..9e9ddce5 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/speed-estimation.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/speed-estimation.md
@@ -33,10 +33,10 @@ keywords: Ultralytics YOLOv8, speed estimation, object tracking, computer vision
## Real World Applications
-| Transportation | Transportation |
-| :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
-|  |  |
-| Speed Estimation on Road using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Speed Estimation on Bridge using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
+| Transportation | Transportation |
+| :------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
+|  |  |
+| Speed Estimation on Road using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Speed Estimation on Bridge using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
!!! Example "Speed Estimation using YOLOv8 Example"
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/steps-of-a-cv-project.md b/docs/en/guides/steps-of-a-cv-project.md
index a1fbdb5e..3b98171d 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/steps-of-a-cv-project.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/steps-of-a-cv-project.md
@@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ Before discussing the details of each step involved in a computer vision project
- Finally, you'd deploy your model into the real world and update it based on new insights and feedback.
- .jpeg) +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-
+

-  +
+ 
-
+

-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
-
+

-
+

-  +
+ 
-  +
+ 
 +
+ ## Table of Contents
diff --git a/docs/en/hub/app/android.md b/docs/en/hub/app/android.md
index 847ae916..c3c19b0c 100644
--- a/docs/en/hub/app/android.md
+++ b/docs/en/hub/app/android.md
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, Android app, real-time object detection, YOLO models, Ten
# Ultralytics Android App: Real-time Object Detection with YOLO Models
-
## Table of Contents
diff --git a/docs/en/hub/app/android.md b/docs/en/hub/app/android.md
index 847ae916..c3c19b0c 100644
--- a/docs/en/hub/app/android.md
+++ b/docs/en/hub/app/android.md
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, Android app, real-time object detection, YOLO models, Ten
# Ultralytics Android App: Real-time Object Detection with YOLO Models
- 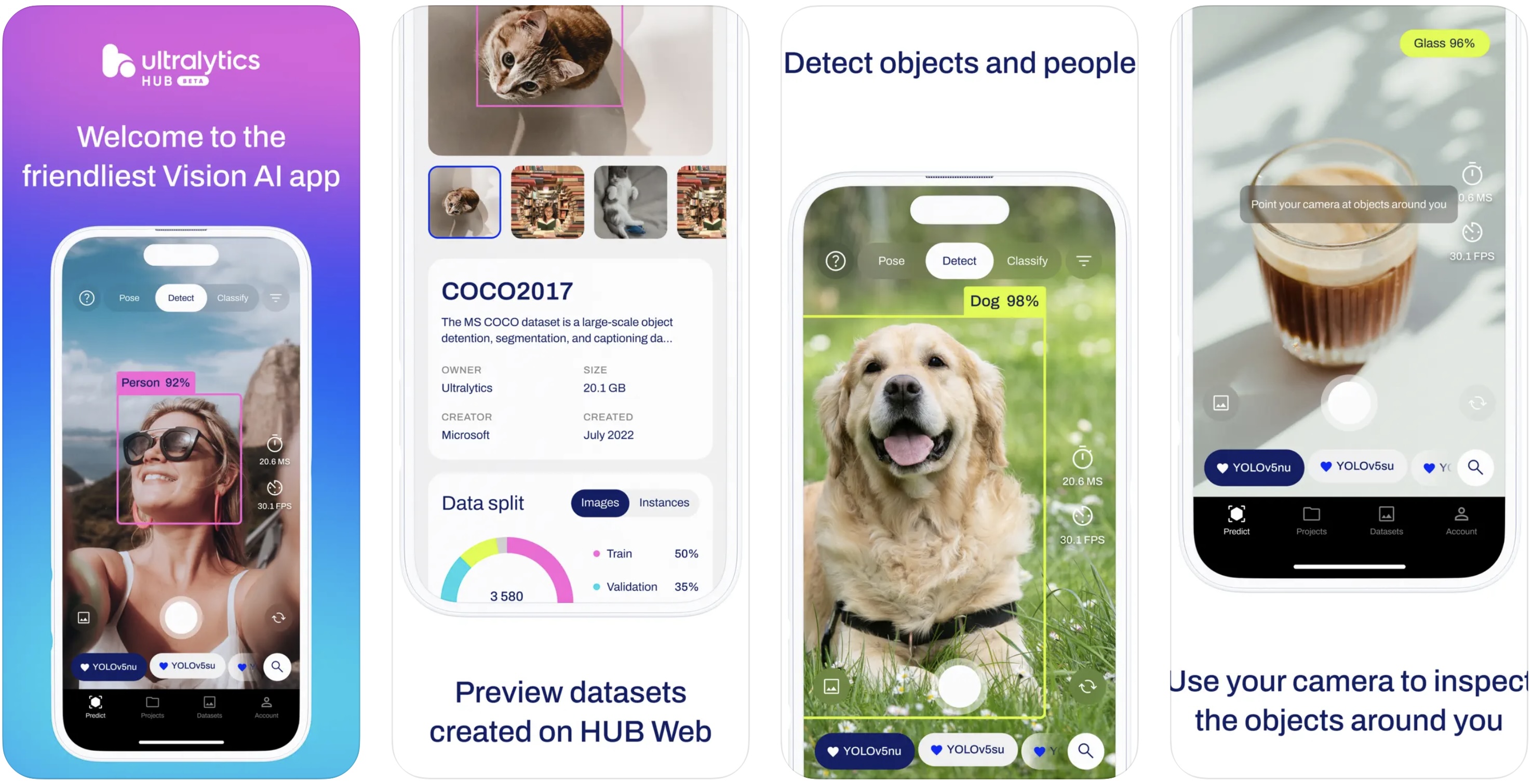 +
+ 
 diff --git a/docs/en/hub/app/index.md b/docs/en/hub/app/index.md
index 7d1731d4..9266a0bd 100644
--- a/docs/en/hub/app/index.md
+++ b/docs/en/hub/app/index.md
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics HUB, YOLO models, mobile app, iOS, Android, hardware accel
# Ultralytics HUB App
-
diff --git a/docs/en/hub/app/index.md b/docs/en/hub/app/index.md
index 7d1731d4..9266a0bd 100644
--- a/docs/en/hub/app/index.md
+++ b/docs/en/hub/app/index.md
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics HUB, YOLO models, mobile app, iOS, Android, hardware accel
# Ultralytics HUB App
-  +
+ 
 diff --git a/docs/en/hub/app/ios.md b/docs/en/hub/app/ios.md
index 2bbeb465..5468633f 100644
--- a/docs/en/hub/app/ios.md
+++ b/docs/en/hub/app/ios.md
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, iOS App, YOLO models, real-time object detection, Apple N
# Ultralytics iOS App: Real-time Object Detection with YOLO Models
-
diff --git a/docs/en/hub/app/ios.md b/docs/en/hub/app/ios.md
index 2bbeb465..5468633f 100644
--- a/docs/en/hub/app/ios.md
+++ b/docs/en/hub/app/ios.md
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, iOS App, YOLO models, real-time object detection, Apple N
# Ultralytics iOS App: Real-time Object Detection with YOLO Models
-  +
+ 
 diff --git a/docs/en/hub/cloud-training.md b/docs/en/hub/cloud-training.md
index ab22a767..9d09a18f 100644
--- a/docs/en/hub/cloud-training.md
+++ b/docs/en/hub/cloud-training.md
@@ -26,13 +26,13 @@ In order to train models using Ultralytics Cloud Training, you need to [upgrade]
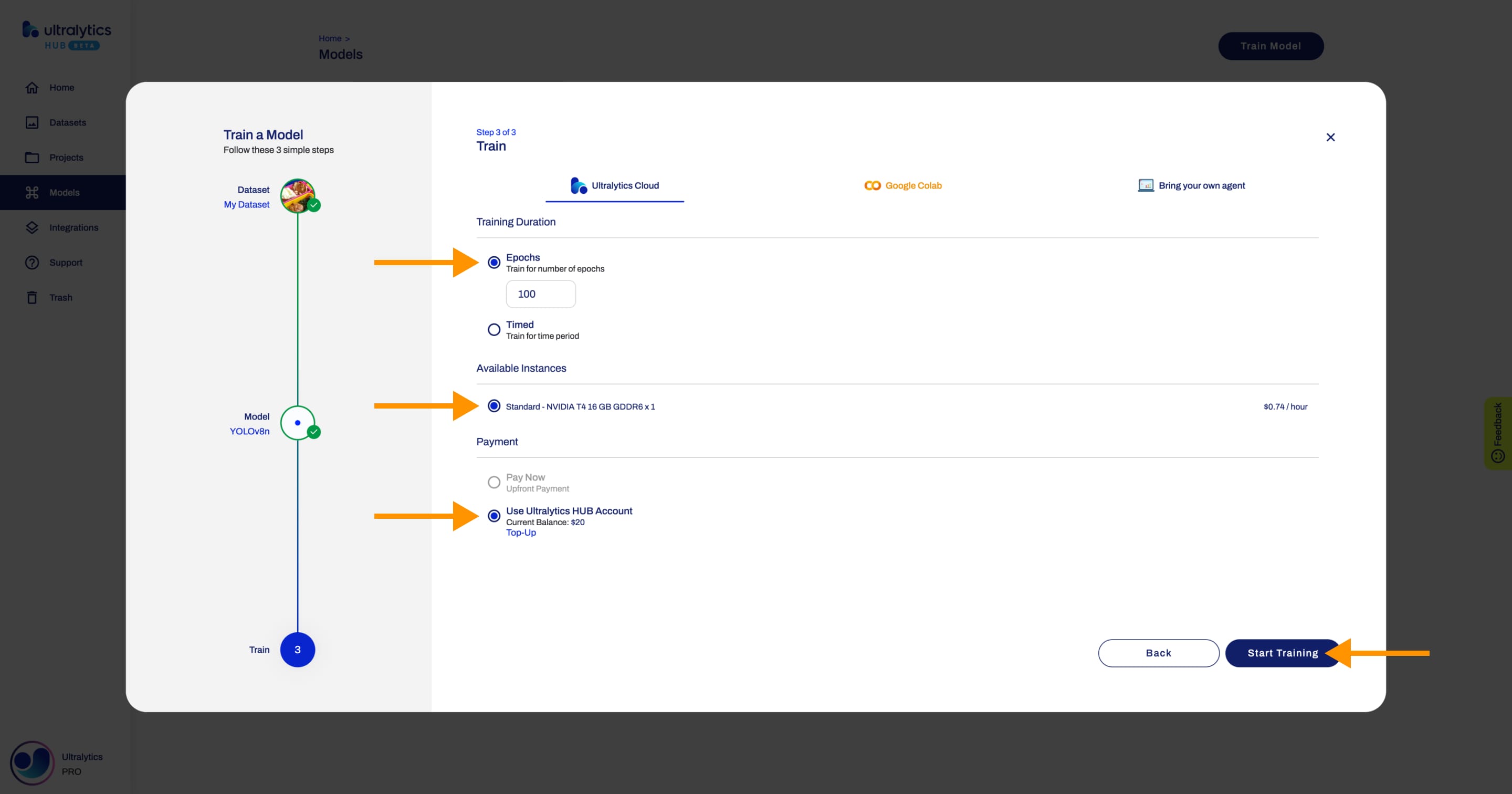
Follow the [Train Model](./models.md#train-model) instructions from the [Models](./models.md) page until you reach the third step ([Train](./models.md#3-train)) of the **Train Model** dialog. Once you are on this step, simply select the training duration (Epochs or Timed), the training instance, the payment method, and click the **Start Training** button. That's it!
-
+
??? note "Note"
When you are on this step, you have the option to close the **Train Model** dialog and start training your model from the Model page later.
- 
+ 
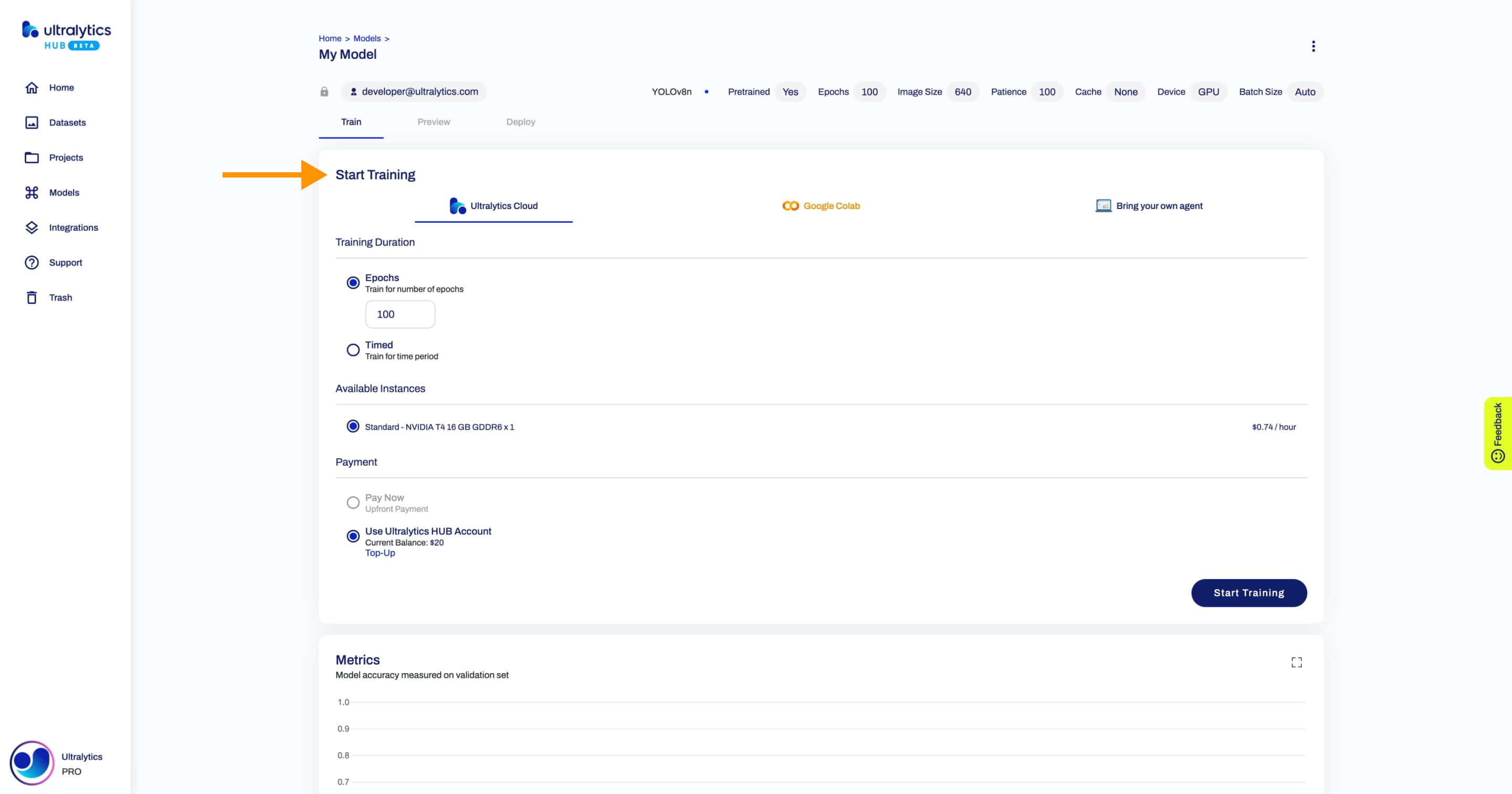
Most of the times, you will use the Epochs training. The number of epochs can be adjusted on this step (if the training didn't start yet) and represents the number of times your dataset needs to go through the cycle of train, label, and test. The exact pricing based on the number of epochs is hard to determine, reason why we only allow the [Account Balance](./pro.md#account-balance) payment method.
@@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ Most of the times, you will use the Epochs training. The number of epochs can be
When using the Epochs training, your [account balance](./pro.md#account-balance) needs to be at least US$5.00 to start training. In case you have a low balance, you can top-up directly from this step.
- 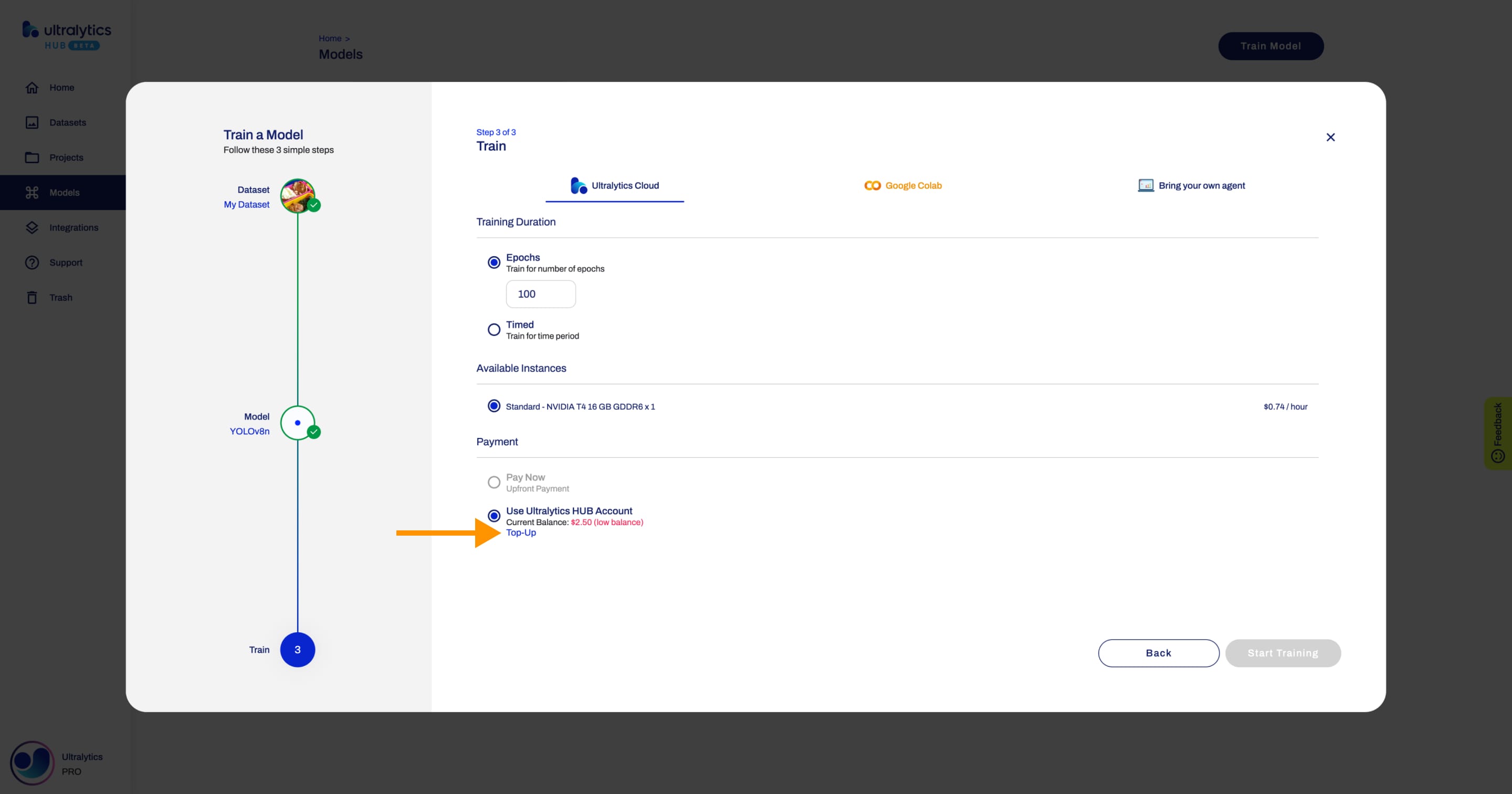
+ 
!!! note "Note"
@@ -48,21 +48,21 @@ Most of the times, you will use the Epochs training. The number of epochs can be
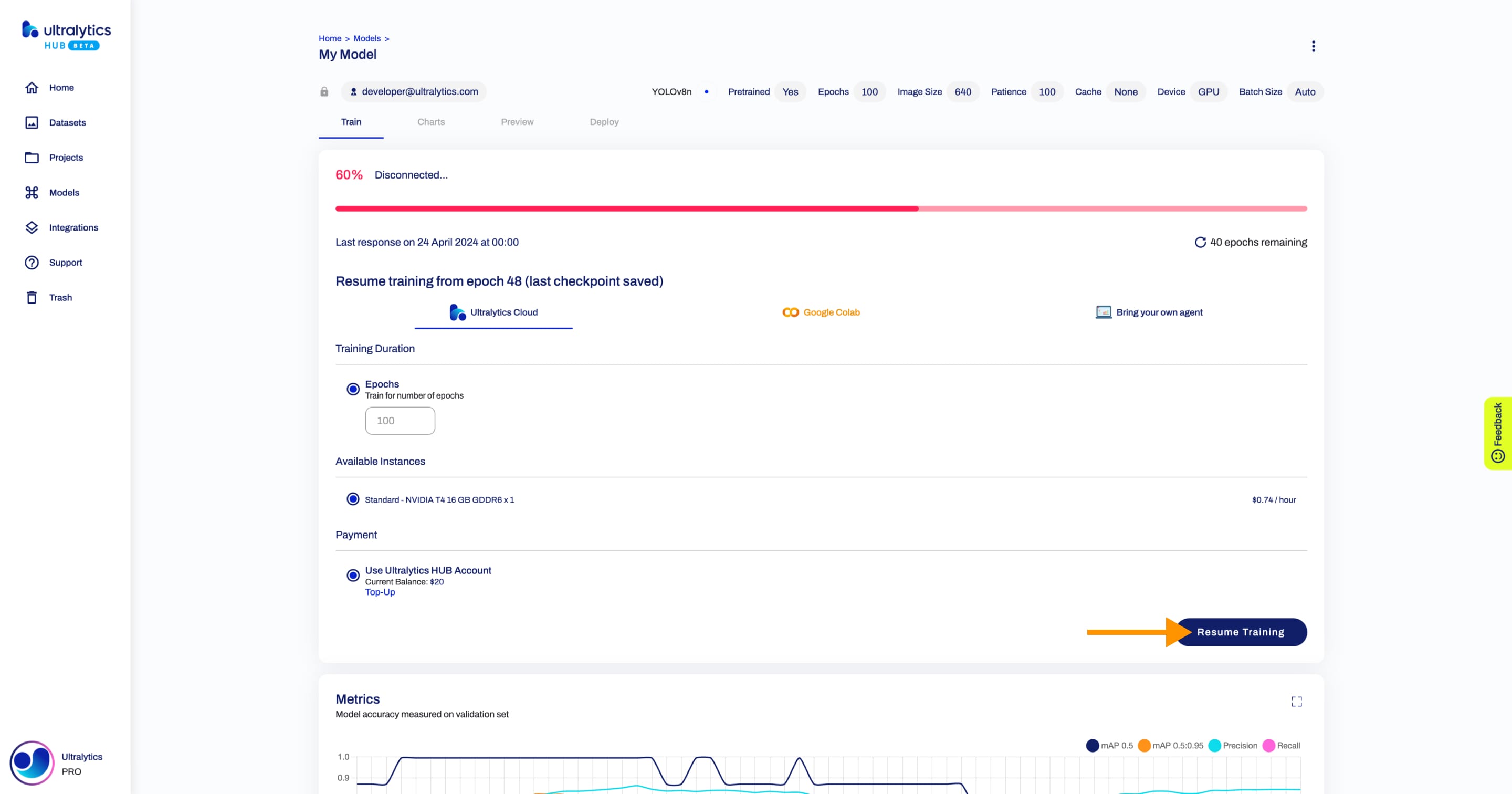
Also, after every epoch, we check if you have enough [account balance](./pro.md#account-balance) for the next epoch. In case you don't have enough [account balance](./pro.md#account-balance) for the next epoch, we will stop the training session, allowing you to resume training your model from the last checkpoint saved.
- 
+ 
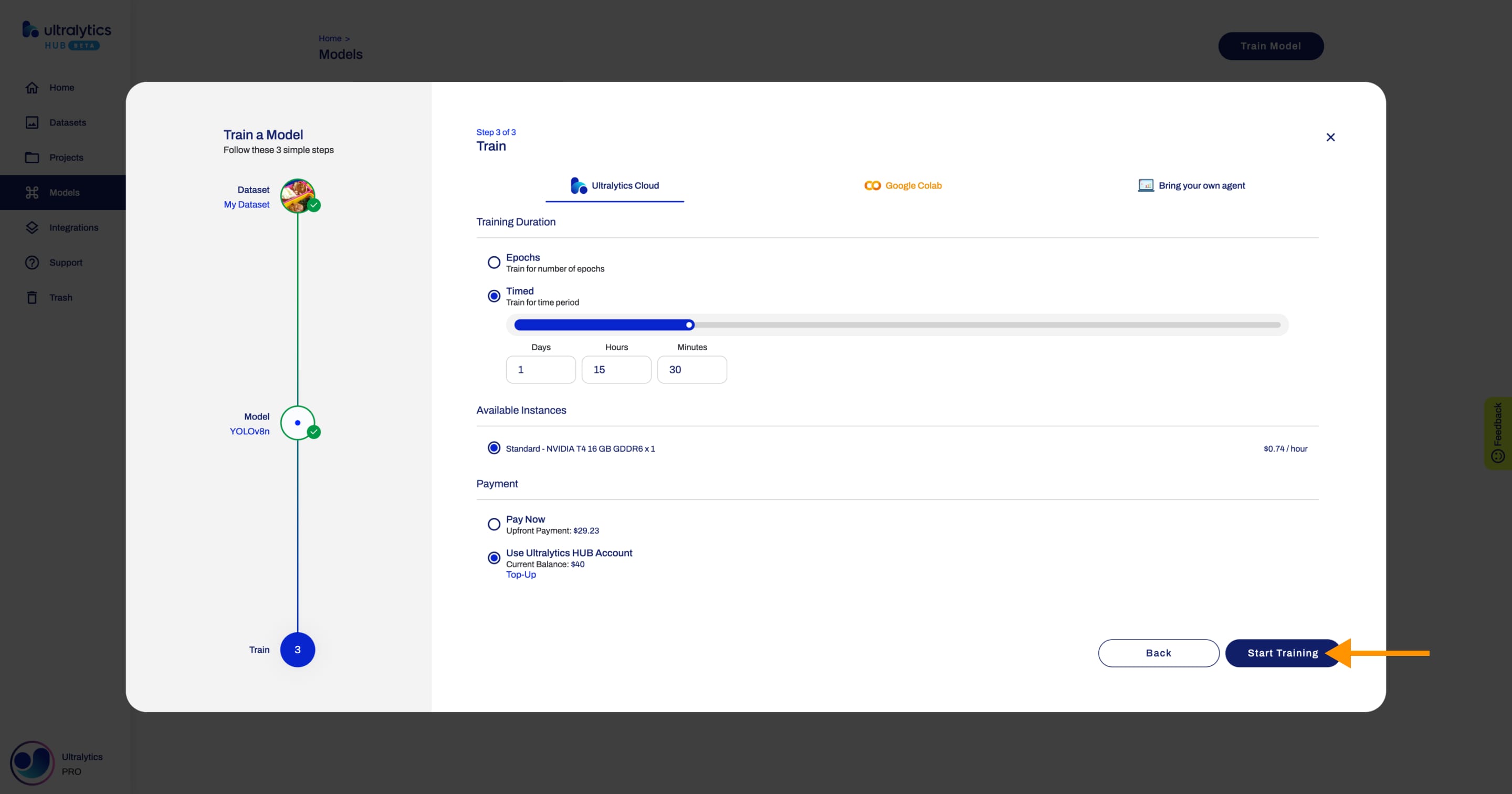
Alternatively, you can use the Timed training. This option allows you to set the training duration. In this case, we can determine the exact pricing. You can pay upfront or using your [account balance](./pro.md#account-balance).
If you have enough [account balance](./pro.md#account-balance), you can use the [Account Balance](./pro.md#account-balance) payment method.
-
+
If you don't have enough [account balance](./pro.md#account-balance), you won't be able to use the [Account Balance](./pro.md#account-balance) payment method. You can pay upfront or top-up directly from this step.
-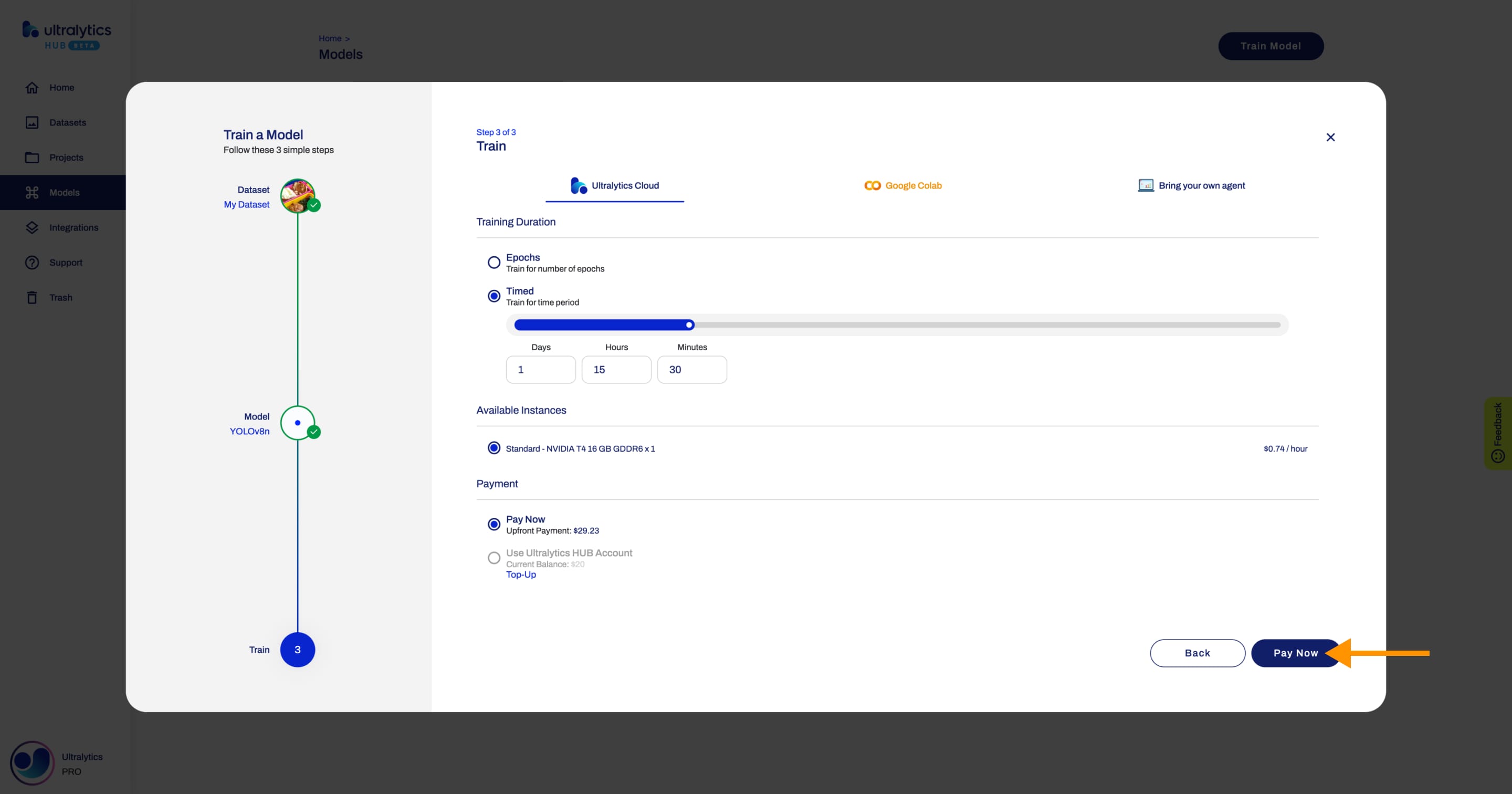
+
Before the training session starts, the initialization process spins up a dedicated instance equipped with GPU resources, which can sometimes take a while depending on the current demand and availability of GPU resources.
-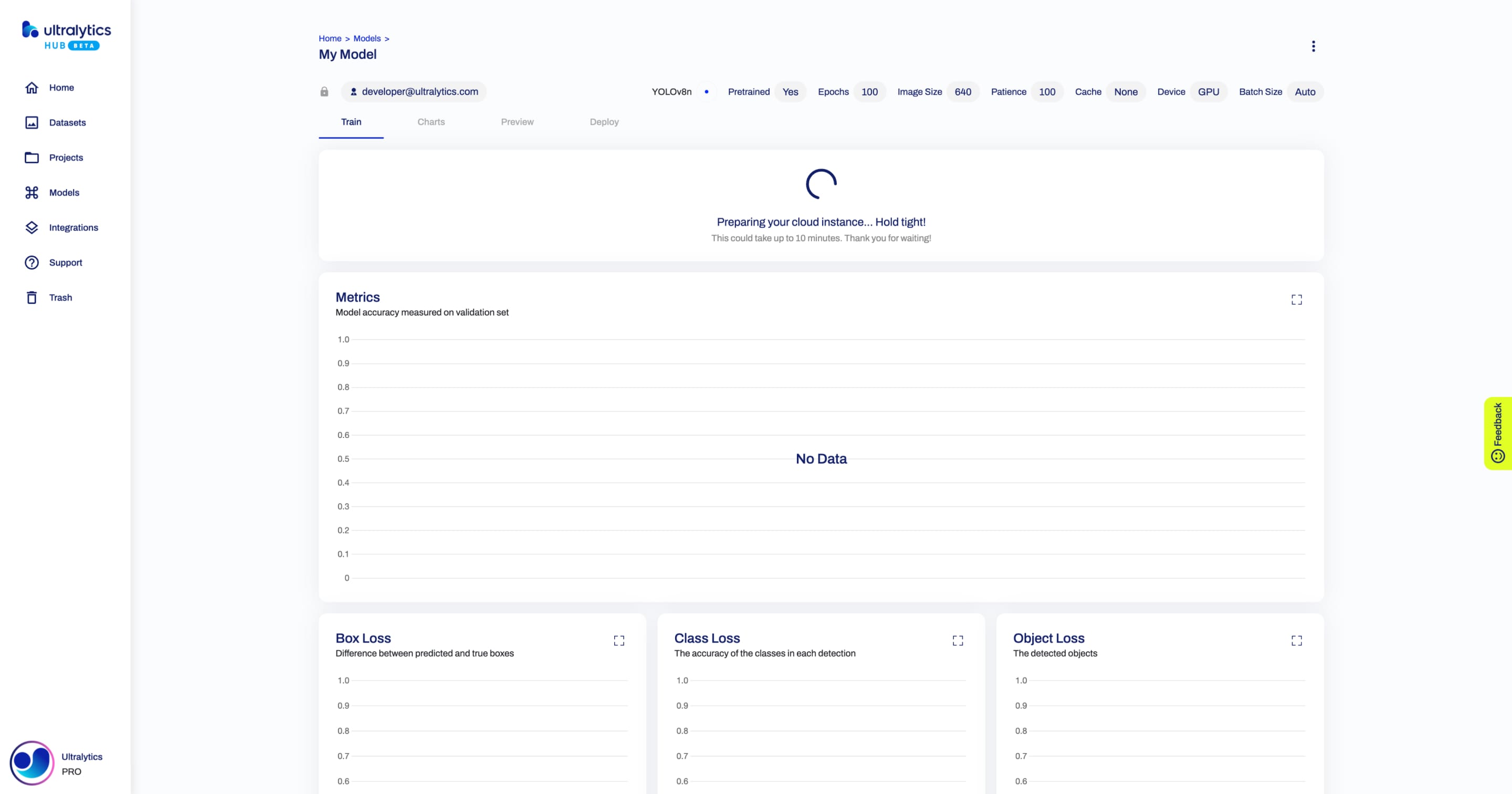
+
!!! note "Note"
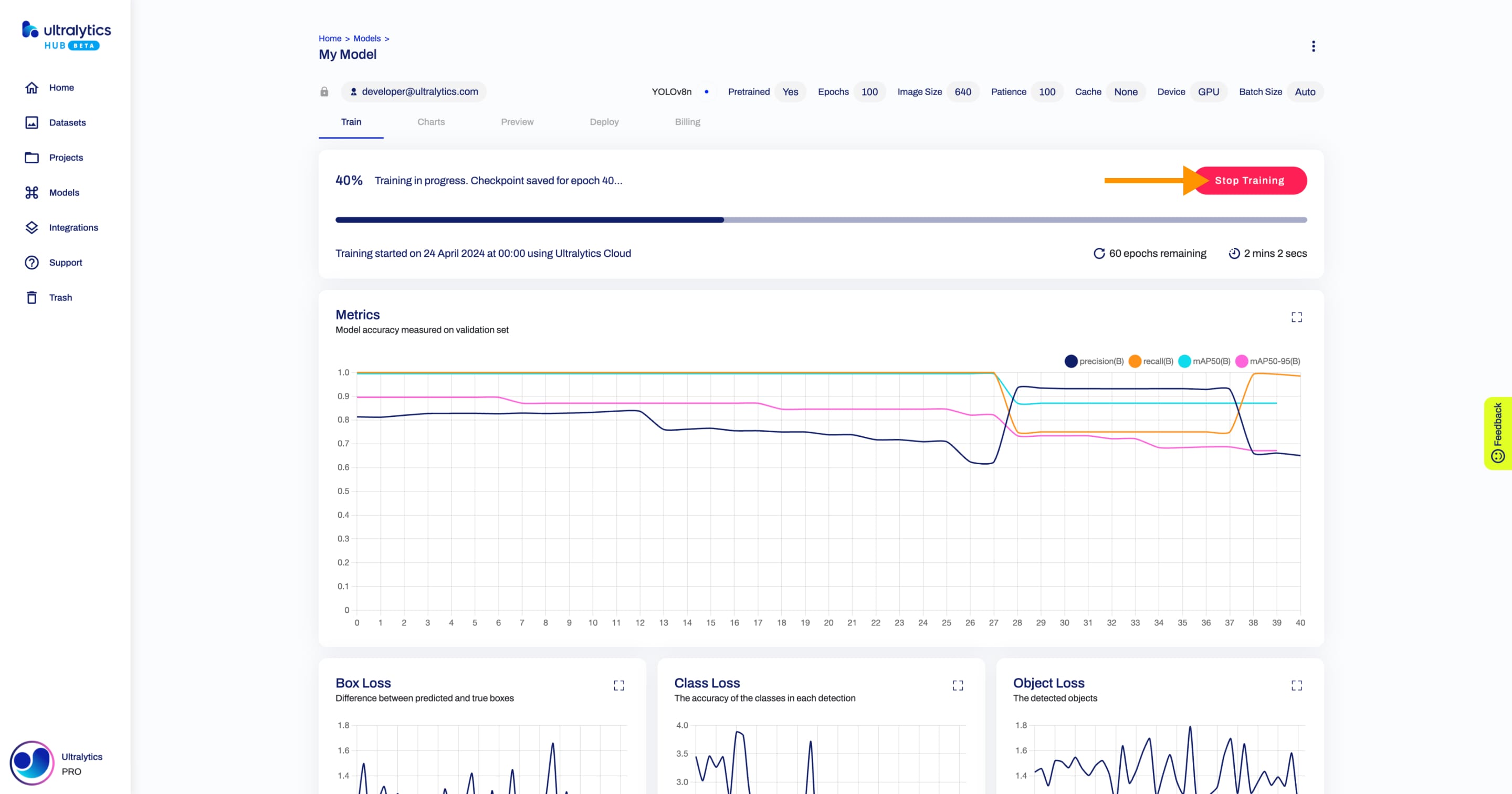
@@ -72,13 +72,13 @@ After the training session starts, you can monitor each step of the progress.
If needed, you can stop the training by clicking on the **Stop Training** button.
-
+
!!! note "Note"
You can resume training your model from the last checkpoint saved.
- 
+ 
diff --git a/docs/en/hub/cloud-training.md b/docs/en/hub/cloud-training.md
index ab22a767..9d09a18f 100644
--- a/docs/en/hub/cloud-training.md
+++ b/docs/en/hub/cloud-training.md
@@ -26,13 +26,13 @@ In order to train models using Ultralytics Cloud Training, you need to [upgrade]
Follow the [Train Model](./models.md#train-model) instructions from the [Models](./models.md) page until you reach the third step ([Train](./models.md#3-train)) of the **Train Model** dialog. Once you are on this step, simply select the training duration (Epochs or Timed), the training instance, the payment method, and click the **Start Training** button. That's it!
-
+
??? note "Note"
When you are on this step, you have the option to close the **Train Model** dialog and start training your model from the Model page later.
- 
+ 
Most of the times, you will use the Epochs training. The number of epochs can be adjusted on this step (if the training didn't start yet) and represents the number of times your dataset needs to go through the cycle of train, label, and test. The exact pricing based on the number of epochs is hard to determine, reason why we only allow the [Account Balance](./pro.md#account-balance) payment method.
@@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ Most of the times, you will use the Epochs training. The number of epochs can be
When using the Epochs training, your [account balance](./pro.md#account-balance) needs to be at least US$5.00 to start training. In case you have a low balance, you can top-up directly from this step.
- 
+ 
!!! note "Note"
@@ -48,21 +48,21 @@ Most of the times, you will use the Epochs training. The number of epochs can be
Also, after every epoch, we check if you have enough [account balance](./pro.md#account-balance) for the next epoch. In case you don't have enough [account balance](./pro.md#account-balance) for the next epoch, we will stop the training session, allowing you to resume training your model from the last checkpoint saved.
- 
+ 
Alternatively, you can use the Timed training. This option allows you to set the training duration. In this case, we can determine the exact pricing. You can pay upfront or using your [account balance](./pro.md#account-balance).
If you have enough [account balance](./pro.md#account-balance), you can use the [Account Balance](./pro.md#account-balance) payment method.
-
+
If you don't have enough [account balance](./pro.md#account-balance), you won't be able to use the [Account Balance](./pro.md#account-balance) payment method. You can pay upfront or top-up directly from this step.
-
+
Before the training session starts, the initialization process spins up a dedicated instance equipped with GPU resources, which can sometimes take a while depending on the current demand and availability of GPU resources.
-
+
!!! note "Note"
@@ -72,13 +72,13 @@ After the training session starts, you can monitor each step of the progress.
If needed, you can stop the training by clicking on the **Stop Training** button.
-
+
!!! note "Note"
You can resume training your model from the last checkpoint saved.
- 
+ 