Add Chinese Modes and Tasks Docs (#6274)
Signed-off-by: Glenn Jocher <glenn.jocher@ultralytics.com> Co-authored-by: pre-commit-ci[bot] <66853113+pre-commit-ci[bot]@users.noreply.github.com>
This commit is contained in:
parent
795b95bdcb
commit
e3a538bbde
293 changed files with 3681 additions and 736 deletions
88
docs/en/yolov5/environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial.md
Normal file
88
docs/en/yolov5/environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
comments: true
|
||||
description: Step-by-step guide to run YOLOv5 on AWS Deep Learning instance. Learn how to create an instance, connect to it and train, validate and deploy models.
|
||||
keywords: AWS, YOLOv5, instance, deep learning, Ultralytics, guide, training, deployment, object detection
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# YOLOv5 🚀 on AWS Deep Learning Instance: A Comprehensive Guide
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will help new users run YOLOv5 on an Amazon Web Services (AWS) Deep Learning instance. AWS offers a [Free Tier](https://aws.amazon.com/free/) and a [credit program](https://aws.amazon.com/activate/) for a quick and affordable start.
|
||||
|
||||
Other quickstart options for YOLOv5 include our [Colab Notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb) <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>, [GCP Deep Learning VM](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial), and our Docker image at [Docker Hub](https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>. *Updated: 21 April 2023*.
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. AWS Console Sign-in
|
||||
|
||||
Create an account or sign in to the AWS console at [https://aws.amazon.com/console/](https://aws.amazon.com/console/) and select the **EC2** service.
|
||||
|
||||
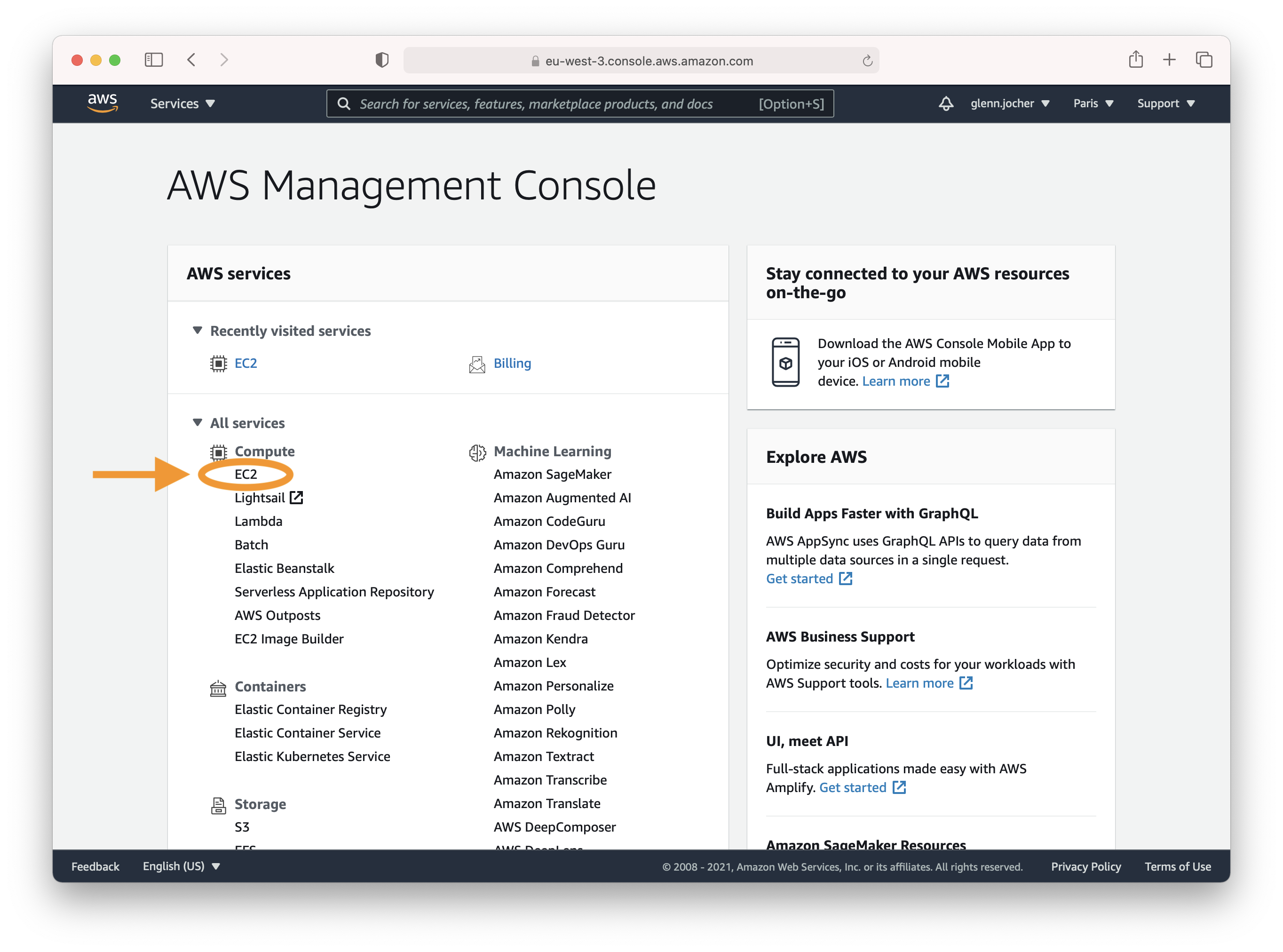
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. Launch Instance
|
||||
|
||||
In the EC2 section of the AWS console, click the **Launch instance** button.
|
||||
|
||||
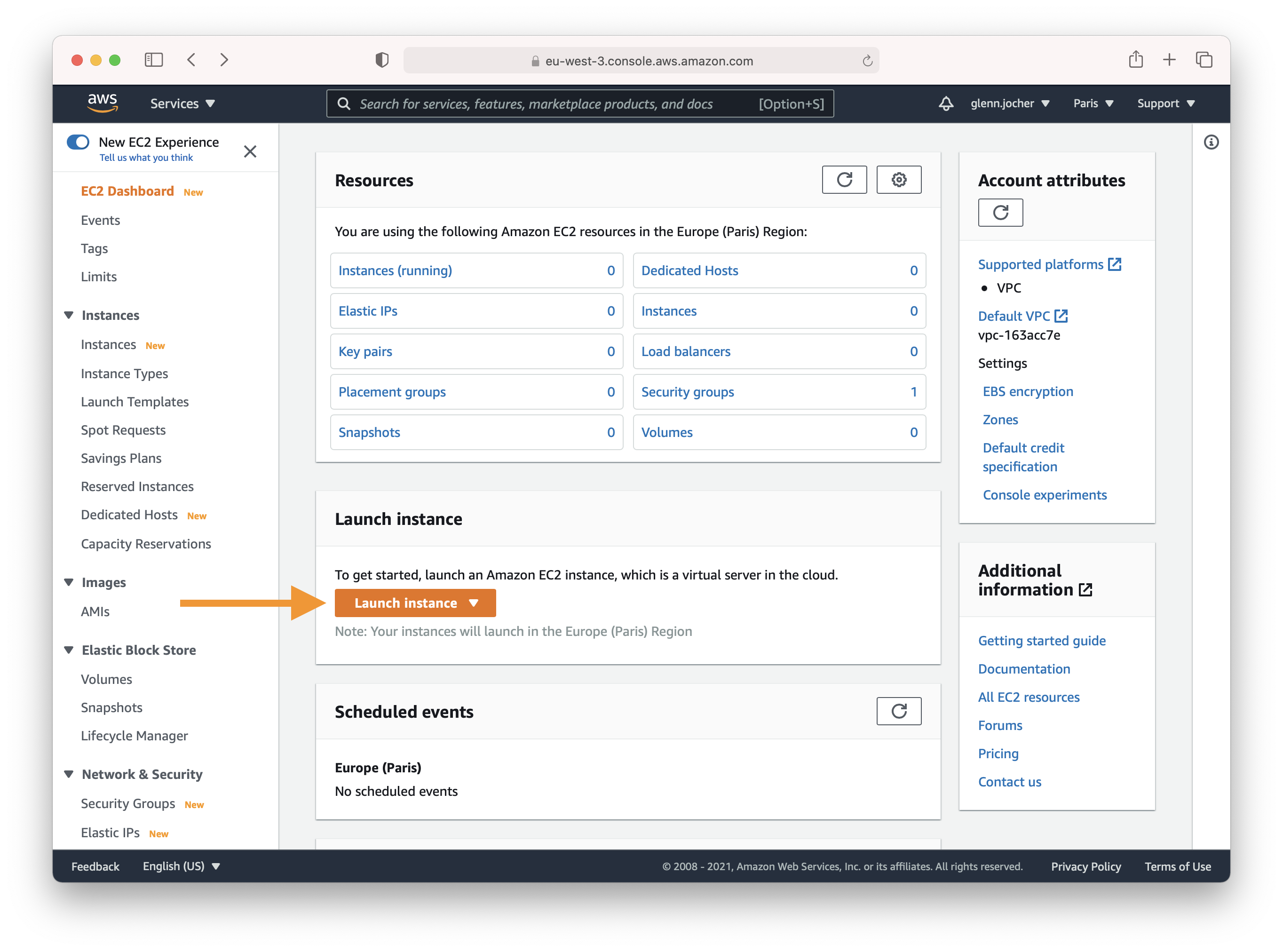
|
||||
|
||||
### Choose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
|
||||
|
||||
Enter 'Deep Learning' in the search field and select the most recent Ubuntu Deep Learning AMI (recommended), or an alternative Deep Learning AMI. For more information on selecting an AMI, see [Choosing Your DLAMI](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/dlami/latest/devguide/options.html).
|
||||
|
||||
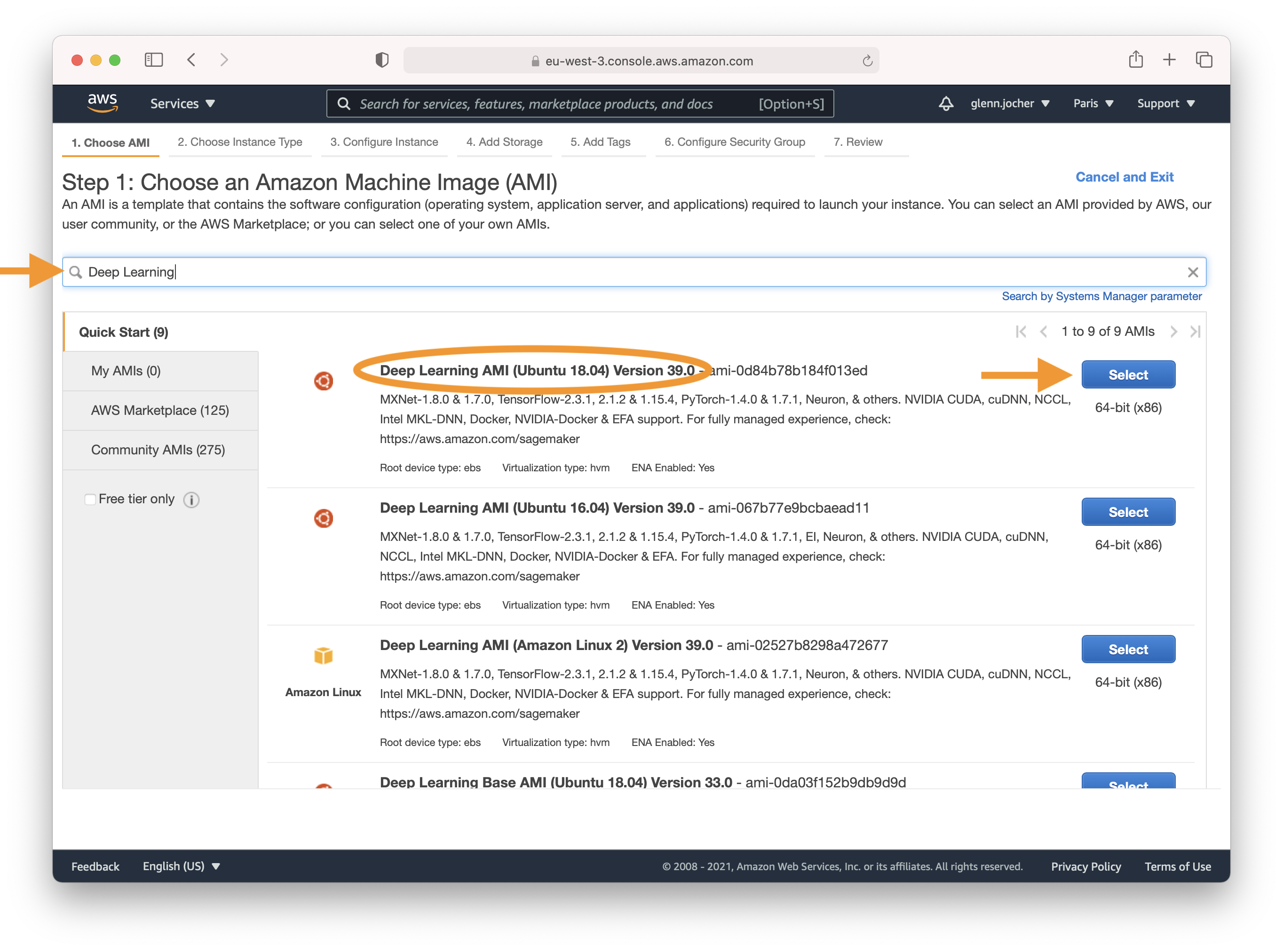
|
||||
|
||||
### Select an Instance Type
|
||||
|
||||
A GPU instance is recommended for most deep learning purposes. Training new models will be faster on a GPU instance than a CPU instance. Multi-GPU instances or distributed training across multiple instances with GPUs can offer sub-linear scaling. To set up distributed training, see [Distributed Training](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/dlami/latest/devguide/distributed-training.html).
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** The size of your model should be a factor in selecting an instance. If your model exceeds an instance's available RAM, select a different instance type with enough memory for your application.
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to [EC2 Instance Types](https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/instance-types/) and choose Accelerated Computing to see the different GPU instance options.
|
||||
|
||||
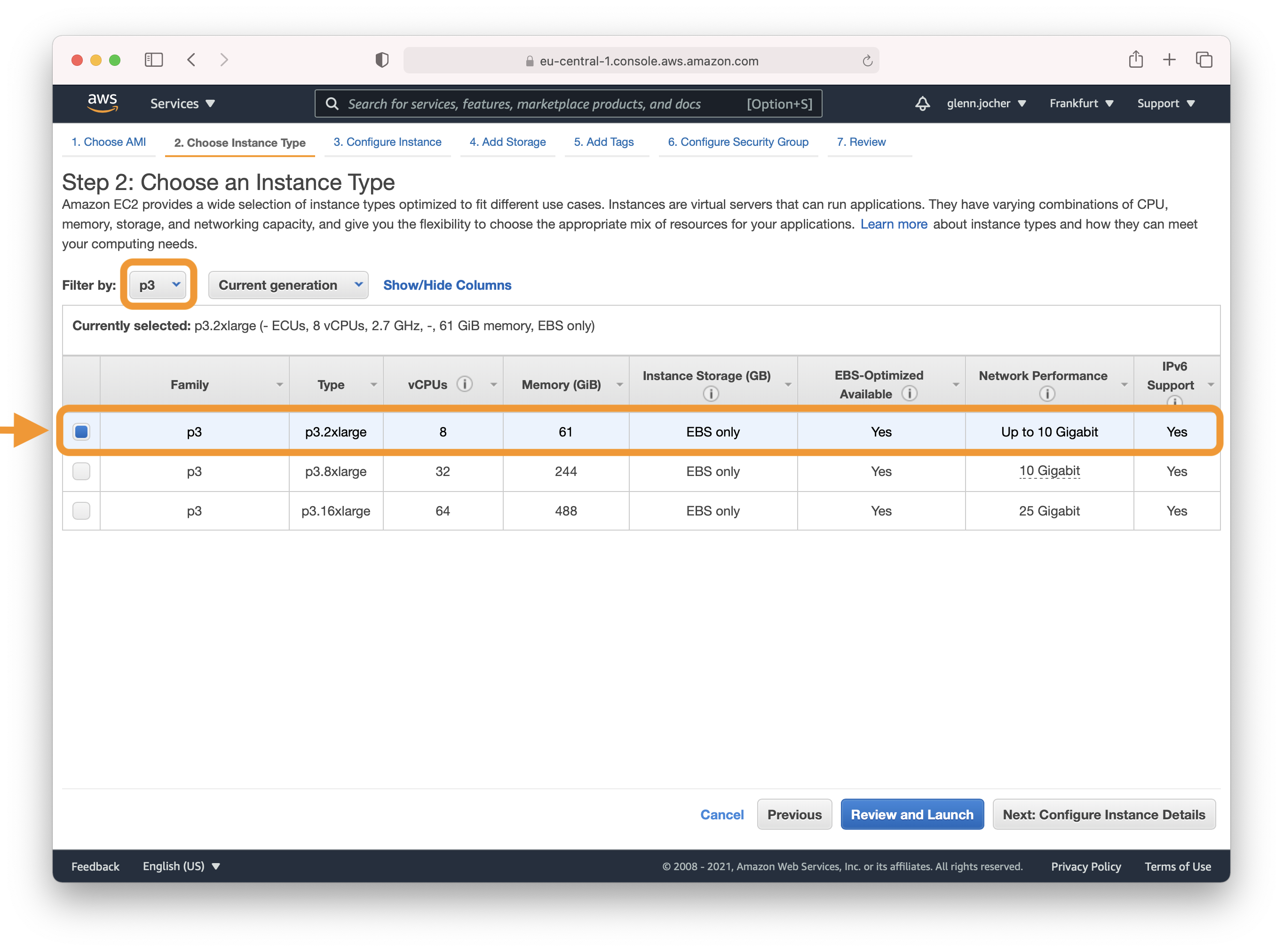
|
||||
|
||||
For more information on GPU monitoring and optimization, see [GPU Monitoring and Optimization](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/dlami/latest/devguide/tutorial-gpu.html). For pricing, see [On-Demand Pricing](https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/pricing/on-demand/) and [Spot Pricing](https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/spot/pricing/).
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure Instance Details
|
||||
|
||||
Amazon EC2 Spot Instances let you take advantage of unused EC2 capacity in the AWS cloud. Spot Instances are available at up to a 70% discount compared to On-Demand prices. We recommend a persistent spot instance, which will save your data and restart automatically when spot instance availability returns after spot instance termination. For full-price On-Demand instances, leave these settings at their default values.
|
||||
|
||||
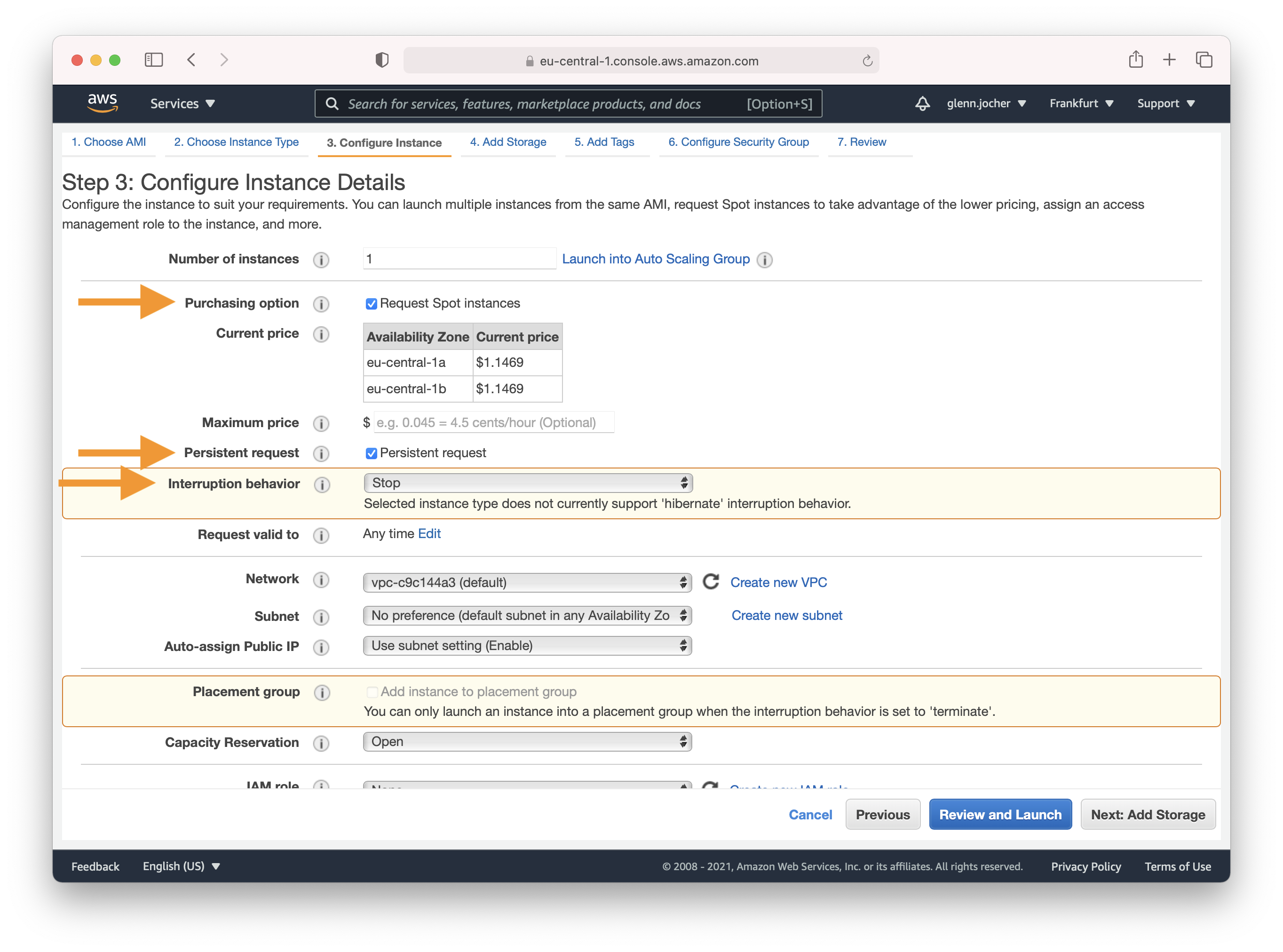
|
||||
|
||||
Complete Steps 4-7 to finalize your instance hardware and security settings, and then launch the instance.
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. Connect to Instance
|
||||
|
||||
Select the checkbox next to your running instance, and then click Connect. Copy and paste the SSH terminal command into a terminal of your choice to connect to your instance.
|
||||
|
||||
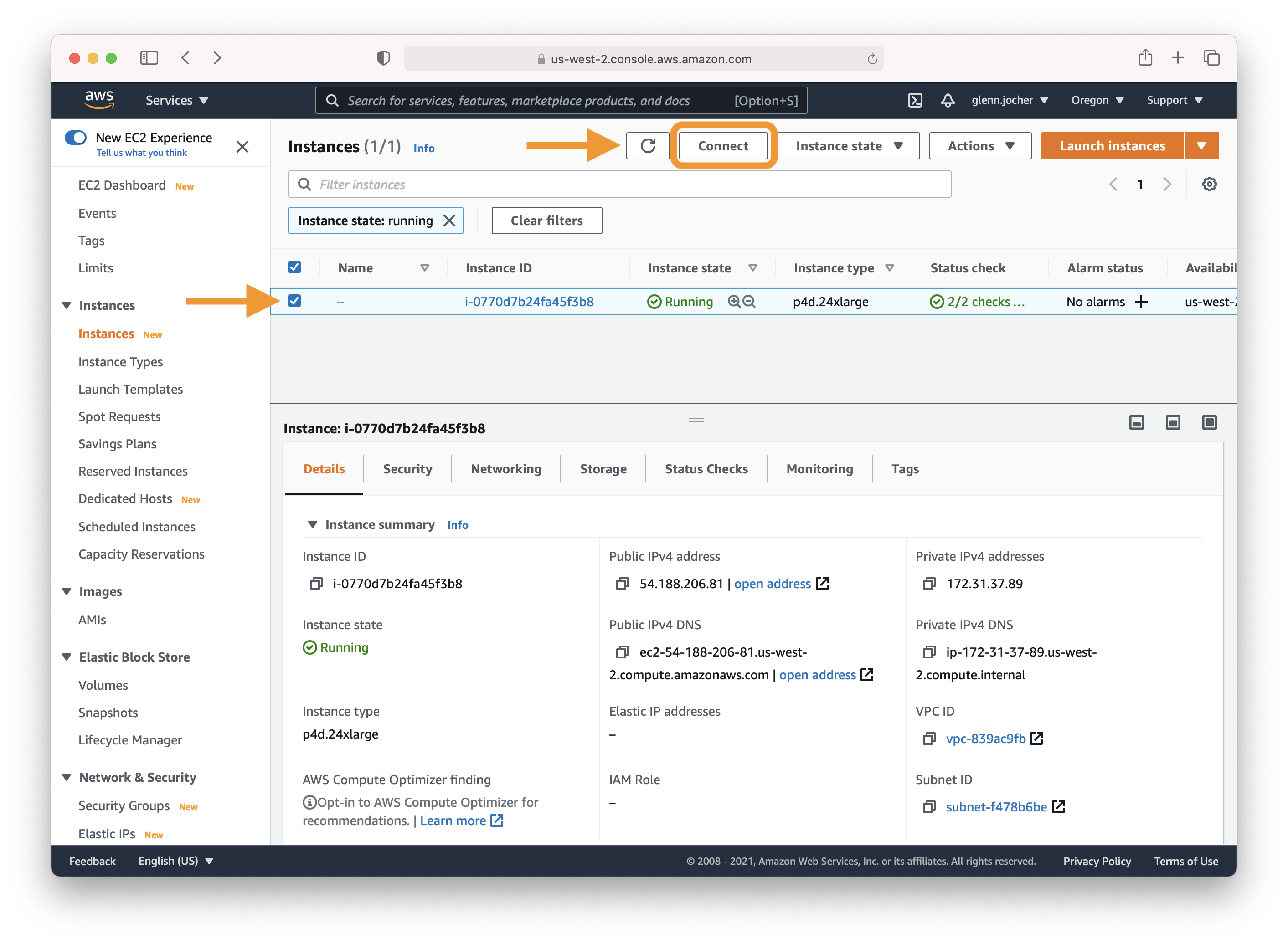
|
||||
|
||||
## 4. Run YOLOv5
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have logged in to your instance, clone the repository and install the dependencies in a [**Python>=3.8.0**](https://www.python.org/) environment, including [**PyTorch>=1.8**](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/). [Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/tree/master/models) and [datasets](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/tree/master/data) download automatically from the latest YOLOv5 [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases).
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 # clone
|
||||
cd yolov5
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt # install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, start training, testing, detecting, and exporting YOLOv5 models:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python train.py # train a model
|
||||
python val.py --weights yolov5s.pt # validate a model for Precision, Recall, and mAP
|
||||
python detect.py --weights yolov5s.pt --source path/to/images # run inference on images and videos
|
||||
python export.py --weights yolov5s.pt --include onnx coreml tflite # export models to other formats
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Optional Extras
|
||||
|
||||
Add 64GB of swap memory (to `--cache` large datasets):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo fallocate -l 64G /swapfile
|
||||
sudo chmod 600 /swapfile
|
||||
sudo mkswap /swapfile
|
||||
sudo swapon /swapfile
|
||||
free -h # check memory
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you have successfully set up and run YOLOv5 on an AWS Deep Learning instance. Enjoy training, testing, and deploying your object detection models!
|
||||
95
docs/en/yolov5/environments/azureml_quickstart_tutorial.md
Normal file
95
docs/en/yolov5/environments/azureml_quickstart_tutorial.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
comments: true
|
||||
description: Azure Machine Learning YOLOv5 quickstart
|
||||
keywords: Ultralytics, YOLO, Deep Learning, Object detection, quickstart, Azure, AzureML
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# YOLOv5 🚀 on AzureML
|
||||
|
||||
This guide provides a quickstart to use YOLOv5 from an AzureML compute instance.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that this guide is a quickstart for quick trials. If you want to unlock the full power AzureML, you can find the documentation to:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Create a data asset](https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/machine-learning/how-to-create-data-assets)
|
||||
- [Create an AzureML job](https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/machine-learning/how-to-train-model)
|
||||
- [Register a model](https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/machine-learning/how-to-manage-models)
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
You need an [AzureML workspace](https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/machine-learning/concept-workspace?view=azureml-api-2).
|
||||
|
||||
## Create a compute instance
|
||||
|
||||
From your AzureML workspace, select Compute > Compute instances > New, select the instance with the resources you need.
|
||||
|
||||
<img width="1741" alt="create-compute-arrow" src="https://github.com/ouphi/ultralytics/assets/17216799/3e92fcc0-a08e-41a4-af81-d289cfe3b8f2">
|
||||
|
||||
## Open a Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
Now from the Notebooks view, open a Terminal and select your compute.
|
||||
|
||||
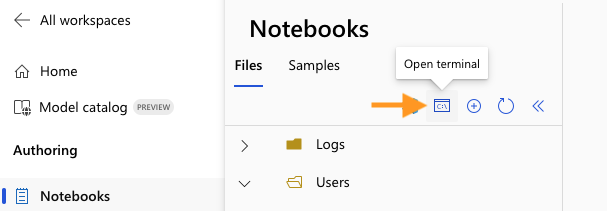
|
||||
|
||||
## Setup and run YOLOv5
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can, create a virtual environment:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
conda create --name yolov5env -y
|
||||
conda activate yolov5env
|
||||
conda install pip -y
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Clone YOLOv5 repository with its submodules:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
|
||||
cd yolov5
|
||||
git submodule update --init --recursive # Note that you might have a message asking you to add your folder as a safe.directory just copy the recommended command
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Install the required dependencies:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -r yolov5/requirements.txt
|
||||
pip install onnx>=1.10.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Train the YOLOv5 model:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python train.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Validate the model for Precision, Recall, and mAP
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python val.py --weights yolov5s.pt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run inference on images and videos:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python detect.py --weights yolov5s.pt --source path/to/images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Export models to other formats:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python detect.py --weights yolov5s.pt --source path/to/images
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Notes on using a notebook
|
||||
|
||||
Note that if you want to run these commands from a Notebook, you need to [create a new Kernel](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/how-to-access-terminal?view=azureml-api-2#add-new-kernels)
|
||||
and select your new Kernel on the top of your Notebook.
|
||||
|
||||
If you create Python cells it will automatically use your custom environment, but if you add bash cells, you will need to run `source activate <your-env>` on each of these cells to make sure it uses your custom environment.
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
%%bash
|
||||
source activate newenv
|
||||
python val.py --weights yolov5s.pt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
comments: true
|
||||
description: Learn how to set up and run YOLOv5 in a Docker container. This tutorial includes the prerequisites and step-by-step instructions.
|
||||
keywords: YOLOv5, Docker, Ultralytics, Image Detection, YOLOv5 Docker Image, Docker Container, Machine Learning, AI
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Get Started with YOLOv5 🚀 in Docker
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial will guide you through the process of setting up and running YOLOv5 in a Docker container.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also explore other quickstart options for YOLOv5, such as our [Colab Notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb) <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>, [GCP Deep Learning VM](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial), and [Amazon AWS](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial). *Updated: 21 April 2023*.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Nvidia Driver**: Version 455.23 or higher. Download from [Nvidia's website](https://www.nvidia.com/Download/index.aspx).
|
||||
2. **Nvidia-Docker**: Allows Docker to interact with your local GPU. Installation instructions are available on the [Nvidia-Docker GitHub repository](https://github.com/NVIDIA/nvidia-docker).
|
||||
3. **Docker Engine - CE**: Version 19.03 or higher. Download and installation instructions can be found on the [Docker website](https://docs.docker.com/install/).
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1: Pull the YOLOv5 Docker Image
|
||||
|
||||
The Ultralytics YOLOv5 DockerHub repository is available at [https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5](https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5). Docker Autobuild ensures that the `ultralytics/yolov5:latest` image is always in sync with the most recent repository commit. To pull the latest image, run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo docker pull ultralytics/yolov5:latest
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2: Run the Docker Container
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic container:
|
||||
|
||||
Run an interactive instance of the YOLOv5 Docker image (called a "container") using the `-it` flag:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo docker run --ipc=host -it ultralytics/yolov5:latest
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Container with local file access:
|
||||
|
||||
To run a container with access to local files (e.g., COCO training data in `/datasets`), use the `-v` flag:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo docker run --ipc=host -it -v "$(pwd)"/datasets:/usr/src/datasets ultralytics/yolov5:latest
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Container with GPU access:
|
||||
|
||||
To run a container with GPU access, use the `--gpus all` flag:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo docker run --ipc=host -it --gpus all ultralytics/yolov5:latest
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 3: Use YOLOv5 🚀 within the Docker Container
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can train, test, detect, and export YOLOv5 models within the running Docker container:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python train.py # train a model
|
||||
python val.py --weights yolov5s.pt # validate a model for Precision, Recall, and mAP
|
||||
python detect.py --weights yolov5s.pt --source path/to/images # run inference on images and videos
|
||||
python export.py --weights yolov5s.pt --include onnx coreml tflite # export models to other formats
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center"><img width="1000" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26833433/142224770-6e57caaf-ac01-4719-987f-c37d1b6f401f.png"></p>
|
||||
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
comments: true
|
||||
description: Step-by-step tutorial on how to set up and run YOLOv5 on Google Cloud Platform Deep Learning VM. Perfect guide for beginners and GCP new users!.
|
||||
keywords: YOLOv5, Google Cloud Platform, GCP, Deep Learning VM, Ultralytics
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Run YOLOv5 🚀 on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Deep Learning Virtual Machine (VM) ⭐
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial will guide you through the process of setting up and running YOLOv5 on a GCP Deep Learning VM. New GCP users are eligible for a [$300 free credit offer](https://cloud.google.com/free/docs/gcp-free-tier#free-trial).
|
||||
|
||||
You can also explore other quickstart options for YOLOv5, such as our [Colab Notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb) <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>, [Amazon AWS](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial) and our Docker image at [Docker Hub](https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>. *Updated: 21 April 2023*.
|
||||
|
||||
**Last Updated**: 6 May 2022
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 1: Create a Deep Learning VM
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to the [GCP marketplace](https://console.cloud.google.com/marketplace/details/click-to-deploy-images/deeplearning) and select a **Deep Learning VM**.
|
||||
2. Choose an **n1-standard-8** instance (with 8 vCPUs and 30 GB memory).
|
||||
3. Add a GPU of your choice.
|
||||
4. Check 'Install NVIDIA GPU driver automatically on first startup?'
|
||||
5. Select a 300 GB SSD Persistent Disk for sufficient I/O speed.
|
||||
6. Click 'Deploy'.
|
||||
|
||||
The preinstalled [Anaconda](https://docs.anaconda.com/anaconda/packages/pkg-docs/) Python environment includes all dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
<img width="1000" alt="GCP Marketplace" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26833433/105811495-95863880-5f61-11eb-841d-c2f2a5aa0ffe.png">
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 2: Set Up the VM
|
||||
|
||||
Clone the YOLOv5 repository and install the [requirements.txt](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/requirements.txt) in a [**Python>=3.8.0**](https://www.python.org/) environment, including [**PyTorch>=1.8**](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/). [Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/tree/master/models) and [datasets](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/tree/master/data) will be downloaded automatically from the latest YOLOv5 [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases).
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 # clone
|
||||
cd yolov5
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt # install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Step 3: Run YOLOv5 🚀 on the VM
|
||||
|
||||
You can now train, test, detect, and export YOLOv5 models on your VM:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python train.py # train a model
|
||||
python val.py --weights yolov5s.pt # validate a model for Precision, Recall, and mAP
|
||||
python detect.py --weights yolov5s.pt --source path/to/images # run inference on images and videos
|
||||
python export.py --weights yolov5s.pt --include onnx coreml tflite # export models to other formats
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img width="1000" alt="GCP terminal" src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26833433/142223900-275e5c9e-e2b5-43f7-a21c-35c4ca7de87c.png">
|
||||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue