 -
-@@ -142,9 +143,11 @@ Here are some questions that might encounter while collecting and annotating dat
- **Q2:** How does automated annotation work? + - **A2:** Automated annotation uses pre-trained models and algorithms to label data without needing human effort. These models, which have been trained on large datasets, can identify patterns and features in new data. Techniques like transfer learning adjust these models for specific tasks, and active learning helps by selecting the most useful data points for labeling. However, this approach is only possible in certain cases where the model has been trained on sufficiently similar data and tasks. - **Q3:** How many images do I need to collect for [YOLOv8 custom training](../modes/train.md)? + - **A3:** For transfer learning and object detection, a good general rule of thumb is to have a minimum of a few hundred annotated objects per class. However, when training a model to detect just one class, it is advisable to start with at least 100 annotated images and train for around 100 epochs. For complex tasks, you may need thousands of images per class to achieve reliable model performance. ## Share Your Thoughts with the Community diff --git a/docs/en/guides/defining-project-goals.md b/docs/en/guides/defining-project-goals.md index 19d46186..7af2509a 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/defining-project-goals.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/defining-project-goals.md @@ -63,9 +63,11 @@ Other tasks, like [object detection](../tasks/detect.md), are not suitable as th The order of model selection, dataset preparation, and training approach depends on the specifics of your project. Here are a few tips to help you decide: - **Clear Understanding of the Problem**: If your problem and objectives are well-defined, start with model selection. Then, prepare your dataset and decide on the training approach based on the model's requirements. + - **Example**: Start by selecting a model for a traffic monitoring system that estimates vehicle speeds. Choose an object tracking model, gather and annotate highway videos, and then train the model with techniques for real-time video processing. - **Unique or Limited Data**: If your project is constrained by unique or limited data, begin with dataset preparation. For instance, if you have a rare dataset of medical images, annotate and prepare the data first. Then, select a model that performs well on such data, followed by choosing a suitable training approach. + - **Example**: Prepare the data first for a facial recognition system with a small dataset. Annotate it, then select a model that works well with limited data, such as a pre-trained model for transfer learning. Finally, decide on a training approach, including data augmentation, to expand the dataset. - **Need for Experimentation**: In projects where experimentation is crucial, start with the training approach. This is common in research projects where you might initially test different training techniques. Refine your model selection after identifying a promising method and prepare the dataset based on your findings. @@ -118,6 +120,7 @@ Here are some questions that might encounter while defining your computer vision - **Q2:** Can the scope of a computer vision project change after the problem statement is defined? + - **A2:** Yes, the scope of a computer vision project can change as new information becomes available or as project requirements evolve. It's important to regularly review and adjust the problem statement and objectives to reflect any new insights or changes in project direction. - **Q3:** What are some common challenges in defining the problem for a computer vision project? @@ -130,7 +133,7 @@ Connecting with other computer vision enthusiasts can be incredibly helpful for ### Community Support Channels - **GitHub Issues:** Head over to the YOLOv8 GitHub repository. You can use the [Issues tab](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/issues) to raise questions, report bugs, and suggest features. The community and maintainers can assist with specific problems you encounter. -- **Ultralytics Discord Server:** Become part of the [Ultralytics Discord server](https://ultralytics.com/discord/). Connect with fellow users and developers, seek support, exchange knowledge, and discuss ideas. +- **Ultralytics Discord Server:** Become part of the [Ultralytics Discord server](https://ultralytics.com/discord/). Connect with fellow users and developers, seek support, exchange knowledge, and discuss ideas. ### Comprehensive Guides and Documentation diff --git a/docs/en/guides/distance-calculation.md b/docs/en/guides/distance-calculation.md index ba68ca47..fadc5857 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/distance-calculation.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/distance-calculation.md @@ -23,8 +23,8 @@ Measuring the gap between two objects is known as distance calculation within a ## Visuals -| Distance Calculation using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | -|:-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:| +| Distance Calculation using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | +| :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | |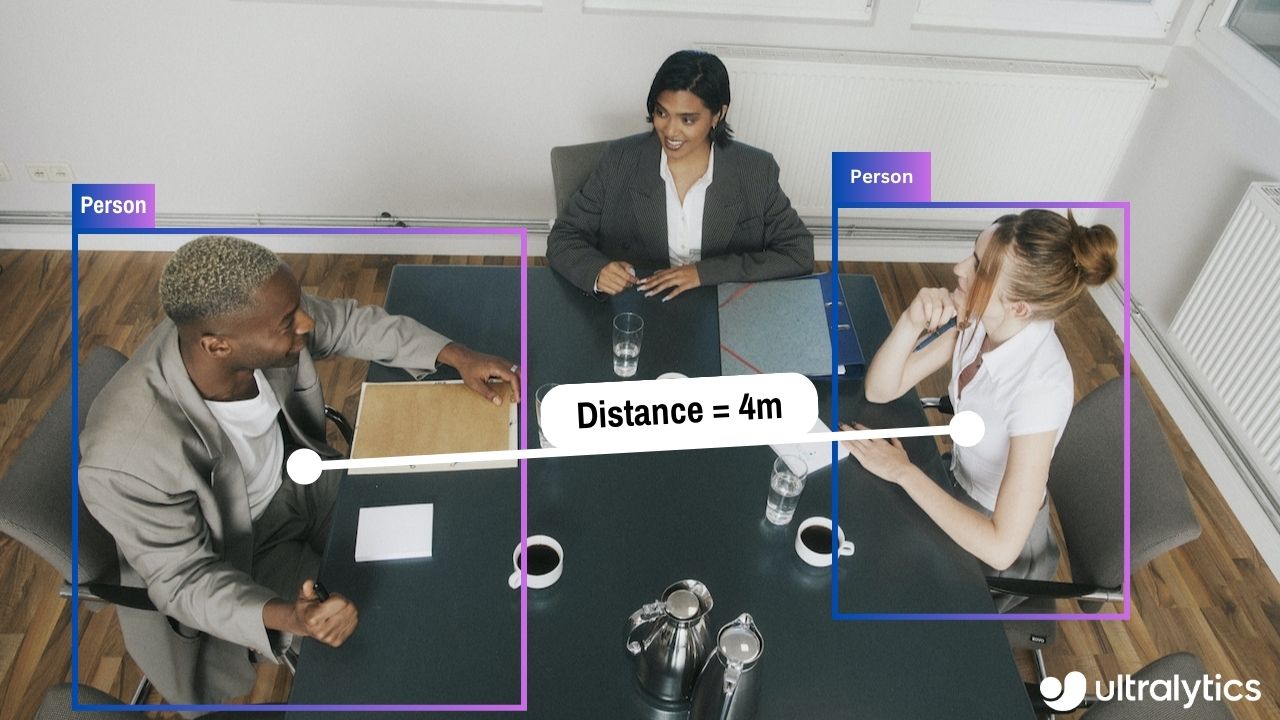  | ## Advantages of Distance Calculation? @@ -82,7 +82,7 @@ Measuring the gap between two objects is known as distance calculation within a ### Arguments `DistanceCalculation()` | `Name` | `Type` | `Default` | Description | -|--------------------|---------|-----------------|-----------------------------------------------------------| +| ------------------ | ------- | --------------- | --------------------------------------------------------- | | `names` | `dict` | `None` | Dictionary mapping class indices to class names. | | `pixels_per_meter` | `int` | `10` | Conversion factor from pixels to meters. | | `view_img` | `bool` | `False` | Flag to indicate if the video stream should be displayed. | @@ -93,7 +93,7 @@ Measuring the gap between two objects is known as distance calculation within a ### Arguments `model.track` | Name | Type | Default | Description | -|-----------|---------|----------------|-------------------------------------------------------------| +| --------- | ------- | -------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------- | | `source` | `im0` | `None` | source directory for images or videos | | `persist` | `bool` | `False` | persisting tracks between frames | | `tracker` | `str` | `botsort.yaml` | Tracking method 'bytetrack' or 'botsort' | diff --git a/docs/en/guides/docker-quickstart.md b/docs/en/guides/docker-quickstart.md index 4469e69f..a7466967 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/docker-quickstart.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/docker-quickstart.md @@ -168,7 +168,7 @@ Setup and configuration of an X11 or Wayland display server is outside the scope ??? info "Use GPUs" If you're using [GPUs](#using-gpus), you can add the `--gpus all` flag to the command. - + === "X11" If you're using X11, you can run the following command to allow the Docker container to access the X11 socket: diff --git a/docs/en/guides/heatmaps.md b/docs/en/guides/heatmaps.md index 055a77ba..41badf0d 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/heatmaps.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/heatmaps.md @@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ A heatmap generated with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ult ## Real World Applications | Transportation | Retail | -|:-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:| +| :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | |  |  | | Ultralytics YOLOv8 Transportation Heatmap | Ultralytics YOLOv8 Retail Heatmap | @@ -119,7 +119,7 @@ A heatmap generated with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ult video_writer.release() cv2.destroyAllWindows() ``` - + === "Polygon Counting" ```python import cv2 @@ -271,7 +271,7 @@ A heatmap generated with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ult ### Arguments `Heatmap()` | Name | Type | Default | Description | -|--------------------|------------------|--------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------| +| ------------------ | ---------------- | ------------------ | ----------------------------------------------------------------- | | `classes_names` | `dict` | `None` | Dictionary of class names. | | `imw` | `int` | `0` | Image width. | | `imh` | `int` | `0` | Image height. | @@ -293,7 +293,7 @@ A heatmap generated with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ult ### Arguments `model.track` | Name | Type | Default | Description | -|-----------|---------|----------------|-------------------------------------------------------------| +| --------- | ------- | -------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------- | | `source` | `im0` | `None` | source directory for images or videos | | `persist` | `bool` | `False` | persisting tracks between frames | | `tracker` | `str` | `botsort.yaml` | Tracking method 'bytetrack' or 'botsort' | @@ -304,7 +304,7 @@ A heatmap generated with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ult ### Heatmap COLORMAPs | Colormap Name | Description | -|---------------------------------|----------------------------------------| +| ------------------------------- | -------------------------------------- | | `cv::COLORMAP_AUTUMN` | Autumn color map | | `cv::COLORMAP_BONE` | Bone color map | | `cv::COLORMAP_JET` | Jet color map | diff --git a/docs/en/guides/hyperparameter-tuning.md b/docs/en/guides/hyperparameter-tuning.md index 36d4c4da..555f2470 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/hyperparameter-tuning.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/hyperparameter-tuning.md @@ -116,36 +116,37 @@ This YAML file contains the best-performing hyperparameters found during the tun - **Format**: YAML - **Usage**: Hyperparameter results - **Example**: - ```yaml - # 558/900 iterations complete ✅ (45536.81s) - # Results saved to /usr/src/ultralytics/runs/detect/tune - # Best fitness=0.64297 observed at iteration 498 - # Best fitness metrics are {'metrics/precision(B)': 0.87247, 'metrics/recall(B)': 0.71387, 'metrics/mAP50(B)': 0.79106, 'metrics/mAP50-95(B)': 0.62651, 'val/box_loss': 2.79884, 'val/cls_loss': 2.72386, 'val/dfl_loss': 0.68503, 'fitness': 0.64297} - # Best fitness model is /usr/src/ultralytics/runs/detect/train498 - # Best fitness hyperparameters are printed below. - lr0: 0.00269 - lrf: 0.00288 - momentum: 0.73375 - weight_decay: 0.00015 - warmup_epochs: 1.22935 - warmup_momentum: 0.1525 - box: 18.27875 - cls: 1.32899 - dfl: 0.56016 - hsv_h: 0.01148 - hsv_s: 0.53554 - hsv_v: 0.13636 - degrees: 0.0 - translate: 0.12431 - scale: 0.07643 - shear: 0.0 - perspective: 0.0 - flipud: 0.0 - fliplr: 0.08631 - mosaic: 0.42551 - mixup: 0.0 - copy_paste: 0.0 + ```yaml + # 558/900 iterations complete ✅ (45536.81s) + # Results saved to /usr/src/ultralytics/runs/detect/tune + # Best fitness=0.64297 observed at iteration 498 + # Best fitness metrics are {'metrics/precision(B)': 0.87247, 'metrics/recall(B)': 0.71387, 'metrics/mAP50(B)': 0.79106, 'metrics/mAP50-95(B)': 0.62651, 'val/box_loss': 2.79884, 'val/cls_loss': 2.72386, 'val/dfl_loss': 0.68503, 'fitness': 0.64297} + # Best fitness model is /usr/src/ultralytics/runs/detect/train498 + # Best fitness hyperparameters are printed below. + + lr0: 0.00269 + lrf: 0.00288 + momentum: 0.73375 + weight_decay: 0.00015 + warmup_epochs: 1.22935 + warmup_momentum: 0.1525 + box: 18.27875 + cls: 1.32899 + dfl: 0.56016 + hsv_h: 0.01148 + hsv_s: 0.53554 + hsv_v: 0.13636 + degrees: 0.0 + translate: 0.12431 + scale: 0.07643 + shear: 0.0 + perspective: 0.0 + flipud: 0.0 + fliplr: 0.08631 + mosaic: 0.42551 + mixup: 0.0 + copy_paste: 0.0 ``` #### best_fitness.png diff --git a/docs/en/guides/index.md b/docs/en/guides/index.md index 99f5fa4f..df331adf 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/index.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/index.md @@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ Here's a compilation of in-depth guides to help you master different aspects of - [OpenVINO Latency vs Throughput Modes](optimizing-openvino-latency-vs-throughput-modes.md) - Learn latency and throughput optimization techniques for peak YOLO inference performance. - [Steps of a Computer Vision Project ](steps-of-a-cv-project.md) 🚀 NEW: Learn about the key steps involved in a computer vision project, including defining goals, selecting models, preparing data, and evaluating results. - [Defining A Computer Vision Project's Goals](defining-project-goals.md) 🚀 NEW: Walk through how to effectively define clear and measurable goals for your computer vision project. Learn the importance of a well-defined problem statement and how it creates a roadmap for your project. -- - [Data Collection and Annotation](data-collection-and-annotation.md)🚀 NEW: Explore the tools, techniques, and best practices for collecting and annotating data to create high-quality inputs for your computer vision models. +- [Data Collection and Annotation](data-collection-and-annotation.md)🚀 NEW: Explore the tools, techniques, and best practices for collecting and annotating data to create high-quality inputs for your computer vision models. - [Preprocessing Annotated Data](preprocessing_annotated_data.md)🚀 NEW: Learn about preprocessing and augmenting image data in computer vision projects using YOLOv8, including normalization, dataset augmentation, splitting, and exploratory data analysis (EDA). ## Contribute to Our Guides diff --git a/docs/en/guides/instance-segmentation-and-tracking.md b/docs/en/guides/instance-segmentation-and-tracking.md index 48b6ee2c..8f50e47e 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/instance-segmentation-and-tracking.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/instance-segmentation-and-tracking.md @@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ There are two types of instance segmentation tracking available in the Ultralyti ## Samples | Instance Segmentation | Instance Segmentation + Object Tracking | -|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|:------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:| +| :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | |  |  | | Ultralytics Instance Segmentation 😍 | Ultralytics Instance Segmentation with Object Tracking 🔥 | @@ -126,7 +126,7 @@ There are two types of instance segmentation tracking available in the Ultralyti ### `seg_bbox` Arguments | Name | Type | Default | Description | -|---------------|---------|-----------------|----------------------------------------| +| ------------- | ------- | --------------- | -------------------------------------- | | `mask` | `array` | `None` | Segmentation mask coordinates | | `mask_color` | `tuple` | `(255, 0, 255)` | Mask color for every segmented box | | `det_label` | `str` | `None` | Label for segmented object | diff --git a/docs/en/guides/isolating-segmentation-objects.md b/docs/en/guides/isolating-segmentation-objects.md index 2b283f09..3885e624 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/isolating-segmentation-objects.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/isolating-segmentation-objects.md @@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab ## Recipe Walk Through -1. Begin with the necessary imports +1. Begin with the necessary imports ```python from pathlib import Path @@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab *** -2. Load a model and run `predict()` method on a source. +2. Load a model and run `predict()` method on a source. ```python from ultralytics import YOLO @@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab *** -3. Now iterate over the results and the contours. For workflows that want to save an image to file, the source image `base-name` and the detection `class-label` are retrieved for later use (optional). +3. Now iterate over the results and the contours. For workflows that want to save an image to file, the source image `base-name` and the detection `class-label` are retrieved for later use (optional). ```{ .py .annotate } # (2) Iterate detection results (helpful for multiple images) @@ -81,7 +81,7 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab *** -4. Start with generating a binary mask from the source image and then draw a filled contour onto the mask. This will allow the object to be isolated from the other parts of the image. An example from `bus.jpg` for one of the detected `person` class objects is shown on the right. +4. Start with generating a binary mask from the source image and then draw a filled contour onto the mask. This will allow the object to be isolated from the other parts of the image. An example from `bus.jpg` for one of the detected `person` class objects is shown on the right. { width="240", align="right" } @@ -140,7 +140,7 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab *** -5. Next there are 2 options for how to move forward with the image from this point and a subsequent option for each. +5. Next there are 2 options for how to move forward with the image from this point and a subsequent option for each. ### Object Isolation Options @@ -251,7 +251,7 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab *** -6. What to do next is entirely left to you as the developer. A basic example of one possible next step (saving the image to file for future use) is shown. +6. What to do next is entirely left to you as the developer. A basic example of one possible next step (saving the image to file for future use) is shown. - **NOTE:** this step is optional and can be skipped if not required for your specific use case. diff --git a/docs/en/guides/kfold-cross-validation.md b/docs/en/guides/kfold-cross-validation.md index 47d929f6..b18ab3fd 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/kfold-cross-validation.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/kfold-cross-validation.md @@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ Without further ado, let's dive in! - It includes 6 class labels, each with its total instance counts listed below. | Class Label | Instance Count | -|:------------|:--------------:| +| :---------- | :------------: | | Apple | 7049 | | Grapes | 7202 | | Pineapple | 1613 | @@ -173,7 +173,7 @@ The rows index the label files, each corresponding to an image in your dataset, fold_lbl_distrb.loc[f"split_{n}"] = ratio ``` - The ideal scenario is for all class ratios to be reasonably similar for each split and across classes. This, however, will be subject to the specifics of your dataset. + The ideal scenario is for all class ratios to be reasonably similar for each split and across classes. This, however, will be subject to the specifics of your dataset. 4. Next, we create the directories and dataset YAML files for each split. @@ -219,7 +219,7 @@ The rows index the label files, each corresponding to an image in your dataset, 5. Lastly, copy images and labels into the respective directory ('train' or 'val') for each split. - - __NOTE:__ The time required for this portion of the code will vary based on the size of your dataset and your system hardware. + - **NOTE:** The time required for this portion of the code will vary based on the size of your dataset and your system hardware. ```python for image, label in zip(images, labels): diff --git a/docs/en/guides/model-deployment-options.md b/docs/en/guides/model-deployment-options.md index 37113976..e6cb2c5b 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/model-deployment-options.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/model-deployment-options.md @@ -263,7 +263,7 @@ NCNN is a high-performance neural network inference framework optimized for the The following table provides a snapshot of the various deployment options available for YOLOv8 models, helping you to assess which may best fit your project needs based on several critical criteria. For an in-depth look at each deployment option's format, please see the [Ultralytics documentation page on export formats](../modes/export.md#export-formats). | Deployment Option | Performance Benchmarks | Compatibility and Integration | Community Support and Ecosystem | Case Studies | Maintenance and Updates | Security Considerations | Hardware Acceleration | -|-------------------|-------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------| +| ----------------- | ----------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------- | | PyTorch | Good flexibility; may trade off raw performance | Excellent with Python libraries | Extensive resources and community | Research and prototypes | Regular, active development | Dependent on deployment environment | CUDA support for GPU acceleration | | TorchScript | Better for production than PyTorch | Smooth transition from PyTorch to C++ | Specialized but narrower than PyTorch | Industry where Python is a bottleneck | Consistent updates with PyTorch | Improved security without full Python | Inherits CUDA support from PyTorch | | ONNX | Variable depending on runtime | High across different frameworks | Broad ecosystem, supported by many orgs | Flexibility across ML frameworks | Regular updates for new operations | Ensure secure conversion and deployment practices | Various hardware optimizations | diff --git a/docs/en/guides/nvidia-jetson.md b/docs/en/guides/nvidia-jetson.md index adbdc140..cf4de1bb 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/nvidia-jetson.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/nvidia-jetson.md @@ -22,14 +22,14 @@ NVIDIA Jetson is a series of embedded computing boards designed to bring acceler [Jetson Orin](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/autonomous-machines/embedded-systems/jetson-orin/) is the latest iteration of the NVIDIA Jetson family based on NVIDIA Ampere architecture which brings drastically improved AI performance when compared to the previous generations. Below table compared few of the Jetson devices in the ecosystem. -| | Jetson AGX Orin 64GB | Jetson Orin NX 16GB | Jetson Orin Nano 8GB | Jetson AGX Xavier | Jetson Xavier NX | Jetson Nano | -|-------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------| -| AI Performance | 275 TOPS | 100 TOPS | 40 TOPs | 32 TOPS | 21 TOPS | 472 GFLOPS | -| GPU | 2048-core NVIDIA Ampere architecture GPU with 64 Tensor Cores | 1024-core NVIDIA Ampere architecture GPU with 32 Tensor Cores | 1024-core NVIDIA Ampere architecture GPU with 32 Tensor Cores | 512-core NVIDIA Volta architecture GPU with 64 Tensor Cores | 384-core NVIDIA Volta™ architecture GPU with 48 Tensor Cores | 128-core NVIDIA Maxwell™ architecture GPU | -| GPU Max Frequency | 1.3 GHz | 918 MHz | 625 MHz | 1377 MHz | 1100 MHz | 921MHz | -| CPU | 12-core NVIDIA Arm® Cortex A78AE v8.2 64-bit CPU 3MB L2 + 6MB L3 | 8-core NVIDIA Arm® Cortex A78AE v8.2 64-bit CPU 2MB L2 + 4MB L3 | 6-core Arm® Cortex®-A78AE v8.2 64-bit CPU 1.5MB L2 + 4MB L3 | 8-core NVIDIA Carmel Arm®v8.2 64-bit CPU 8MB L2 + 4MB L3 | 6-core NVIDIA Carmel Arm®v8.2 64-bit CPU 6MB L2 + 4MB L3 | Quad-Core Arm® Cortex®-A57 MPCore processor | -| CPU Max Frequency | 2.2 GHz | 2.0 GHz | 1.5 GHz | 2.2 GHz | 1.9 GHz | 1.43GHz | -| Memory | 64GB 256-bit LPDDR5 204.8GB/s | 16GB 128-bit LPDDR5 102.4GB/s | 8GB 128-bit LPDDR5 68 GB/s | 32GB 256-bit LPDDR4x 136.5GB/s | 8GB 128-bit LPDDR4x 59.7GB/s | 4GB 64-bit LPDDR4 25.6GB/s" | +| | Jetson AGX Orin 64GB | Jetson Orin NX 16GB | Jetson Orin Nano 8GB | Jetson AGX Xavier | Jetson Xavier NX | Jetson Nano | +| ----------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------- | +| AI Performance | 275 TOPS | 100 TOPS | 40 TOPs | 32 TOPS | 21 TOPS | 472 GFLOPS | +| GPU | 2048-core NVIDIA Ampere architecture GPU with 64 Tensor Cores | 1024-core NVIDIA Ampere architecture GPU with 32 Tensor Cores | 1024-core NVIDIA Ampere architecture GPU with 32 Tensor Cores | 512-core NVIDIA Volta architecture GPU with 64 Tensor Cores | 384-core NVIDIA Volta™ architecture GPU with 48 Tensor Cores | 128-core NVIDIA Maxwell™ architecture GPU | +| GPU Max Frequency | 1.3 GHz | 918 MHz | 625 MHz | 1377 MHz | 1100 MHz | 921MHz | +| CPU | 12-core NVIDIA Arm® Cortex A78AE v8.2 64-bit CPU 3MB L2 + 6MB L3 | 8-core NVIDIA Arm® Cortex A78AE v8.2 64-bit CPU 2MB L2 + 4MB L3 | 6-core Arm® Cortex®-A78AE v8.2 64-bit CPU 1.5MB L2 + 4MB L3 | 8-core NVIDIA Carmel Arm®v8.2 64-bit CPU 8MB L2 + 4MB L3 | 6-core NVIDIA Carmel Arm®v8.2 64-bit CPU 6MB L2 + 4MB L3 | Quad-Core Arm® Cortex®-A57 MPCore processor | +| CPU Max Frequency | 2.2 GHz | 2.0 GHz | 1.5 GHz | 2.2 GHz | 1.9 GHz | 1.43GHz | +| Memory | 64GB 256-bit LPDDR5 204.8GB/s | 16GB 128-bit LPDDR5 102.4GB/s | 8GB 128-bit LPDDR5 68 GB/s | 32GB 256-bit LPDDR4x 136.5GB/s | 8GB 128-bit LPDDR4x 59.7GB/s | 4GB 64-bit LPDDR4 25.6GB/s" | For a more detailed comparison table, please visit the **Technical Specifications** section of [official NVIDIA Jetson page](https://developer.nvidia.com/embedded/jetson-modules). diff --git a/docs/en/guides/object-blurring.md b/docs/en/guides/object-blurring.md index 1ab5788c..5a43a285 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/object-blurring.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/object-blurring.md @@ -72,7 +72,7 @@ Object blurring with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly ### Arguments `model.predict` | Name | Type | Default | Description | -|-----------------|----------------|------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| --------------- | -------------- | ---------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | `source` | `str` | `'ultralytics/assets'` | source directory for images or videos | | `conf` | `float` | `0.25` | object confidence threshold for detection | | `iou` | `float` | `0.7` | intersection over union (IoU) threshold for NMS | diff --git a/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md b/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md index c75f4083..46f204f7 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md @@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ Object counting with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly ## Real World Applications | Logistics | Aquaculture | -|:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:| +| :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | |  | 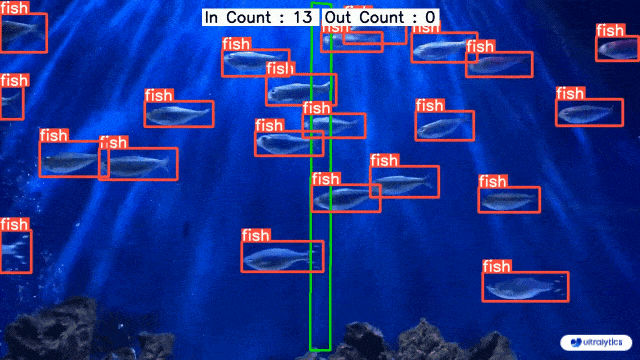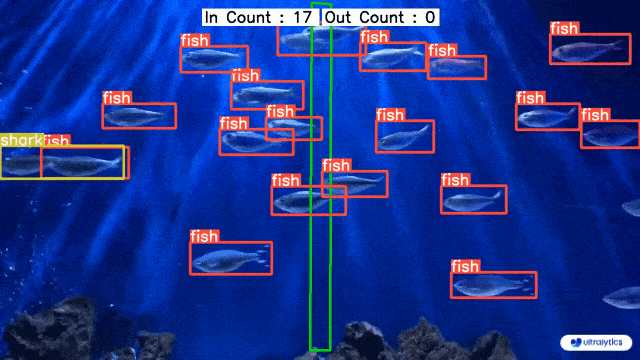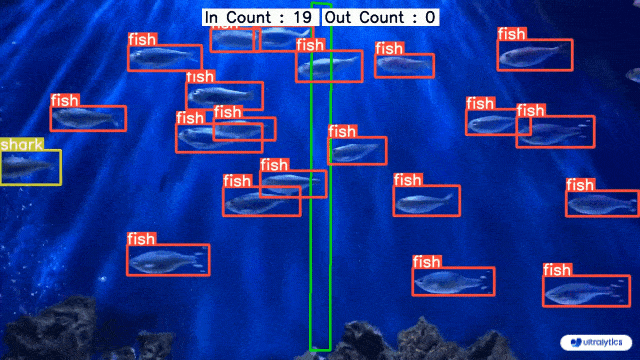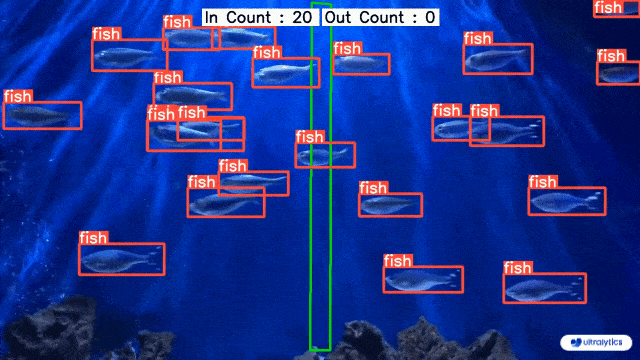 | | Conveyor Belt Packets Counting Using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Fish Counting in Sea using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | @@ -89,7 +89,7 @@ Object counting with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly video_writer.release() cv2.destroyAllWindows() ``` - + === "Count in Polygon" ```python @@ -131,7 +131,7 @@ Object counting with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly video_writer.release() cv2.destroyAllWindows() ``` - + === "Count in Line" ```python @@ -225,7 +225,7 @@ Object counting with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly Here's a table with the `ObjectCounter` arguments: | Name | Type | Default | Description | -|----------------------|---------|----------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| -------------------- | ------- | -------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | | `classes_names` | `dict` | `None` | Dictionary of class names. | | `reg_pts` | `list` | `[(20, 400), (1260, 400)]` | List of points defining the counting region. | | `count_reg_color` | `tuple` | `(255, 0, 255)` | RGB color of the counting region. | @@ -245,7 +245,7 @@ Here's a table with the `ObjectCounter` arguments: ### Arguments `model.track` | Name | Type | Default | Description | -|-----------|---------|----------------|-------------------------------------------------------------| +| --------- | ------- | -------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------- | | `source` | `im0` | `None` | source directory for images or videos | | `persist` | `bool` | `False` | persisting tracks between frames | | `tracker` | `str` | `botsort.yaml` | Tracking method 'bytetrack' or 'botsort' | diff --git a/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md b/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md index cb2d293c..1d8d950e 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md @@ -18,10 +18,10 @@ Object cropping with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly ## Visuals -| Airport Luggage | -|:----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:| +| Airport Luggage | +| :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | | 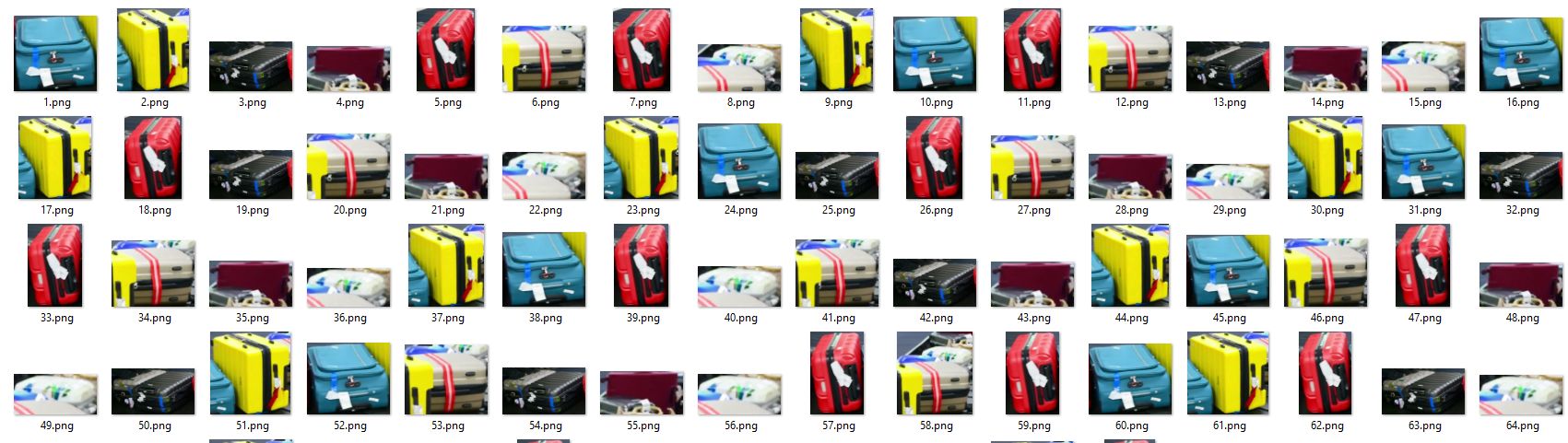 | -| Suitcases Cropping at airport conveyor belt using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | +| Suitcases Cropping at airport conveyor belt using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | !!! Example "Object Cropping using YOLOv8 Example" @@ -84,7 +84,7 @@ Object cropping with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly ### Arguments `model.predict` | Argument | Type | Default | Description | -|-----------------|----------------|------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| --------------- | -------------- | ---------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | | `source` | `str` | `'ultralytics/assets'` | Specifies the data source for inference. Can be an image path, video file, directory, URL, or device ID for live feeds. Supports a wide range of formats and sources, enabling flexible application across different types of input. | | `conf` | `float` | `0.25` | Sets the minimum confidence threshold for detections. Objects detected with confidence below this threshold will be disregarded. Adjusting this value can help reduce false positives. | | `iou` | `float` | `0.7` | Intersection Over Union (IoU) threshold for Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS). Lower values result in fewer detections by eliminating overlapping boxes, useful for reducing duplicates. | diff --git a/docs/en/guides/optimizing-openvino-latency-vs-throughput-modes.md b/docs/en/guides/optimizing-openvino-latency-vs-throughput-modes.md index a907a131..80ae18dc 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/optimizing-openvino-latency-vs-throughput-modes.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/optimizing-openvino-latency-vs-throughput-modes.md @@ -36,12 +36,12 @@ Throughput optimization is crucial for scenarios serving numerous inference requ 1. **OpenVINO Performance Hints:** A high-level, future-proof method to enhance throughput across devices using performance hints. - ```python - import openvino.properties.hint as hints + ```python + import openvino.properties.hint as hints - config = {hints.performance_mode: hints.PerformanceMode.THROUGHPUT} - compiled_model = core.compile_model(model, "GPU", config) - ``` + config = {hints.performance_mode: hints.PerformanceMode.THROUGHPUT} + compiled_model = core.compile_model(model, "GPU", config) + ``` 2. **Explicit Batching and Streams:** A more granular approach involving explicit batching and the use of streams for advanced performance tuning. diff --git a/docs/en/guides/parking-management.md b/docs/en/guides/parking-management.md index 2ca3f103..5f219201 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/parking-management.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/parking-management.md @@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ Parking management with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultr ## Real World Applications | Parking Management System | Parking Management System | -|:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|:------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:| +| :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | |  |  | | Parking management Aerial View using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Parking management Top View using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | @@ -101,7 +101,7 @@ Parking management with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultr ### Optional Arguments `ParkingManagement` | Name | Type | Default | Description | -|--------------------------|---------|-------------------|----------------------------------------| +| ------------------------ | ------- | ----------------- | -------------------------------------- | | `model_path` | `str` | `None` | Path to the YOLOv8 model. | | `txt_color` | `tuple` | `(0, 0, 0)` | RGB color tuple for text. | | `bg_color` | `tuple` | `(255, 255, 255)` | RGB color tuple for background. | @@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ Parking management with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultr ### Arguments `model.track` | Name | Type | Default | Description | -|-----------|---------|----------------|-------------------------------------------------------------| +| --------- | ------- | -------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------- | | `source` | `im0` | `None` | source directory for images or videos | | `persist` | `bool` | `False` | persisting tracks between frames | | `tracker` | `str` | `botsort.yaml` | Tracking method 'bytetrack' or 'botsort' | diff --git a/docs/en/guides/preprocessing_annotated_data.md b/docs/en/guides/preprocessing_annotated_data.md index 08a5a520..1156c2a0 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/preprocessing_annotated_data.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/preprocessing_annotated_data.md @@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ keywords: data preprocessing, computer vision, image resizing, normalization, da ## Introduction -After you've defined your computer vision [project's goals](./defining-project-goals.md) and [collected and annotated data](./data-collection-and-annotation.md), the next step is to preprocess annotated data and prepare it for model training. Clean and consistent data are vital to creating a model that performs well. +After you've defined your computer vision [project's goals](./defining-project-goals.md) and [collected and annotated data](./data-collection-and-annotation.md), the next step is to preprocess annotated data and prepare it for model training. Clean and consistent data are vital to creating a model that performs well. Preprocessing is a step in the [computer vision project workflow](./steps-of-a-cv-project.md) that includes resizing images, normalizing pixel values, augmenting the dataset, and splitting the data into training, validation, and test sets. Let's explore the essential techniques and best practices for cleaning your data! @@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ We are already collecting and annotating our data carefully with multiple consid ## Data Preprocessing Techniques -One of the first and foremost steps in data preprocessing is resizing. Some models are designed to handle variable input sizes, but many models require a consistent input size. Resizing images makes them uniform and reduces computational complexity. +One of the first and foremost steps in data preprocessing is resizing. Some models are designed to handle variable input sizes, but many models require a consistent input size. Resizing images makes them uniform and reduces computational complexity. ### Resizing Images @@ -31,12 +31,12 @@ You can resize your images using the following methods: - **Bilinear Interpolation**: Smooths pixel values by taking a weighted average of the four nearest pixel values. - **Nearest Neighbor**: Assigns the nearest pixel value without averaging, leading to a blocky image but faster computation. -To make resizing a simpler task, you can use the following tools: +To make resizing a simpler task, you can use the following tools: - **OpenCV**: A popular computer vision library with extensive functions for image processing. - **PIL (Pillow)**: A Python Imaging Library for opening, manipulating, and saving image files. -With respect to YOLOv8, the 'imgsz' parameter during [model training](../modes/train.md) allows for flexible input sizes. When set to a specific size, such as 640, the model will resize input images so their largest dimension is 640 pixels while maintaining the original aspect ratio. +With respect to YOLOv8, the 'imgsz' parameter during [model training](../modes/train.md) allows for flexible input sizes. When set to a specific size, such as 640, the model will resize input images so their largest dimension is 640 pixels while maintaining the original aspect ratio. By evaluating your model's and dataset's specific needs, you can determine whether resizing is a necessary preprocessing step or if your model can efficiently handle images of varying sizes. @@ -47,16 +47,16 @@ Another preprocessing technique is normalization. Normalization scales the pixel - **Min-Max Scaling**: Scales pixel values to a range of 0 to 1. - **Z-Score Normalization**: Scales pixel values based on their mean and standard deviation. -With respect to YOLOv8, normalization is seamlessly handled as part of its preprocessing pipeline during model training. YOLOv8 automatically performs several preprocessing steps, including conversion to RGB, scaling pixel values to the range [0, 1], and normalization using predefined mean and standard deviation values. +With respect to YOLOv8, normalization is seamlessly handled as part of its preprocessing pipeline during model training. YOLOv8 automatically performs several preprocessing steps, including conversion to RGB, scaling pixel values to the range [0, 1], and normalization using predefined mean and standard deviation values. ### Splitting the Dataset -Once you've cleaned the data, you are ready to split the dataset. Splitting the data into training, validation, and test sets is done to ensure that the model can be evaluated on unseen data to assess its generalization performance. A common split is 70% for training, 20% for validation, and 10% for testing. There are various tools and libraries that you can use to split your data like scikit-learn or TensorFlow. +Once you've cleaned the data, you are ready to split the dataset. Splitting the data into training, validation, and test sets is done to ensure that the model can be evaluated on unseen data to assess its generalization performance. A common split is 70% for training, 20% for validation, and 10% for testing. There are various tools and libraries that you can use to split your data like scikit-learn or TensorFlow. Consider the following when splitting your dataset: + - **Maintaining Data Distribution**: Ensure that the data distribution of classes is maintained across training, validation, and test sets. -- **Avoiding Data Leakage**: Typically, data augmentation is done after the dataset is split. Data augmentation and any other preprocessing should only be applied to the training set to prevent information from the validation or test sets from influencing the model training. --**Balancing Classes**: For imbalanced datasets, consider techniques such as oversampling the minority class or under-sampling the majority class within the training set. +- **Avoiding Data Leakage**: Typically, data augmentation is done after the dataset is split. Data augmentation and any other preprocessing should only be applied to the training set to prevent information from the validation or test sets from influencing the model training. -**Balancing Classes**: For imbalanced datasets, consider techniques such as oversampling the minority class or under-sampling the majority class within the training set. ### What is Data Augmentation? @@ -89,13 +89,13 @@ Also, you can adjust the intensity of these augmentation techniques through spec ## A Case Study of Preprocessing -Consider a project aimed at developing a model to detect and classify different types of vehicles in traffic images using YOLOv8. We've collected traffic images and annotated them with bounding boxes and labels. +Consider a project aimed at developing a model to detect and classify different types of vehicles in traffic images using YOLOv8. We've collected traffic images and annotated them with bounding boxes and labels. Here's what each step of preprocessing would look like for this project: - Resizing Images: Since YOLOv8 handles flexible input sizes and performs resizing automatically, manual resizing is not required. The model will adjust the image size according to the specified 'imgsz' parameter during training. - Normalizing Pixel Values: YOLOv8 automatically normalizes pixel values to a range of 0 to 1 during preprocessing, so it's not required. -- Splitting the Dataset: Divide the dataset into training (70%), validation (20%), and test (10%) sets using tools like scikit-learn. +- Splitting the Dataset: Divide the dataset into training (70%), validation (20%), and test (10%) sets using tools like scikit-learn. - Data Augmentation: Modify the dataset configuration file (.yaml) to include data augmentation techniques such as random crops, horizontal flips, and brightness adjustments. These steps make sure the dataset is prepared without any potential issues and is ready for Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA). @@ -104,11 +104,11 @@ These steps make sure the dataset is prepared without any potential issues and i After preprocessing and augmenting your dataset, the next step is to gain insights through Exploratory Data Analysis. EDA uses statistical techniques and visualization tools to understand the patterns and distributions in your data. You can identify issues like class imbalances or outliers and make informed decisions about further data preprocessing or model training adjustments. -### Statistical EDA Techniques +### Statistical EDA Techniques Statistical techniques often begin with calculating basic metrics such as mean, median, standard deviation, and range. These metrics provide a quick overview of your image dataset's properties, such as pixel intensity distributions. Understanding these basic statistics helps you grasp the overall quality and characteristics of your data, allowing you to spot any irregularities early on. -### Visual EDA Techniques +### Visual EDA Techniques Visualizations are key in EDA for image datasets. For example, class imbalance analysis is another vital aspect of EDA. It helps determine if certain classes are underrepresented in your dataset, Visualizing the distribution of different image classes or categories using bar charts can quickly reveal any imbalances. Similarly, outliers can be identified using visualization tools like box plots, which highlight anomalies in pixel intensity or feature distributions. Outlier detection prevents unusual data points from skewing your results. @@ -131,9 +131,11 @@ For a more advanced approach to EDA, you can use the Ultralytics Explorer tool. Here are some questions that might come up while you prepare your dataset: - **Q1:** How much preprocessing is too much? + - **A1:** Preprocessing is essential but should be balanced. Overdoing it can lead to loss of critical information, overfitting, increased complexity, and higher computational costs. Focus on necessary steps like resizing, normalization, and basic augmentation, adjusting based on model performance. - **Q2:** What are the common pitfalls in EDA? + - **A2:** Common pitfalls in Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) include ignoring data quality issues like missing values and outliers, confirmation bias, overfitting visualizations, neglecting data distribution, and overlooking correlations. A systematic approach helps gain accurate and valuable insights. ## Reach Out and Connect diff --git a/docs/en/guides/queue-management.md b/docs/en/guides/queue-management.md index e16c3280..43e9f20c 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/queue-management.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/queue-management.md @@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ Queue management using [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultra ## Real World Applications | Logistics | Retail | -|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|:----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:| +| :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | | 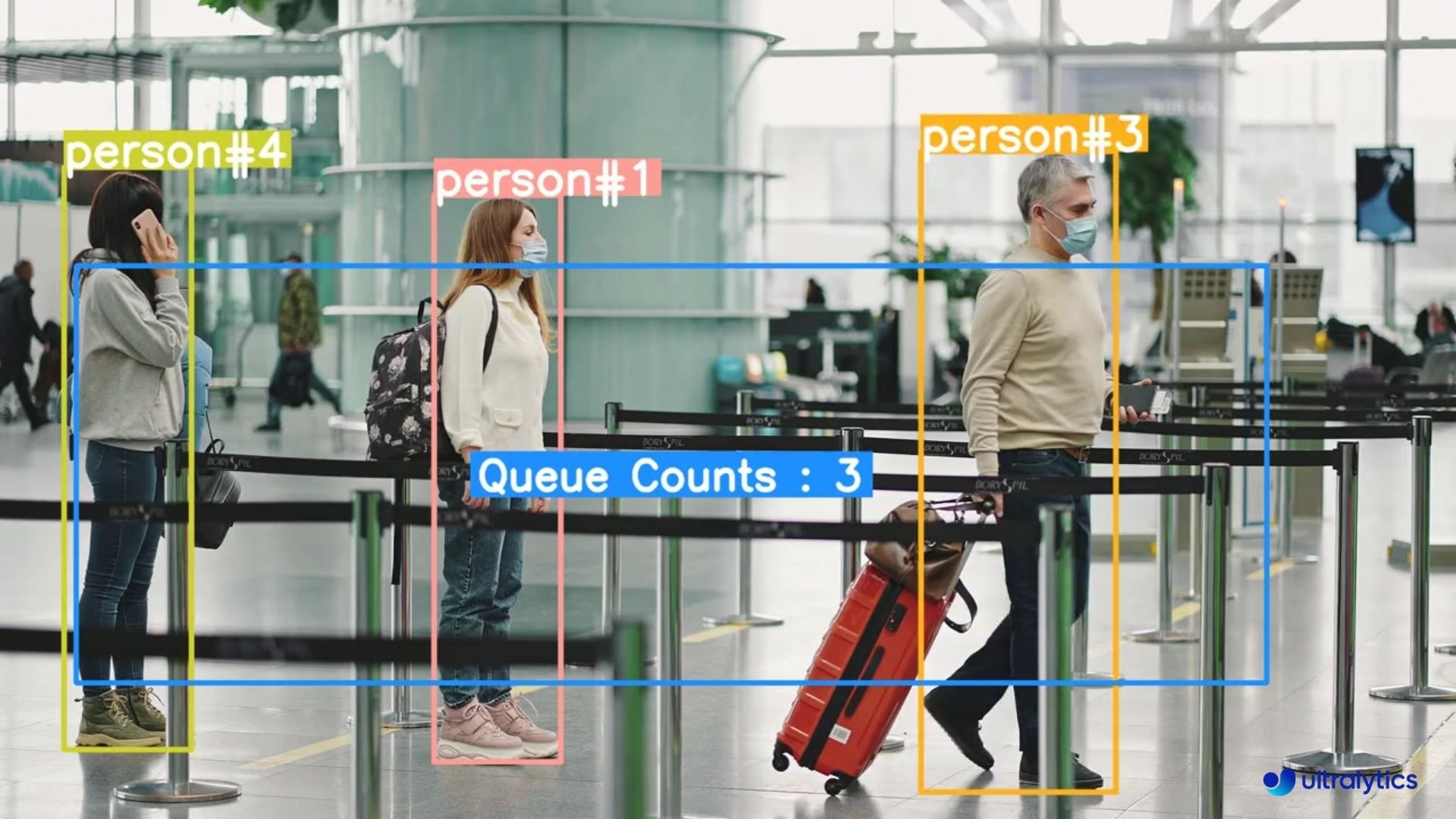 | 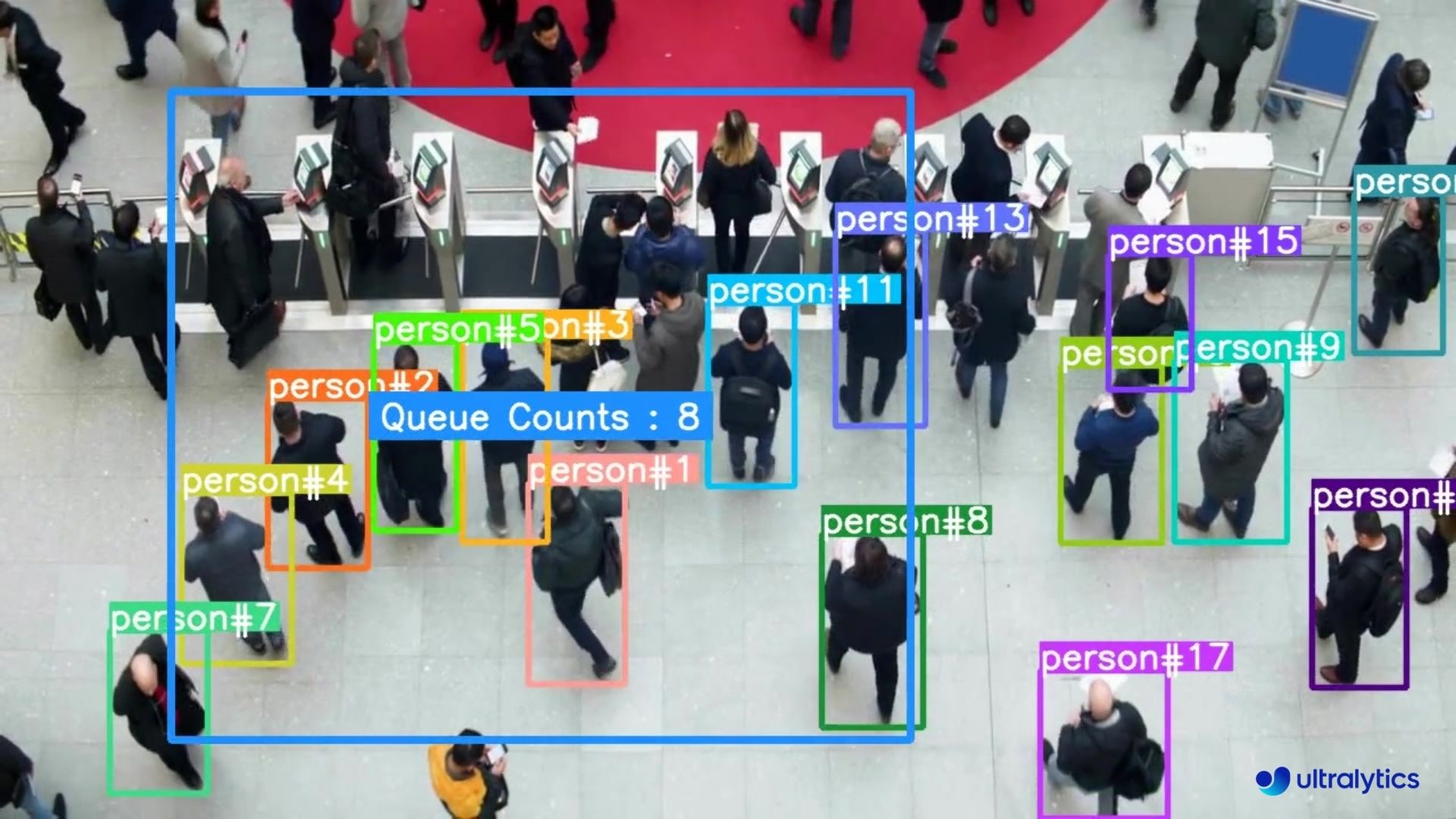 | | Queue management at airport ticket counter Using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Queue monitoring in crowd Ultralytics YOLOv8 | @@ -115,7 +115,7 @@ Queue management using [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultra ### Arguments `QueueManager` | Name | Type | Default | Description | -|---------------------|------------------|----------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| ------------------- | ---------------- | -------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | `classes_names` | `dict` | `model.names` | A dictionary mapping class IDs to class names. | | `reg_pts` | `list of tuples` | `[(20, 400), (1260, 400)]` | Points defining the counting region polygon. Defaults to a predefined rectangle. | | `line_thickness` | `int` | `2` | Thickness of the annotation lines. | @@ -132,7 +132,7 @@ Queue management using [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultra ### Arguments `model.track` | Name | Type | Default | Description | -|-----------|---------|----------------|-------------------------------------------------------------| +| --------- | ------- | -------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------- | | `source` | `im0` | `None` | source directory for images or videos | | `persist` | `bool` | `False` | persisting tracks between frames | | `tracker` | `str` | `botsort.yaml` | Tracking method 'bytetrack' or 'botsort' | diff --git a/docs/en/guides/raspberry-pi.md b/docs/en/guides/raspberry-pi.md index d0544b65..9514ea81 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/raspberry-pi.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/raspberry-pi.md @@ -29,15 +29,15 @@ Raspberry Pi is a small, affordable, single-board computer. It has become popula ## Raspberry Pi Series Comparison -| | Raspberry Pi 3 | Raspberry Pi 4 | Raspberry Pi 5 | -|-------------------|----------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------| -| CPU | Broadcom BCM2837, Cortex-A53 64Bit SoC | Broadcom BCM2711, Cortex-A72 64Bit SoC | Broadcom BCM2712, Cortex-A76 64Bit SoC | -| CPU Max Frequency | 1.4GHz | 1.8GHz | 2.4GHz | -| GPU | Videocore IV | Videocore VI | VideoCore VII | -| GPU Max Frequency | 400Mhz | 500Mhz | 800Mhz | -| Memory | 1GB LPDDR2 SDRAM | 1GB, 2GB, 4GB, 8GB LPDDR4-3200 SDRAM | 4GB, 8GB LPDDR4X-4267 SDRAM | -| PCIe | N/A | N/A | 1xPCIe 2.0 Interface | -| Max Power Draw | 2.5A@5V | 3A@5V | 5A@5V (PD enabled) | +| | Raspberry Pi 3 | Raspberry Pi 4 | Raspberry Pi 5 | +| ----------------- | -------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------- | +| CPU | Broadcom BCM2837, Cortex-A53 64Bit SoC | Broadcom BCM2711, Cortex-A72 64Bit SoC | Broadcom BCM2712, Cortex-A76 64Bit SoC | +| CPU Max Frequency | 1.4GHz | 1.8GHz | 2.4GHz | +| GPU | Videocore IV | Videocore VI | VideoCore VII | +| GPU Max Frequency | 400Mhz | 500Mhz | 800Mhz | +| Memory | 1GB LPDDR2 SDRAM | 1GB, 2GB, 4GB, 8GB LPDDR4-3200 SDRAM | 4GB, 8GB LPDDR4X-4267 SDRAM | +| PCIe | N/A | N/A | 1xPCIe 2.0 Interface | +| Max Power Draw | 2.5A@5V | 3A@5V | 5A@5V (PD enabled) | ## What is Raspberry Pi OS? @@ -190,7 +190,7 @@ The below table represents the benchmark results for two different models (YOLOv | TF Lite | ✅ | 42.8 | 0.7136 | 1013.27 | | PaddlePaddle | ✅ | 85.5 | 0.7136 | 1560.23 | | NCNN | ✅ | 42.7 | 0.7204 | 211.26 | - + === "YOLOv8n on RPi4" | Format | Status | Size on disk (MB) | mAP50-95(B) | Inference time (ms/im) | @@ -267,7 +267,7 @@ rpicam-hello !!! Tip - Learn more about [`rpicam-hello` usage on official Raspberry Pi documentation](https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/computers/camera_software.html#rpicam-hello) + Learn more about [`rpicam-hello` usage on official Raspberry Pi documentation](https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/computers/camera_software.html#rpicam-hello) ### Inference with Camera @@ -329,7 +329,7 @@ There are 2 methods of using the Raspberry Pi Camera to inference YOLOv8 models. rpicam-vid -n -t 0 --inline --listen -o tcp://127.0.0.1:8888 ``` - Learn more about [`rpicam-vid` usage on official Raspberry Pi documentation](https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/computers/camera_software.html#rpicam-vid) + Learn more about [`rpicam-vid` usage on official Raspberry Pi documentation](https://www.raspberrypi.com/documentation/computers/camera_software.html#rpicam-vid) !!! Example diff --git a/docs/en/guides/region-counting.md b/docs/en/guides/region-counting.md index 6c2d9ec3..b5b40580 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/region-counting.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/region-counting.md @@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ keywords: object counting, regions, YOLOv8, computer vision, Ultralytics, effici ## Real World Applications | Retail | Market Streets | -|:------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|:-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:| +| :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | | 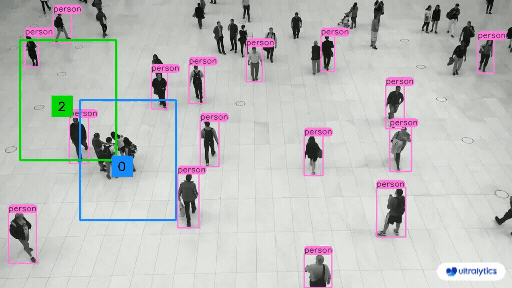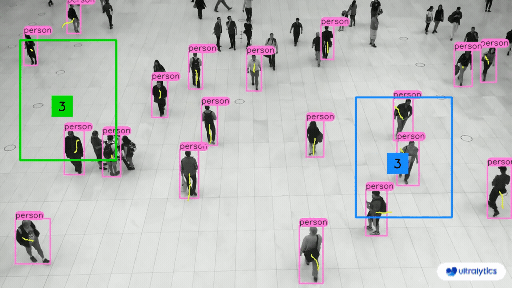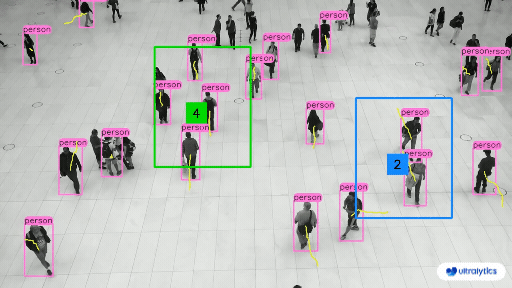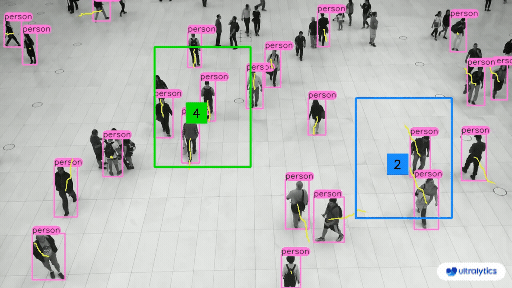 | 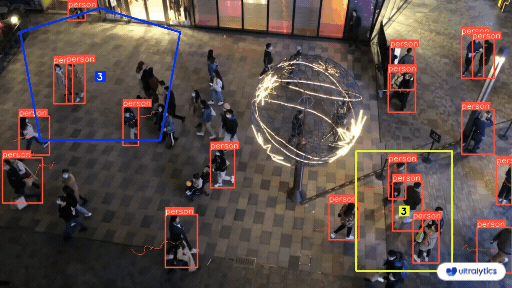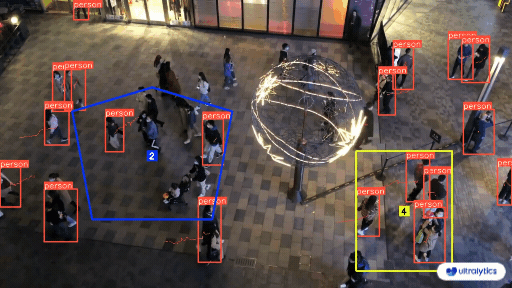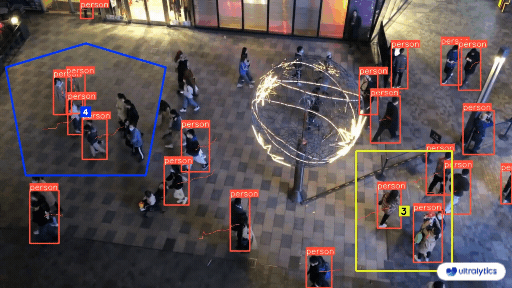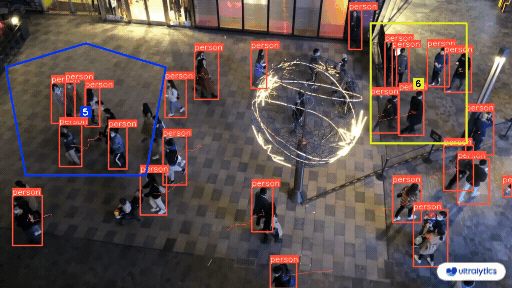 | | People Counting in Different Region using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Crowd Counting in Different Region using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | @@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ python yolov8_region_counter.py --source "path/to/video.mp4" --view-img ### Optional Arguments | Name | Type | Default | Description | -|----------------------|--------|--------------|--------------------------------------------| +| -------------------- | ------ | ------------ | ------------------------------------------ | | `--source` | `str` | `None` | Path to video file, for webcam 0 | | `--line_thickness` | `int` | `2` | Bounding Box thickness | | `--save-img` | `bool` | `False` | Save the predicted video/image | diff --git a/docs/en/guides/speed-estimation.md b/docs/en/guides/speed-estimation.md index 382e197d..7096ba65 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/speed-estimation.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/speed-estimation.md @@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics YOLOv8, speed estimation, object tracking, computer vision ## Real World Applications | Transportation | Transportation | -|:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:| +| :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | |  |  | | Speed Estimation on Road using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Speed Estimation on Bridge using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | @@ -89,7 +89,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics YOLOv8, speed estimation, object tracking, computer vision ### Arguments `SpeedEstimator` | Name | Type | Default | Description | -|--------------------|--------|----------------------------|------------------------------------------------------| +| ------------------ | ------ | -------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------- | | `names` | `dict` | `None` | Dictionary of class names. | | `reg_pts` | `list` | `[(20, 400), (1260, 400)]` | List of region points for speed estimation. | | `view_img` | `bool` | `False` | Whether to display the image with annotations. | @@ -100,7 +100,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics YOLOv8, speed estimation, object tracking, computer vision ### Arguments `model.track` | Name | Type | Default | Description | -|-----------|---------|----------------|-------------------------------------------------------------| +| --------- | ------- | -------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------- | | `source` | `im0` | `None` | source directory for images or videos | | `persist` | `bool` | `False` | persisting tracks between frames | | `tracker` | `str` | `botsort.yaml` | Tracking method 'bytetrack' or 'botsort' | diff --git a/docs/en/guides/steps-of-a-cv-project.md b/docs/en/guides/steps-of-a-cv-project.md index 7a89e49b..8ed50f49 100644 --- a/docs/en/guides/steps-of-a-cv-project.md +++ b/docs/en/guides/steps-of-a-cv-project.md @@ -41,9 +41,11 @@ The first step in any computer vision project is clearly defining the problem yo Here are some examples of project objectives and the computer vision tasks that can be used to reach these objectives: - **Objective:** To develop a system that can monitor and manage the flow of different vehicle types on highways, improving traffic management and safety. + - **Computer Vision Task:** Object detection is ideal for traffic monitoring because it efficiently locates and identifies multiple vehicles. It is less computationally demanding than image segmentation, which provides unnecessary detail for this task, ensuring faster, real-time analysis. - **Objective:** To develop a tool that assists radiologists by providing precise, pixel-level outlines of tumors in medical imaging scans. + - **Computer Vision Task:** Image segmentation is suitable for medical imaging because it provides accurate and detailed boundaries of tumors that are crucial for assessing size, shape, and treatment planning. - **Objective:** To create a digital system that categorizes various documents (e.g., invoices, receipts, legal paperwork) to improve organizational efficiency and document retrieval. @@ -103,7 +105,7 @@ After splitting your data, you can perform data augmentation by applying transfo
 -
-
-
 -
-
 +
👋 Hello from the [Ultralytics](https://ultralytics.com/) Team! We've been working hard these last few months to launch [Ultralytics HUB](https://bit.ly/ultralytics_hub), a new web tool for training and deploying all your YOLOv5 and YOLOv8 🚀 models from one spot!
@@ -47,7 +48,6 @@ We hope that the resources here will help you get the most out of HUB. Please br
+
👋 Hello from the [Ultralytics](https://ultralytics.com/) Team! We've been working hard these last few months to launch [Ultralytics HUB](https://bit.ly/ultralytics_hub), a new web tool for training and deploying all your YOLOv5 and YOLOv8 🚀 models from one spot!
@@ -47,7 +48,6 @@ We hope that the resources here will help you get the most out of HUB. Please br
 -
## Introduction
[Ultralytics HUB](https://bit.ly/ultralytics_hub) is designed to be user-friendly and intuitive, allowing users to quickly upload their datasets and train new YOLO models. It also offers a range of pre-trained models to choose from, making it extremely easy for users to get started. Once a model is trained, it can be effortlessly previewed in the [Ultralytics HUB App](app/index.md) before being deployed for real-time classification, object detection, and instance segmentation tasks.
diff --git a/docs/en/hub/inference-api.md b/docs/en/hub/inference-api.md
index 7938bdb4..68f9ef9e 100644
--- a/docs/en/hub/inference-api.md
+++ b/docs/en/hub/inference-api.md
@@ -70,7 +70,7 @@ curl -X POST "https://api.ultralytics.com/v1/predict/MODEL_ID" \
See the table below for a full list of available inference arguments.
| Argument | Default | Type | Description |
-|--------------|---------|---------|----------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| ------------ | ------- | ------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `image` | | `image` | Image file to be used for inference. |
| `url` | | `str` | URL of the image if not passing a file. |
| `size` | `640` | `int` | Size of the input image, valid range is `32` - `1280` pixels. |
diff --git a/docs/en/hub/integrations.md b/docs/en/hub/integrations.md
index 02bd6194..ee8472c2 100644
--- a/docs/en/hub/integrations.md
+++ b/docs/en/hub/integrations.md
@@ -103,20 +103,20 @@ After you [train a model](./models.md#train-model), you can [export it](./models
The available export formats are presented in the table below.
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
-|---------------------------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|----------|----------------------------------------------------------------------|
-| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - |
-| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` |
-| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` |
-| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` |
-| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` |
+| ------------------------------------------------- | ----------------- | ------------------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - |
+| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` |
+| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` |
+| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` |
+| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` |
## Exciting New Features on the Way 🎉
diff --git a/docs/en/index.md b/docs/en/index.md
index c65c1349..b90a85b5 100644
--- a/docs/en/index.md
+++ b/docs/en/index.md
@@ -52,7 +52,6 @@ Explore the YOLOv8 Docs, a comprehensive resource designed to help you understan
-
## Introduction
[Ultralytics HUB](https://bit.ly/ultralytics_hub) is designed to be user-friendly and intuitive, allowing users to quickly upload their datasets and train new YOLO models. It also offers a range of pre-trained models to choose from, making it extremely easy for users to get started. Once a model is trained, it can be effortlessly previewed in the [Ultralytics HUB App](app/index.md) before being deployed for real-time classification, object detection, and instance segmentation tasks.
diff --git a/docs/en/hub/inference-api.md b/docs/en/hub/inference-api.md
index 7938bdb4..68f9ef9e 100644
--- a/docs/en/hub/inference-api.md
+++ b/docs/en/hub/inference-api.md
@@ -70,7 +70,7 @@ curl -X POST "https://api.ultralytics.com/v1/predict/MODEL_ID" \
See the table below for a full list of available inference arguments.
| Argument | Default | Type | Description |
-|--------------|---------|---------|----------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| ------------ | ------- | ------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `image` | | `image` | Image file to be used for inference. |
| `url` | | `str` | URL of the image if not passing a file. |
| `size` | `640` | `int` | Size of the input image, valid range is `32` - `1280` pixels. |
diff --git a/docs/en/hub/integrations.md b/docs/en/hub/integrations.md
index 02bd6194..ee8472c2 100644
--- a/docs/en/hub/integrations.md
+++ b/docs/en/hub/integrations.md
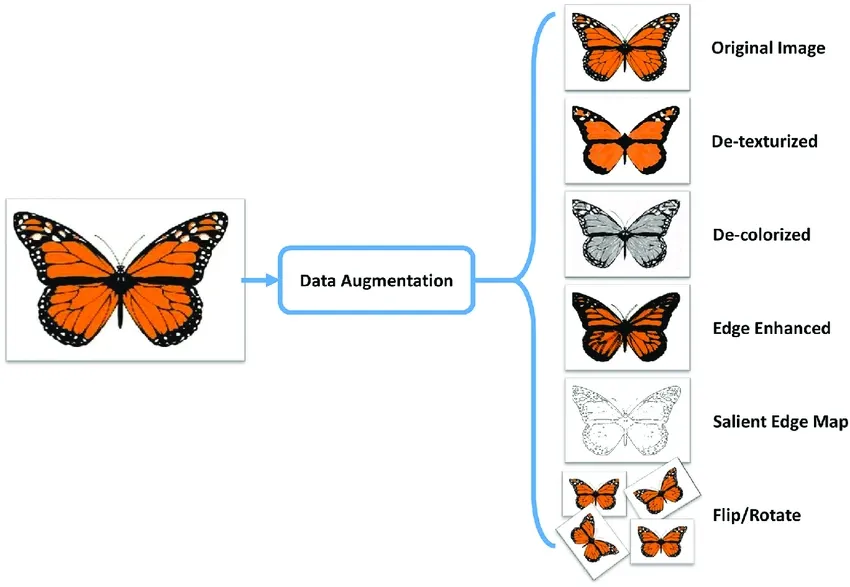
@@ -103,20 +103,20 @@ After you [train a model](./models.md#train-model), you can [export it](./models
The available export formats are presented in the table below.
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
-|---------------------------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|----------|----------------------------------------------------------------------|
-| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - |
-| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` |
-| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` |
-| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` |
-| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` |
+| ------------------------------------------------- | ----------------- | ------------------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - |
+| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` |
+| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` |
+| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` |
+| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` |
## Exciting New Features on the Way 🎉
diff --git a/docs/en/index.md b/docs/en/index.md
index c65c1349..b90a85b5 100644
--- a/docs/en/index.md
+++ b/docs/en/index.md
@@ -52,7 +52,6 @@ Explore the YOLOv8 Docs, a comprehensive resource designed to help you understan
 -
## Where to Start
- **Install** `ultralytics` with pip and get up and running in minutes [:material-clock-fast: Get Started](quickstart.md){ .md-button }
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/coreml.md b/docs/en/integrations/coreml.md
index e20e6a71..b17624f3 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/coreml.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/coreml.md
@@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ To install the required package, run:
!!! Tip "Installation"
=== "CLI"
-
+
```bash
# Install the required package for YOLOv8
pip install ultralytics
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/edge-tpu.md b/docs/en/integrations/edge-tpu.md
index b497cfbf..3797c0da 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/edge-tpu.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/edge-tpu.md
@@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ To install the required package, run:
!!! Tip "Installation"
=== "CLI"
-
+
```bash
# Install the required package for YOLOv8
pip install ultralytics
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/gradio.md b/docs/en/integrations/gradio.md
index 0f2bd0e1..94126656 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/gradio.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/gradio.md
@@ -23,9 +23,9 @@ This Gradio interface provides an easy and interactive way to perform object det
## Why Use Gradio for Object Detection?
-* **User-Friendly Interface:** Gradio offers a straightforward platform for users to upload images and visualize detection results without any coding requirement.
-* **Real-Time Adjustments:** Parameters such as confidence and IoU thresholds can be adjusted on the fly, allowing for immediate feedback and optimization of detection results.
-* **Broad Accessibility:** The Gradio web interface can be accessed by anyone, making it an excellent tool for demonstrations, educational purposes, and quick experiments.
+- **User-Friendly Interface:** Gradio offers a straightforward platform for users to upload images and visualize detection results without any coding requirement.
+- **Real-Time Adjustments:** Parameters such as confidence and IoU thresholds can be adjusted on the fly, allowing for immediate feedback and optimization of detection results.
+- **Broad Accessibility:** The Gradio web interface can be accessed by anyone, making it an excellent tool for demonstrations, educational purposes, and quick experiments.
-
## Where to Start
- **Install** `ultralytics` with pip and get up and running in minutes [:material-clock-fast: Get Started](quickstart.md){ .md-button }
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/coreml.md b/docs/en/integrations/coreml.md
index e20e6a71..b17624f3 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/coreml.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/coreml.md
@@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ To install the required package, run:
!!! Tip "Installation"
=== "CLI"
-
+
```bash
# Install the required package for YOLOv8
pip install ultralytics
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/edge-tpu.md b/docs/en/integrations/edge-tpu.md
index b497cfbf..3797c0da 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/edge-tpu.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/edge-tpu.md
@@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ To install the required package, run:
!!! Tip "Installation"
=== "CLI"
-
+
```bash
# Install the required package for YOLOv8
pip install ultralytics
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/gradio.md b/docs/en/integrations/gradio.md
index 0f2bd0e1..94126656 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/gradio.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/gradio.md
@@ -23,9 +23,9 @@ This Gradio interface provides an easy and interactive way to perform object det
## Why Use Gradio for Object Detection?
-* **User-Friendly Interface:** Gradio offers a straightforward platform for users to upload images and visualize detection results without any coding requirement.
-* **Real-Time Adjustments:** Parameters such as confidence and IoU thresholds can be adjusted on the fly, allowing for immediate feedback and optimization of detection results.
-* **Broad Accessibility:** The Gradio web interface can be accessed by anyone, making it an excellent tool for demonstrations, educational purposes, and quick experiments.
+- **User-Friendly Interface:** Gradio offers a straightforward platform for users to upload images and visualize detection results without any coding requirement.
+- **Real-Time Adjustments:** Parameters such as confidence and IoU thresholds can be adjusted on the fly, allowing for immediate feedback and optimization of detection results.
+- **Broad Accessibility:** The Gradio web interface can be accessed by anyone, making it an excellent tool for demonstrations, educational purposes, and quick experiments.
@@ -41,14 +41,14 @@ pip install gradio
1. **Upload Image:** Click on 'Upload Image' to choose an image file for object detection.
2. **Adjust Parameters:**
- * **Confidence Threshold:** Slider to set the minimum confidence level for detecting objects.
- * **IoU Threshold:** Slider to set the IoU threshold for distinguishing different objects.
+ - **Confidence Threshold:** Slider to set the minimum confidence level for detecting objects.
+ - **IoU Threshold:** Slider to set the IoU threshold for distinguishing different objects.
3. **View Results:** The processed image with detected objects and their labels will be displayed.
## Example Use Cases
-* **Sample Image 1:** Bus detection with default thresholds.
-* **Sample Image 2:** Detection on a sports image with default thresholds.
+- **Sample Image 1:** Bus detection with default thresholds.
+- **Sample Image 2:** Detection on a sports image with default thresholds.
## Usage Example
@@ -104,7 +104,7 @@ if __name__ == "__main__":
## Parameters Explanation
| Parameter Name | Type | Description |
-|------------------|---------|----------------------------------------------------------|
+| ---------------- | ------- | -------------------------------------------------------- |
| `img` | `Image` | The image on which object detection will be performed. |
| `conf_threshold` | `float` | Confidence threshold for detecting objects. |
| `iou_threshold` | `float` | Intersection-over-union threshold for object separation. |
@@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ if __name__ == "__main__":
### Gradio Interface Components
| Component | Description |
-|--------------|------------------------------------------|
+| ------------ | ---------------------------------------- |
| Image Input | To upload the image for detection. |
| Sliders | To adjust confidence and IoU thresholds. |
| Image Output | To display the detection results. |
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/index.md b/docs/en/integrations/index.md
index 1ed45844..29f17a60 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/index.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/index.md
@@ -86,20 +86,20 @@ Welcome to the Ultralytics Integrations page! This page provides an overview of
We also support a variety of model export formats for deployment in different environments. Here are the available formats:
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
-|---------------------------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|----------|----------------------------------------------------------------------|
-| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - |
-| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` |
-| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` |
-| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` |
-| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
-| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` |
+| ------------------------------------------------- | ----------------- | ------------------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - |
+| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` |
+| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` |
+| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` |
+| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` |
Explore the links to learn more about each integration and how to get the most out of them with Ultralytics. See full `export` details in the [Export](../modes/export.md) page.
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/mlflow.md b/docs/en/integrations/mlflow.md
index 7cae9d30..b0a461ae 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/mlflow.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/mlflow.md
@@ -68,7 +68,7 @@ Make sure that MLflow logging is enabled in Ultralytics settings. Usually, this
export MLFLOW_EXPERIMENT_NAME=

@@ -74,9 +75,9 @@ This example provides simple RT-DETR training and inference examples. For full d This table presents the model types, the specific pre-trained weights, the tasks supported by each model, and the various modes ([Train](../modes/train.md) , [Val](../modes/val.md), [Predict](../modes/predict.md), [Export](../modes/export.md)) that are supported, indicated by ✅ emojis. | Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export | -|---------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------|-----------|------------|----------|--------| -| RT-DETR Large | [rtdetr-l.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/rtdetr-l.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | -| RT-DETR Extra-Large | [rtdetr-x.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/rtdetr-x.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| ------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------- | --------- | ---------- | -------- | ------ | +| RT-DETR Large | [rtdetr-l.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/rtdetr-l.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| RT-DETR Extra-Large | [rtdetr-x.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/rtdetr-x.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ## Citations and Acknowledgements diff --git a/docs/en/models/sam.md b/docs/en/models/sam.md index b4e0d1fd..5dc97a85 100644 --- a/docs/en/models/sam.md +++ b/docs/en/models/sam.md @@ -30,9 +30,9 @@ For an in-depth look at the Segment Anything Model and the SA-1B dataset, please This table presents the available models with their specific pre-trained weights, the tasks they support, and their compatibility with different operating modes like [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md), indicated by ✅ emojis for supported modes and ❌ emojis for unsupported modes. | Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export | -|------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------|-----------|------------|----------|--------| -| SAM base | [sam_b.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/sam_b.pt) | [Instance Segmentation](../tasks/segment.md) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | -| SAM large | [sam_l.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/sam_l.pt) | [Instance Segmentation](../tasks/segment.md) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | +| ---------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------- | --------- | ---------- | -------- | ------ | +| SAM base | [sam_b.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/sam_b.pt) | [Instance Segmentation](../tasks/segment.md) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | +| SAM large | [sam_l.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/sam_l.pt) | [Instance Segmentation](../tasks/segment.md) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ## How to Use SAM: Versatility and Power in Image Segmentation @@ -135,7 +135,7 @@ The Segment Anything Model can be employed for a multitude of downstream tasks t Here we compare Meta's smallest SAM model, SAM-b, with Ultralytics smallest segmentation model, [YOLOv8n-seg](../tasks/segment.md): | Model | Size | Parameters | Speed (CPU) | -|------------------------------------------------|----------------------------|------------------------|----------------------------| +| ---------------------------------------------- | -------------------------- | ---------------------- | -------------------------- | | Meta's SAM-b | 358 MB | 94.7 M | 51096 ms/im | | [MobileSAM](mobile-sam.md) | 40.7 MB | 10.1 M | 46122 ms/im | | [FastSAM-s](fast-sam.md) with YOLOv8 backbone | 23.7 MB | 11.8 M | 115 ms/im | @@ -192,7 +192,7 @@ To auto-annotate your dataset with the Ultralytics framework, use the `auto_anno ``` | Argument | Type | Description | Default | -|------------|---------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|--------------| +| ---------- | ------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------ | | data | str | Path to a folder containing images to be annotated. | | | det_model | str, optional | Pre-trained YOLO detection model. Defaults to 'yolov8x.pt'. | 'yolov8x.pt' | | sam_model | str, optional | Pre-trained SAM segmentation model. Defaults to 'sam_b.pt'. | 'sam_b.pt' | diff --git a/docs/en/models/yolo-nas.md b/docs/en/models/yolo-nas.md index 7df22b0f..fbcd7e44 100644 --- a/docs/en/models/yolo-nas.md +++ b/docs/en/models/yolo-nas.md @@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ Developed by Deci AI, YOLO-NAS is a groundbreaking object detection foundational Experience the power of next-generation object detection with the pre-trained YOLO-NAS models provided by Ultralytics. These models are designed to deliver top-notch performance in terms of both speed and accuracy. Choose from a variety of options tailored to your specific needs: | Model | mAP | Latency (ms) | -|------------------|-------|--------------| +| ---------------- | ----- | ------------ | | YOLO-NAS S | 47.5 | 3.21 | | YOLO-NAS M | 51.55 | 5.85 | | YOLO-NAS L | 52.22 | 7.87 | @@ -90,10 +90,10 @@ We offer three variants of the YOLO-NAS models: Small (s), Medium (m), and Large Below is a detailed overview of each model, including links to their pre-trained weights, the tasks they support, and their compatibility with different operating modes. | Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export | -|------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------|-----------|------------|----------|--------| -| YOLO-NAS-s | [yolo_nas_s.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolo_nas_s.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | -| YOLO-NAS-m | [yolo_nas_m.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolo_nas_m.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | -| YOLO-NAS-l | [yolo_nas_l.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolo_nas_l.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | +| ---------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------- | --------- | ---------- | -------- | ------ | +| YOLO-NAS-s | [yolo_nas_s.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolo_nas_s.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | +| YOLO-NAS-m | [yolo_nas_m.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolo_nas_m.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | +| YOLO-NAS-l | [yolo_nas_l.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolo_nas_l.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ## Citations and Acknowledgements diff --git a/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md b/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md index d2cc3b20..2d94ee1a 100644 --- a/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md +++ b/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md @@ -48,20 +48,20 @@ This section details the models available with their specific pre-trained weight All the YOLOv8-World weights have been directly migrated from the official [YOLO-World](https://github.com/AILab-CVC/YOLO-World) repository, highlighting their excellent contributions. | Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export | -|-----------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------|-----------|------------|----------|--------| -| YOLOv8s-world | [yolov8s-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8s-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | -| YOLOv8s-worldv2 | [yolov8s-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8s-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | -| YOLOv8m-world | [yolov8m-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8m-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | -| YOLOv8m-worldv2 | [yolov8m-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8m-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | -| YOLOv8l-world | [yolov8l-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8l-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | -| YOLOv8l-worldv2 | [yolov8l-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8l-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | -| YOLOv8x-world | [yolov8x-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8x-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | -| YOLOv8x-worldv2 | [yolov8x-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8x-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| --------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------- | --------- | ---------- | -------- | ------ | +| YOLOv8s-world | [yolov8s-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8s-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | +| YOLOv8s-worldv2 | [yolov8s-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8s-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| YOLOv8m-world | [yolov8m-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8m-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | +| YOLOv8m-worldv2 | [yolov8m-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8m-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| YOLOv8l-world | [yolov8l-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8l-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | +| YOLOv8l-worldv2 | [yolov8l-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8l-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| YOLOv8x-world | [yolov8x-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8x-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | +| YOLOv8x-worldv2 | [yolov8x-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8x-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ## Zero-shot Transfer on COCO Dataset | Model Type | mAP | mAP50 | mAP75 | -|-----------------|------|-------|-------| +| --------------- | ---- | ----- | ----- | | yolov8s-world | 37.4 | 52.0 | 40.6 | | yolov8s-worldv2 | 37.7 | 52.2 | 41.0 | | yolov8m-world | 42.0 | 57.0 | 45.6 | @@ -272,7 +272,7 @@ This approach provides a powerful means of customizing state-of-the-art object d - Train data | Dataset | Type | Samples | Boxes | Annotation Files | -|-------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------|---------|-------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| ----------------------------------------------------------------- | --------- | ------- | ----- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | | [Objects365v1](https://opendatalab.com/OpenDataLab/Objects365_v1) | Detection | 609k | 9621k | [objects365_train.json](https://opendatalab.com/OpenDataLab/Objects365_v1) | | [GQA](https://nlp.stanford.edu/data/gqa/images.zip) | Grounding | 621k | 3681k | [final_mixed_train_no_coco.json](https://huggingface.co/GLIPModel/GLIP/blob/main/mdetr_annotations/final_mixed_train_no_coco.json) | | [Flickr30k](https://shannon.cs.illinois.edu/DenotationGraph/) | Grounding | 149k | 641k | [final_flickr_separateGT_train.json](https://huggingface.co/GLIPModel/GLIP/blob/main/mdetr_annotations/final_flickr_separateGT_train.json) | @@ -280,7 +280,7 @@ This approach provides a powerful means of customizing state-of-the-art object d - Val data | Dataset | Type | Annotation Files | -|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | | [LVIS minival](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/cfg/datasets/lvis.yaml) | Detection | [minival.txt](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/cfg/datasets/lvis.yaml) | ### Launch training from scratch diff --git a/docs/en/models/yolov10.md b/docs/en/models/yolov10.md index b111cf8a..056cab46 100644 --- a/docs/en/models/yolov10.md +++ b/docs/en/models/yolov10.md @@ -45,11 +45,11 @@ YOLOv10 comes in various model scales to cater to different application needs: YOLOv10 outperforms previous YOLO versions and other state-of-the-art models in terms of accuracy and efficiency. For example, YOLOv10-S is 1.8x faster than RT-DETR-R18 with similar AP on the COCO dataset, and YOLOv10-B has 46% less latency and 25% fewer parameters than YOLOv9-C with the same performance. | Model | Input Size | APval | FLOPs (G) | Latency (ms) | -|-----------|------------|------------------|-----------|--------------| -| YOLOv10-N | 640 | 38.5 | **6.7** | **1.84** | +| --------- | ---------- | ---------------- | --------- | ------------ | +| YOLOv10-N | 640 | 38.5 | **6.7** | **1.84** | | YOLOv10-S | 640 | 46.3 | 21.6 | 2.49 | | YOLOv10-M | 640 | 51.1 | 59.1 | 4.74 | -| YOLOv10-B | 640 | 52.5 | 92.0 | 5.74 | +| YOLOv10-B | 640 | 52.5 | 92.0 | 5.74 | | YOLOv10-L | 640 | 53.2 | 120.3 | 7.28 | | YOLOv10-X | 640 | **54.4** | 160.4 | 10.70 | @@ -91,7 +91,7 @@ Compared to other state-of-the-art detectors: Here is a detailed comparison of YOLOv10 variants with other state-of-the-art models: | Model | Params (M) | FLOPs (G) | APval (%) | Latency (ms) | Latency (Forward) (ms) | -|---------------|------------|-----------|-----------|--------------|------------------------| +| ------------- | ---------- | --------- | --------- | ------------ | ---------------------- | | YOLOv6-3.0-N | 4.7 | 11.4 | 37.0 | 2.69 | **1.76** | | Gold-YOLO-N | 5.6 | 12.1 | **39.6** | 2.92 | 1.82 | | YOLOv8-N | 3.2 | 8.7 | 37.3 | 6.16 | 1.77 | diff --git a/docs/en/models/yolov3.md b/docs/en/models/yolov3.md index ce1fd439..8ea1ee01 100644 --- a/docs/en/models/yolov3.md +++ b/docs/en/models/yolov3.md @@ -33,10 +33,10 @@ The YOLOv3 series, including YOLOv3, YOLOv3-Ultralytics, and YOLOv3u, are design All three models support a comprehensive set of modes, ensuring versatility in various stages of model deployment and development. These modes include [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md), providing users with a complete toolkit for effective object detection. | Model Type | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export | -|--------------------|----------------------------------------|-----------|------------|----------|--------| -| YOLOv3 | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | -| YOLOv3-Ultralytics | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | -| YOLOv3u | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| ------------------ | -------------------------------------- | --------- | ---------- | -------- | ------ | +| YOLOv3 | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| YOLOv3-Ultralytics | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| YOLOv3u | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | This table provides an at-a-glance view of the capabilities of each YOLOv3 variant, highlighting their versatility and suitability for various tasks and operational modes in object detection workflows. diff --git a/docs/en/models/yolov5.md b/docs/en/models/yolov5.md index 1fc76c49..e3128f70 100644 --- a/docs/en/models/yolov5.md +++ b/docs/en/models/yolov5.md @@ -25,8 +25,8 @@ YOLOv5u represents an advancement in object detection methodologies. Originating The YOLOv5u models, with various pre-trained weights, excel in [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) tasks. They support a comprehensive range of modes, making them suitable for diverse applications, from development to deployment. | Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Task | Inference | Validation | Training | Export | -|------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------|-----------|------------|----------|--------| -| YOLOv5u | `yolov5nu`, `yolov5su`, `yolov5mu`, `yolov5lu`, `yolov5xu`, `yolov5n6u`, `yolov5s6u`, `yolov5m6u`, `yolov5l6u`, `yolov5x6u` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| ---------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------- | --------- | ---------- | -------- | ------ | +| YOLOv5u | `yolov5nu`, `yolov5su`, `yolov5mu`, `yolov5lu`, `yolov5xu`, `yolov5n6u`, `yolov5s6u`, `yolov5m6u`, `yolov5l6u`, `yolov5x6u` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | This table provides a detailed overview of the YOLOv5u model variants, highlighting their applicability in object detection tasks and support for various operational modes such as [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md). This comprehensive support ensures that users can fully leverage the capabilities of YOLOv5u models in a wide range of object detection scenarios. diff --git a/docs/en/models/yolov6.md b/docs/en/models/yolov6.md index f40b106a..fa4b483d 100644 --- a/docs/en/models/yolov6.md +++ b/docs/en/models/yolov6.md @@ -75,12 +75,12 @@ This example provides simple YOLOv6 training and inference examples. For full do The YOLOv6 series offers a range of models, each optimized for high-performance [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md). These models cater to varying computational needs and accuracy requirements, making them versatile for a wide array of applications. | Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export | -|------------|---------------------|----------------------------------------|-----------|------------|----------|--------| -| YOLOv6-N | `yolov6-n.pt` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | -| YOLOv6-S | `yolov6-s.pt` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | -| YOLOv6-M | `yolov6-m.pt` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | -| YOLOv6-L | `yolov6-l.pt` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | -| YOLOv6-L6 | `yolov6-l6.pt` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| ---------- | ------------------- | -------------------------------------- | --------- | ---------- | -------- | ------ | +| YOLOv6-N | `yolov6-n.pt` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| YOLOv6-S | `yolov6-s.pt` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| YOLOv6-M | `yolov6-m.pt` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| YOLOv6-L | `yolov6-l.pt` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| YOLOv6-L6 | `yolov6-l6.pt` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | This table provides a detailed overview of the YOLOv6 model variants, highlighting their capabilities in object detection tasks and their compatibility with various operational modes such as [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md). This comprehensive support ensures that users can fully leverage the capabilities of YOLOv6 models in a broad range of object detection scenarios. diff --git a/docs/en/models/yolov8.md b/docs/en/models/yolov8.md index 8a24cdc6..d932a154 100644 --- a/docs/en/models/yolov8.md +++ b/docs/en/models/yolov8.md @@ -37,12 +37,12 @@ The YOLOv8 series offers a diverse range of models, each specialized for specifi Each variant of the YOLOv8 series is optimized for its respective task, ensuring high performance and accuracy. Additionally, these models are compatible with various operational modes including [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md), facilitating their use in different stages of deployment and development. | Model | Filenames | Task | Inference | Validation | Training | Export | -|-------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------|-----------|------------|----------|--------| -| YOLOv8 | `yolov8n.pt` `yolov8s.pt` `yolov8m.pt` `yolov8l.pt` `yolov8x.pt` | [Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | -| YOLOv8-seg | `yolov8n-seg.pt` `yolov8s-seg.pt` `yolov8m-seg.pt` `yolov8l-seg.pt` `yolov8x-seg.pt` | [Instance Segmentation](../tasks/segment.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | -| YOLOv8-pose | `yolov8n-pose.pt` `yolov8s-pose.pt` `yolov8m-pose.pt` `yolov8l-pose.pt` `yolov8x-pose.pt` `yolov8x-pose-p6.pt` | [Pose/Keypoints](../tasks/pose.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | -| YOLOv8-obb | `yolov8n-obb.pt` `yolov8s-obb.pt` `yolov8m-obb.pt` `yolov8l-obb.pt` `yolov8x-obb.pt` | [Oriented Detection](../tasks/obb.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | -| YOLOv8-cls | `yolov8n-cls.pt` `yolov8s-cls.pt` `yolov8m-cls.pt` `yolov8l-cls.pt` `yolov8x-cls.pt` | [Classification](../tasks/classify.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| ----------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------- | --------- | ---------- | -------- | ------ | +| YOLOv8 | `yolov8n.pt` `yolov8s.pt` `yolov8m.pt` `yolov8l.pt` `yolov8x.pt` | [Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| YOLOv8-seg | `yolov8n-seg.pt` `yolov8s-seg.pt` `yolov8m-seg.pt` `yolov8l-seg.pt` `yolov8x-seg.pt` | [Instance Segmentation](../tasks/segment.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| YOLOv8-pose | `yolov8n-pose.pt` `yolov8s-pose.pt` `yolov8m-pose.pt` `yolov8l-pose.pt` `yolov8x-pose.pt` `yolov8x-pose-p6.pt` | [Pose/Keypoints](../tasks/pose.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| YOLOv8-obb | `yolov8n-obb.pt` `yolov8s-obb.pt` `yolov8m-obb.pt` `yolov8l-obb.pt` `yolov8x-obb.pt` | [Oriented Detection](../tasks/obb.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| YOLOv8-cls | `yolov8n-cls.pt` `yolov8s-cls.pt` `yolov8m-cls.pt` `yolov8l-cls.pt` `yolov8x-cls.pt` | [Classification](../tasks/classify.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | This table provides an overview of the YOLOv8 model variants, highlighting their applicability in specific tasks and their compatibility with various operational modes such as Inference, Validation, Training, and Export. It showcases the versatility and robustness of the YOLOv8 series, making them suitable for a variety of applications in computer vision. diff --git a/docs/en/models/yolov9.md b/docs/en/models/yolov9.md index ebdad9f3..14c44929 100644 --- a/docs/en/models/yolov9.md +++ b/docs/en/models/yolov9.md @@ -153,9 +153,9 @@ This example provides simple YOLOv9 training and inference examples. For full do The YOLOv9 series offers a range of models, each optimized for high-performance [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md). These models cater to varying computational needs and accuracy requirements, making them versatile for a wide array of applications. | Model | Filenames | Tasks | Inference | Validation | Training | Export | -|------------|-----------------------------------|----------------------------------------------|-----------|------------|----------|--------| -| YOLOv9 | `yolov9c.pt` `yolov9e.pt` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | -| YOLOv9-seg | `yolov9c-seg.pt` `yolov9e-seg.pt` | [Instance Segmentation](../tasks/segment.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| ---------- | --------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------- | --------- | ---------- | -------- | ------ | +| YOLOv9 | `yolov9c.pt` `yolov9e.pt` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | +| YOLOv9-seg | `yolov9c-seg.pt` `yolov9e-seg.pt` | [Instance Segmentation](../tasks/segment.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | This table provides a detailed overview of the YOLOv9 model variants, highlighting their capabilities in object detection tasks and their compatibility with various operational modes such as [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md). This comprehensive support ensures that users can fully leverage the capabilities of YOLOv9 models in a broad range of object detection scenarios. diff --git a/docs/en/modes/benchmark.md b/docs/en/modes/benchmark.md index c9bfc697..ab952550 100644 --- a/docs/en/modes/benchmark.md +++ b/docs/en/modes/benchmark.md @@ -74,7 +74,7 @@ Run YOLOv8n benchmarks on all supported export formats including ONNX, TensorRT Arguments such as `model`, `data`, `imgsz`, `half`, `device`, and `verbose` provide users with the flexibility to fine-tune the benchmarks to their specific needs and compare the performance of different export formats with ease. | Key | Default Value | Description | -|-----------|---------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| --------- | ------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | `model` | `None` | Specifies the path to the model file. Accepts both `.pt` and `.yaml` formats, e.g., `"yolov8n.pt"` for pre-trained models or configuration files. | | `data` | `None` | Path to a YAML file defining the dataset for benchmarking, typically including paths and settings for validation data. Example: `"coco8.yaml"`. | | `imgsz` | `640` | The input image size for the model. Can be a single integer for square images or a tuple `(width, height)` for non-square, e.g., `(640, 480)`. | @@ -88,19 +88,19 @@ Arguments such as `model`, `data`, `imgsz`, `half`, `device`, and `verbose` prov Benchmarks will attempt to run automatically on all possible export formats below. | Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments | -|---------------------------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|----------|----------------------------------------------------------------------| -| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - | -| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` | -| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` | -| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` | -| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` | -| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` | -| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` | -| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` | -| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` | -| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` | -| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` | -| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` | -| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` | +| ------------------------------------------------- | ----------------- | ------------------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------- | +| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - | +| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` | +| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` | +| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` | +| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` | +| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` | +| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` | +| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` | +| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` | +| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` | +| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` | +| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` | +| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` | See full `export` details in the [Export](../modes/export.md) page. diff --git a/docs/en/modes/export.md b/docs/en/modes/export.md index bb081bda..d0744e0f 100644 --- a/docs/en/modes/export.md +++ b/docs/en/modes/export.md @@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ Export a YOLOv8n model to a different format like ONNX or TensorRT. See Argument This table details the configurations and options available for exporting YOLO models to different formats. These settings are critical for optimizing the exported model's performance, size, and compatibility across various platforms and environments. Proper configuration ensures that the model is ready for deployment in the intended application with optimal efficiency. | Argument | Type | Default | Description | -|-------------|------------------|-----------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| ----------- | ---------------- | --------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | `format` | `str` | `'torchscript'` | Target format for the exported model, such as `'onnx'`, `'torchscript'`, `'tensorflow'`, or others, defining compatibility with various deployment environments. | | `imgsz` | `int` or `tuple` | `640` | Desired image size for the model input. Can be an integer for square images or a tuple `(height, width)` for specific dimensions. | | `keras` | `bool` | `False` | Enables export to Keras format for TensorFlow SavedModel, providing compatibility with TensorFlow serving and APIs. | @@ -83,11 +83,11 @@ This table details the configurations and options available for exporting YOLO m | `half` | `bool` | `False` | Enables FP16 (half-precision) quantization, reducing model size and potentially speeding up inference on supported hardware. | | `int8` | `bool` | `False` | Activates INT8 quantization, further compressing the model and speeding up inference with minimal accuracy loss, primarily for edge devices. | | `dynamic` | `bool` | `False` | Allows dynamic input sizes for ONNX and TensorRT exports, enhancing flexibility in handling varying image dimensions. | -| `simplify` | `bool` | `False` | Simplifies the model graph for ONNX exports with `onnxslim`, potentially improving performance and compatibility. | +| `simplify` | `bool` | `False` | Simplifies the model graph for ONNX exports with `onnxslim`, potentially improving performance and compatibility. | | `opset` | `int` | `None` | Specifies the ONNX opset version for compatibility with different ONNX parsers and runtimes. If not set, uses the latest supported version. | | `workspace` | `float` | `4.0` | Sets the maximum workspace size in GiB for TensorRT optimizations, balancing memory usage and performance. | | `nms` | `bool` | `False` | Adds Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) to the CoreML export, essential for accurate and efficient detection post-processing. | -| `batch` | `int` | `1` | Specifies export model batch inference size or the max number of images the exported model will process concurrently in `predict` mode. | +| `batch` | `int` | `1` | Specifies export model batch inference size or the max number of images the exported model will process concurrently in `predict` mode. | Adjusting these parameters allows for customization of the export process to fit specific requirements, such as deployment environment, hardware constraints, and performance targets. Selecting the appropriate format and settings is essential for achieving the best balance between model size, speed, and accuracy. @@ -96,17 +96,17 @@ Adjusting these parameters allows for customization of the export process to fit Available YOLOv8 export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`. You can predict or validate directly on exported models, i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your model after export completes. | Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments | -|---------------------------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|----------|----------------------------------------------------------------------| -| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - | -| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` | -| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` | -| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` | -| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` | -| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` | -| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` | -| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` | -| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` | -| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` | -| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` | -| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` | -| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` | +| ------------------------------------------------- | ----------------- | ------------------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------- | +| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - | +| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` | +| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` | +| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` | +| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` | +| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` | +| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` | +| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` | +| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` | +| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` | +| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` | +| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` | +| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` | diff --git a/docs/en/modes/predict.md b/docs/en/modes/predict.md index e7ca24d2..1fb021dc 100644 --- a/docs/en/modes/predict.md +++ b/docs/en/modes/predict.md @@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ In the world of machine learning and computer vision, the process of making sens ## Real-world Applications | Manufacturing | Sports | Safety | -|:-------------------------------------------------:|:----------------------------------------------------:|:-------------------------------------------:| +| :-----------------------------------------------: | :--------------------------------------------------: | :-----------------------------------------: | | ![Vehicle Spare Parts Detection][car spare parts] | ![Football Player Detection][football player detect] | ![People Fall Detection][human fall detect] | | Vehicle Spare Parts Detection | Football Player Detection | People Fall Detection | @@ -104,16 +104,16 @@ YOLOv8 can process different types of input sources for inference, as shown in t Use `stream=True` for processing long videos or large datasets to efficiently manage memory. When `stream=False`, the results for all frames or data points are stored in memory, which can quickly add up and cause out-of-memory errors for large inputs. In contrast, `stream=True` utilizes a generator, which only keeps the results of the current frame or data point in memory, significantly reducing memory consumption and preventing out-of-memory issues. -| Source | Argument | Type | Notes | -|----------------|--------------------------------------------|-----------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| -| image | `'image.jpg'` | `str` or `Path` | Single image file. | -| URL | `'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'` | `str` | URL to an image. | -| screenshot | `'screen'` | `str` | Capture a screenshot. | -| PIL | `Image.open('im.jpg')` | `PIL.Image` | HWC format with RGB channels. | -| OpenCV | `cv2.imread('im.jpg')` | `np.ndarray` | HWC format with BGR channels `uint8 (0-255)`. | -| numpy | `np.zeros((640,1280,3))` | `np.ndarray` | HWC format with BGR channels `uint8 (0-255)`. | -| torch | `torch.zeros(16,3,320,640)` | `torch.Tensor` | BCHW format with RGB channels `float32 (0.0-1.0)`. | -| CSV | `'sources.csv'` | `str` or `Path` | CSV file containing paths to images, videos, or directories. | +| Source | Argument | Type | Notes | +| --------------- | ------------------------------------------ | --------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | +| image | `'image.jpg'` | `str` or `Path` | Single image file. | +| URL | `'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'` | `str` | URL to an image. | +| screenshot | `'screen'` | `str` | Capture a screenshot. | +| PIL | `Image.open('im.jpg')` | `PIL.Image` | HWC format with RGB channels. | +| OpenCV | `cv2.imread('im.jpg')` | `np.ndarray` | HWC format with BGR channels `uint8 (0-255)`. | +| numpy | `np.zeros((640,1280,3))` | `np.ndarray` | HWC format with BGR channels `uint8 (0-255)`. | +| torch | `torch.zeros(16,3,320,640)` | `torch.Tensor` | BCHW format with RGB channels `float32 (0.0-1.0)`. | +| CSV | `'sources.csv'` | `str` or `Path` | CSV file containing paths to images, videos, or directories. | | video ✅ | `'video.mp4'` | `str` or `Path` | Video file in formats like MP4, AVI, etc. | | directory ✅ | `'path/'` | `str` or `Path` | Path to a directory containing images or videos. | | glob ✅ | `'path/*.jpg'` | `str` | Glob pattern to match multiple files. Use the `*` character as a wildcard. | @@ -368,7 +368,7 @@ Below are code examples for using each source type: Inference arguments: | Argument | Type | Default | Description | -|-----------------|----------------|------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| --------------- | -------------- | ---------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | | `source` | `str` | `'ultralytics/assets'` | Specifies the data source for inference. Can be an image path, video file, directory, URL, or device ID for live feeds. Supports a wide range of formats and sources, enabling flexible application across different types of input. | | `conf` | `float` | `0.25` | Sets the minimum confidence threshold for detections. Objects detected with confidence below this threshold will be disregarded. Adjusting this value can help reduce false positives. | | `iou` | `float` | `0.7` | Intersection Over Union (IoU) threshold for Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS). Lower values result in fewer detections by eliminating overlapping boxes, useful for reducing duplicates. | @@ -388,7 +388,7 @@ Inference arguments: Visualization arguments: | Argument | Type | Default | Description | -|---------------|---------------|---------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| ------------- | ------------- | ------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | `show` | `bool` | `False` | If `True`, displays the annotated images or videos in a window. Useful for immediate visual feedback during development or testing. | | `save` | `bool` | `False` | Enables saving of the annotated images or videos to file. Useful for documentation, further analysis, or sharing results. | | `save_frames` | `bool` | `False` | When processing videos, saves individual frames as images. Useful for extracting specific frames or for detailed frame-by-frame analysis. | @@ -409,7 +409,7 @@ YOLOv8 supports various image and video formats, as specified in [ultralytics/da The below table contains valid Ultralytics image formats. | Image Suffixes | Example Predict Command | Reference | -|----------------|----------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| -------------- | -------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | `.bmp` | `yolo predict source=image.bmp` | [Microsoft BMP File Format](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BMP_file_format) | | `.dng` | `yolo predict source=image.dng` | [Adobe DNG](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_Negative) | | `.jpeg` | `yolo predict source=image.jpeg` | [JPEG](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/JPEG) | @@ -426,7 +426,7 @@ The below table contains valid Ultralytics image formats. The below table contains valid Ultralytics video formats. | Video Suffixes | Example Predict Command | Reference | -|----------------|----------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| -------------- | -------------------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | `.asf` | `yolo predict source=video.asf` | [Advanced Systems Format](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Advanced_Systems_Format) | | `.avi` | `yolo predict source=video.avi` | [Audio Video Interleave](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Audio_Video_Interleave) | | `.gif` | `yolo predict source=video.gif` | [Graphics Interchange Format](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GIF) | @@ -460,7 +460,7 @@ All Ultralytics `predict()` calls will return a list of `Results` objects: `Results` objects have the following attributes: | Attribute | Type | Description | -|--------------|-----------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| ------------ | --------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | `orig_img` | `numpy.ndarray` | The original image as a numpy array. | | `orig_shape` | `tuple` | The original image shape in (height, width) format. | | `boxes` | `Boxes, optional` | A Boxes object containing the detection bounding boxes. | @@ -475,7 +475,7 @@ All Ultralytics `predict()` calls will return a list of `Results` objects: `Results` objects have the following methods: | Method | Return Type | Description | -|---------------|-----------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| ------------- | --------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | `update()` | `None` | Update the boxes, masks, and probs attributes of the Results object. | | `cpu()` | `Results` | Return a copy of the Results object with all tensors on CPU memory. | | `numpy()` | `Results` | Return a copy of the Results object with all tensors as numpy arrays. | @@ -515,7 +515,7 @@ For more details see the [`Results` class documentation](../reference/engine/res Here is a table for the `Boxes` class methods and properties, including their name, type, and description: | Name | Type | Description | -|-----------|---------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------| +| --------- | ------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------ | | `cpu()` | Method | Move the object to CPU memory. | | `numpy()` | Method | Convert the object to a numpy array. | | `cuda()` | Method | Move the object to CUDA memory. | @@ -553,7 +553,7 @@ For more details see the [`Boxes` class documentation](../reference/engine/resul Here is a table for the `Masks` class methods and properties, including their name, type, and description: | Name | Type | Description | -|-----------|---------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------| +| --------- | ------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------- | | `cpu()` | Method | Returns the masks tensor on CPU memory. | | `numpy()` | Method | Returns the masks tensor as a numpy array. | | `cuda()` | Method | Returns the masks tensor on GPU memory. | @@ -586,7 +586,7 @@ For more details see the [`Masks` class documentation](../reference/engine/resul Here is a table for the `Keypoints` class methods and properties, including their name, type, and description: | Name | Type | Description | -|-----------|---------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------| +| --------- | ------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------- | | `cpu()` | Method | Returns the keypoints tensor on CPU memory. | | `numpy()` | Method | Returns the keypoints tensor as a numpy array. | | `cuda()` | Method | Returns the keypoints tensor on GPU memory. | @@ -620,7 +620,7 @@ For more details see the [`Keypoints` class documentation](../reference/engine/r Here's a table summarizing the methods and properties for the `Probs` class: | Name | Type | Description | -|------------|---------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| ---------- | ------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------- | | `cpu()` | Method | Returns a copy of the probs tensor on CPU memory. | | `numpy()` | Method | Returns a copy of the probs tensor as a numpy array. | | `cuda()` | Method | Returns a copy of the probs tensor on GPU memory. | @@ -655,7 +655,7 @@ For more details see the [`Probs` class documentation](../reference/engine/resul Here is a table for the `OBB` class methods and properties, including their name, type, and description: | Name | Type | Description | -|-------------|---------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------| +| ----------- | ------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------- | | `cpu()` | Method | Move the object to CPU memory. | | `numpy()` | Method | Convert the object to a numpy array. | | `cuda()` | Method | Move the object to CUDA memory. | @@ -705,7 +705,7 @@ The `plot()` method in `Results` objects facilitates visualization of prediction The `plot()` method supports various arguments to customize the output: | Argument | Type | Description | Default | -|--------------|-----------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------| +| ------------ | --------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------- | | `conf` | `bool` | Include detection confidence scores. | `True` | | `line_width` | `float` | Line width of bounding boxes. Scales with image size if `None`. | `None` | | `font_size` | `float` | Text font size. Scales with image size if `None`. | `None` | @@ -800,7 +800,5 @@ Here's a Python script using OpenCV (`cv2`) and YOLOv8 to run inference on video This script will run predictions on each frame of the video, visualize the results, and display them in a window. The loop can be exited by pressing 'q'. [car spare parts]: https://github.com/RizwanMunawar/ultralytics/assets/62513924/a0f802a8-0776-44cf-8f17-93974a4a28a1 - [football player detect]: https://github.com/RizwanMunawar/ultralytics/assets/62513924/7d320e1f-fc57-4d7f-a691-78ee579c3442 - [human fall detect]: https://github.com/RizwanMunawar/ultralytics/assets/62513924/86437c4a-3227-4eee-90ef-9efb697bdb43 diff --git a/docs/en/modes/track.md b/docs/en/modes/track.md index e45254d5..3db39fb2 100644 --- a/docs/en/modes/track.md +++ b/docs/en/modes/track.md @@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ The output from Ultralytics trackers is consistent with standard object detectio ## Real-world Applications | Transportation | Retail | Aquaculture | -|:----------------------------------:|:--------------------------------:|:----------------------------:| +| :--------------------------------: | :------------------------------: | :--------------------------: | | ![Vehicle Tracking][vehicle track] | ![People Tracking][people track] | ![Fish Tracking][fish track] | | Vehicle Tracking | People Tracking | Fish Tracking | @@ -365,7 +365,5 @@ To initiate your contribution, please refer to our [Contributing Guide](../help/ Together, let's enhance the tracking capabilities of the Ultralytics YOLO ecosystem 🙏! [fish track]: https://github.com/RizwanMunawar/ultralytics/assets/62513924/a5146d0f-bfa8-4e0a-b7df-3c1446cd8142 - [people track]: https://github.com/RizwanMunawar/ultralytics/assets/62513924/93bb4ee2-77a0-4e4e-8eb6-eb8f527f0527 - [vehicle track]: https://github.com/RizwanMunawar/ultralytics/assets/62513924/ee6e6038-383b-4f21-ac29-b2a1c7d386ab diff --git a/docs/en/modes/train.md b/docs/en/modes/train.md index a0bac4ba..7de2d681 100644 --- a/docs/en/modes/train.md +++ b/docs/en/modes/train.md @@ -176,7 +176,7 @@ Remember that checkpoints are saved at the end of every epoch by default, or at The training settings for YOLO models encompass various hyperparameters and configurations used during the training process. These settings influence the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Key training settings include batch size, learning rate, momentum, and weight decay. Additionally, the choice of optimizer, loss function, and training dataset composition can impact the training process. Careful tuning and experimentation with these settings are crucial for optimizing performance. | Argument | Default | Description | -|-------------------|----------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| ----------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | `model` | `None` | Specifies the model file for training. Accepts a path to either a `.pt` pretrained model or a `.yaml` configuration file. Essential for defining the model structure or initializing weights. | | `data` | `None` | Path to the dataset configuration file (e.g., `coco8.yaml`). This file contains dataset-specific parameters, including paths to training and validation data, class names, and number of classes. | | `epochs` | `100` | Total number of training epochs. Each epoch represents a full pass over the entire dataset. Adjusting this value can affect training duration and model performance. | @@ -227,9 +227,9 @@ The training settings for YOLO models encompass various hyperparameters and conf | `plots` | `False` | Generates and saves plots of training and validation metrics, as well as prediction examples, providing visual insights into model performance and learning progression. | !!! info "Note on Batch-size Settings" - + The `batch` argument can be configured in three ways: - + - **Fixed Batch Size**: Set an integer value (e.g., `batch=16`), specifying the number of images per batch directly. - **Auto Mode (60% GPU Memory)**: Use `batch=-1` to automatically adjust batch size for approximately 60% CUDA memory utilization. - **Auto Mode with Utilization Fraction**: Set a fraction value (e.g., `batch=0.70`) to adjust batch size based on the specified fraction of GPU memory usage. @@ -239,7 +239,7 @@ The training settings for YOLO models encompass various hyperparameters and conf Augmentation techniques are essential for improving the robustness and performance of YOLO models by introducing variability into the training data, helping the model generalize better to unseen data. The following table outlines the purpose and effect of each augmentation argument: | Argument | Type | Default | Range | Description | -|-----------------|---------|---------------|---------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| --------------- | ------- | ------------- | ------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | `hsv_h` | `float` | `0.015` | `0.0 - 1.0` | Adjusts the hue of the image by a fraction of the color wheel, introducing color variability. Helps the model generalize across different lighting conditions. | | `hsv_s` | `float` | `0.7` | `0.0 - 1.0` | Alters the saturation of the image by a fraction, affecting the intensity of colors. Useful for simulating different environmental conditions. | | `hsv_v` | `float` | `0.4` | `0.0 - 1.0` | Modifies the value (brightness) of the image by a fraction, helping the model to perform well under various lighting conditions. | diff --git a/docs/en/modes/val.md b/docs/en/modes/val.md index 83197845..a7e21f94 100644 --- a/docs/en/modes/val.md +++ b/docs/en/modes/val.md @@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ Validate trained YOLOv8n model accuracy on the COCO8 dataset. No argument need t When validating YOLO models, several arguments can be fine-tuned to optimize the evaluation process. These arguments control aspects such as input image size, batch processing, and performance thresholds. Below is a detailed breakdown of each argument to help you customize your validation settings effectively. | Argument | Type | Default | Description | -|---------------|---------|---------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| +| ------------- | ------- | ------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | | `data` | `str` | `None` | Specifies the path to the dataset configuration file (e.g., `coco8.yaml`). This file includes paths to validation data, class names, and number of classes. | | `imgsz` | `int` | `640` | Defines the size of input images. All images are resized to this dimension before processing. | | `batch` | `int` | `16` | Sets the number of images per batch. Use `-1` for AutoBatch, which automatically adjusts based on GPU memory availability. | diff --git a/docs/en/quickstart.md b/docs/en/quickstart.md index 5ae1de12..c38ee9b8 100644 --- a/docs/en/quickstart.md +++ b/docs/en/quickstart.md @@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ Ultralytics provides various installation methods including pip, conda, and Dock
!!! Example "Install" - +
=== "Pip install (recommended)"
@@ -318,7 +318,7 @@ Ultralytics allows users to easily modify their settings. Changes can be perform
The table below provides an overview of the settings available for adjustment within Ultralytics. Each setting is outlined along with an example value, the data type, and a brief description.
| Name | Example Value | Data Type | Description |
-|--------------------|-----------------------|-----------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| ------------------ | --------------------- | --------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `settings_version` | `'0.0.4'` | `str` | Ultralytics _settings_ version (different from Ultralytics [pip](https://pypi.org/project/ultralytics/) version) |
| `datasets_dir` | `'/path/to/datasets'` | `str` | The directory where the datasets are stored |
| `weights_dir` | `'/path/to/weights'` | `str` | The directory where the model weights are stored |
diff --git a/docs/en/tasks/classify.md b/docs/en/tasks/classify.md
index c307f599..69da254e 100644
--- a/docs/en/tasks/classify.md
+++ b/docs/en/tasks/classify.md
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ YOLOv8 pretrained Classify models are shown here. Detect, Segment and Pose model
[Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/cfg/models) download automatically from the latest Ultralytics [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases) on first use.
| Model | size
(pixels) | acc
top1 | acc
top5 | Speed
CPU ONNX
(ms) | Speed
A100 TensorRT
(ms) | params
(M) | FLOPs
(B) at 640 |
-|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------|------------------|------------------|--------------------------------|-------------------------------------|--------------------|--------------------------|
+| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------- | ---------------- | ---------------- | ------------------------------ | ----------------------------------- | ------------------ | ------------------------ |
| [YOLOv8n-cls](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8n-cls.pt) | 224 | 69.0 | 88.3 | 12.9 | 0.31 | 2.7 | 4.3 |
| [YOLOv8s-cls](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8s-cls.pt) | 224 | 73.8 | 91.7 | 23.4 | 0.35 | 6.4 | 13.5 |
| [YOLOv8m-cls](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8m-cls.pt) | 224 | 76.8 | 93.5 | 85.4 | 0.62 | 17.0 | 42.7 |
@@ -163,19 +163,19 @@ Export a YOLOv8n-cls model to a different format like ONNX, CoreML, etc.
Available YOLOv8-cls export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`. You can predict or validate directly on exported models, i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n-cls.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your model after export completes.
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
-|---------------------------------------------------|-------------------|-------------------------------|----------|----------------------------------------------------------------------|
-| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n-cls.pt` | ✅ | - |
-| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n-cls.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` |
-| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n-cls.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` |
-| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n-cls_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n-cls.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n-cls.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` |
-| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n-cls_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n-cls.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n-cls.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n-cls_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
-| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n-cls_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n-cls_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n-cls_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` |
+| ------------------------------------------------- | ----------------- | ----------------------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n-cls.pt` | ✅ | - |
+| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n-cls.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` |
+| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n-cls.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` |
+| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n-cls_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n-cls.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n-cls.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` |
+| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n-cls_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n-cls.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n-cls.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n-cls_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n-cls_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n-cls_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n-cls_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` |
See full `export` details in the [Export](../modes/export.md) page.
diff --git a/docs/en/tasks/detect.md b/docs/en/tasks/detect.md
index 9b24fa1a..7ccc49ba 100644
--- a/docs/en/tasks/detect.md
+++ b/docs/en/tasks/detect.md
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ YOLOv8 pretrained Detect models are shown here. Detect, Segment and Pose models
[Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/cfg/models) download automatically from the latest Ultralytics [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases) on first use.
| Model | size
(pixels) | mAPval
50-95 | Speed
CPU ONNX
(ms) | Speed
A100 TensorRT
(ms) | params
(M) | FLOPs
(B) |
-|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------|----------------------|--------------------------------|-------------------------------------|--------------------|-------------------|
+| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | --------------------- | -------------------- | ------------------------------ | ----------------------------------- | ------------------ | ----------------- |
| [YOLOv8n](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8n.pt) | 640 | 37.3 | 80.4 | 0.99 | 3.2 | 8.7 |
| [YOLOv8s](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8s.pt) | 640 | 44.9 | 128.4 | 1.20 | 11.2 | 28.6 |
| [YOLOv8m](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8m.pt) | 640 | 50.2 | 234.7 | 1.83 | 25.9 | 78.9 |
@@ -164,19 +164,19 @@ Export a YOLOv8n model to a different format like ONNX, CoreML, etc.
Available YOLOv8 export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`. You can predict or validate directly on exported models, i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your model after export completes.
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
-|---------------------------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|----------|----------------------------------------------------------------------|
-| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - |
-| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` |
-| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` |
-| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` |
-| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
-| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` |
+| ------------------------------------------------- | ----------------- | ------------------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - |
+| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` |
+| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` |
+| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` |
+| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` |
See full `export` details in the [Export](../modes/export.md) page.
diff --git a/docs/en/tasks/obb.md b/docs/en/tasks/obb.md
index e29561bb..6655def9 100644
--- a/docs/en/tasks/obb.md
+++ b/docs/en/tasks/obb.md
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ The output of an oriented object detector is a set of rotated bounding boxes tha
## Visual Samples
| Ships Detection using OBB | Vehicle Detection using OBB |
-|:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|
+| :-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
|  | 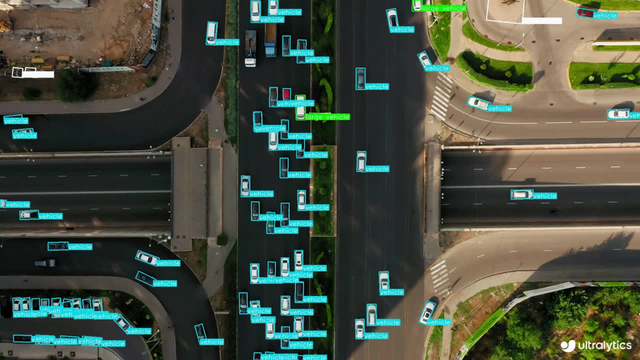 |
## [Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/cfg/models/v8)
@@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ YOLOv8 pretrained OBB models are shown here, which are pretrained on the [DOTAv1
[Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/cfg/models) download automatically from the latest Ultralytics [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases) on first use.
| Model | size
(pixels) | mAPtest
50 | Speed
CPU ONNX
(ms) | Speed
A100 TensorRT
(ms) | params
(M) | FLOPs
(B) |
-|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------|--------------------|--------------------------------|-------------------------------------|--------------------|-------------------|
+| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------- | ------------------ | ------------------------------ | ----------------------------------- | ------------------ | ----------------- |
| [YOLOv8n-obb](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8n-obb.pt) | 1024 | 78.0 | 204.77 | 3.57 | 3.1 | 23.3 |
| [YOLOv8s-obb](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8s-obb.pt) | 1024 | 79.5 | 424.88 | 4.07 | 11.4 | 76.3 |
| [YOLOv8m-obb](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8m-obb.pt) | 1024 | 80.5 | 763.48 | 7.61 | 26.4 | 208.6 |
@@ -185,19 +185,19 @@ Export a YOLOv8n-obb model to a different format like ONNX, CoreML, etc.
Available YOLOv8-obb export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`. You can predict or validate directly on exported models, i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n-obb.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your model after export completes.
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
-|---------------------------------------------------|-------------------|-------------------------------|----------|----------------------------------------------------------------------|
-| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n-obb.pt` | ✅ | - |
-| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n-obb.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` |
-| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n-obb.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` |
-| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n-obb_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n-obb.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n-obb.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` |
-| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n-obb_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n-obb.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n-obb.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n-obb_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
-| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n-obb_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n-obb_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n-obb_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` |
+| ------------------------------------------------- | ----------------- | ----------------------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n-obb.pt` | ✅ | - |
+| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n-obb.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` |
+| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n-obb.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` |
+| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n-obb_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n-obb.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n-obb.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` |
+| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n-obb_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n-obb.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n-obb.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n-obb_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n-obb_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n-obb_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n-obb_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` |
See full `export` details in the [Export](../modes/export.md) page.
diff --git a/docs/en/tasks/pose.md b/docs/en/tasks/pose.md
index 24416937..75aa96a7 100644
--- a/docs/en/tasks/pose.md
+++ b/docs/en/tasks/pose.md
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ YOLOv8 pretrained Pose models are shown here. Detect, Segment and Pose models ar
[Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/cfg/models) download automatically from the latest Ultralytics [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases) on first use.
| Model | size
(pixels) | mAPpose
50-95 | mAPpose
50 | Speed
CPU ONNX
(ms) | Speed
A100 TensorRT
(ms) | params
(M) | FLOPs
(B) |
-|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------|-----------------------|--------------------|--------------------------------|-------------------------------------|--------------------|-------------------|
+| ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------- | --------------------- | ------------------ | ------------------------------ | ----------------------------------- | ------------------ | ----------------- |
| [YOLOv8n-pose](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8n-pose.pt) | 640 | 50.4 | 80.1 | 131.8 | 1.18 | 3.3 | 9.2 |
| [YOLOv8s-pose](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8s-pose.pt) | 640 | 60.0 | 86.2 | 233.2 | 1.42 | 11.6 | 30.2 |
| [YOLOv8m-pose](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8m-pose.pt) | 640 | 65.0 | 88.8 | 456.3 | 2.00 | 26.4 | 81.0 |
@@ -179,19 +179,19 @@ Export a YOLOv8n Pose model to a different format like ONNX, CoreML, etc.
Available YOLOv8-pose export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`. You can predict or validate directly on exported models, i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n-pose.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your model after export completes.
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
-|---------------------------------------------------|-------------------|--------------------------------|----------|----------------------------------------------------------------------|
-| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n-pose.pt` | ✅ | - |
-| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n-pose.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` |
-| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n-pose.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` |
-| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n-pose_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n-pose.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n-pose.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` |
-| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n-pose_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n-pose.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n-pose.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n-pose_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
-| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n-pose_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n-pose_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n-pose_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` |
+| ------------------------------------------------- | ----------------- | ------------------------------ | -------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n-pose.pt` | ✅ | - |
+| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n-pose.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` |
+| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n-pose.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` |
+| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n-pose_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n-pose.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n-pose.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` |
+| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n-pose_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n-pose.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n-pose.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n-pose_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n-pose_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n-pose_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n-pose_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` |
See full `export` details in the [Export](../modes/export.md) page.
diff --git a/docs/en/tasks/segment.md b/docs/en/tasks/segment.md
index 161f2981..bdc865c3 100644
--- a/docs/en/tasks/segment.md
+++ b/docs/en/tasks/segment.md
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ YOLOv8 pretrained Segment models are shown here. Detect, Segment and Pose models
[Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/cfg/models) download automatically from the latest Ultralytics [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases) on first use.
| Model | size
(pixels) | mAPbox
50-95 | mAPmask
50-95 | Speed
CPU ONNX
(ms) | Speed
A100 TensorRT
(ms) | params
(M) | FLOPs
(B) |
-|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------|----------------------|-----------------------|--------------------------------|-------------------------------------|--------------------|-------------------|
+| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------- | -------------------- | --------------------- | ------------------------------ | ----------------------------------- | ------------------ | ----------------- |
| [YOLOv8n-seg](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8n-seg.pt) | 640 | 36.7 | 30.5 | 96.1 | 1.21 | 3.4 | 12.6 |
| [YOLOv8s-seg](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8s-seg.pt) | 640 | 44.6 | 36.8 | 155.7 | 1.47 | 11.8 | 42.6 |
| [YOLOv8m-seg](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8m-seg.pt) | 640 | 49.9 | 40.8 | 317.0 | 2.18 | 27.3 | 110.2 |
@@ -169,19 +169,19 @@ Export a YOLOv8n-seg model to a different format like ONNX, CoreML, etc.
Available YOLOv8-seg export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`. You can predict or validate directly on exported models, i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n-seg.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your model after export completes.
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
-|---------------------------------------------------|-------------------|-------------------------------|----------|----------------------------------------------------------------------|
-| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n-seg.pt` | ✅ | - |
-| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n-seg.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` |
-| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n-seg.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` |
-| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n-seg_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n-seg.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n-seg.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` |
-| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n-seg_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n-seg.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n-seg.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n-seg_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
-| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n-seg_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n-seg_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n-seg_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` |
+| ------------------------------------------------- | ----------------- | ----------------------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n-seg.pt` | ✅ | - |
+| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n-seg.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` |
+| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n-seg.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` |
+| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n-seg_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n-seg.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n-seg.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` |
+| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n-seg_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n-seg.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n-seg.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n-seg_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n-seg_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n-seg_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n-seg_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` |
See full `export` details in the [Export](../modes/export.md) page.
diff --git a/docs/en/usage/callbacks.md b/docs/en/usage/callbacks.md
index b0ea8313..e88ffac8 100644
--- a/docs/en/usage/callbacks.md
+++ b/docs/en/usage/callbacks.md
@@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ Here are all supported callbacks. See callbacks [source code](https://github.com
### Trainer Callbacks
| Callback | Description |
-|-----------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------|
+| --------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------- |
| `on_pretrain_routine_start` | Triggered at the beginning of pre-training routine |
| `on_pretrain_routine_end` | Triggered at the end of pre-training routine |
| `on_train_start` | Triggered when the training starts |
@@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ Here are all supported callbacks. See callbacks [source code](https://github.com
### Validator Callbacks
| Callback | Description |
-|----------------------|-------------------------------------------------|
+| -------------------- | ----------------------------------------------- |
| `on_val_start` | Triggered when the validation starts |
| `on_val_batch_start` | Triggered at the start of each validation batch |
| `on_val_batch_end` | Triggered at the end of each validation batch |
@@ -86,7 +86,7 @@ Here are all supported callbacks. See callbacks [source code](https://github.com
### Predictor Callbacks
| Callback | Description |
-|------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------|
+| ---------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------- |
| `on_predict_start` | Triggered when the prediction process starts |
| `on_predict_batch_start` | Triggered at the start of each prediction batch |
| `on_predict_postprocess_end` | Triggered at the end of prediction postprocessing |
@@ -96,6 +96,6 @@ Here are all supported callbacks. See callbacks [source code](https://github.com
### Exporter Callbacks
| Callback | Description |
-|-------------------|------------------------------------------|
+| ----------------- | ---------------------------------------- |
| `on_export_start` | Triggered when the export process starts |
| `on_export_end` | Triggered when the export process ends |
diff --git a/docs/en/usage/cfg.md b/docs/en/usage/cfg.md
index d8cb5bc7..5b91dc08 100644
--- a/docs/en/usage/cfg.md
+++ b/docs/en/usage/cfg.md
@@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ YOLO models can be used for a variety of tasks, including detection, segmentatio
- **OBB**: Oriented (i.e. rotated) bounding boxes suitable for satellite or medical imagery.
| Argument | Default | Description |
-|----------|------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| -------- | ---------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `task` | `'detect'` | Specifies the YOLO task to be executed. Options include `detect` for object detection, `segment` for segmentation, `classify` for classification, `pose` for pose estimation and `OBB` for oriented bounding boxes. Each task is tailored to specific types of output and problems within image and video analysis. |
[Tasks Guide](../tasks/index.md){ .md-button }
@@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ YOLO models can be used in different modes depending on the specific problem you
- **Benchmark**: For benchmarking YOLOv8 exports (ONNX, TensorRT, etc.) speed and accuracy.
| Argument | Default | Description |
-|----------|-----------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| -------- | --------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `mode` | `'train'` | Specifies the mode in which the YOLO model operates. Options are `train` for model training, `val` for validation, `predict` for inference on new data, `export` for model conversion to deployment formats, `track` for object tracking, and `benchmark` for performance evaluation. Each mode is designed for different stages of the model lifecycle, from development through deployment. |
[Modes Guide](../modes/index.md){ .md-button }
@@ -85,7 +85,7 @@ YOLO models can be used in different modes depending on the specific problem you
The training settings for YOLO models encompass various hyperparameters and configurations used during the training process. These settings influence the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Key training settings include batch size, learning rate, momentum, and weight decay. Additionally, the choice of optimizer, loss function, and training dataset composition can impact the training process. Careful tuning and experimentation with these settings are crucial for optimizing performance.
| Argument | Default | Description |
-|-------------------|----------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| ----------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `model` | `None` | Specifies the model file for training. Accepts a path to either a `.pt` pretrained model or a `.yaml` configuration file. Essential for defining the model structure or initializing weights. |
| `data` | `None` | Path to the dataset configuration file (e.g., `coco8.yaml`). This file contains dataset-specific parameters, including paths to training and validation data, class names, and number of classes. |
| `epochs` | `100` | Total number of training epochs. Each epoch represents a full pass over the entire dataset. Adjusting this value can affect training duration and model performance. |
@@ -136,9 +136,9 @@ The training settings for YOLO models encompass various hyperparameters and conf
| `plots` | `False` | Generates and saves plots of training and validation metrics, as well as prediction examples, providing visual insights into model performance and learning progression. |
!!! info "Note on Batch-size Settings"
-
+
The `batch` argument can be configured in three ways:
-
+
- **Fixed Batch Size**: Set an integer value (e.g., `batch=16`), specifying the number of images per batch directly.
- **Auto Mode (60% GPU Memory)**: Use `batch=-1` to automatically adjust batch size for approximately 60% CUDA memory utilization.
- **Auto Mode with Utilization Fraction**: Set a fraction value (e.g., `batch=0.70`) to adjust batch size based on the specified fraction of GPU memory usage.
@@ -152,7 +152,7 @@ The prediction settings for YOLO models encompass a range of hyperparameters and
Inference arguments:
| Argument | Type | Default | Description |
-|-----------------|----------------|------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| --------------- | -------------- | ---------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| `source` | `str` | `'ultralytics/assets'` | Specifies the data source for inference. Can be an image path, video file, directory, URL, or device ID for live feeds. Supports a wide range of formats and sources, enabling flexible application across different types of input. |
| `conf` | `float` | `0.25` | Sets the minimum confidence threshold for detections. Objects detected with confidence below this threshold will be disregarded. Adjusting this value can help reduce false positives. |
| `iou` | `float` | `0.7` | Intersection Over Union (IoU) threshold for Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS). Lower values result in fewer detections by eliminating overlapping boxes, useful for reducing duplicates. |
@@ -172,7 +172,7 @@ Inference arguments:
Visualization arguments:
| Argument | Type | Default | Description |
-|---------------|---------------|---------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| ------------- | ------------- | ------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `show` | `bool` | `False` | If `True`, displays the annotated images or videos in a window. Useful for immediate visual feedback during development or testing. |
| `save` | `bool` | `False` | Enables saving of the annotated images or videos to file. Useful for documentation, further analysis, or sharing results. |
| `save_frames` | `bool` | `False` | When processing videos, saves individual frames as images. Useful for extracting specific frames or for detailed frame-by-frame analysis. |
@@ -191,7 +191,7 @@ Visualization arguments:
The val (validation) settings for YOLO models involve various hyperparameters and configurations used to evaluate the model's performance on a validation dataset. These settings influence the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Common YOLO validation settings include batch size, validation frequency during training, and performance evaluation metrics. Other factors affecting the validation process include the validation dataset's size and composition, as well as the specific task the model is employed for.
| Argument | Type | Default | Description |
-|---------------|---------|---------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| ------------- | ------- | ------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `data` | `str` | `None` | Specifies the path to the dataset configuration file (e.g., `coco8.yaml`). This file includes paths to validation data, class names, and number of classes. |
| `imgsz` | `int` | `640` | Defines the size of input images. All images are resized to this dimension before processing. |
| `batch` | `int` | `16` | Sets the number of images per batch. Use `-1` for AutoBatch, which automatically adjusts based on GPU memory availability. |
@@ -216,7 +216,7 @@ Careful tuning and experimentation with these settings are crucial to ensure opt
Export settings for YOLO models encompass configurations and options related to saving or exporting the model for use in different environments or platforms. These settings can impact the model's performance, size, and compatibility with various systems. Key export settings include the exported model file format (e.g., ONNX, TensorFlow SavedModel), the target device (e.g., CPU, GPU), and additional features such as masks or multiple labels per box. The export process may also be affected by the model's specific task and the requirements or constraints of the destination environment or platform.
| Argument | Type | Default | Description |
-|-------------|------------------|-----------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| ----------- | ---------------- | --------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `format` | `str` | `'torchscript'` | Target format for the exported model, such as `'onnx'`, `'torchscript'`, `'tensorflow'`, or others, defining compatibility with various deployment environments. |
| `imgsz` | `int` or `tuple` | `640` | Desired image size for the model input. Can be an integer for square images or a tuple `(height, width)` for specific dimensions. |
| `keras` | `bool` | `False` | Enables export to Keras format for TensorFlow SavedModel, providing compatibility with TensorFlow serving and APIs. |
@@ -238,7 +238,7 @@ It is crucial to thoughtfully configure these settings to ensure the exported mo
Augmentation techniques are essential for improving the robustness and performance of YOLO models by introducing variability into the training data, helping the model generalize better to unseen data. The following table outlines the purpose and effect of each augmentation argument:
| Argument | Type | Default | Range | Description |
-|-----------------|---------|---------------|---------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| --------------- | ------- | ------------- | ------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `hsv_h` | `float` | `0.015` | `0.0 - 1.0` | Adjusts the hue of the image by a fraction of the color wheel, introducing color variability. Helps the model generalize across different lighting conditions. |
| `hsv_s` | `float` | `0.7` | `0.0 - 1.0` | Alters the saturation of the image by a fraction, affecting the intensity of colors. Useful for simulating different environmental conditions. |
| `hsv_v` | `float` | `0.4` | `0.0 - 1.0` | Modifies the value (brightness) of the image by a fraction, helping the model to perform well under various lighting conditions. |
@@ -271,7 +271,7 @@ Logging, checkpoints, plotting, and file management are important considerations
Effective logging, checkpointing, plotting, and file management can help you keep track of the model's progress and make it easier to debug and optimize the training process.
| Argument | Default | Description |
-|------------|----------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| ---------- | -------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| `project` | `'runs'` | Specifies the root directory for saving training runs. Each run will be saved in a separate subdirectory within this directory. |
| `name` | `'exp'` | Defines the name of the experiment. If not specified, YOLO automatically increments this name for each run, e.g., `exp`, `exp2`, etc., to avoid overwriting previous experiments. |
| `exist_ok` | `False` | Determines whether to overwrite an existing experiment directory if one with the same name already exists. Setting this to `True` allows overwriting, while `False` prevents it. |
diff --git a/docs/en/usage/cli.md b/docs/en/usage/cli.md
index 8b73efc7..2bf11b68 100644
--- a/docs/en/usage/cli.md
+++ b/docs/en/usage/cli.md
@@ -171,20 +171,20 @@ Export a YOLOv8n model to a different format like ONNX, CoreML, etc.
Available YOLOv8 export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`.
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
-|---------------------------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|----------|----------------------------------------------------------------------|
-| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - |
-| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` |
-| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` |
-| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` |
-| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
-| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
-| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
-| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` |
+| ------------------------------------------------- | ----------------- | ------------------------- | -------- | -------------------------------------------------------------------- |
+| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - |
+| [TorchScript](../integrations/torchscript.md) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` |
+| [ONNX](../integrations/onnx.md) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` |
+| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TensorRT](../integrations/tensorrt.md) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [CoreML](../integrations/coreml.md) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` |
+| [TF SavedModel](../integrations/tf-savedmodel.md) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TF GraphDef](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [TF Lite](../integrations/tflite.md) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [TF Edge TPU](../integrations/edge-tpu.md) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [TF.js](../integrations/tfjs.md) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` |
+| [PaddlePaddle](../integrations/paddlepaddle.md) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` |
+| [NCNN](../integrations/ncnn.md) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` |
See full `export` details in the [Export](../modes/export.md) page.
diff --git a/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/architecture_description.md b/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/architecture_description.md
index 86c4baf6..789f3264 100644
--- a/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/architecture_description.md
+++ b/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/architecture_description.md
@@ -108,29 +108,29 @@ YOLOv5 employs various data augmentation techniques to improve the model's abili
- **Mosaic Augmentation**: An image processing technique that combines four training images into one in ways that encourage object detection models to better handle various object scales and translations.
- 
+ 
- **Copy-Paste Augmentation**: An innovative data augmentation method that copies random patches from an image and pastes them onto another randomly chosen image, effectively generating a new training sample.
- 
+ 
- **Random Affine Transformations**: This includes random rotation, scaling, translation, and shearing of the images.
- 
+ 
- **MixUp Augmentation**: A method that creates composite images by taking a linear combination of two images and their associated labels.
- 
+ 
- **Albumentations**: A powerful library for image augmenting that supports a wide variety of augmentation techniques.
- **HSV Augmentation**: Random changes to the Hue, Saturation, and Value of the images.
- 
+ 
- **Random Horizontal Flip**: An augmentation method that randomly flips images horizontally.
- 
+ 
## 3. Training Strategies
diff --git a/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/hyperparameter_evolution.md b/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/hyperparameter_evolution.md
index 049f104c..dd84d4da 100644
--- a/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/hyperparameter_evolution.md
+++ b/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/hyperparameter_evolution.md
@@ -28,35 +28,35 @@ YOLOv5 has about 30 hyperparameters used for various training settings. These ar
# python train.py --batch 64 --cfg yolov5n6.yaml --weights '' --data coco.yaml --img 640 --epochs 300 --linear
# See tutorials for hyperparameter evolution https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5#tutorials
-lr0: 0.01 # initial learning rate (SGD=1E-2, Adam=1E-3)
-lrf: 0.01 # final OneCycleLR learning rate (lr0 * lrf)
-momentum: 0.937 # SGD momentum/Adam beta1
-weight_decay: 0.0005 # optimizer weight decay 5e-4
-warmup_epochs: 3.0 # warmup epochs (fractions ok)
-warmup_momentum: 0.8 # warmup initial momentum
-warmup_bias_lr: 0.1 # warmup initial bias lr
-box: 0.05 # box loss gain
-cls: 0.5 # cls loss gain
-cls_pw: 1.0 # cls BCELoss positive_weight
-obj: 1.0 # obj loss gain (scale with pixels)
-obj_pw: 1.0 # obj BCELoss positive_weight
-iou_t: 0.20 # IoU training threshold
-anchor_t: 4.0 # anchor-multiple threshold
+lr0: 0.01 # initial learning rate (SGD=1E-2, Adam=1E-3)
+lrf: 0.01 # final OneCycleLR learning rate (lr0 * lrf)
+momentum: 0.937 # SGD momentum/Adam beta1
+weight_decay: 0.0005 # optimizer weight decay 5e-4
+warmup_epochs: 3.0 # warmup epochs (fractions ok)
+warmup_momentum: 0.8 # warmup initial momentum
+warmup_bias_lr: 0.1 # warmup initial bias lr
+box: 0.05 # box loss gain
+cls: 0.5 # cls loss gain
+cls_pw: 1.0 # cls BCELoss positive_weight
+obj: 1.0 # obj loss gain (scale with pixels)
+obj_pw: 1.0 # obj BCELoss positive_weight
+iou_t: 0.20 # IoU training threshold
+anchor_t: 4.0 # anchor-multiple threshold
# anchors: 3 # anchors per output layer (0 to ignore)
-fl_gamma: 0.0 # focal loss gamma (efficientDet default gamma=1.5)
-hsv_h: 0.015 # image HSV-Hue augmentation (fraction)
-hsv_s: 0.7 # image HSV-Saturation augmentation (fraction)
-hsv_v: 0.4 # image HSV-Value augmentation (fraction)
-degrees: 0.0 # image rotation (+/- deg)
-translate: 0.1 # image translation (+/- fraction)
-scale: 0.5 # image scale (+/- gain)
-shear: 0.0 # image shear (+/- deg)
-perspective: 0.0 # image perspective (+/- fraction), range 0-0.001
-flipud: 0.0 # image flip up-down (probability)
-fliplr: 0.5 # image flip left-right (probability)
-mosaic: 1.0 # image mosaic (probability)
-mixup: 0.0 # image mixup (probability)
-copy_paste: 0.0 # segment copy-paste (probability)
+fl_gamma: 0.0 # focal loss gamma (efficientDet default gamma=1.5)
+hsv_h: 0.015 # image HSV-Hue augmentation (fraction)
+hsv_s: 0.7 # image HSV-Saturation augmentation (fraction)
+hsv_v: 0.4 # image HSV-Value augmentation (fraction)
+degrees: 0.0 # image rotation (+/- deg)
+translate: 0.1 # image translation (+/- fraction)
+scale: 0.5 # image scale (+/- gain)
+shear: 0.0 # image shear (+/- deg)
+perspective: 0.0 # image perspective (+/- fraction), range 0-0.001
+flipud: 0.0 # image flip up-down (probability)
+fliplr: 0.5 # image flip left-right (probability)
+mosaic: 1.0 # image mosaic (probability)
+mixup: 0.0 # image mixup (probability)
+copy_paste: 0.0 # segment copy-paste (probability)
```
## 2. Define Fitness
@@ -110,35 +110,35 @@ The main genetic operators are **crossover** and **mutation**. In this work muta
# metrics/precision, metrics/recall, metrics/mAP_0.5, metrics/mAP_0.5:0.95, val/box_loss, val/obj_loss, val/cls_loss
# 0.54634, 0.55625, 0.58201, 0.33665, 0.056451, 0.042892, 0.013441
-lr0: 0.01 # initial learning rate (SGD=1E-2, Adam=1E-3)
-lrf: 0.2 # final OneCycleLR learning rate (lr0 * lrf)
-momentum: 0.937 # SGD momentum/Adam beta1
-weight_decay: 0.0005 # optimizer weight decay 5e-4
-warmup_epochs: 3.0 # warmup epochs (fractions ok)
-warmup_momentum: 0.8 # warmup initial momentum
-warmup_bias_lr: 0.1 # warmup initial bias lr
-box: 0.05 # box loss gain
-cls: 0.5 # cls loss gain
-cls_pw: 1.0 # cls BCELoss positive_weight
-obj: 1.0 # obj loss gain (scale with pixels)
-obj_pw: 1.0 # obj BCELoss positive_weight
-iou_t: 0.20 # IoU training threshold
-anchor_t: 4.0 # anchor-multiple threshold
+lr0: 0.01 # initial learning rate (SGD=1E-2, Adam=1E-3)
+lrf: 0.2 # final OneCycleLR learning rate (lr0 * lrf)
+momentum: 0.937 # SGD momentum/Adam beta1
+weight_decay: 0.0005 # optimizer weight decay 5e-4
+warmup_epochs: 3.0 # warmup epochs (fractions ok)
+warmup_momentum: 0.8 # warmup initial momentum
+warmup_bias_lr: 0.1 # warmup initial bias lr
+box: 0.05 # box loss gain
+cls: 0.5 # cls loss gain
+cls_pw: 1.0 # cls BCELoss positive_weight
+obj: 1.0 # obj loss gain (scale with pixels)
+obj_pw: 1.0 # obj BCELoss positive_weight
+iou_t: 0.20 # IoU training threshold
+anchor_t: 4.0 # anchor-multiple threshold
# anchors: 3 # anchors per output layer (0 to ignore)
-fl_gamma: 0.0 # focal loss gamma (efficientDet default gamma=1.5)
-hsv_h: 0.015 # image HSV-Hue augmentation (fraction)
-hsv_s: 0.7 # image HSV-Saturation augmentation (fraction)
-hsv_v: 0.4 # image HSV-Value augmentation (fraction)
-degrees: 0.0 # image rotation (+/- deg)
-translate: 0.1 # image translation (+/- fraction)
-scale: 0.5 # image scale (+/- gain)
-shear: 0.0 # image shear (+/- deg)
-perspective: 0.0 # image perspective (+/- fraction), range 0-0.001
-flipud: 0.0 # image flip up-down (probability)
-fliplr: 0.5 # image flip left-right (probability)
-mosaic: 1.0 # image mosaic (probability)
-mixup: 0.0 # image mixup (probability)
-copy_paste: 0.0 # segment copy-paste (probability)
+fl_gamma: 0.0 # focal loss gamma (efficientDet default gamma=1.5)
+hsv_h: 0.015 # image HSV-Hue augmentation (fraction)
+hsv_s: 0.7 # image HSV-Saturation augmentation (fraction)
+hsv_v: 0.4 # image HSV-Value augmentation (fraction)
+degrees: 0.0 # image rotation (+/- deg)
+translate: 0.1 # image translation (+/- fraction)
+scale: 0.5 # image scale (+/- gain)
+shear: 0.0 # image shear (+/- deg)
+perspective: 0.0 # image perspective (+/- fraction), range 0-0.001
+flipud: 0.0 # image flip up-down (probability)
+fliplr: 0.5 # image flip left-right (probability)
+mosaic: 1.0 # image mosaic (probability)
+mixup: 0.0 # image mixup (probability)
+copy_paste: 0.0 # segment copy-paste (probability)
```
We recommend a minimum of 300 generations of evolution for best results. Note that **evolution is generally expensive and time-consuming**, as the base scenario is trained hundreds of times, possibly requiring hundreds or thousands of GPU hours.
diff --git a/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/model_export.md b/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/model_export.md
index 3db687b0..81e0a3f3 100644
--- a/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/model_export.md
+++ b/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/model_export.md
@@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ YOLOv5 inference is officially supported in 11 formats:
💡 ProTip: Export to ONNX or OpenVINO for up to 3x CPU speedup. See [CPU Benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/6613). 💡 ProTip: Export to TensorRT for up to 5x GPU speedup. See [GPU Benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/6963).
| Format | `export.py --include` | Model |
-|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------|:----------------------|:--------------------------|
+| :------------------------------------------------------------------------- | :-------------------- | :------------------------ |
| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov5s.pt` |
| [TorchScript](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/jit.html) | `torchscript` | `yolov5s.torchscript` |
| [ONNX](https://onnx.ai/) | `onnx` | `yolov5s.onnx` |
diff --git a/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/multi_gpu_training.md b/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/multi_gpu_training.md
index 38c07c2a..f61ffc93 100644
--- a/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/multi_gpu_training.md
+++ b/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/multi_gpu_training.md
@@ -143,7 +143,7 @@ python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node 8 train.py --batch-size 128 --d
| GPUs
A100 | batch-size | CUDA_mem
device0 (G) | COCO
train | COCO
val |
-|--------------|------------|------------------------------|--------------------|------------------|
+| ------------ | ---------- | ---------------------------- | ------------------ | ---------------- |
| 1x | 16 | 26GB | 20:39 | 0:55 |
| 2x | 32 | 26GB | 11:43 | 0:57 |
| 4x | 64 | 26GB | 5:57 | 0:55 |
diff --git a/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/pytorch_hub_model_loading.md b/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/pytorch_hub_model_loading.md
index 4ac4c9e9..b1c4392e 100644
--- a/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/pytorch_hub_model_loading.md
+++ b/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/pytorch_hub_model_loading.md
@@ -285,42 +285,42 @@ results.pandas().xyxy[0].to_json(orient="records") # JSON img1 predictions
```json
[
- {
- "xmin": 749.5,
- "ymin": 43.5,
- "xmax": 1148.0,
- "ymax": 704.5,
- "confidence": 0.8740234375,
- "class": 0,
- "name": "person"
- },
- {
- "xmin": 433.5,
- "ymin": 433.5,
- "xmax": 517.5,
- "ymax": 714.5,
- "confidence": 0.6879882812,
- "class": 27,
- "name": "tie"
- },
- {
- "xmin": 115.25,
- "ymin": 195.75,
- "xmax": 1096.0,
- "ymax": 708.0,
- "confidence": 0.6254882812,
- "class": 0,
- "name": "person"
- },
- {
- "xmin": 986.0,
- "ymin": 304.0,
- "xmax": 1028.0,
- "ymax": 420.0,
- "confidence": 0.2873535156,
- "class": 27,
- "name": "tie"
- }
+ {
+ "xmin": 749.5,
+ "ymin": 43.5,
+ "xmax": 1148.0,
+ "ymax": 704.5,
+ "confidence": 0.8740234375,
+ "class": 0,
+ "name": "person"
+ },
+ {
+ "xmin": 433.5,
+ "ymin": 433.5,
+ "xmax": 517.5,
+ "ymax": 714.5,
+ "confidence": 0.6879882812,
+ "class": 27,
+ "name": "tie"
+ },
+ {
+ "xmin": 115.25,
+ "ymin": 195.75,
+ "xmax": 1096.0,
+ "ymax": 708.0,
+ "confidence": 0.6254882812,
+ "class": 0,
+ "name": "person"
+ },
+ {
+ "xmin": 986.0,
+ "ymin": 304.0,
+ "xmax": 1028.0,
+ "ymax": 420.0,
+ "confidence": 0.2873535156,
+ "class": 27,
+ "name": "tie"
+ }
]
```
diff --git a/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/running_on_jetson_nano.md b/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/running_on_jetson_nano.md
index 6d5303cb..cb3dd080 100644
--- a/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/running_on_jetson_nano.md
+++ b/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/running_on_jetson_nano.md
@@ -308,7 +308,7 @@ The above result is running on **Jetson Xavier NX** with **INT8** and **YOLOv5s
The following table summarizes how different models perform on **Jetson Xavier NX**.
| Model Name | Precision | Inference Size | Inference Time (ms) | FPS |
-|------------|-----------|----------------|---------------------|-----|
+| ---------- | --------- | -------------- | ------------------- | --- |
| YOLOv5s | FP32 | 320x320 | 16.66 | 60 |
| | FP32 | 640x640 | 33.33 | 30 |
| | INT8 | 640x640 | 16.66 | 60 |
diff --git a/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/train_custom_data.md b/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/train_custom_data.md
index 251eccc8..a4713d50 100644
--- a/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/train_custom_data.md
+++ b/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/train_custom_data.md
@@ -81,20 +81,20 @@ Export in `YOLOv5 Pytorch` format, then copy the snippet into your training scri
```yaml
# Train/val/test sets as 1) dir: path/to/imgs, 2) file: path/to/imgs.txt, or 3) list: [path/to/imgs1, path/to/imgs2, ..]
-path: ../datasets/coco128 # dataset root dir
-train: images/train2017 # train images (relative to 'path') 128 images
-val: images/train2017 # val images (relative to 'path') 128 images
-test: # test images (optional)
+path: ../datasets/coco128 # dataset root dir
+train: images/train2017 # train images (relative to 'path') 128 images
+val: images/train2017 # val images (relative to 'path') 128 images
+test: # test images (optional)
# Classes (80 COCO classes)
names:
- 0: person
- 1: bicycle
- 2: car
- # ...
- 77: teddy bear
- 78: hair drier
- 79: toothbrush
+ 0: person
+ 1: bicycle
+ 2: car
+ # ...
+ 77: teddy bear
+ 78: hair drier
+ 79: toothbrush
```
### 2.2 Create Labels
diff --git a/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/transfer_learning_with_frozen_layers.md b/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/transfer_learning_with_frozen_layers.md
index f8c1b5cb..4306d0ea 100644
--- a/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/transfer_learning_with_frozen_layers.md
+++ b/docs/en/yolov5/tutorials/transfer_learning_with_frozen_layers.md
@@ -62,40 +62,39 @@ Looking at the model architecture we can see that the model backbone is layers 0
```yaml
# YOLOv5 v6.0 backbone
backbone:
- # [from, number, module, args]
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 6, 2, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- - [-1, 3, C3, [128]]
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- - [-1, 6, C3, [256]]
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- - [-1, 9, C3, [512]]
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- - [-1, 3, C3, [1024]]
- - [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
-
+ # [from, number, module, args]
+ - [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 6, 2, 2]] # 0-P1/2
+ - [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
+ - [-1, 3, C3, [128]]
+ - [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
+ - [-1, 6, C3, [256]]
+ - [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
+ - [-1, 9, C3, [512]]
+ - [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
+ - [-1, 3, C3, [1024]]
+ - [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv5 v6.0 head
head:
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]]
- - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- - [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- - [-1, 3, C3, [512, False]] # 13
+ - [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]]
+ - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
+ - [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
+ - [-1, 3, C3, [512, False]] # 13
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]]
- - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- - [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- - [-1, 3, C3, [256, False]] # 17 (P3/8-small)
+ - [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]]
+ - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
+ - [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
+ - [-1, 3, C3, [256, False]] # 17 (P3/8-small)
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- - [[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- - [-1, 3, C3, [512, False]] # 20 (P4/16-medium)
+ - [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
+ - [[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
+ - [-1, 3, C3, [512, False]] # 20 (P4/16-medium)
- - [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- - [[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- - [-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]] # 23 (P5/32-large)
+ - [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
+ - [[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
+ - [-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]] # 23 (P5/32-large)
- - [[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
+ - [[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
```
so we can define the freeze list to contain all modules with 'model.0.' - 'model.9.' in their names:
diff --git a/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/README.md b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/README.md
index 331ca56b..f021cfa3 100644
--- a/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/README.md
+++ b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/README.md
@@ -51,14 +51,14 @@ In order to run example, you also need to download coco.yaml. You can download t
## Dependencies ⚙️
-| Dependency | Version |
-| -------------------------------- | -------------- |
-| Onnxruntime(linux,windows,macos) | >=1.14.1 |
-| OpenCV | >=4.0.0 |
-| C++ Standard | >=17 |
-| Cmake | >=3.5 |
-| Cuda (Optional) | >=11.4 \<12.0 |
-| cuDNN (Cuda required) | =8 |
+| Dependency | Version |
+| -------------------------------- | ------------- |
+| Onnxruntime(linux,windows,macos) | >=1.14.1 |
+| OpenCV | >=4.0.0 |
+| C++ Standard | >=17 |
+| Cmake | >=3.5 |
+| Cuda (Optional) | >=11.4 \<12.0 |
+| cuDNN (Cuda required) | =8 |
Note: The dependency on C++17 is due to the usage of the C++17 filesystem feature.
diff --git a/mkdocs.yml b/mkdocs.yml
index df86a92a..b775b1f3 100644
--- a/mkdocs.yml
+++ b/mkdocs.yml
@@ -188,8 +188,19 @@ nav:
- Advanced Customization: usage/engine.md
- Modes:
- modes/index.md
+ - Train: modes/train.md
+ - Val: modes/val.md
+ - Predict: modes/predict.md
+ - Export: modes/export.md
+ - Track: modes/track.md
+ - Benchmark: modes/benchmark.md
- Tasks:
- tasks/index.md
+ - Detect: tasks/detect.md
+ - Segment: tasks/segment.md
+ - Classify: tasks/classify.md
+ - Pose: tasks/pose.md
+ - OBB: tasks/obb.md
- Models:
- models/index.md
- Datasets:
@@ -382,6 +393,7 @@ nav:
- Paperspace Gradient: integrations/paperspace.md
- Google Colab: integrations/google-colab.md
- HUB:
+ - hub/index.md
- Web:
- hub/index.md
- Quickstart: hub/quickstart.md