-
@@ -193,4 +193,4 @@ Congratulations on successfully setting up YOLO on your Raspberry Pi! For furthe
This guide was initially created by Daan Eeltink for Kashmir World Foundation, an organization dedicated to the use of YOLO for the conservation of endangered species. We acknowledge their pioneering work and educational focus in the realm of object detection technologies.
-For more information about Kashmir World Foundation's activities, you can visit their [website](https://www.kashmirworldfoundation.org/).
\ No newline at end of file
+For more information about Kashmir World Foundation's activities, you can visit their [website](https://www.kashmirworldfoundation.org/).
diff --git a/docs/guides/sahi-tiled-inference.md b/docs/guides/sahi-tiled-inference.md
index abed5bde..fe9c599a 100644
--- a/docs/guides/sahi-tiled-inference.md
+++ b/docs/guides/sahi-tiled-inference.md
@@ -182,4 +182,4 @@ If you use SAHI in your research or development work, please cite the original S
}
```
-We extend our thanks to the SAHI research group for creating and maintaining this invaluable resource for the computer vision community. For more information about SAHI and its creators, visit the [SAHI GitHub repository](https://github.com/obss/sahi).
\ No newline at end of file
+We extend our thanks to the SAHI research group for creating and maintaining this invaluable resource for the computer vision community. For more information about SAHI and its creators, visit the [SAHI GitHub repository](https://github.com/obss/sahi).
diff --git a/docs/guides/triton-inference-server.md b/docs/guides/triton-inference-server.md
index b8bcfab4..0be56438 100644
--- a/docs/guides/triton-inference-server.md
+++ b/docs/guides/triton-inference-server.md
@@ -10,9 +10,9 @@ The [Triton Inference Server](https://developer.nvidia.com/nvidia-triton-inferen
-
@@ -60,11 +60,11 @@ The Triton Model Repository is a storage location where Triton can access and lo
```python
from pathlib import Path
-
+
# Define paths
triton_repo_path = Path('tmp') / 'triton_repo'
triton_model_path = triton_repo_path / 'yolo'
-
+
# Create directories
(triton_model_path / '1').mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
```
@@ -73,10 +73,10 @@ The Triton Model Repository is a storage location where Triton can access and lo
```python
from pathlib import Path
-
+
# Move ONNX model to Triton Model path
Path(onnx_file).rename(triton_model_path / '1' / 'model.onnx')
-
+
# Create config file
(triton_model_path / 'config.pdtxt').touch()
```
@@ -134,4 +134,4 @@ subprocess.call(f'docker kill {container_id}', shell=True)
---
-By following the above steps, you can deploy and run Ultralytics YOLOv8 models efficiently on Triton Inference Server, providing a scalable and high-performance solution for deep learning inference tasks. If you face any issues or have further queries, refer to the [official Triton documentation](https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/triton-inference-server/user-guide/docs/index.html) or reach out to the Ultralytics community for support.
\ No newline at end of file
+By following the above steps, you can deploy and run Ultralytics YOLOv8 models efficiently on Triton Inference Server, providing a scalable and high-performance solution for deep learning inference tasks. If you face any issues or have further queries, refer to the [official Triton documentation](https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/triton-inference-server/user-guide/docs/index.html) or reach out to the Ultralytics community for support.
diff --git a/docs/help/CI.md b/docs/help/CI.md
index 55e5dc9f..7d942599 100644
--- a/docs/help/CI.md
+++ b/docs/help/CI.md
@@ -50,8 +50,8 @@ By integrating with Codecov, we aim to maintain and improve the quality of our c
To quickly get a glimpse of the code coverage status of the `ultralytics` python package, we have included a badge and and sunburst visual of the `ultralytics` coverage results. These images show the percentage of code covered by our tests, offering an at-a-glance metric of our testing efforts. For full details please see https://codecov.io/github/ultralytics/ultralytics.
-| Repository | Code Coverage |
-|-----------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| Repository | Code Coverage |
+|-----------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| [ultralytics](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) | [](https://codecov.io/gh/ultralytics/ultralytics) |
In the sunburst graphic below, the inner-most circle is the entire project, moving away from the center are folders then, finally, a single file. The size and color of each slice is representing the number of statements and the coverage, respectively.
@@ -59,4 +59,3 @@ In the sunburst graphic below, the inner-most circle is the entire project, movi
-
diff --git a/docs/help/CLA.md b/docs/help/CLA.md
index 6edc4e37..b33b4880 100644
--- a/docs/help/CLA.md
+++ b/docs/help/CLA.md
@@ -5,66 +5,27 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, Contributor License Agreement, Open Source Software, Cont
# Ultralytics Individual Contributor License Agreement
-Thank you for your interest in contributing to open source software projects (“Projects”) made available by Ultralytics
-SE or its affiliates (“Ultralytics”). This Individual Contributor License Agreement (“Agreement”) sets out the terms
-governing any source code, object code, bug fixes, configuration changes, tools, specifications, documentation, data,
-materials, feedback, information or other works of authorship that you submit or have submitted, in any form and in any
-manner, to Ultralytics in respect of any of the Projects (collectively “Contributions”). If you have any questions
-respecting this Agreement, please contact hello@ultralytics.com.
+Thank you for your interest in contributing to open source software projects (“Projects”) made available by Ultralytics SE or its affiliates (“Ultralytics”). This Individual Contributor License Agreement (“Agreement”) sets out the terms governing any source code, object code, bug fixes, configuration changes, tools, specifications, documentation, data, materials, feedback, information or other works of authorship that you submit or have submitted, in any form and in any manner, to Ultralytics in respect of any of the Projects (collectively “Contributions”). If you have any questions respecting this Agreement, please contact hello@ultralytics.com.
-You agree that the following terms apply to all of your past, present and future Contributions. Except for the licenses
-granted in this Agreement, you retain all of your right, title and interest in and to your Contributions.
+You agree that the following terms apply to all of your past, present and future Contributions. Except for the licenses granted in this Agreement, you retain all of your right, title and interest in and to your Contributions.
-**Copyright License.** You hereby grant, and agree to grant, to Ultralytics a non-exclusive, perpetual, irrevocable,
-worldwide, fully-paid, royalty-free, transferable copyright license to reproduce, prepare derivative works of, publicly
-display, publicly perform, and distribute your Contributions and such derivative works, with the right to sublicense the
-foregoing rights through multiple tiers of sublicensees.
+**Copyright License.** You hereby grant, and agree to grant, to Ultralytics a non-exclusive, perpetual, irrevocable, worldwide, fully-paid, royalty-free, transferable copyright license to reproduce, prepare derivative works of, publicly display, publicly perform, and distribute your Contributions and such derivative works, with the right to sublicense the foregoing rights through multiple tiers of sublicensees.
-**Patent License.** You hereby grant, and agree to grant, to Ultralytics a non-exclusive, perpetual, irrevocable,
-worldwide, fully-paid, royalty-free, transferable patent license to make, have made, use, offer to sell, sell,
-import, and otherwise transfer your Contributions, where such license applies only to those patent claims
-licensable by you that are necessarily infringed by your Contributions alone or by combination of your
-Contributions with the Project to which such Contributions were submitted, with the right to sublicense the
-foregoing rights through multiple tiers of sublicensees.
+**Patent License.** You hereby grant, and agree to grant, to Ultralytics a non-exclusive, perpetual, irrevocable, worldwide, fully-paid, royalty-free, transferable patent license to make, have made, use, offer to sell, sell, import, and otherwise transfer your Contributions, where such license applies only to those patent claims licensable by you that are necessarily infringed by your Contributions alone or by combination of your Contributions with the Project to which such Contributions were submitted, with the right to sublicense the foregoing rights through multiple tiers of sublicensees.
-**Moral Rights.** To the fullest extent permitted under applicable law, you hereby waive, and agree not to
-assert, all of your “moral rights” in or relating to your Contributions for the benefit of Ultralytics, its assigns, and
-their respective direct and indirect sublicensees.
+**Moral Rights.** To the fullest extent permitted under applicable law, you hereby waive, and agree not to assert, all of your “moral rights” in or relating to your Contributions for the benefit of Ultralytics, its assigns, and their respective direct and indirect sublicensees.
-**Third Party Content/Rights.** If your Contribution includes or is based on any source code, object code, bug
-fixes, configuration changes, tools, specifications, documentation, data, materials, feedback, information or
-other works of authorship that were not authored by you (“Third Party Content”) or if you are aware of any
-third party intellectual property or proprietary rights associated with your Contribution (“Third Party Rights”),
-then you agree to include with the submission of your Contribution full details respecting such Third Party
-Content and Third Party Rights, including, without limitation, identification of which aspects of your
-Contribution contain Third Party Content or are associated with Third Party Rights, the owner/author of the
-Third Party Content and Third Party Rights, where you obtained the Third Party Content, and any applicable
-third party license terms or restrictions respecting the Third Party Content and Third Party Rights. For greater
-certainty, the foregoing obligations respecting the identification of Third Party Content and Third Party Rights
-do not apply to any portion of a Project that is incorporated into your Contribution to that same Project.
+**Third Party Content/Rights.
+** If your Contribution includes or is based on any source code, object code, bug fixes, configuration changes, tools, specifications, documentation, data, materials, feedback, information or other works of authorship that were not authored by you (“Third Party Content”) or if you are aware of any third party intellectual property or proprietary rights associated with your Contribution (“Third Party Rights”), then you agree to include with the submission of your Contribution full details respecting such Third Party Content and Third Party Rights, including, without limitation, identification of which aspects of your Contribution contain Third Party Content or are associated with Third Party Rights, the owner/author of the Third Party Content and Third Party Rights, where you obtained the Third Party Content, and any applicable third party license terms or restrictions respecting the Third Party Content and Third Party Rights. For greater certainty, the foregoing obligations respecting the identification of Third Party Content and Third Party Rights do not apply to any portion of a Project that is incorporated into your Contribution to that same Project.
-**Representations.** You represent that, other than the Third Party Content and Third Party Rights identified by
-you in accordance with this Agreement, you are the sole author of your Contributions and are legally entitled
-to grant the foregoing licenses and waivers in respect of your Contributions. If your Contributions were
-created in the course of your employment with your past or present employer(s), you represent that such
-employer(s) has authorized you to make your Contributions on behalf of such employer(s) or such employer
+**Representations.** You represent that, other than the Third Party Content and Third Party Rights identified by you in accordance with this Agreement, you are the sole author of your Contributions and are legally entitled to grant the foregoing licenses and waivers in respect of your Contributions. If your Contributions were created in the course of your employment with your past or present employer(s), you represent that such employer(s) has authorized you to make your Contributions on behalf of such employer(s) or such employer
(s) has waived all of their right, title or interest in or to your Contributions.
**Disclaimer.** To the fullest extent permitted under applicable law, your Contributions are provided on an "asis"
-basis, without any warranties or conditions, express or implied, including, without limitation, any implied
-warranties or conditions of non-infringement, merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. You are not
-required to provide support for your Contributions, except to the extent you desire to provide support.
+basis, without any warranties or conditions, express or implied, including, without limitation, any implied warranties or conditions of non-infringement, merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. You are not required to provide support for your Contributions, except to the extent you desire to provide support.
-**No Obligation.** You acknowledge that Ultralytics is under no obligation to use or incorporate your Contributions
-into any of the Projects. The decision to use or incorporate your Contributions into any of the Projects will be
-made at the sole discretion of Ultralytics or its authorized delegates ..
+**No Obligation.** You acknowledge that Ultralytics is under no obligation to use or incorporate your Contributions into any of the Projects. The decision to use or incorporate your Contributions into any of the Projects will be made at the sole discretion of Ultralytics or its authorized delegates ..
-**Disputes.** This Agreement shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the laws of the State of
-New York, United States of America, without giving effect to its principles or rules regarding conflicts of laws,
-other than such principles directing application of New York law. The parties hereby submit to venue in, and
-jurisdiction of the courts located in New York, New York for purposes relating to this Agreement. In the event
-that any of the provisions of this Agreement shall be held by a court or other tribunal of competent jurisdiction
-to be unenforceable, the remaining portions hereof shall remain in full force and effect.
+**Disputes.** This Agreement shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the laws of the State of New York, United States of America, without giving effect to its principles or rules regarding conflicts of laws, other than such principles directing application of New York law. The parties hereby submit to venue in, and jurisdiction of the courts located in New York, New York for purposes relating to this Agreement. In the event that any of the provisions of this Agreement shall be held by a court or other tribunal of competent jurisdiction to be unenforceable, the remaining portions hereof shall remain in full force and effect.
-**Assignment.** You agree that Ultralytics may assign this Agreement, and all of its rights, obligations and licenses
-hereunder.
+**Assignment.** You agree that Ultralytics may assign this Agreement, and all of its rights, obligations and licenses hereunder.
diff --git a/docs/help/code_of_conduct.md b/docs/help/code_of_conduct.md
index cad1daed..c8c7cdc6 100644
--- a/docs/help/code_of_conduct.md
+++ b/docs/help/code_of_conduct.md
@@ -8,124 +8,78 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, code of conduct, community, contribution, behavior guidel
## Our Pledge
-We as members, contributors, and leaders pledge to make participation in our
-community a harassment-free experience for everyone, regardless of age, body
-size, visible or invisible disability, ethnicity, sex characteristics, gender
-identity and expression, level of experience, education, socio-economic status,
-nationality, personal appearance, race, religion, or sexual identity
-and orientation.
+We as members, contributors, and leaders pledge to make participation in our community a harassment-free experience for everyone, regardless of age, body size, visible or invisible disability, ethnicity, sex characteristics, gender identity and expression, level of experience, education, socio-economic status, nationality, personal appearance, race, religion, or sexual identity and orientation.
-We pledge to act and interact in ways that contribute to an open, welcoming,
-diverse, inclusive, and healthy community.
+We pledge to act and interact in ways that contribute to an open, welcoming, diverse, inclusive, and healthy community.
## Our Standards
-Examples of behavior that contributes to a positive environment for our
-community include:
+Examples of behavior that contributes to a positive environment for our community include:
- Demonstrating empathy and kindness toward other people
- Being respectful of differing opinions, viewpoints, and experiences
- Giving and gracefully accepting constructive feedback
-- Accepting responsibility and apologizing to those affected by our mistakes,
- and learning from the experience
-- Focusing on what is best not just for us as individuals, but for the
- overall community
+- Accepting responsibility and apologizing to those affected by our mistakes, and learning from the experience
+- Focusing on what is best not just for us as individuals, but for the overall community
Examples of unacceptable behavior include:
-- The use of sexualized language or imagery, and sexual attention or
- advances of any kind
+- The use of sexualized language or imagery, and sexual attention or advances of any kind
- Trolling, insulting or derogatory comments, and personal or political attacks
- Public or private harassment
-- Publishing others' private information, such as a physical or email
- address, without their explicit permission
-- Other conduct which could reasonably be considered inappropriate in a
- professional setting
+- Publishing others' private information, such as a physical or email address, without their explicit permission
+- Other conduct which could reasonably be considered inappropriate in a professional setting
## Enforcement Responsibilities
-Community leaders are responsible for clarifying and enforcing our standards of
-acceptable behavior and will take appropriate and fair corrective action in
-response to any behavior that they deem inappropriate, threatening, offensive,
-or harmful.
+Community leaders are responsible for clarifying and enforcing our standards of acceptable behavior and will take appropriate and fair corrective action in response to any behavior that they deem inappropriate, threatening, offensive, or harmful.
-Community leaders have the right and responsibility to remove, edit, or reject
-comments, commits, code, wiki edits, issues, and other contributions that are
-not aligned to this Code of Conduct, and will communicate reasons for moderation
-decisions when appropriate.
+Community leaders have the right and responsibility to remove, edit, or reject comments, commits, code, wiki edits, issues, and other contributions that are not aligned to this Code of Conduct, and will communicate reasons for moderation decisions when appropriate.
## Scope
-This Code of Conduct applies within all community spaces, and also applies when
-an individual is officially representing the community in public spaces.
-Examples of representing our community include using an official e-mail address,
-posting via an official social media account, or acting as an appointed
-representative at an online or offline event.
+This Code of Conduct applies within all community spaces, and also applies when an individual is officially representing the community in public spaces. Examples of representing our community include using an official e-mail address, posting via an official social media account, or acting as an appointed representative at an online or offline event.
## Enforcement
-Instances of abusive, harassing, or otherwise unacceptable behavior may be
-reported to the community leaders responsible for enforcement at
-hello@ultralytics.com.
-All complaints will be reviewed and investigated promptly and fairly.
+Instances of abusive, harassing, or otherwise unacceptable behavior may be reported to the community leaders responsible for enforcement at hello@ultralytics.com. All complaints will be reviewed and investigated promptly and fairly.
-All community leaders are obligated to respect the privacy and security of the
-reporter of any incident.
+All community leaders are obligated to respect the privacy and security of the reporter of any incident.
## Enforcement Guidelines
-Community leaders will follow these Community Impact Guidelines in determining
-the consequences for any action they deem in violation of this Code of Conduct:
+Community leaders will follow these Community Impact Guidelines in determining the consequences for any action they deem in violation of this Code of Conduct:
### 1. Correction
-**Community Impact**: Use of inappropriate language or other behavior deemed
-unprofessional or unwelcome in the community.
+**Community Impact**: Use of inappropriate language or other behavior deemed unprofessional or unwelcome in the community.
-**Consequence**: A private, written warning from community leaders, providing
-clarity around the nature of the violation and an explanation of why the
-behavior was inappropriate. A public apology may be requested.
+**Consequence**: A private, written warning from community leaders, providing clarity around the nature of the violation and an explanation of why the behavior was inappropriate. A public apology may be requested.
### 2. Warning
-**Community Impact**: A violation through a single incident or series
-of actions.
+**Community Impact**: A violation through a single incident or series of actions.
-**Consequence**: A warning with consequences for continued behavior. No
-interaction with the people involved, including unsolicited interaction with
-those enforcing the Code of Conduct, for a specified period of time. This
-includes avoiding interactions in community spaces as well as external channels
-like social media. Violating these terms may lead to a temporary or
-permanent ban.
+**Consequence**: A warning with consequences for continued behavior. No interaction with the people involved, including unsolicited interaction with those enforcing the Code of Conduct, for a specified period of time. This includes avoiding interactions in community spaces as well as external channels like social media. Violating these terms may lead to a temporary or permanent ban.
### 3. Temporary Ban
-**Community Impact**: A serious violation of community standards, including
-sustained inappropriate behavior.
+**Community Impact**: A serious violation of community standards, including sustained inappropriate behavior.
-**Consequence**: A temporary ban from any sort of interaction or public
-communication with the community for a specified period of time. No public or
-private interaction with the people involved, including unsolicited interaction
-with those enforcing the Code of Conduct, is allowed during this period.
-Violating these terms may lead to a permanent ban.
+**Consequence**: A temporary ban from any sort of interaction or public communication with the community for a specified period of time. No public or private interaction with the people involved, including unsolicited interaction with those enforcing the Code of Conduct, is allowed during this period. Violating these terms may lead to a permanent ban.
### 4. Permanent Ban
-**Community Impact**: Demonstrating a pattern of violation of community
-standards, including sustained inappropriate behavior, harassment of an
-individual, or aggression toward or disparagement of classes of individuals.
+**Community Impact**: Demonstrating a pattern of violation of community standards, including sustained inappropriate behavior, harassment of an individual, or aggression toward or disparagement of classes of individuals.
-**Consequence**: A permanent ban from any sort of public interaction within
-the community.
+**Consequence**: A permanent ban from any sort of public interaction within the community.
## Attribution
-This Code of Conduct is adapted from the [Contributor Covenant][homepage],
-version 2.0, available at
+This Code of Conduct is adapted from the [Contributor Covenant][homepage], version 2.0, available at
https://www.contributor-covenant.org/version/2/0/code_of_conduct.html.
-Community Impact Guidelines were inspired by [Mozilla's code of conduct
-enforcement ladder](https://github.com/mozilla/diversity).
+Community Impact Guidelines were inspired by [Mozilla's code of conduct enforcement ladder](https://github.com/mozilla/diversity).
For answers to common questions about this code of conduct, see the FAQ at
https://www.contributor-covenant.org/faq. Translations are available at
diff --git a/docs/hub/index.md b/docs/hub/index.md
index 3fbdc632..76bf9e6d 100644
--- a/docs/hub/index.md
+++ b/docs/hub/index.md
@@ -26,9 +26,9 @@ HUB is designed to be user-friendly and intuitive, with a drag-and-drop interfac
-
diff --git a/docs/hub/integrations.md b/docs/hub/integrations.md
index 3fa0fc2e..162a0f02 100644
--- a/docs/hub/integrations.md
+++ b/docs/hub/integrations.md
@@ -12,9 +12,9 @@ Welcome to the Integrations guide for [Ultralytics HUB](https://hub.ultralytics.
-
diff --git a/docs/hub/quickstart.md b/docs/hub/quickstart.md
index 4a78cfbf..3728dc4b 100644
--- a/docs/hub/quickstart.md
+++ b/docs/hub/quickstart.md
@@ -12,9 +12,9 @@ Thank you for visiting the Quickstart guide for [Ultralytics HUB](https://hub.ul
-
diff --git a/docs/index.md b/docs/index.md
index 00951dd2..cf391a50 100644
--- a/docs/index.md
+++ b/docs/index.md
@@ -32,9 +32,9 @@ Explore the YOLOv8 Docs, a comprehensive resource designed to help you understan
-
diff --git a/docs/integrations/index.md b/docs/integrations/index.md
index 9a8a1daa..9ed2589a 100644
--- a/docs/integrations/index.md
+++ b/docs/integrations/index.md
@@ -68,4 +68,4 @@ By writing a guide or tutorial, you can help expand our documentation and provid
To contribute, please check out our [Contributing Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/help/contributing) for instructions on how to submit a Pull Request (PR) 🛠️. We eagerly await your contributions!
-Let's collaborate to make the Ultralytics YOLO ecosystem more expansive and feature-rich 🙏!
\ No newline at end of file
+Let's collaborate to make the Ultralytics YOLO ecosystem more expansive and feature-rich 🙏!
diff --git a/docs/integrations/openvino.md b/docs/integrations/openvino.md
index aae2afab..9fba90d1 100644
--- a/docs/integrations/openvino.md
+++ b/docs/integrations/openvino.md
@@ -14,9 +14,9 @@ OpenVINO, short for Open Visual Inference & Neural Network Optimization toolkit,
-
diff --git a/docs/integrations/ray-tune.md b/docs/integrations/ray-tune.md
index 267e1691..ec7817c0 100644
--- a/docs/integrations/ray-tune.md
+++ b/docs/integrations/ray-tune.md
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ To install the required packages, run:
```bash
# Install and update Ultralytics and Ray Tune packages
pip install -U ultralytics "ray[tune]"
-
+
# Optionally install W&B for logging
pip install wandb
```
@@ -48,10 +48,10 @@ To install the required packages, run:
```python
from ultralytics import YOLO
-
+
# Load a YOLOv8n model
model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
-
+
# Start tuning hyperparameters for YOLOv8n training on the COCO8 dataset
result_grid = model.tune(data='coco8.yaml', use_ray=True)
```
diff --git a/docs/models/fast-sam.md b/docs/models/fast-sam.md
index d41ca479..2e839a5a 100644
--- a/docs/models/fast-sam.md
+++ b/docs/models/fast-sam.md
@@ -55,7 +55,7 @@ To perform object detection on an image, use the `predict` method as shown below
# Run inference on an image
everything_results = model(source, device='cpu', retina_masks=True, imgsz=1024, conf=0.4, iou=0.9)
-
+
# Prepare a Prompt Process object
prompt_process = FastSAMPrompt(source, everything_results, device='cpu')
@@ -74,7 +74,7 @@ To perform object detection on an image, use the `predict` method as shown below
ann = prompt_process.point_prompt(points=[[200, 200]], pointlabel=[1])
prompt_process.plot(annotations=ann, output='./')
```
-
+
=== "CLI"
```bash
# Load a FastSAM model and segment everything with it
diff --git a/docs/models/mobile-sam.md b/docs/models/mobile-sam.md
index e224046d..be753c29 100644
--- a/docs/models/mobile-sam.md
+++ b/docs/models/mobile-sam.md
@@ -66,10 +66,10 @@ You can download the model [here](https://github.com/ChaoningZhang/MobileSAM/blo
=== "Python"
```python
from ultralytics import SAM
-
+
# Load the model
model = SAM('mobile_sam.pt')
-
+
# Predict a segment based on a point prompt
model.predict('ultralytics/assets/zidane.jpg', points=[900, 370], labels=[1])
```
@@ -81,10 +81,10 @@ You can download the model [here](https://github.com/ChaoningZhang/MobileSAM/blo
=== "Python"
```python
from ultralytics import SAM
-
+
# Load the model
model = SAM('mobile_sam.pt')
-
+
# Predict a segment based on a box prompt
model.predict('ultralytics/assets/zidane.jpg', bboxes=[439, 437, 524, 709])
```
diff --git a/docs/models/rtdetr.md b/docs/models/rtdetr.md
index 608e7aa6..63d53237 100644
--- a/docs/models/rtdetr.md
+++ b/docs/models/rtdetr.md
@@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ You can use RT-DETR for object detection tasks using the `ultralytics` pip packa
=== "CLI"
- ```bash
+ ```bash
# Load a COCO-pretrained RT-DETR-l model and train it on the COCO8 example dataset for 100 epochs
yolo train model=rtdetr-l.pt data=coco8.yaml epochs=100 imgsz=640
diff --git a/docs/models/sam.md b/docs/models/sam.md
index 5b781cd2..45b5c58b 100644
--- a/docs/models/sam.md
+++ b/docs/models/sam.md
@@ -152,28 +152,27 @@ This comparison shows the order-of-magnitude differences in the model sizes and
Tests run on a 2023 Apple M2 Macbook with 16GB of RAM. To reproduce this test:
-
!!! example ""
=== "Python"
```python
from ultralytics import FastSAM, SAM, YOLO
-
+
# Profile SAM-b
model = SAM('sam_b.pt')
model.info()
model('ultralytics/assets')
-
+
# Profile MobileSAM
model = SAM('mobile_sam.pt')
model.info()
model('ultralytics/assets')
-
+
# Profile FastSAM-s
model = FastSAM('FastSAM-s.pt')
model.info()
model('ultralytics/assets')
-
+
# Profile YOLOv8n-seg
model = YOLO('yolov8n-seg.pt')
model.info()
@@ -193,7 +192,7 @@ To auto-annotate your dataset with the Ultralytics framework, use the `auto_anno
=== "Python"
```python
from ultralytics.data.annotator import auto_annotate
-
+
auto_annotate(data="path/to/images", det_model="yolov8x.pt", sam_model='sam_b.pt')
```
diff --git a/docs/models/yolov6.md b/docs/models/yolov6.md
index 047b9d6c..5edf7453 100644
--- a/docs/models/yolov6.md
+++ b/docs/models/yolov6.md
@@ -12,8 +12,7 @@ keywords: Meituan YOLOv6, object detection, Ultralytics, YOLOv6 docs, Bi-directi

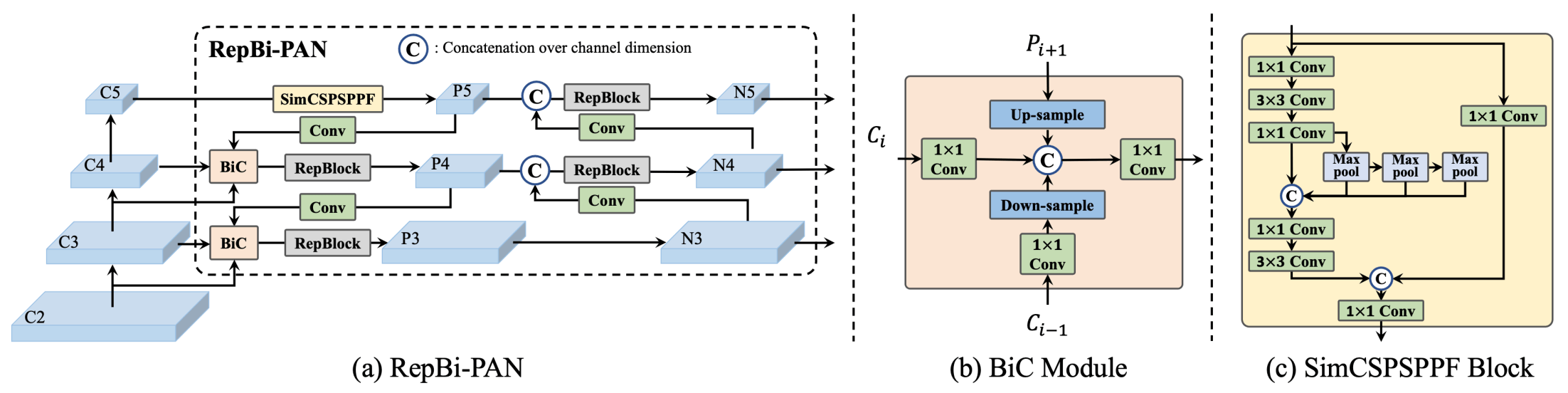
-**Overview of YOLOv6.** Model architecture diagram showing the redesigned network components and training strategies that have led to significant performance improvements. (a) The neck of YOLOv6 (N and S are shown). Note for M/L, RepBlocks is replaced with CSPStackRep. (b) The
-structure of a BiC module. (c) A SimCSPSPPF block. ([source](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.05586.pdf)).
+**Overview of YOLOv6.** Model architecture diagram showing the redesigned network components and training strategies that have led to significant performance improvements. (a) The neck of YOLOv6 (N and S are shown). Note for M/L, RepBlocks is replaced with CSPStackRep. (b) The structure of a BiC module. (c) A SimCSPSPPF block. ([source](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.05586.pdf)).
### Key Features
diff --git a/docs/models/yolov8.md b/docs/models/yolov8.md
index cfeae9ee..a05656f4 100644
--- a/docs/models/yolov8.md
+++ b/docs/models/yolov8.md
@@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ YOLOv8 is the latest iteration in the YOLO series of real-time object detectors,
=== "Detection (Open Images V7)"
See [Detection Docs](https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect/) for usage examples with these models trained on [Open Image V7](https://docs.ultralytics.com/datasets/detect/open-images-v7/), which include 600 pre-trained classes.
-
+
| Model | size
(pixels) | mAPval
50-95 | Speed
CPU ONNX
(ms) | Speed
A100 TensorRT
(ms) | params
(M) | FLOPs
(B) |
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------- | -------------------- | ------------------------------ | ----------------------------------- | ------------------ | ----------------- |
| [YOLOv8n](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v0.0.0/yolov8n-oiv7.pt) | 640 | 18.4 | 142.4 | 1.21 | 3.5 | 10.5 |
diff --git a/docs/modes/export.md b/docs/modes/export.md
index 6c2c1e1d..5345172c 100644
--- a/docs/modes/export.md
+++ b/docs/modes/export.md
@@ -14,9 +14,9 @@ The ultimate goal of training a model is to deploy it for real-world application
-
diff --git a/docs/modes/predict.md b/docs/modes/predict.md
index 011670c9..be1c71f6 100644
--- a/docs/modes/predict.md
+++ b/docs/modes/predict.md
@@ -14,9 +14,9 @@ In the world of machine learning and computer vision, the process of making sens
-
@@ -415,10 +415,10 @@ All Ultralytics `predict()` calls will return a list of `Results` objects:
```python
from ultralytics import YOLO
-
+
# Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
-
+
# Run inference on an image
results = model('bus.jpg') # list of 1 Results object
results = model(['bus.jpg', 'zidane.jpg']) # list of 2 Results objects
@@ -467,13 +467,13 @@ For more details see the `Results` class [documentation](../reference/engine/res
```python
from ultralytics import YOLO
-
+
# Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
-
+
# Run inference on an image
results = model('bus.jpg') # results list
-
+
# View results
for r in results:
print(r.boxes) # print the Boxes object containing the detection bounding boxes
@@ -505,13 +505,13 @@ For more details see the `Boxes` class [documentation](../reference/engine/resul
```python
from ultralytics import YOLO
-
+
# Load a pretrained YOLOv8n-seg Segment model
model = YOLO('yolov8n-seg.pt')
-
+
# Run inference on an image
results = model('bus.jpg') # results list
-
+
# View results
for r in results:
print(r.masks) # print the Masks object containing the detected instance masks
@@ -538,13 +538,13 @@ For more details see the `Masks` class [documentation](../reference/engine/resul
```python
from ultralytics import YOLO
-
+
# Load a pretrained YOLOv8n-pose Pose model
model = YOLO('yolov8n-pose.pt')
-
+
# Run inference on an image
results = model('bus.jpg') # results list
-
+
# View results
for r in results:
print(r.keypoints) # print the Keypoints object containing the detected keypoints
@@ -572,13 +572,13 @@ For more details see the `Keypoints` class [documentation](../reference/engine/r
```python
from ultralytics import YOLO
-
+
# Load a pretrained YOLOv8n-cls Classify model
model = YOLO('yolov8n-cls.pt')
-
+
# Run inference on an image
results = model('bus.jpg') # results list
-
+
# View results
for r in results:
print(r.probs) # print the Probs object containing the detected class probabilities
@@ -622,9 +622,9 @@ You can use the `plot()` method of a `Result` objects to visualize predictions.
im.show() # show image
im.save('results.jpg') # save image
```
-
+
The `plot()` method supports the following arguments:
-
+
| Argument | Type | Description | Default |
|--------------|-----------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------|
| `conf` | `bool` | Whether to plot the detection confidence score. | `True` |
diff --git a/docs/modes/track.md b/docs/modes/track.md
index eac82c38..b2a40d05 100644
--- a/docs/modes/track.md
+++ b/docs/modes/track.md
@@ -21,9 +21,9 @@ The output from Ultralytics trackers is consistent with standard object detectio
-
@@ -86,7 +86,7 @@ To run the tracker on video streams, use a trained Detect, Segment or Pose model
yolo track model=path/to/best.pt source="https://youtu.be/LNwODJXcvt4" # Custom trained model
# Track using ByteTrack tracker
- yolo track model=path/to/best.pt tracker="bytetrack.yaml"
+ yolo track model=path/to/best.pt tracker="bytetrack.yaml"
```
As can be seen in the above usage, tracking is available for all Detect, Segment and Pose models run on videos or streaming sources.
@@ -199,38 +199,38 @@ In the following example, we demonstrate how to utilize YOLOv8's tracking capabi
```python
from collections import defaultdict
-
+
import cv2
import numpy as np
-
+
from ultralytics import YOLO
-
+
# Load the YOLOv8 model
model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
-
+
# Open the video file
video_path = "path/to/video.mp4"
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
-
+
# Store the track history
track_history = defaultdict(lambda: [])
-
+
# Loop through the video frames
while cap.isOpened():
# Read a frame from the video
success, frame = cap.read()
-
+
if success:
# Run YOLOv8 tracking on the frame, persisting tracks between frames
results = model.track(frame, persist=True)
-
+
# Get the boxes and track IDs
boxes = results[0].boxes.xywh.cpu()
track_ids = results[0].boxes.id.int().cpu().tolist()
-
+
# Visualize the results on the frame
annotated_frame = results[0].plot()
-
+
# Plot the tracks
for box, track_id in zip(boxes, track_ids):
x, y, w, h = box
@@ -238,21 +238,21 @@ In the following example, we demonstrate how to utilize YOLOv8's tracking capabi
track.append((float(x), float(y))) # x, y center point
if len(track) > 30: # retain 90 tracks for 90 frames
track.pop(0)
-
+
# Draw the tracking lines
points = np.hstack(track).astype(np.int32).reshape((-1, 1, 2))
cv2.polylines(annotated_frame, [points], isClosed=False, color=(230, 230, 230), thickness=10)
-
+
# Display the annotated frame
cv2.imshow("YOLOv8 Tracking", annotated_frame)
-
+
# Break the loop if 'q' is pressed
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord("q"):
break
else:
# Break the loop if the end of the video is reached
break
-
+
# Release the video capture object and close the display window
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
@@ -283,36 +283,36 @@ Finally, after all threads have completed their task, the windows displaying the
def run_tracker_in_thread(filename, model, file_index):
"""
Runs a video file or webcam stream concurrently with the YOLOv8 model using threading.
-
+
This function captures video frames from a given file or camera source and utilizes the YOLOv8 model for object
tracking. The function runs in its own thread for concurrent processing.
-
+
Args:
filename (str): The path to the video file or the identifier for the webcam/external camera source.
model (obj): The YOLOv8 model object.
file_index (int): An index to uniquely identify the file being processed, used for display purposes.
-
+
Note:
Press 'q' to quit the video display window.
"""
video = cv2.VideoCapture(filename) # Read the video file
-
+
while True:
ret, frame = video.read() # Read the video frames
-
+
# Exit the loop if no more frames in either video
if not ret:
break
-
+
# Track objects in frames if available
results = model.track(frame, persist=True)
res_plotted = results[0].plot()
cv2.imshow(f"Tracking_Stream_{file_index}", res_plotted)
-
+
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key == ord('q'):
break
-
+
# Release video sources
video.release()
diff --git a/docs/modes/train.md b/docs/modes/train.md
index 3506a7f7..7bb462e9 100644
--- a/docs/modes/train.md
+++ b/docs/modes/train.md
@@ -14,9 +14,9 @@ Training a deep learning model involves feeding it data and adjusting its parame
-
@@ -240,7 +240,7 @@ To use Comet:
```python
# pip install comet_ml
import comet_ml
-
+
comet_ml.init()
```
@@ -258,7 +258,7 @@ To use ClearML:
```python
# pip install clearml
import clearml
-
+
clearml.browser_login()
```
diff --git a/docs/quickstart.md b/docs/quickstart.md
index af10dc82..3baed00d 100644
--- a/docs/quickstart.md
+++ b/docs/quickstart.md
@@ -20,8 +20,8 @@ Ultralytics provides various installation methods including pip, conda, and Dock
pip install ultralytics
```
- You can also install the `ultralytics` package directly from the GitHub [repository](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics). This might be useful if you want the latest development version. Make sure to have the Git command-line tool installed on your system. The `@main` command installs the `main` branch and may be modified to another branch, i.e. `@my-branch`, or removed alltogether to default to `main` branch.
-
+ You can also install the `ultralytics` package directly from the GitHub [repository](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics). This might be useful if you want the latest development version. Make sure to have the Git command-line tool installed on your system. The `@main` command installs the `main` branch and may be modified to another branch, i.e. `@my-branch`, or removed entirely to default to `main` branch.
+
```bash
# Install the ultralytics package from GitHub
pip install git+https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics.git@main
@@ -40,15 +40,15 @@ Ultralytics provides various installation methods including pip, conda, and Dock
```
!!! note
-
+
If you are installing in a CUDA environment best practice is to install `ultralytics`, `pytorch` and `pytorch-cuda` in the same command to allow the conda package manager to resolve any conflicts, or else to install `pytorch-cuda` last to allow it override the CPU-specific `pytorch` package if necessary.
```bash
# Install all packages together using conda
- conda install -c pytorch -c nvidia -c conda-forge pytorch torchvision pytorch-cuda=11.8 ultralytics
+ conda install -c pytorch -c nvidia -c conda-forge pytorch torchvision pytorch-cuda=11.8 ultralytics
```
### Conda Docker Image
-
+
Ultralytics Conda Docker images are also available from [DockerHub](https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/ultralytics). These images are based on [Miniconda3](https://docs.conda.io/projects/miniconda/en/latest/) and are an simple way to start using `ultralytics` in a Conda environment.
```bash
@@ -79,7 +79,7 @@ Ultralytics provides various installation methods including pip, conda, and Dock
=== "Docker"
Utilize Docker to effortlessly execute the `ultralytics` package in an isolated container, ensuring consistent and smooth performance across various environments. By choosing one of the official `ultralytics` images from [Docker Hub](https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/ultralytics), you not only avoid the complexity of local installation but also benefit from access to a verified working environment. Ultralytics offers 5 main supported Docker images, each designed to provide high compatibility and efficiency for different platforms and use cases:
-
+

-
diff --git a/docs/tasks/pose.md b/docs/tasks/pose.md
index 5fe838d7..4dc4e022 100644
--- a/docs/tasks/pose.md
+++ b/docs/tasks/pose.md
@@ -15,9 +15,9 @@ The output of a pose estimation model is a set of points that represent the keyp
-
diff --git a/docs/tasks/segment.md b/docs/tasks/segment.md
index f5b73330..93622a82 100644
--- a/docs/tasks/segment.md
+++ b/docs/tasks/segment.md
@@ -14,9 +14,9 @@ The output of an instance segmentation model is a set of masks or contours that
-
diff --git a/docs/usage/callbacks.md b/docs/usage/callbacks.md
index e2e68857..647b62da 100644
--- a/docs/usage/callbacks.md
+++ b/docs/usage/callbacks.md
@@ -6,9 +6,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLO, callbacks guide, training callback, validation call
## Callbacks
-Ultralytics framework supports callbacks as entry points in strategic stages of train, val, export, and predict modes.
-Each callback accepts a `Trainer`, `Validator`, or `Predictor` object depending on the operation type. All properties of
-these objects can be found in Reference section of the docs.
+Ultralytics framework supports callbacks as entry points in strategic stages of train, val, export, and predict modes. Each callback accepts a `Trainer`, `Validator`, or `Predictor` object depending on the operation type. All properties of these objects can be found in Reference section of the docs.
## Examples
diff --git a/docs/usage/cli.md b/docs/usage/cli.md
index ac2832cb..550d469b 100644
--- a/docs/usage/cli.md
+++ b/docs/usage/cli.md
@@ -6,8 +6,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLO, CLI, train, validation, prediction, command line in
# Command Line Interface Usage
-The YOLO command line interface (CLI) allows for simple single-line commands without the need for a Python environment.
-CLI requires no customization or Python code. You can simply run all tasks from the terminal with the `yolo` command.
+The YOLO command line interface (CLI) allows for simple single-line commands without the need for a Python environment. CLI requires no customization or Python code. You can simply run all tasks from the terminal with the `yolo` command.
!!! example
@@ -65,11 +64,9 @@ CLI requires no customization or Python code. You can simply run all tasks from
Where:
-- `TASK` (optional) is one of `[detect, segment, classify]`. If it is not passed explicitly YOLOv8 will try to guess
- the `TASK` from the model type.
+- `TASK` (optional) is one of `[detect, segment, classify]`. If it is not passed explicitly YOLOv8 will try to guess the `TASK` from the model type.
- `MODE` (required) is one of `[train, val, predict, export, track]`
-- `ARGS` (optional) are any number of custom `arg=value` pairs like `imgsz=320` that override defaults.
- For a full list of available `ARGS` see the [Configuration](cfg.md) page and `defaults.yaml`
+- `ARGS` (optional) are any number of custom `arg=value` pairs like `imgsz=320` that override defaults. For a full list of available `ARGS` see the [Configuration](cfg.md) page and `defaults.yaml`
GitHub [source](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/cfg/default.yaml).
!!! warning "Warning"
@@ -82,8 +79,7 @@ Where:
## Train
-Train YOLOv8n on the COCO128 dataset for 100 epochs at image size 640. For a full list of available arguments see
-the [Configuration](cfg.md) page.
+Train YOLOv8n on the COCO128 dataset for 100 epochs at image size 640. For a full list of available arguments see the [Configuration](cfg.md) page.
!!! example "Example"
@@ -103,8 +99,7 @@ the [Configuration](cfg.md) page.
## Val
-Validate trained YOLOv8n model accuracy on the COCO128 dataset. No argument need to passed as the `model` retains it's
-training `data` and arguments as model attributes.
+Validate trained YOLOv8n model accuracy on the COCO128 dataset. No argument need to passed as the `model` retains it's training `data` and arguments as model attributes.
!!! example "Example"
@@ -162,8 +157,7 @@ Export a YOLOv8n model to a different format like ONNX, CoreML, etc.
yolo export model=path/to/best.pt format=onnx
```
-Available YOLOv8 export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument,
-i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`.
+Available YOLOv8 export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`.
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
|--------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|----------|-----------------------------------------------------|
@@ -207,13 +201,11 @@ Default arguments can be overridden by simply passing them as arguments in the C
## Overriding default config file
-You can override the `default.yaml` config file entirely by passing a new file with the `cfg` arguments,
-i.e. `cfg=custom.yaml`.
+You can override the `default.yaml` config file entirely by passing a new file with the `cfg` arguments, i.e. `cfg=custom.yaml`.
To do this first create a copy of `default.yaml` in your current working dir with the `yolo copy-cfg` command.
-This will create `default_copy.yaml`, which you can then pass as `cfg=default_copy.yaml` along with any additional args,
-like `imgsz=320` in this example:
+This will create `default_copy.yaml`, which you can then pass as `cfg=default_copy.yaml` along with any additional args, like `imgsz=320` in this example:
!!! example ""
diff --git a/docs/usage/engine.md b/docs/usage/engine.md
index 4edf3315..12c58782 100644
--- a/docs/usage/engine.md
+++ b/docs/usage/engine.md
@@ -4,18 +4,14 @@ description: Discover how to customize and extend base Ultralytics YOLO Trainer
keywords: Ultralytics, YOLO, trainer engines, BaseTrainer, DetectionTrainer, customizing trainers, extending trainers, custom model, custom dataloader
---
-Both the Ultralytics YOLO command-line and python interfaces are simply a high-level abstraction on the base engine
-executors. Let's take a look at the Trainer engine.
+Both the Ultralytics YOLO command-line and python interfaces are simply a high-level abstraction on the base engine executors. Let's take a look at the Trainer engine.
## BaseTrainer
-BaseTrainer contains the generic boilerplate training routine. It can be customized for any task based over overriding
-the required functions or operations as long the as correct formats are followed. For example, you can support your own
-custom model and dataloader by just overriding these functions:
+BaseTrainer contains the generic boilerplate training routine. It can be customized for any task based over overriding the required functions or operations as long the as correct formats are followed. For example, you can support your own custom model and dataloader by just overriding these functions:
* `get_model(cfg, weights)` - The function that builds the model to be trained
-* `get_dataloader()` - The function that builds the dataloader
- More details and source code can be found in [`BaseTrainer` Reference](../reference/engine/trainer.md)
+* `get_dataloader()` - The function that builds the dataloader More details and source code can be found in [`BaseTrainer` Reference](../reference/engine/trainer.md)
## DetectionTrainer
@@ -31,8 +27,7 @@ trained_model = trainer.best # get best model
### Customizing the DetectionTrainer
-Let's customize the trainer **to train a custom detection model** that is not supported directly. You can do this by
-simply overloading the existing the `get_model` functionality:
+Let's customize the trainer **to train a custom detection model** that is not supported directly. You can do this by simply overloading the existing the `get_model` functionality:
```python
from ultralytics.models.yolo.detect import DetectionTrainer
diff --git a/docs/usage/python.md b/docs/usage/python.md
index 9f301cf5..200383c0 100644
--- a/docs/usage/python.md
+++ b/docs/usage/python.md
@@ -6,14 +6,9 @@ keywords: YOLOv8, Ultralytics, Python, object detection, segmentation, classific
# Python Usage
-Welcome to the YOLOv8 Python Usage documentation! This guide is designed to help you seamlessly integrate YOLOv8 into
-your Python projects for object detection, segmentation, and classification. Here, you'll learn how to load and use
-pretrained models, train new models, and perform predictions on images. The easy-to-use Python interface is a valuable
-resource for anyone looking to incorporate YOLOv8 into their Python projects, allowing you to quickly implement advanced
-object detection capabilities. Let's get started!
+Welcome to the YOLOv8 Python Usage documentation! This guide is designed to help you seamlessly integrate YOLOv8 into your Python projects for object detection, segmentation, and classification. Here, you'll learn how to load and use pretrained models, train new models, and perform predictions on images. The easy-to-use Python interface is a valuable resource for anyone looking to incorporate YOLOv8 into their Python projects, allowing you to quickly implement advanced object detection capabilities. Let's get started!
-For example, users can load a model, train it, evaluate its performance on a validation set, and even export it to ONNX
-format with just a few lines of code.
+For example, users can load a model, train it, evaluate its performance on a validation set, and even export it to ONNX format with just a few lines of code.
!!! example "Python"
@@ -41,9 +36,7 @@ format with just a few lines of code.
## [Train](../modes/train.md)
-Train mode is used for training a YOLOv8 model on a custom dataset. In this mode, the model is trained using the
-specified dataset and hyperparameters. The training process involves optimizing the model's parameters so that it can
-accurately predict the classes and locations of objects in an image.
+Train mode is used for training a YOLOv8 model on a custom dataset. In this mode, the model is trained using the specified dataset and hyperparameters. The training process involves optimizing the model's parameters so that it can accurately predict the classes and locations of objects in an image.
!!! example "Train"
@@ -73,9 +66,7 @@ accurately predict the classes and locations of objects in an image.
## [Val](../modes/val.md)
-Val mode is used for validating a YOLOv8 model after it has been trained. In this mode, the model is evaluated on a
-validation set to measure its accuracy and generalization performance. This mode can be used to tune the hyperparameters
-of the model to improve its performance.
+Val mode is used for validating a YOLOv8 model after it has been trained. In this mode, the model is evaluated on a validation set to measure its accuracy and generalization performance. This mode can be used to tune the hyperparameters of the model to improve its performance.
!!! example "Val"
@@ -103,9 +94,7 @@ of the model to improve its performance.
## [Predict](../modes/predict.md)
-Predict mode is used for making predictions using a trained YOLOv8 model on new images or videos. In this mode, the
-model is loaded from a checkpoint file, and the user can provide images or videos to perform inference. The model
-predicts the classes and locations of objects in the input images or videos.
+Predict mode is used for making predictions using a trained YOLOv8 model on new images or videos. In this mode, the model is loaded from a checkpoint file, and the user can provide images or videos to perform inference. The model predicts the classes and locations of objects in the input images or videos.
!!! example "Predict"
@@ -173,9 +162,7 @@ predicts the classes and locations of objects in the input images or videos.
## [Export](../modes/export.md)
-Export mode is used for exporting a YOLOv8 model to a format that can be used for deployment. In this mode, the model is
-converted to a format that can be used by other software applications or hardware devices. This mode is useful when
-deploying the model to production environments.
+Export mode is used for exporting a YOLOv8 model to a format that can be used for deployment. In this mode, the model is converted to a format that can be used by other software applications or hardware devices. This mode is useful when deploying the model to production environments.
!!! example "Export"
@@ -203,9 +190,7 @@ deploying the model to production environments.
## [Track](../modes/track.md)
-Track mode is used for tracking objects in real-time using a YOLOv8 model. In this mode, the model is loaded from a
-checkpoint file, and the user can provide a live video stream to perform real-time object tracking. This mode is useful
-for applications such as surveillance systems or self-driving cars.
+Track mode is used for tracking objects in real-time using a YOLOv8 model. In this mode, the model is loaded from a checkpoint file, and the user can provide a live video stream to perform real-time object tracking. This mode is useful for applications such as surveillance systems or self-driving cars.
!!! example "Track"
@@ -228,11 +213,8 @@ for applications such as surveillance systems or self-driving cars.
## [Benchmark](../modes/benchmark.md)
-Benchmark mode is used to profile the speed and accuracy of various export formats for YOLOv8. The benchmarks provide
-information on the size of the exported format, its `mAP50-95` metrics (for object detection and segmentation)
-or `accuracy_top5` metrics (for classification), and the inference time in milliseconds per image across various export
-formats like ONNX, OpenVINO, TensorRT and others. This information can help users choose the optimal export format for
-their specific use case based on their requirements for speed and accuracy.
+Benchmark mode is used to profile the speed and accuracy of various export formats for YOLOv8. The benchmarks provide information on the size of the exported format, its `mAP50-95` metrics (for object detection and segmentation)
+or `accuracy_top5` metrics (for classification), and the inference time in milliseconds per image across various export formats like ONNX, OpenVINO, TensorRT and others. This information can help users choose the optimal export format for their specific use case based on their requirements for speed and accuracy.
!!! example "Benchmark"
@@ -250,8 +232,7 @@ their specific use case based on their requirements for speed and accuracy.
## Using Trainers
-`YOLO` model class is a high-level wrapper on the Trainer classes. Each YOLO task has its own trainer that inherits
-from `BaseTrainer`.
+`YOLO` model class is a high-level wrapper on the Trainer classes. Each YOLO task has its own trainer that inherits from `BaseTrainer`.
!!! tip "Detection Trainer Example"
@@ -276,8 +257,6 @@ from `BaseTrainer`.
trainer = detect.DetectionTrainer(overrides=overrides)
```
-You can easily customize Trainers to support custom tasks or explore R&D ideas.
-Learn more about Customizing `Trainers`, `Validators` and `Predictors` to suit your project needs in the Customization
-Section.
+You can easily customize Trainers to support custom tasks or explore R&D ideas. Learn more about Customizing `Trainers`, `Validators` and `Predictors` to suit your project needs in the Customization Section.
[Customization tutorials](engine.md){ .md-button .md-button--primary}
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/environments/azureml_quickstart_tutorial.md b/docs/yolov5/environments/azureml_quickstart_tutorial.md
index 844ce4d3..e1e58a4e 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/environments/azureml_quickstart_tutorial.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/environments/azureml_quickstart_tutorial.md
@@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ Clone YOLOv5 repository with its submodules:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
cd yolov5
-git submodule update --init --recursive # Note that you might have a message asking you to add your folder as a safe.directory just copy the recommended command
+git submodule update --init --recursive # Note that you might have a message asking you to add your folder as a safe.directory just copy the recommended command
```
Install the required dependencies:
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/index.md b/docs/yolov5/index.md
index 290608ac..1b943cfb 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/index.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/index.md
@@ -53,8 +53,7 @@ Here's a compilation of comprehensive tutorials that will guide you through diff
YOLOv5 is designed to be run in the following up-to-date, verified environments, with all dependencies (including [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda)/[CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/), and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/)) pre-installed:
-- **Notebooks** with free
- GPU: 



 diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/clearml_logging_integration.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/clearml_logging_integration.md
index 667f566d..43c8395c 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/clearml_logging_integration.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/clearml_logging_integration.md
@@ -64,8 +64,7 @@ pip install clearml>=1.2.0
This will enable integration with the YOLOv5 training script. Every training run from now on, will be captured and stored by the ClearML experiment manager.
-If you want to change the `project_name` or `task_name`, use the `--project` and `--name` arguments of the `train.py` script, by default the project will be called `YOLOv5` and the task `Training`.
-PLEASE NOTE: ClearML uses `/` as a delimiter for subprojects, so be careful when using `/` in your project name!
+If you want to change the `project_name` or `task_name`, use the `--project` and `--name` arguments of the `train.py` script, by default the project will be called `YOLOv5` and the task `Training`. PLEASE NOTE: ClearML uses `/` as a delimiter for subprojects, so be careful when using `/` in your project name!
```bash
python train.py --img 640 --batch 16 --epochs 3 --data coco128.yaml --weights yolov5s.pt --cache
@@ -92,8 +91,7 @@ This will capture:
- Validation images per epoch
- ...
-That's a lot right? 🤯
-Now, we can visualize all of this information in the ClearML UI to get an overview of our training progress. Add custom columns to the table view (such as e.g. mAP_0.5) so you can easily sort on the best performing model. Or select multiple experiments and directly compare them!
+That's a lot right? 🤯 Now, we can visualize all of this information in the ClearML UI to get an overview of our training progress. Add custom columns to the table view (such as e.g. mAP_0.5) so you can easily sort on the best performing model. Or select multiple experiments and directly compare them!
There even more we can do with all of this information, like hyperparameter optimization and remote execution, so keep reading if you want to see how that works!
@@ -187,8 +185,7 @@ python utils/loggers/clearml/hpo.py
## 🤯 Remote Execution (advanced)
-Running HPO locally is really handy, but what if we want to run our experiments on a remote machine instead? Maybe you have access to a very powerful GPU machine on-site, or you have some budget to use cloud GPUs.
-This is where the ClearML Agent comes into play. Check out what the agent can do here:
+Running HPO locally is really handy, but what if we want to run our experiments on a remote machine instead? Maybe you have access to a very powerful GPU machine on-site, or you have some budget to use cloud GPUs. This is where the ClearML Agent comes into play. Check out what the agent can do here:
- [YouTube video](https://youtu.be/MX3BrXnaULs)
- [Documentation](https://clear.ml/docs/latest/docs/clearml_agent)
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/comet_logging_integration.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/comet_logging_integration.md
index f2c6ba84..c70d2920 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/comet_logging_integration.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/comet_logging_integration.md
@@ -90,8 +90,7 @@ By default, Comet will log the following items
# Configure Comet Logging
-Comet can be configured to log additional data either through command line flags passed to the training script
-or through environment variables.
+Comet can be configured to log additional data either through command line flags passed to the training script or through environment variables.
```shell
export COMET_MODE=online # Set whether to run Comet in 'online' or 'offline' mode. Defaults to online
@@ -106,8 +105,7 @@ export COMET_LOG_PREDICTIONS=true # Set this to false to disable logging model p
## Logging Checkpoints with Comet
-Logging Models to Comet is disabled by default. To enable it, pass the `save-period` argument to the training script. This will save the
-logged checkpoints to Comet based on the interval value provided by `save-period`
+Logging Models to Comet is disabled by default. To enable it, pass the `save-period` argument to the training script. This will save the logged checkpoints to Comet based on the interval value provided by `save-period`
```shell
python train.py \
@@ -240,8 +238,7 @@ python utils/loggers/comet/hpo.py \
--comet_optimizer_config "utils/loggers/comet/optimizer_config.json"
```
-The `hpo.py` script accepts the same arguments as `train.py`. If you wish to pass additional arguments to your sweep simply add them after
-the script.
+The `hpo.py` script accepts the same arguments as `train.py`. If you wish to pass additional arguments to your sweep simply add them after the script.
```shell
python utils/loggers/comet/hpo.py \
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_ensembling.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_ensembling.md
index 8227a7d6..efb77c49 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_ensembling.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_ensembling.md
@@ -4,8 +4,7 @@ description: Learn how to ensemble YOLOv5 models for improved mAP and Recall! Cl
keywords: YOLOv5, object detection, ensemble learning, mAP, Recall
---
-📚 This guide explains how to use YOLOv5 🚀 **model ensembling** during testing and inference for improved mAP and Recall.
-UPDATED 25 September 2022.
+📚 This guide explains how to use YOLOv5 🚀 **model ensembling** during testing and inference for improved mAP and Recall. UPDATED 25 September 2022.
From [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ensemble_learning](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ensemble_learning):
> Ensemble modeling is a process where multiple diverse models are created to predict an outcome, either by using many different modeling algorithms or using different training data sets. The ensemble model then aggregates the prediction of each base model and results in once final prediction for the unseen data. The motivation for using ensemble models is to reduce the generalization error of the prediction. As long as the base models are diverse and independent, the prediction error of the model decreases when the ensemble approach is used. The approach seeks the wisdom of crowds in making a prediction. Even though the ensemble model has multiple base models within the model, it acts and performs as a single model.
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_export.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_export.md
index 6bad7ac2..192de827 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_export.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_export.md
@@ -6,8 +6,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv5, model export, PyTorch, TorchScript, ONNX, OpenVIN
# TFLite, ONNX, CoreML, TensorRT Export
-📚 This guide explains how to export a trained YOLOv5 🚀 model from PyTorch to ONNX and TorchScript formats.
-UPDATED 8 December 2022.
+📚 This guide explains how to export a trained YOLOv5 🚀 model from PyTorch to ONNX and TorchScript formats. UPDATED 8 December 2022.
## Before You Start
@@ -25,8 +24,7 @@ For [TensorRT](https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt) export example (requires G
YOLOv5 inference is officially supported in 11 formats:
-💡 ProTip: Export to ONNX or OpenVINO for up to 3x CPU speedup. See [CPU Benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/6613).
-💡 ProTip: Export to TensorRT for up to 5x GPU speedup. See [GPU Benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/6963).
+💡 ProTip: Export to ONNX or OpenVINO for up to 3x CPU speedup. See [CPU Benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/6613). 💡 ProTip: Export to TensorRT for up to 5x GPU speedup. See [GPU Benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/6963).
| Format | `export.py --include` | Model |
|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------|:----------------------|:--------------------------|
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_pruning_and_sparsity.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_pruning_and_sparsity.md
index bf2d647f..44ea6962 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_pruning_and_sparsity.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_pruning_and_sparsity.md
@@ -4,8 +4,7 @@ description: Improve YOLOv5 model efficiency by pruning with Ultralytics. Unders
keywords: YOLOv5, YOLO, Ultralytics, model pruning, PyTorch, machine learning, deep learning, computer vision, object detection
---
-📚 This guide explains how to apply **pruning** to YOLOv5 🚀 models.
-UPDATED 25 September 2022.
+📚 This guide explains how to apply **pruning** to YOLOv5 🚀 models. UPDATED 25 September 2022.
## Before You Start
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/multi_gpu_training.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/multi_gpu_training.md
index 7fe8355d..6740f61d 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/multi_gpu_training.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/multi_gpu_training.md
@@ -4,8 +4,7 @@ description: Learn how to train datasets on single or multiple GPUs using YOLOv5
keywords: YOLOv5, multi-GPU Training, YOLOv5 training, deep learning, machine learning, object detection, Ultralytics
---
-📚 This guide explains how to properly use **multiple** GPUs to train a dataset with YOLOv5 🚀 on single or multiple machine(s).
-UPDATED 25 December 2022.
+📚 This guide explains how to properly use **multiple** GPUs to train a dataset with YOLOv5 🚀 on single or multiple machine(s). UPDATED 25 December 2022.
## Before You Start
@@ -103,8 +102,7 @@ python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node G --nnodes N --node_rank 0 --ma
python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node G --nnodes N --node_rank R --master_addr "192.168.1.1" --master_port 1234 train.py --batch 64 --data coco.yaml --cfg yolov5s.yaml --weights ''
```
-where `G` is number of GPU per machine, `N` is the number of machines, and `R` is the machine number from `0...(N-1)`.
-Let's say I have two machines with two GPUs each, it would be `G = 2` , `N = 2`, and `R = 1` for the above.
+where `G` is number of GPU per machine, `N` is the number of machines, and `R` is the machine number from `0...(N-1)`. Let's say I have two machines with two GPUs each, it would be `G = 2` , `N = 2`, and `R = 1` for the above.
Training will not start until all `N` machines are connected. Output will only be shown on master machine!
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/neural_magic_pruning_quantization.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/neural_magic_pruning_quantization.md
index 8b978f7a..bfba5e0a 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/neural_magic_pruning_quantization.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/neural_magic_pruning_quantization.md
@@ -30,8 +30,7 @@ DeepSparse is an inference runtime with exceptional performance on CPUs. For ins
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/clearml_logging_integration.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/clearml_logging_integration.md
index 667f566d..43c8395c 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/clearml_logging_integration.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/clearml_logging_integration.md
@@ -64,8 +64,7 @@ pip install clearml>=1.2.0
This will enable integration with the YOLOv5 training script. Every training run from now on, will be captured and stored by the ClearML experiment manager.
-If you want to change the `project_name` or `task_name`, use the `--project` and `--name` arguments of the `train.py` script, by default the project will be called `YOLOv5` and the task `Training`.
-PLEASE NOTE: ClearML uses `/` as a delimiter for subprojects, so be careful when using `/` in your project name!
+If you want to change the `project_name` or `task_name`, use the `--project` and `--name` arguments of the `train.py` script, by default the project will be called `YOLOv5` and the task `Training`. PLEASE NOTE: ClearML uses `/` as a delimiter for subprojects, so be careful when using `/` in your project name!
```bash
python train.py --img 640 --batch 16 --epochs 3 --data coco128.yaml --weights yolov5s.pt --cache
@@ -92,8 +91,7 @@ This will capture:
- Validation images per epoch
- ...
-That's a lot right? 🤯
-Now, we can visualize all of this information in the ClearML UI to get an overview of our training progress. Add custom columns to the table view (such as e.g. mAP_0.5) so you can easily sort on the best performing model. Or select multiple experiments and directly compare them!
+That's a lot right? 🤯 Now, we can visualize all of this information in the ClearML UI to get an overview of our training progress. Add custom columns to the table view (such as e.g. mAP_0.5) so you can easily sort on the best performing model. Or select multiple experiments and directly compare them!
There even more we can do with all of this information, like hyperparameter optimization and remote execution, so keep reading if you want to see how that works!
@@ -187,8 +185,7 @@ python utils/loggers/clearml/hpo.py
## 🤯 Remote Execution (advanced)
-Running HPO locally is really handy, but what if we want to run our experiments on a remote machine instead? Maybe you have access to a very powerful GPU machine on-site, or you have some budget to use cloud GPUs.
-This is where the ClearML Agent comes into play. Check out what the agent can do here:
+Running HPO locally is really handy, but what if we want to run our experiments on a remote machine instead? Maybe you have access to a very powerful GPU machine on-site, or you have some budget to use cloud GPUs. This is where the ClearML Agent comes into play. Check out what the agent can do here:
- [YouTube video](https://youtu.be/MX3BrXnaULs)
- [Documentation](https://clear.ml/docs/latest/docs/clearml_agent)
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/comet_logging_integration.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/comet_logging_integration.md
index f2c6ba84..c70d2920 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/comet_logging_integration.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/comet_logging_integration.md
@@ -90,8 +90,7 @@ By default, Comet will log the following items
# Configure Comet Logging
-Comet can be configured to log additional data either through command line flags passed to the training script
-or through environment variables.
+Comet can be configured to log additional data either through command line flags passed to the training script or through environment variables.
```shell
export COMET_MODE=online # Set whether to run Comet in 'online' or 'offline' mode. Defaults to online
@@ -106,8 +105,7 @@ export COMET_LOG_PREDICTIONS=true # Set this to false to disable logging model p
## Logging Checkpoints with Comet
-Logging Models to Comet is disabled by default. To enable it, pass the `save-period` argument to the training script. This will save the
-logged checkpoints to Comet based on the interval value provided by `save-period`
+Logging Models to Comet is disabled by default. To enable it, pass the `save-period` argument to the training script. This will save the logged checkpoints to Comet based on the interval value provided by `save-period`
```shell
python train.py \
@@ -240,8 +238,7 @@ python utils/loggers/comet/hpo.py \
--comet_optimizer_config "utils/loggers/comet/optimizer_config.json"
```
-The `hpo.py` script accepts the same arguments as `train.py`. If you wish to pass additional arguments to your sweep simply add them after
-the script.
+The `hpo.py` script accepts the same arguments as `train.py`. If you wish to pass additional arguments to your sweep simply add them after the script.
```shell
python utils/loggers/comet/hpo.py \
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_ensembling.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_ensembling.md
index 8227a7d6..efb77c49 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_ensembling.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_ensembling.md
@@ -4,8 +4,7 @@ description: Learn how to ensemble YOLOv5 models for improved mAP and Recall! Cl
keywords: YOLOv5, object detection, ensemble learning, mAP, Recall
---
-📚 This guide explains how to use YOLOv5 🚀 **model ensembling** during testing and inference for improved mAP and Recall.
-UPDATED 25 September 2022.
+📚 This guide explains how to use YOLOv5 🚀 **model ensembling** during testing and inference for improved mAP and Recall. UPDATED 25 September 2022.
From [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ensemble_learning](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ensemble_learning):
> Ensemble modeling is a process where multiple diverse models are created to predict an outcome, either by using many different modeling algorithms or using different training data sets. The ensemble model then aggregates the prediction of each base model and results in once final prediction for the unseen data. The motivation for using ensemble models is to reduce the generalization error of the prediction. As long as the base models are diverse and independent, the prediction error of the model decreases when the ensemble approach is used. The approach seeks the wisdom of crowds in making a prediction. Even though the ensemble model has multiple base models within the model, it acts and performs as a single model.
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_export.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_export.md
index 6bad7ac2..192de827 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_export.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_export.md
@@ -6,8 +6,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv5, model export, PyTorch, TorchScript, ONNX, OpenVIN
# TFLite, ONNX, CoreML, TensorRT Export
-📚 This guide explains how to export a trained YOLOv5 🚀 model from PyTorch to ONNX and TorchScript formats.
-UPDATED 8 December 2022.
+📚 This guide explains how to export a trained YOLOv5 🚀 model from PyTorch to ONNX and TorchScript formats. UPDATED 8 December 2022.
## Before You Start
@@ -25,8 +24,7 @@ For [TensorRT](https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt) export example (requires G
YOLOv5 inference is officially supported in 11 formats:
-💡 ProTip: Export to ONNX or OpenVINO for up to 3x CPU speedup. See [CPU Benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/6613).
-💡 ProTip: Export to TensorRT for up to 5x GPU speedup. See [GPU Benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/6963).
+💡 ProTip: Export to ONNX or OpenVINO for up to 3x CPU speedup. See [CPU Benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/6613). 💡 ProTip: Export to TensorRT for up to 5x GPU speedup. See [GPU Benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/6963).
| Format | `export.py --include` | Model |
|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------|:----------------------|:--------------------------|
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_pruning_and_sparsity.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_pruning_and_sparsity.md
index bf2d647f..44ea6962 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_pruning_and_sparsity.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/model_pruning_and_sparsity.md
@@ -4,8 +4,7 @@ description: Improve YOLOv5 model efficiency by pruning with Ultralytics. Unders
keywords: YOLOv5, YOLO, Ultralytics, model pruning, PyTorch, machine learning, deep learning, computer vision, object detection
---
-📚 This guide explains how to apply **pruning** to YOLOv5 🚀 models.
-UPDATED 25 September 2022.
+📚 This guide explains how to apply **pruning** to YOLOv5 🚀 models. UPDATED 25 September 2022.
## Before You Start
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/multi_gpu_training.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/multi_gpu_training.md
index 7fe8355d..6740f61d 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/multi_gpu_training.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/multi_gpu_training.md
@@ -4,8 +4,7 @@ description: Learn how to train datasets on single or multiple GPUs using YOLOv5
keywords: YOLOv5, multi-GPU Training, YOLOv5 training, deep learning, machine learning, object detection, Ultralytics
---
-📚 This guide explains how to properly use **multiple** GPUs to train a dataset with YOLOv5 🚀 on single or multiple machine(s).
-UPDATED 25 December 2022.
+📚 This guide explains how to properly use **multiple** GPUs to train a dataset with YOLOv5 🚀 on single or multiple machine(s). UPDATED 25 December 2022.
## Before You Start
@@ -103,8 +102,7 @@ python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node G --nnodes N --node_rank 0 --ma
python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node G --nnodes N --node_rank R --master_addr "192.168.1.1" --master_port 1234 train.py --batch 64 --data coco.yaml --cfg yolov5s.yaml --weights ''
```
-where `G` is number of GPU per machine, `N` is the number of machines, and `R` is the machine number from `0...(N-1)`.
-Let's say I have two machines with two GPUs each, it would be `G = 2` , `N = 2`, and `R = 1` for the above.
+where `G` is number of GPU per machine, `N` is the number of machines, and `R` is the machine number from `0...(N-1)`. Let's say I have two machines with two GPUs each, it would be `G = 2` , `N = 2`, and `R = 1` for the above.
Training will not start until all `N` machines are connected. Output will only be shown on master machine!
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/neural_magic_pruning_quantization.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/neural_magic_pruning_quantization.md
index 8b978f7a..bfba5e0a 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/neural_magic_pruning_quantization.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/neural_magic_pruning_quantization.md
@@ -30,8 +30,7 @@ DeepSparse is an inference runtime with exceptional performance on CPUs. For ins

 @@ -96,8 +92,7 @@ wget -O basilica.jpg https://raw.githubusercontent.com/neuralmagic/deepsparse/ma
#### Python API
-`Pipelines` wrap pre-processing and output post-processing around the runtime, providing a clean interface for adding DeepSparse to an application.
-The DeepSparse-Ultralytics integration includes an out-of-the-box `Pipeline` that accepts raw images and outputs the bounding boxes.
+`Pipelines` wrap pre-processing and output post-processing around the runtime, providing a clean interface for adding DeepSparse to an application. The DeepSparse-Ultralytics integration includes an out-of-the-box `Pipeline` that accepts raw images and outputs the bounding boxes.
Create a `Pipeline` and run inference:
@@ -127,9 +122,7 @@ apt-get install libgl1-mesa-glx
#### HTTP Server
-DeepSparse Server runs on top of the popular FastAPI web framework and Uvicorn web server. With just a single CLI command, you can easily setup a model
-service endpoint with DeepSparse. The Server supports any Pipeline from DeepSparse, including object detection with YOLOv5, enabling you to send raw
-images to the endpoint and receive the bounding boxes.
+DeepSparse Server runs on top of the popular FastAPI web framework and Uvicorn web server. With just a single CLI command, you can easily setup a model service endpoint with DeepSparse. The Server supports any Pipeline from DeepSparse, including object detection with YOLOv5, enabling you to send raw images to the endpoint and receive the bounding boxes.
Spin up the Server with the pruned-quantized YOLOv5s:
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/pytorch_hub_model_loading.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/pytorch_hub_model_loading.md
index adc1da94..5d9a10ad 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/pytorch_hub_model_loading.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/pytorch_hub_model_loading.md
@@ -4,8 +4,7 @@ description: Detailed guide on loading YOLOv5 from PyTorch Hub. Includes example
keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv5, PyTorch, loading YOLOv5, PyTorch Hub, inference, multi-GPU inference, training
---
-📚 This guide explains how to load YOLOv5 🚀 from PyTorch Hub at [https://pytorch.org/hub/ultralytics_yolov5](https://pytorch.org/hub/ultralytics_yolov5).
-UPDATED 26 March 2023.
+📚 This guide explains how to load YOLOv5 🚀 from PyTorch Hub at [https://pytorch.org/hub/ultralytics_yolov5](https://pytorch.org/hub/ultralytics_yolov5). UPDATED 26 March 2023.
## Before You Start
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/roboflow_datasets_integration.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/roboflow_datasets_integration.md
index f4953370..7247fff4 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/roboflow_datasets_integration.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/roboflow_datasets_integration.md
@@ -6,8 +6,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv5, Roboflow, data organization, data labelling, data
# Roboflow Datasets
-You can now use Roboflow to organize, label, prepare, version, and host your datasets for training YOLOv5 🚀 models. Roboflow is free to use with YOLOv5 if you make your workspace public.
-UPDATED 7 June 2023.
+You can now use Roboflow to organize, label, prepare, version, and host your datasets for training YOLOv5 🚀 models. Roboflow is free to use with YOLOv5 if you make your workspace public. UPDATED 7 June 2023.
!!! warning
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/running_on_jetson_nano.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/running_on_jetson_nano.md
index cb4d95ec..1cb47454 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/running_on_jetson_nano.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/running_on_jetson_nano.md
@@ -6,8 +6,7 @@ keywords: TensorRT, NVIDIA Jetson, DeepStream SDK, deployment, Ultralytics, YOLO
# Deploy on NVIDIA Jetson using TensorRT and DeepStream SDK
-📚 This guide explains how to deploy a trained model into NVIDIA Jetson Platform and perform inference using TensorRT and DeepStream SDK. Here we use TensorRT to maximize the inference performance on the Jetson platform.
-UPDATED 18 November 2022.
+📚 This guide explains how to deploy a trained model into NVIDIA Jetson Platform and perform inference using TensorRT and DeepStream SDK. Here we use TensorRT to maximize the inference performance on the Jetson platform. UPDATED 18 November 2022.
## Hardware Verification
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/test_time_augmentation.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/test_time_augmentation.md
index 553f6340..a1901977 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/test_time_augmentation.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/test_time_augmentation.md
@@ -6,8 +6,7 @@ keywords: YOLOv5, Ultralytics, Test-Time Augmentation, TTA, mAP, Recall, model p
# Test-Time Augmentation (TTA)
-📚 This guide explains how to use Test Time Augmentation (TTA) during testing and inference for improved mAP and Recall with YOLOv5 🚀.
-UPDATED 25 September 2022.
+📚 This guide explains how to use Test Time Augmentation (TTA) during testing and inference for improved mAP and Recall with YOLOv5 🚀. UPDATED 25 September 2022.
## Before You Start
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/tips_for_best_training_results.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/tips_for_best_training_results.md
index cd162a53..11538808 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/tips_for_best_training_results.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/tips_for_best_training_results.md
@@ -4,8 +4,7 @@ description: Our comprehensive guide provides insights on how to train your YOLO
keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv5, Training guide, dataset preparation, model selection, training settings, mAP results, Machine Learning, Object Detection
---
-📚 This guide explains how to produce the best mAP and training results with YOLOv5 🚀.
-UPDATED 25 May 2022.
+📚 This guide explains how to produce the best mAP and training results with YOLOv5 🚀. UPDATED 25 May 2022.
Most of the time good results can be obtained with no changes to the models or training settings, **provided your dataset is sufficiently large and well labelled**. If at first you don't get good results, there are steps you might be able to take to improve, but we always recommend users **first train with all default settings** before considering any changes. This helps establish a performance baseline and spot areas for improvement.
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/train_custom_data.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/train_custom_data.md
index 4dccbffc..2ac3ce24 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/train_custom_data.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/train_custom_data.md
@@ -4,8 +4,7 @@ description: Learn how to train your data on custom datasets using YOLOv5. Simpl
keywords: YOLOv5, train on custom dataset, image collection, model training, object detection, image labelling, Ultralytics, PyTorch, machine learning
---
-📚 This guide explains how to train your own **custom dataset** with [YOLOv5](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5) 🚀.
-UPDATED 7 June 2023.
+📚 This guide explains how to train your own **custom dataset** with [YOLOv5](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5) 🚀. UPDATED 7 June 2023.
## Before You Start
@@ -49,35 +48,27 @@ Once you have collected images, you will need to annotate the objects of interes
@@ -96,8 +92,7 @@ wget -O basilica.jpg https://raw.githubusercontent.com/neuralmagic/deepsparse/ma
#### Python API
-`Pipelines` wrap pre-processing and output post-processing around the runtime, providing a clean interface for adding DeepSparse to an application.
-The DeepSparse-Ultralytics integration includes an out-of-the-box `Pipeline` that accepts raw images and outputs the bounding boxes.
+`Pipelines` wrap pre-processing and output post-processing around the runtime, providing a clean interface for adding DeepSparse to an application. The DeepSparse-Ultralytics integration includes an out-of-the-box `Pipeline` that accepts raw images and outputs the bounding boxes.
Create a `Pipeline` and run inference:
@@ -127,9 +122,7 @@ apt-get install libgl1-mesa-glx
#### HTTP Server
-DeepSparse Server runs on top of the popular FastAPI web framework and Uvicorn web server. With just a single CLI command, you can easily setup a model
-service endpoint with DeepSparse. The Server supports any Pipeline from DeepSparse, including object detection with YOLOv5, enabling you to send raw
-images to the endpoint and receive the bounding boxes.
+DeepSparse Server runs on top of the popular FastAPI web framework and Uvicorn web server. With just a single CLI command, you can easily setup a model service endpoint with DeepSparse. The Server supports any Pipeline from DeepSparse, including object detection with YOLOv5, enabling you to send raw images to the endpoint and receive the bounding boxes.
Spin up the Server with the pruned-quantized YOLOv5s:
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/pytorch_hub_model_loading.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/pytorch_hub_model_loading.md
index adc1da94..5d9a10ad 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/pytorch_hub_model_loading.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/pytorch_hub_model_loading.md
@@ -4,8 +4,7 @@ description: Detailed guide on loading YOLOv5 from PyTorch Hub. Includes example
keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv5, PyTorch, loading YOLOv5, PyTorch Hub, inference, multi-GPU inference, training
---
-📚 This guide explains how to load YOLOv5 🚀 from PyTorch Hub at [https://pytorch.org/hub/ultralytics_yolov5](https://pytorch.org/hub/ultralytics_yolov5).
-UPDATED 26 March 2023.
+📚 This guide explains how to load YOLOv5 🚀 from PyTorch Hub at [https://pytorch.org/hub/ultralytics_yolov5](https://pytorch.org/hub/ultralytics_yolov5). UPDATED 26 March 2023.
## Before You Start
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/roboflow_datasets_integration.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/roboflow_datasets_integration.md
index f4953370..7247fff4 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/roboflow_datasets_integration.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/roboflow_datasets_integration.md
@@ -6,8 +6,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv5, Roboflow, data organization, data labelling, data
# Roboflow Datasets
-You can now use Roboflow to organize, label, prepare, version, and host your datasets for training YOLOv5 🚀 models. Roboflow is free to use with YOLOv5 if you make your workspace public.
-UPDATED 7 June 2023.
+You can now use Roboflow to organize, label, prepare, version, and host your datasets for training YOLOv5 🚀 models. Roboflow is free to use with YOLOv5 if you make your workspace public. UPDATED 7 June 2023.
!!! warning
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/running_on_jetson_nano.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/running_on_jetson_nano.md
index cb4d95ec..1cb47454 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/running_on_jetson_nano.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/running_on_jetson_nano.md
@@ -6,8 +6,7 @@ keywords: TensorRT, NVIDIA Jetson, DeepStream SDK, deployment, Ultralytics, YOLO
# Deploy on NVIDIA Jetson using TensorRT and DeepStream SDK
-📚 This guide explains how to deploy a trained model into NVIDIA Jetson Platform and perform inference using TensorRT and DeepStream SDK. Here we use TensorRT to maximize the inference performance on the Jetson platform.
-UPDATED 18 November 2022.
+📚 This guide explains how to deploy a trained model into NVIDIA Jetson Platform and perform inference using TensorRT and DeepStream SDK. Here we use TensorRT to maximize the inference performance on the Jetson platform. UPDATED 18 November 2022.
## Hardware Verification
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/test_time_augmentation.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/test_time_augmentation.md
index 553f6340..a1901977 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/test_time_augmentation.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/test_time_augmentation.md
@@ -6,8 +6,7 @@ keywords: YOLOv5, Ultralytics, Test-Time Augmentation, TTA, mAP, Recall, model p
# Test-Time Augmentation (TTA)
-📚 This guide explains how to use Test Time Augmentation (TTA) during testing and inference for improved mAP and Recall with YOLOv5 🚀.
-UPDATED 25 September 2022.
+📚 This guide explains how to use Test Time Augmentation (TTA) during testing and inference for improved mAP and Recall with YOLOv5 🚀. UPDATED 25 September 2022.
## Before You Start
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/tips_for_best_training_results.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/tips_for_best_training_results.md
index cd162a53..11538808 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/tips_for_best_training_results.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/tips_for_best_training_results.md
@@ -4,8 +4,7 @@ description: Our comprehensive guide provides insights on how to train your YOLO
keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv5, Training guide, dataset preparation, model selection, training settings, mAP results, Machine Learning, Object Detection
---
-📚 This guide explains how to produce the best mAP and training results with YOLOv5 🚀.
-UPDATED 25 May 2022.
+📚 This guide explains how to produce the best mAP and training results with YOLOv5 🚀. UPDATED 25 May 2022.
Most of the time good results can be obtained with no changes to the models or training settings, **provided your dataset is sufficiently large and well labelled**. If at first you don't get good results, there are steps you might be able to take to improve, but we always recommend users **first train with all default settings** before considering any changes. This helps establish a performance baseline and spot areas for improvement.
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/train_custom_data.md b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/train_custom_data.md
index 4dccbffc..2ac3ce24 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/tutorials/train_custom_data.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/tutorials/train_custom_data.md
@@ -4,8 +4,7 @@ description: Learn how to train your data on custom datasets using YOLOv5. Simpl
keywords: YOLOv5, train on custom dataset, image collection, model training, object detection, image labelling, Ultralytics, PyTorch, machine learning
---
-📚 This guide explains how to train your own **custom dataset** with [YOLOv5](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5) 🚀.
-UPDATED 7 June 2023.
+📚 This guide explains how to train your own **custom dataset** with [YOLOv5](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5) 🚀. UPDATED 7 June 2023.
## Before You Start
@@ -49,35 +48,27 @@ Once you have collected images, you will need to annotate the objects of interes