Docs: HUB Updates (#12804)
Signed-off-by: Glenn Jocher <glenn.jocher@ultralytics.com> Co-authored-by: Glenn Jocher <glenn.jocher@ultralytics.com>
This commit is contained in:
parent
4afcb35186
commit
d25dd182d6
14 changed files with 760 additions and 514 deletions
|
|
@ -1,17 +1,16 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
comments: true
|
||||
description: Access object detection capabilities of YOLOv8 via our RESTful API. Learn how to use the YOLO Inference API with Python or cURL for swift object detection.
|
||||
keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv8, Inference API, object detection, RESTful API, Python, cURL, Quickstart
|
||||
description: Effortlessly run AI model inferences with Ultralytics HUB Inference API. Perfect for developers!.
|
||||
keywords: Ultralytics HUB, Inference API, YOLO, REST API, machine learning, AI model inference, remote inference
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# YOLO Inference API
|
||||
# Ultralytics HUB Inference API
|
||||
|
||||
The YOLO Inference API allows you to access the YOLOv8 object detection capabilities via a RESTful API. This enables you to run object detection on images without the need to install and set up the YOLOv8 environment locally.
|
||||
The [Ultralytics HUB](https://bit.ly/ultralytics_hub) Inference API allows you to run inference through our REST API without the need to install and set up the Ultralytics YOLO environment locally.
|
||||
|
||||
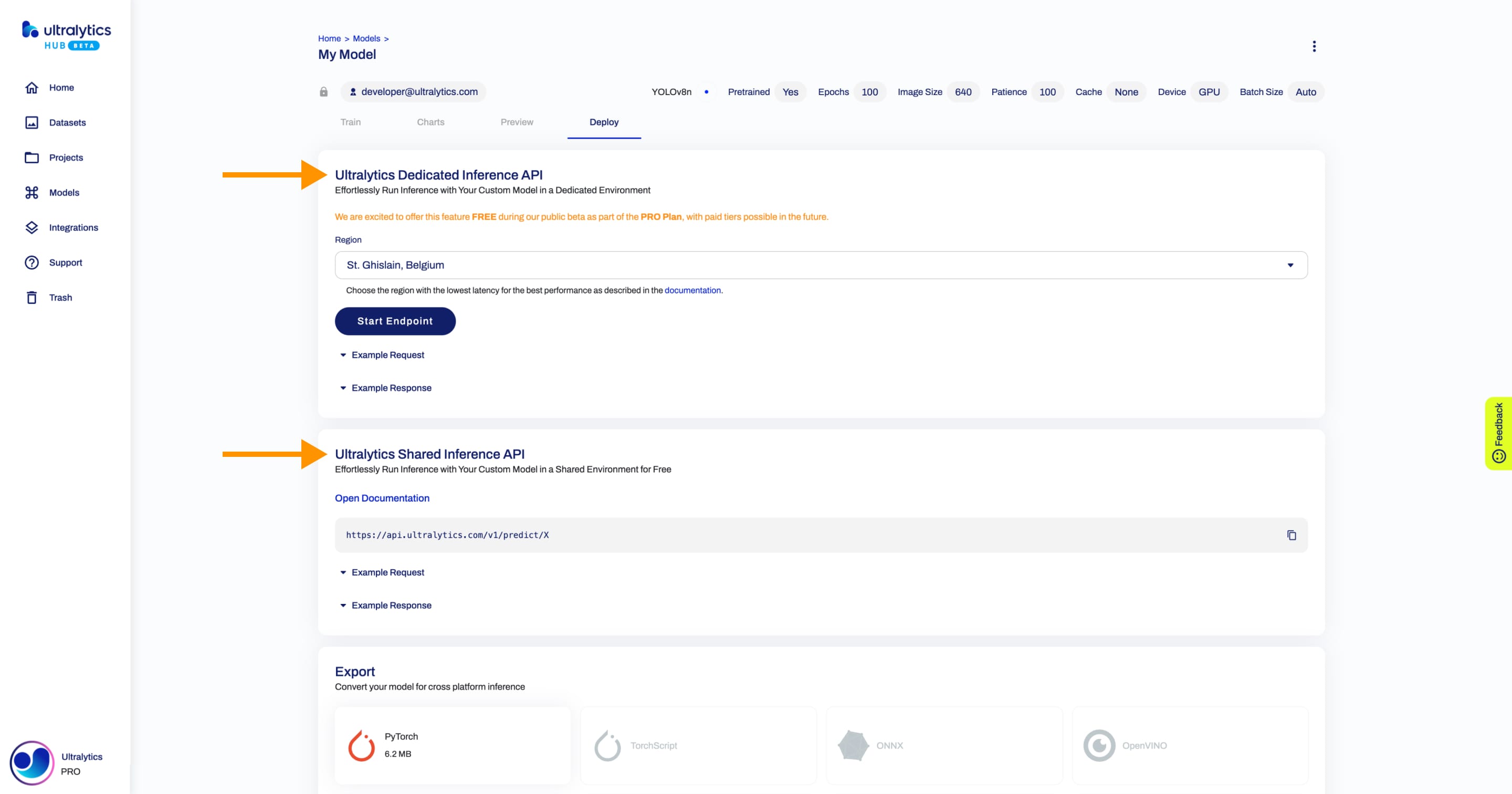
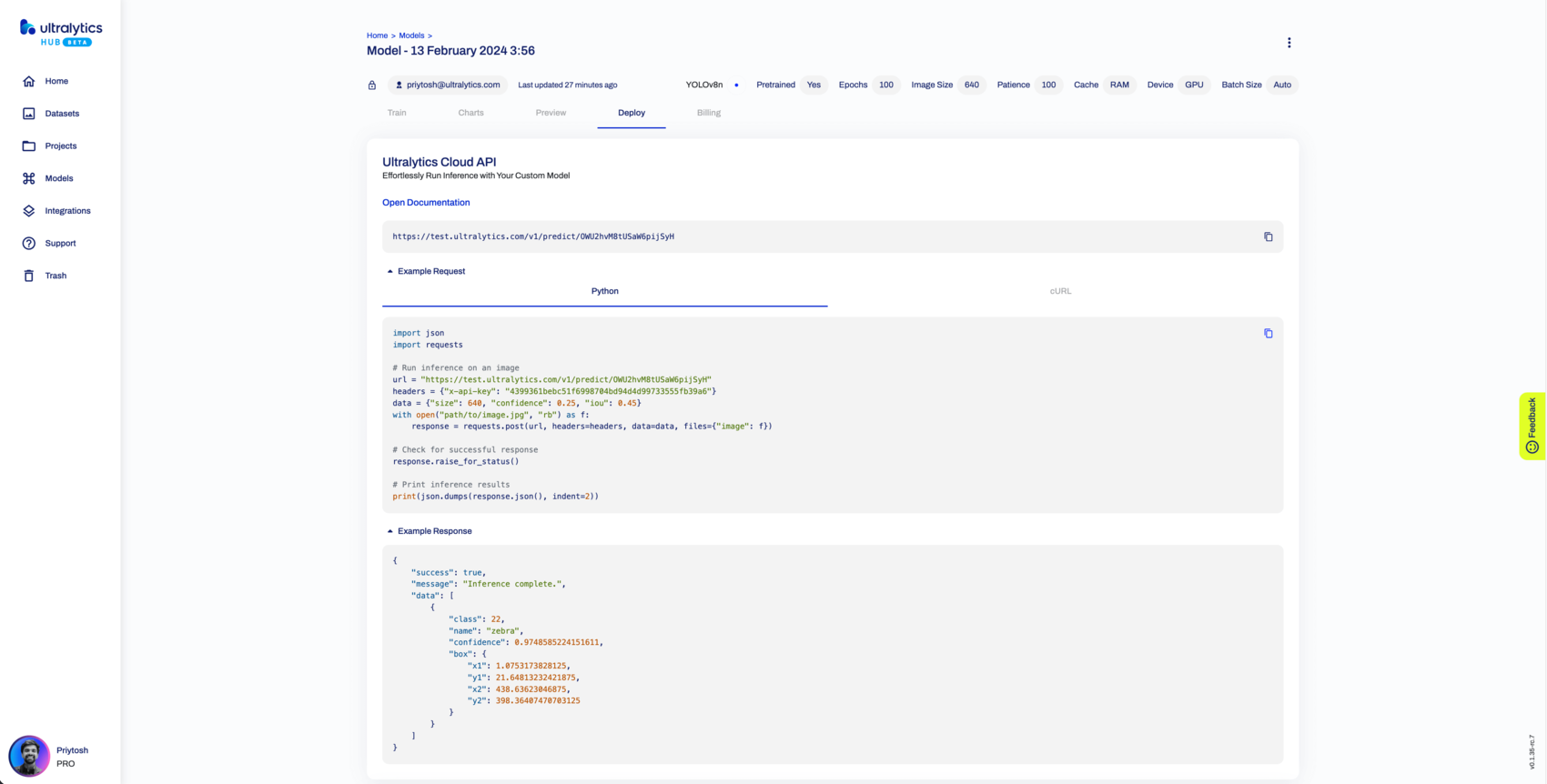 Screenshot of the Inference API section in the trained model Preview tab.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<iframe loading="lazy" width="720" height="405" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/OpWpBI35A5Y"
|
||||
title="YouTube video player" frameborder="0"
|
||||
allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share"
|
||||
|
|
@ -21,17 +20,9 @@ The YOLO Inference API allows you to access the YOLOv8 object detection capabili
|
|||
<strong>Watch:</strong> Ultralytics HUB Inference API Walkthrough
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
## API URL
|
||||
## Python
|
||||
|
||||
The API URL is the address used to access the YOLO Inference API. In this case, the base URL is:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
https://api.ultralytics.com/v1/predict
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Example Usage in Python
|
||||
|
||||
To access the YOLO Inference API with the specified model and API key using Python, you can use the following code:
|
||||
To access the [Ultralytics HUB](https://bit.ly/ultralytics_hub) Inference API using Python, use the following code:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
|
|
@ -53,11 +44,13 @@ with open("path/to/image.jpg", "rb") as image_file:
|
|||
print(response.json())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, replace `API_KEY` with your actual API key, `MODEL_ID` with the desired model ID, and `path/to/image.jpg` with the path to the image you want to analyze.
|
||||
!!! note "Note"
|
||||
|
||||
## Example Usage with cURL
|
||||
Replace `MODEL_ID` with the desired model ID, `API_KEY` with your actual API key, and `path/to/image.jpg` with the path to the image you want to run inference on.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the YOLO Inference API with client URL (cURL) by utilizing the `curl` command. Replace `API_KEY` with your actual API key, `MODEL_ID` with the desired model ID, and `image.jpg` with the path to the image you want to analyze:
|
||||
## cURL
|
||||
|
||||
To access the [Ultralytics HUB](https://bit.ly/ultralytics_hub) Inference API using cURL, use the following code:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl -X POST "https://api.ultralytics.com/v1/predict/MODEL_ID" \
|
||||
|
|
@ -68,55 +61,97 @@ curl -X POST "https://api.ultralytics.com/v1/predict/MODEL_ID" \
|
|||
-F "iou=0.45"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Passing Arguments
|
||||
!!! note "Note"
|
||||
|
||||
This command sends a POST request to the YOLO Inference API with the specified `MODEL_ID` in the URL and the `API_KEY` in the request `headers`, along with the image file specified by `@path/to/image.jpg`.
|
||||
Replace `MODEL_ID` with the desired model ID, `API_KEY` with your actual API key, and `path/to/image.jpg` with the path to the image you want to run inference on.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example of passing the `size`, `confidence`, and `iou` arguments via the API URL using the `requests` library in Python:
|
||||
## Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
See the table below for a full list of available inference arguments.
|
||||
|
||||
# API URL, use actual MODEL_ID
|
||||
url = f"https://api.ultralytics.com/v1/predict/MODEL_ID"
|
||||
| Argument | Default | Type | Description |
|
||||
| ------------ | ------- | ------- | -------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| `image` | | `image` | image file |
|
||||
| `url` | | `str` | URL of the image if not passing a file |
|
||||
| `size` | `640` | `int` | valid range `32` - `1280` pixels |
|
||||
| `confidence` | `0.25` | `float` | valid range `0.01` - `1.0` |
|
||||
| `iou` | `0.45` | `float` | valid range `0.0` - `0.95` |
|
||||
|
||||
# Headers, use actual API_KEY
|
||||
headers = {"x-api-key": "API_KEY"}
|
||||
## Response
|
||||
|
||||
# Inference arguments (optional)
|
||||
data = {"size": 640, "confidence": 0.25, "iou": 0.45}
|
||||
The [Ultralytics HUB](https://bit.ly/ultralytics_hub) Inference API returns a JSON response.
|
||||
|
||||
# Load image and send request
|
||||
with open("path/to/image.jpg", "rb") as image_file:
|
||||
files = {"image": image_file}
|
||||
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, files=files, data=data)
|
||||
### Classification
|
||||
|
||||
print(response.json())
|
||||
```
|
||||
!!! Example "Classification Model"
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, the `data` dictionary contains the query arguments `size`, `confidence`, and `iou`, which tells the API to run inference at image size 640 with confidence and IoU thresholds of 0.25 and 0.45.
|
||||
=== "`ultralytics`"
|
||||
|
||||
This will send the query parameters along with the file in the POST request. See the table below for a full list of available inference arguments.
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
| Inference Argument | Default | Type | Notes |
|
||||
|--------------------|---------|---------|------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| `size` | `640` | `int` | valid range is `32` - `1280` pixels |
|
||||
| `confidence` | `0.25` | `float` | valid range is `0.01` - `1.0` |
|
||||
| `iou` | `0.45` | `float` | valid range is `0.0` - `0.95` |
|
||||
| `url` | `''` | `str` | optional image URL if not image file is passed |
|
||||
| `normalize` | `False` | `bool` | |
|
||||
# Load model
|
||||
model = YOLO('yolov8n-cls.pt')
|
||||
|
||||
## Return JSON format
|
||||
# Run inference
|
||||
results = model('image.jpg')
|
||||
|
||||
The YOLO Inference API returns a JSON list with the detection results. The format of the JSON list will be the same as the one produced locally by the `results[0].tojson()` command.
|
||||
# Print image.jpg results in JSON format
|
||||
print(results[0].tojson())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The JSON list contains information about the detected objects, their coordinates, classes, and confidence scores.
|
||||
=== "cURL"
|
||||
|
||||
### Detect Model Format
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl -X POST "https://api.ultralytics.com/v1/predict/MODEL_ID" \
|
||||
-H "x-api-key: API_KEY" \
|
||||
-F "image=@/path/to/image.jpg" \
|
||||
-F "size=640" \
|
||||
-F "confidence=0.25" \
|
||||
-F "iou=0.45"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
YOLO detection models, such as `yolov8n.pt`, can return JSON responses from local inference, cURL inference, and Python inference. All of these methods produce the same JSON response format.
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Detect Model JSON Response"
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
|
||||
# API URL, use actual MODEL_ID
|
||||
url = f"https://api.ultralytics.com/v1/predict/MODEL_ID"
|
||||
|
||||
# Headers, use actual API_KEY
|
||||
headers = {"x-api-key": "API_KEY"}
|
||||
|
||||
# Inference arguments (optional)
|
||||
data = {"size": 640, "confidence": 0.25, "iou": 0.45}
|
||||
|
||||
# Load image and send request
|
||||
with open("path/to/image.jpg", "rb") as image_file:
|
||||
files = {"image": image_file}
|
||||
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, files=files, data=data)
|
||||
|
||||
print(response.json())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Response"
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
success: true,
|
||||
message: "Inference complete.",
|
||||
data: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
class: 0,
|
||||
name: "person",
|
||||
confidence: 0.92
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Detection
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Detection Model"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "`ultralytics`"
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -166,55 +201,103 @@ YOLO detection models, such as `yolov8n.pt`, can return JSON responses from loca
|
|||
print(response.json())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "JSON Response"
|
||||
=== "Response"
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"success": True,
|
||||
"message": "Inference complete.",
|
||||
"data": [
|
||||
success: true,
|
||||
message: "Inference complete.",
|
||||
data: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "person",
|
||||
"class": 0,
|
||||
"confidence": 0.8359682559967041,
|
||||
"box": {
|
||||
"x1": 0.08974208831787109,
|
||||
"y1": 0.27418340047200523,
|
||||
"x2": 0.8706787109375,
|
||||
"y2": 0.9887352837456598
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "person",
|
||||
"class": 0,
|
||||
"confidence": 0.8189555406570435,
|
||||
"box": {
|
||||
"x1": 0.5847355842590332,
|
||||
"y1": 0.05813225640190972,
|
||||
"x2": 0.8930277824401855,
|
||||
"y2": 0.9903111775716146
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "tie",
|
||||
"class": 27,
|
||||
"confidence": 0.2909725308418274,
|
||||
"box": {
|
||||
"x1": 0.3433395862579346,
|
||||
"y1": 0.6070465511745877,
|
||||
"x2": 0.40964522361755373,
|
||||
"y2": 0.9849439832899306
|
||||
}
|
||||
class: 0,
|
||||
name: "person",
|
||||
confidence: 0.92,
|
||||
width: 0.4893378019332886,
|
||||
height: 0.7437513470649719,
|
||||
xcenter: 0.4434437155723572,
|
||||
ycenter: 0.5198975801467896
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Segment Model Format
|
||||
### OBB
|
||||
|
||||
YOLO segmentation models, such as `yolov8n-seg.pt`, can return JSON responses from local inference, cURL inference, and Python inference. All of these methods produce the same JSON response format.
|
||||
!!! Example "OBB Model"
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Segment Model JSON Response"
|
||||
=== "`ultralytics`"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Load model
|
||||
model = YOLO('yolov8n-obb.pt')
|
||||
|
||||
# Run inference
|
||||
results = model('image.jpg')
|
||||
|
||||
# Print image.jpg results in JSON format
|
||||
print(results[0].tojson())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "cURL"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
curl -X POST "https://api.ultralytics.com/v1/predict/MODEL_ID" \
|
||||
-H "x-api-key: API_KEY" \
|
||||
-F "image=@/path/to/image.jpg" \
|
||||
-F "size=640" \
|
||||
-F "confidence=0.25" \
|
||||
-F "iou=0.45"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
|
||||
# API URL, use actual MODEL_ID
|
||||
url = f"https://api.ultralytics.com/v1/predict/MODEL_ID"
|
||||
|
||||
# Headers, use actual API_KEY
|
||||
headers = {"x-api-key": "API_KEY"}
|
||||
|
||||
# Inference arguments (optional)
|
||||
data = {"size": 640, "confidence": 0.25, "iou": 0.45}
|
||||
|
||||
# Load image and send request
|
||||
with open("path/to/image.jpg", "rb") as image_file:
|
||||
files = {"image": image_file}
|
||||
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, files=files, data=data)
|
||||
|
||||
print(response.json())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Response"
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
success: true,
|
||||
message: "Inference complete.",
|
||||
data: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
class: 0,
|
||||
name: "person",
|
||||
confidence: 0.92,
|
||||
obb: [
|
||||
0.669310450553894,
|
||||
0.6247171759605408,
|
||||
0.9847468137741089,
|
||||
...
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Segmentation
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Segmentation Model"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "`ultralytics`"
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -264,98 +347,26 @@ YOLO segmentation models, such as `yolov8n-seg.pt`, can return JSON responses fr
|
|||
print(response.json())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "JSON Response"
|
||||
=== "Response"
|
||||
|
||||
Note `segments` `x` and `y` lengths may vary from one object to another. Larger or more complex objects may have more segment points.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"success": True,
|
||||
"message": "Inference complete.",
|
||||
"data": [
|
||||
success: true,
|
||||
message: "Inference complete.",
|
||||
data: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "person",
|
||||
"class": 0,
|
||||
"confidence": 0.856913149356842,
|
||||
"box": {
|
||||
"x1": 0.1064866065979004,
|
||||
"y1": 0.2798851860894097,
|
||||
"x2": 0.8738358497619629,
|
||||
"y2": 0.9894873725043403
|
||||
},
|
||||
"segments": {
|
||||
"x": [
|
||||
0.421875,
|
||||
0.4203124940395355,
|
||||
0.41718751192092896
|
||||
...
|
||||
],
|
||||
"y": [
|
||||
0.2888889014720917,
|
||||
0.2916666567325592,
|
||||
0.2916666567325592
|
||||
...
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "person",
|
||||
"class": 0,
|
||||
"confidence": 0.8512625694274902,
|
||||
"box": {
|
||||
"x1": 0.5757311820983887,
|
||||
"y1": 0.053943040635850696,
|
||||
"x2": 0.8960096359252929,
|
||||
"y2": 0.985154045952691
|
||||
},
|
||||
"segments": {
|
||||
"x": [
|
||||
0.7515624761581421,
|
||||
0.75,
|
||||
0.7437499761581421
|
||||
...
|
||||
],
|
||||
"y": [
|
||||
0.0555555559694767,
|
||||
0.05833333358168602,
|
||||
0.05833333358168602
|
||||
...
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "tie",
|
||||
"class": 27,
|
||||
"confidence": 0.6485961675643921,
|
||||
"box": {
|
||||
"x1": 0.33911995887756347,
|
||||
"y1": 0.6057066175672743,
|
||||
"x2": 0.4081430912017822,
|
||||
"y2": 0.9916408962673611
|
||||
},
|
||||
"segments": {
|
||||
"x": [
|
||||
0.37187498807907104,
|
||||
0.37031251192092896,
|
||||
0.3687500059604645
|
||||
...
|
||||
],
|
||||
"y": [
|
||||
0.6111111044883728,
|
||||
0.6138888597488403,
|
||||
0.6138888597488403
|
||||
...
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
class: 0,
|
||||
name: "person",
|
||||
confidence: 0.92,
|
||||
segment: [0.44140625, 0.15625, 0.439453125, ...]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Pose Model Format
|
||||
### Pose
|
||||
|
||||
YOLO pose models, such as `yolov8n-pose.pt`, can return JSON responses from local inference, cURL inference, and Python inference. All of these methods produce the same JSON response format.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Pose Model JSON Response"
|
||||
!!! Example "Pose Model"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "`ultralytics`"
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -363,7 +374,7 @@ YOLO pose models, such as `yolov8n-pose.pt`, can return JSON responses from loca
|
|||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Load model
|
||||
model = YOLO('yolov8n-seg.pt')
|
||||
model = YOLO('yolov8n-pose.pt')
|
||||
|
||||
# Run inference
|
||||
results = model('image.jpg')
|
||||
|
|
@ -405,75 +416,29 @@ YOLO pose models, such as `yolov8n-pose.pt`, can return JSON responses from loca
|
|||
print(response.json())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "JSON Response"
|
||||
=== "Response"
|
||||
|
||||
Note COCO-keypoints pretrained models will have 17 human keypoints. The `visible` part of the keypoints indicates whether a keypoint is visible or obscured. Obscured keypoints may be outside the image or may not be visible, i.e. a person's eyes facing away from the camera.
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"success": True,
|
||||
"message": "Inference complete.",
|
||||
"data": [
|
||||
success: true,
|
||||
message: "Inference complete.",
|
||||
data: [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "person",
|
||||
"class": 0,
|
||||
"confidence": 0.8439509868621826,
|
||||
"box": {
|
||||
"x1": 0.1125,
|
||||
"y1": 0.28194444444444444,
|
||||
"x2": 0.7953125,
|
||||
"y2": 0.9902777777777778
|
||||
},
|
||||
"keypoints": {
|
||||
"x": [
|
||||
0.5058594942092896,
|
||||
0.5103894472122192,
|
||||
0.4920862317085266
|
||||
...
|
||||
],
|
||||
"y": [
|
||||
0.48964157700538635,
|
||||
0.4643048942089081,
|
||||
0.4465252459049225
|
||||
...
|
||||
],
|
||||
"visible": [
|
||||
0.8726999163627625,
|
||||
0.653947651386261,
|
||||
0.9130823612213135
|
||||
...
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "person",
|
||||
"class": 0,
|
||||
"confidence": 0.7474289536476135,
|
||||
"box": {
|
||||
"x1": 0.58125,
|
||||
"y1": 0.0625,
|
||||
"x2": 0.8859375,
|
||||
"y2": 0.9888888888888889
|
||||
},
|
||||
"keypoints": {
|
||||
"x": [
|
||||
0.778544008731842,
|
||||
0.7976160049438477,
|
||||
0.7530890107154846
|
||||
...
|
||||
],
|
||||
"y": [
|
||||
0.27595141530036926,
|
||||
0.2378823608160019,
|
||||
0.23644638061523438
|
||||
...
|
||||
],
|
||||
"visible": [
|
||||
0.8900790810585022,
|
||||
0.789978563785553,
|
||||
0.8974530100822449
|
||||
...
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
class: 0,
|
||||
name: "person",
|
||||
confidence: 0.92,
|
||||
keypoints: [
|
||||
0.5290805697441101,
|
||||
0.20698919892311096,
|
||||
1.0,
|
||||
0.5263055562973022,
|
||||
0.19584226608276367,
|
||||
1.0,
|
||||
0.5094948410987854,
|
||||
0.19120082259178162,
|
||||
1.0,
|
||||
...
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue