Docs partial mdformat improvements (#7378)
Signed-off-by: Glenn Jocher <glenn.jocher@ultralytics.com> Co-authored-by: pre-commit-ci[bot] <66853113+pre-commit-ci[bot]@users.noreply.github.com>
This commit is contained in:
parent
ed73c0fedc
commit
bb1326a8ea
52 changed files with 231 additions and 261 deletions
|
|
@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ Here are some of the key models supported:
|
|||
|
||||
## Getting Started: Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
This example provides simple YOLO training and inference examples. For full documentation on these and other [modes](../modes/index.md) see the [Predict](../modes/predict.md), [Train](../modes/train.md), [Val](../modes/val.md) and [Export](../modes/export.md) docs pages.
|
||||
This example provides simple YOLO training and inference examples. For full documentation on these and other [modes](../modes/index.md) see the [Predict](../modes/predict.md), [Train](../modes/train.md), [Val](../modes/val.md) and [Export](../modes/export.md) docs pages.
|
||||
|
||||
Note the below example is for YOLOv8 [Detect](../tasks/detect.md) models for object detection. For additional supported tasks see the [Segment](../tasks/segment.md), [Classify](../tasks/classify.md) and [Pose](../tasks/pose.md) docs.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -10,8 +10,7 @@ keywords: RT-DETR, Baidu, Vision Transformers, object detection, real-time perfo
|
|||
|
||||
Real-Time Detection Transformer (RT-DETR), developed by Baidu, is a cutting-edge end-to-end object detector that provides real-time performance while maintaining high accuracy. It leverages the power of Vision Transformers (ViT) to efficiently process multiscale features by decoupling intra-scale interaction and cross-scale fusion. RT-DETR is highly adaptable, supporting flexible adjustment of inference speed using different decoder layers without retraining. The model excels on accelerated backends like CUDA with TensorRT, outperforming many other real-time object detectors.
|
||||
|
||||
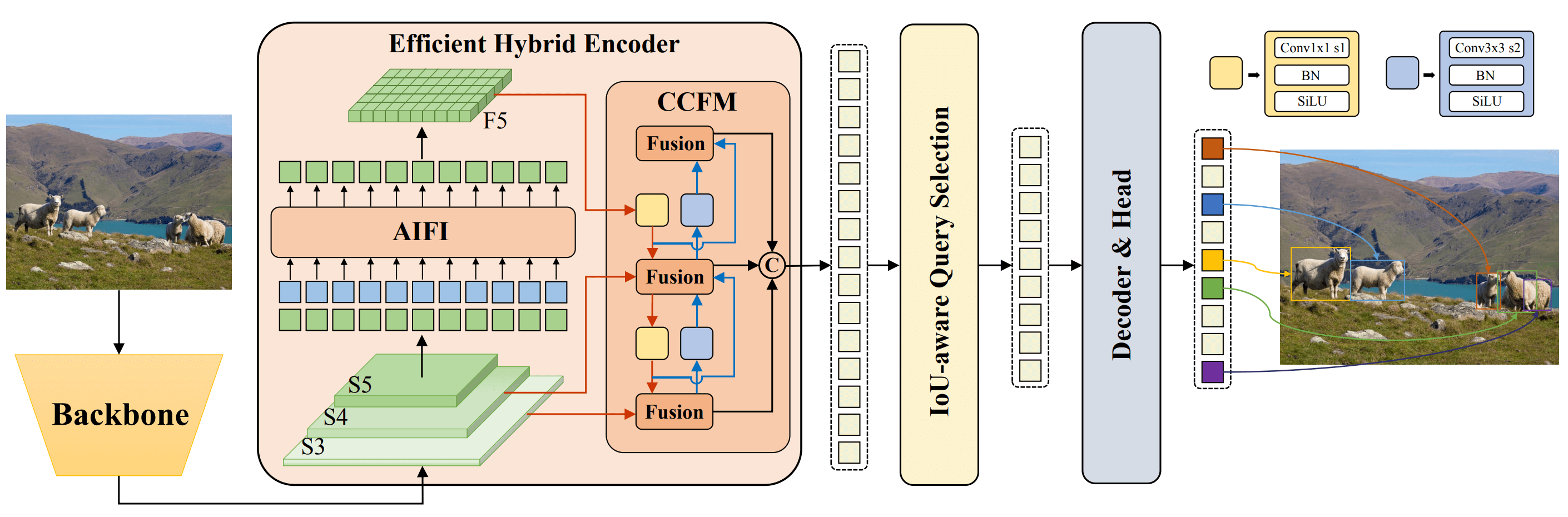
|
||||
**Overview of Baidu's RT-DETR.** The RT-DETR model architecture diagram shows the last three stages of the backbone {S3, S4, S5} as the input to the encoder. The efficient hybrid encoder transforms multiscale features into a sequence of image features through intrascale feature interaction (AIFI) and cross-scale feature-fusion module (CCFM). The IoU-aware query selection is employed to select a fixed number of image features to serve as initial object queries for the decoder. Finally, the decoder with auxiliary prediction heads iteratively optimizes object queries to generate boxes and confidence scores ([source](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.08069.pdf)).
|
||||
 **Overview of Baidu's RT-DETR.** The RT-DETR model architecture diagram shows the last three stages of the backbone {S3, S4, S5} as the input to the encoder. The efficient hybrid encoder transforms multiscale features into a sequence of image features through intrascale feature interaction (AIFI) and cross-scale feature-fusion module (CCFM). The IoU-aware query selection is employed to select a fixed number of image features to serve as initial object queries for the decoder. Finally, the decoder with auxiliary prediction heads iteratively optimizes object queries to generate boxes and confidence scores ([source](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.08069.pdf)).
|
||||
|
||||
### Key Features
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -28,7 +27,7 @@ The Ultralytics Python API provides pre-trained PaddlePaddle RT-DETR models with
|
|||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
This example provides simple RT-DETRR training and inference examples. For full documentation on these and other [modes](../modes/index.md) see the [Predict](../modes/predict.md), [Train](../modes/train.md), [Val](../modes/val.md) and [Export](../modes/export.md) docs pages.
|
||||
This example provides simple RT-DETRR training and inference examples. For full documentation on these and other [modes](../modes/index.md) see the [Predict](../modes/predict.md), [Train](../modes/train.md), [Val](../modes/val.md) and [Export](../modes/export.md) docs pages.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -14,8 +14,7 @@ The Segment Anything Model, or SAM, is a cutting-edge image segmentation model t
|
|||
|
||||
SAM's advanced design allows it to adapt to new image distributions and tasks without prior knowledge, a feature known as zero-shot transfer. Trained on the expansive [SA-1B dataset](https://ai.facebook.com/datasets/segment-anything/), which contains more than 1 billion masks spread over 11 million carefully curated images, SAM has displayed impressive zero-shot performance, surpassing previous fully supervised results in many cases.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Example images with overlaid masks from our newly introduced dataset, SA-1B. SA-1B contains 11M diverse, high-resolution, licensed, and privacy protecting images and 1.1B high-quality segmentation masks. These masks were annotated fully automatically by SAM, and as verified by human ratings and numerous experiments, are of high quality and diversity. Images are grouped by number of masks per image for visualization (there are ∼100 masks per image on average).
|
||||
 **SA-1B Example images.** Dataset images overlaid masks from the newly introduced SA-1B dataset. SA-1B contains 11M diverse, high-resolution, licensed, and privacy protecting images and 1.1B high-quality segmentation masks. These masks were annotated fully automatically by SAM, and as verified by human ratings and numerous experiments, are of high quality and diversity. Images are grouped by number of masks per image for visualization (there are ∼100 masks per image on average).
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Features of the Segment Anything Model (SAM)
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -10,8 +10,7 @@ keywords: YOLO-NAS, Deci AI, object detection, deep learning, neural architectur
|
|||
|
||||
Developed by Deci AI, YOLO-NAS is a groundbreaking object detection foundational model. It is the product of advanced Neural Architecture Search technology, meticulously designed to address the limitations of previous YOLO models. With significant improvements in quantization support and accuracy-latency trade-offs, YOLO-NAS represents a major leap in object detection.
|
||||
|
||||
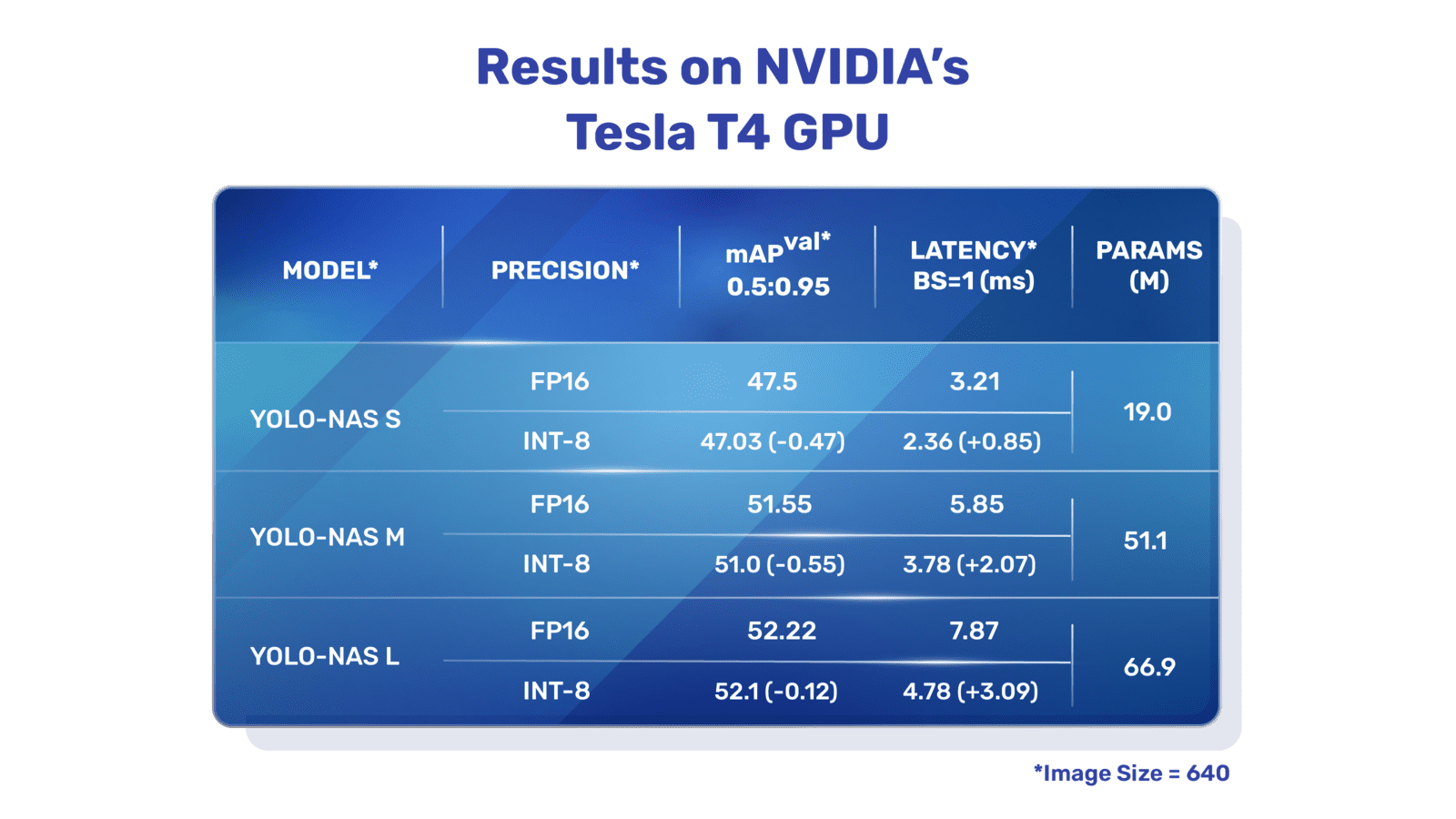
|
||||
**Overview of YOLO-NAS.** YOLO-NAS employs quantization-aware blocks and selective quantization for optimal performance. The model, when converted to its INT8 quantized version, experiences a minimal precision drop, a significant improvement over other models. These advancements culminate in a superior architecture with unprecedented object detection capabilities and outstanding performance.
|
||||
 **Overview of YOLO-NAS.** YOLO-NAS employs quantization-aware blocks and selective quantization for optimal performance. The model, when converted to its INT8 quantized version, experiences a minimal precision drop, a significant improvement over other models. These advancements culminate in a superior architecture with unprecedented object detection capabilities and outstanding performance.
|
||||
|
||||
### Key Features
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ This table provides an at-a-glance view of the capabilities of each YOLOv3 varia
|
|||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
This example provides simple YOLOv3 training and inference examples. For full documentation on these and other [modes](../modes/index.md) see the [Predict](../modes/predict.md), [Train](../modes/train.md), [Val](../modes/val.md) and [Export](../modes/export.md) docs pages.
|
||||
This example provides simple YOLOv3 training and inference examples. For full documentation on these and other [modes](../modes/index.md) see the [Predict](../modes/predict.md), [Train](../modes/train.md), [Val](../modes/val.md) and [Export](../modes/export.md) docs pages.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -8,8 +8,7 @@ keywords: ultralytics, YOLOv4, object detection, neural network, real-time detec
|
|||
|
||||
Welcome to the Ultralytics documentation page for YOLOv4, a state-of-the-art, real-time object detector launched in 2020 by Alexey Bochkovskiy at [https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet](https://github.com/AlexeyAB/darknet). YOLOv4 is designed to provide the optimal balance between speed and accuracy, making it an excellent choice for many applications.
|
||||
|
||||
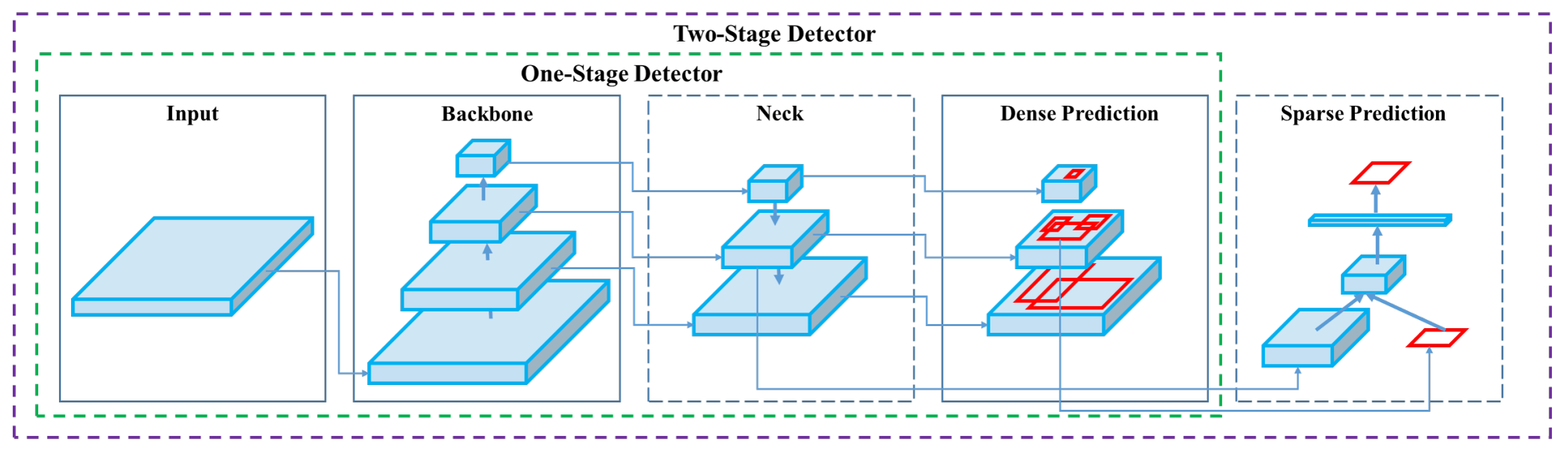
|
||||
**YOLOv4 architecture diagram**. Showcasing the intricate network design of YOLOv4, including the backbone, neck, and head components, and their interconnected layers for optimal real-time object detection.
|
||||
 **YOLOv4 architecture diagram**. Showcasing the intricate network design of YOLOv4, including the backbone, neck, and head components, and their interconnected layers for optimal real-time object detection.
|
||||
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ This table provides a detailed overview of the YOLOv5u model variants, highlight
|
|||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
This example provides simple YOLOv5 training and inference examples. For full documentation on these and other [modes](../modes/index.md) see the [Predict](../modes/predict.md), [Train](../modes/train.md), [Val](../modes/val.md) and [Export](../modes/export.md) docs pages.
|
||||
This example provides simple YOLOv5 training and inference examples. For full documentation on these and other [modes](../modes/index.md) see the [Predict](../modes/predict.md), [Train](../modes/train.md), [Val](../modes/val.md) and [Export](../modes/export.md) docs pages.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -11,8 +11,7 @@ keywords: Meituan YOLOv6, object detection, Ultralytics, YOLOv6 docs, Bi-directi
|
|||
[Meituan](https://about.meituan.com/) YOLOv6 is a cutting-edge object detector that offers remarkable balance between speed and accuracy, making it a popular choice for real-time applications. This model introduces several notable enhancements on its architecture and training scheme, including the implementation of a Bi-directional Concatenation (BiC) module, an anchor-aided training (AAT) strategy, and an improved backbone and neck design for state-of-the-art accuracy on the COCO dataset.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
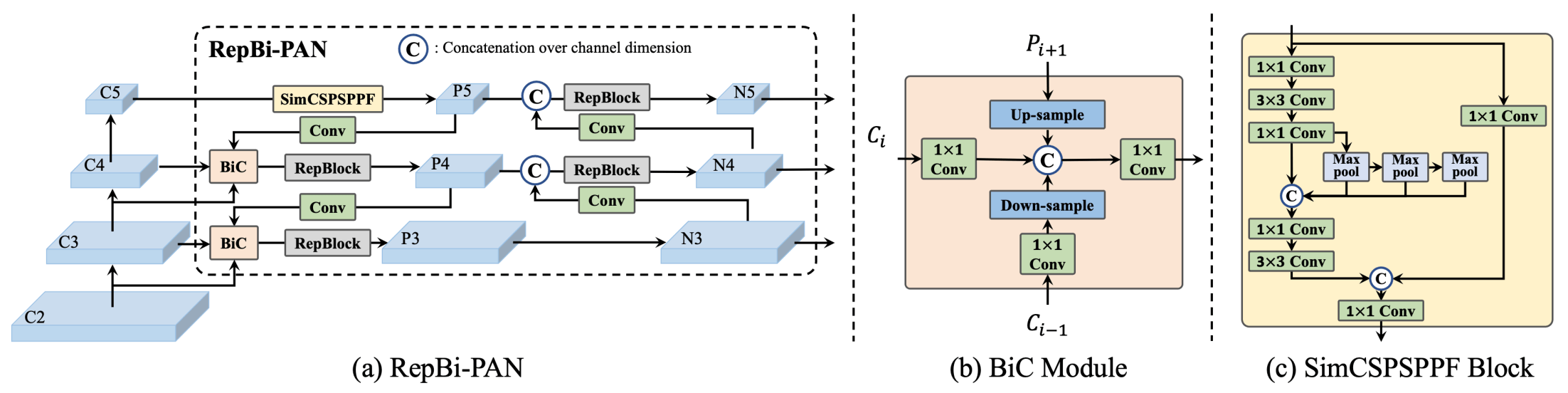
|
||||
**Overview of YOLOv6.** Model architecture diagram showing the redesigned network components and training strategies that have led to significant performance improvements. (a) The neck of YOLOv6 (N and S are shown). Note for M/L, RepBlocks is replaced with CSPStackRep. (b) The structure of a BiC module. (c) A SimCSPSPPF block. ([source](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.05586.pdf)).
|
||||
 **Overview of YOLOv6.** Model architecture diagram showing the redesigned network components and training strategies that have led to significant performance improvements. (a) The neck of YOLOv6 (N and S are shown). Note for M/L, RepBlocks is replaced with CSPStackRep. (b) The structure of a BiC module. (c) A SimCSPSPPF block. ([source](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2301.05586.pdf)).
|
||||
|
||||
### Key Features
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -35,7 +34,7 @@ YOLOv6 also provides quantized models for different precisions and models optimi
|
|||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
This example provides simple YOLOv6 training and inference examples. For full documentation on these and other [modes](../modes/index.md) see the [Predict](../modes/predict.md), [Train](../modes/train.md), [Val](../modes/val.md) and [Export](../modes/export.md) docs pages.
|
||||
This example provides simple YOLOv6 training and inference examples. For full documentation on these and other [modes](../modes/index.md) see the [Predict](../modes/predict.md), [Train](../modes/train.md), [Val](../modes/val.md) and [Export](../modes/export.md) docs pages.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -8,8 +8,8 @@ keywords: YOLOv7, real-time object detector, state-of-the-art, Ultralytics, MS C
|
|||
|
||||
YOLOv7 is a state-of-the-art real-time object detector that surpasses all known object detectors in both speed and accuracy in the range from 5 FPS to 160 FPS. It has the highest accuracy (56.8% AP) among all known real-time object detectors with 30 FPS or higher on GPU V100. Moreover, YOLOv7 outperforms other object detectors such as YOLOR, YOLOX, Scaled-YOLOv4, YOLOv5, and many others in speed and accuracy. The model is trained on the MS COCO dataset from scratch without using any other datasets or pre-trained weights. Source code for YOLOv7 is available on GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
**Comparison of state-of-the-art object detectors.** From the results in Table 2 we know that the proposed method has the best speed-accuracy trade-off comprehensively. If we compare YOLOv7-tiny-SiLU with YOLOv5-N (r6.1), our method is 127 fps faster and 10.7% more accurate on AP. In addition, YOLOv7 has 51.4% AP at frame rate of 161 fps, while PPYOLOE-L with the same AP has only 78 fps frame rate. In terms of parameter usage, YOLOv7 is 41% less than PPYOLOE-L. If we compare YOLOv7-X with 114 fps inference speed to YOLOv5-L (r6.1) with 99 fps inference speed, YOLOv7-X can improve AP by 3.9%. If YOLOv7-X is compared with YOLOv5-X (r6.1) of similar scale, the inference speed of YOLOv7-X is 31 fps faster. In addition, in terms the amount of parameters and computation, YOLOv7-X reduces 22% of parameters and 8% of computation compared to YOLOv5-X (r6.1), but improves AP by 2.2% ([Source](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2207.02696.pdf)).
|
||||
 **Comparison of state-of-the-art object detectors.
|
||||
** From the results in Table 2 we know that the proposed method has the best speed-accuracy trade-off comprehensively. If we compare YOLOv7-tiny-SiLU with YOLOv5-N (r6.1), our method is 127 fps faster and 10.7% more accurate on AP. In addition, YOLOv7 has 51.4% AP at frame rate of 161 fps, while PPYOLOE-L with the same AP has only 78 fps frame rate. In terms of parameter usage, YOLOv7 is 41% less than PPYOLOE-L. If we compare YOLOv7-X with 114 fps inference speed to YOLOv5-L (r6.1) with 99 fps inference speed, YOLOv7-X can improve AP by 3.9%. If YOLOv7-X is compared with YOLOv5-X (r6.1) of similar scale, the inference speed of YOLOv7-X is 31 fps faster. In addition, in terms the amount of parameters and computation, YOLOv7-X reduces 22% of parameters and 8% of computation compared to YOLOv5-X (r6.1), but improves AP by 2.2% ([Source](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2207.02696.pdf)).
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -125,7 +125,7 @@ This table provides an overview of the YOLOv8 model variants, highlighting their
|
|||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
This example provides simple YOLOv8 training and inference examples. For full documentation on these and other [modes](../modes/index.md) see the [Predict](../modes/predict.md), [Train](../modes/train.md), [Val](../modes/val.md) and [Export](../modes/export.md) docs pages.
|
||||
This example provides simple YOLOv8 training and inference examples. For full documentation on these and other [modes](../modes/index.md) see the [Predict](../modes/predict.md), [Train](../modes/train.md), [Val](../modes/val.md) and [Export](../modes/export.md) docs pages.
|
||||
|
||||
Note the below example is for YOLOv8 [Detect](../tasks/detect.md) models for object detection. For additional supported tasks see the [Segment](../tasks/segment.md), [Classify](../tasks/classify.md), [Obb](../tasks/obb.md) docs and [Pose](../tasks/pose.md) docs.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue