diff --git a/.github/workflows/ci.yaml b/.github/workflows/ci.yaml
index 3d505d56..67a70ebf 100644
--- a/.github/workflows/ci.yaml
+++ b/.github/workflows/ci.yaml
@@ -125,16 +125,16 @@ jobs:
pip list
- name: Benchmark DetectionModel
shell: bash
- run: yolo benchmark model='path with spaces/${{ matrix.model }}.pt' imgsz=160, verbose=0.26
+ run: yolo benchmark model='path with spaces/${{ matrix.model }}.pt' imgsz=160 verbose=0.26
- name: Benchmark SegmentationModel
shell: bash
- run: yolo benchmark model='path with spaces/${{ matrix.model }}-seg.pt' imgsz=160, verbose=0.30
+ run: yolo benchmark model='path with spaces/${{ matrix.model }}-seg.pt' imgsz=160 verbose=0.30
- name: Benchmark ClassificationModel
shell: bash
- run: yolo benchmark model='path with spaces/${{ matrix.model }}-cls.pt' imgsz=160, verbose=0.36
+ run: yolo benchmark model='path with spaces/${{ matrix.model }}-cls.pt' imgsz=160 verbose=0.36
- name: Benchmark PoseModel
shell: bash
- run: yolo benchmark model='path with spaces/${{ matrix.model }}-pose.pt' imgsz=160, verbose=0.17
+ run: yolo benchmark model='path with spaces/${{ matrix.model }}-pose.pt' imgsz=160 verbose=0.17
- name: Benchmark Summary
run: |
cat benchmarks.log
diff --git a/.github/workflows/docker.yaml b/.github/workflows/docker.yaml
index 1cf4b490..eb78e9a0 100644
--- a/.github/workflows/docker.yaml
+++ b/.github/workflows/docker.yaml
@@ -74,7 +74,8 @@ jobs:
docker run ultralytics/ultralytics:${{ matrix.tags }} /bin/bash -c "pip install pytest && pytest tests"
- name: Run Benchmarks
- if: (github.event_name == 'push' || github.event.inputs.dockerfile == matrix.dockerfile) && matrix.platforms == 'linux/amd64' # arm64 images not supported on GitHub CI runners
+ # WARNING: Dockerfile (GPU) error on TF.js export 'module 'numpy' has no attribute 'object'.
+ if: (github.event_name == 'push' || github.event.inputs.dockerfile == matrix.dockerfile) && matrix.platforms == 'linux/amd64' && matrix.dockerfile != 'Dockerfile' # arm64 images not supported on GitHub CI runners
run: |
docker run ultralytics/ultralytics:${{ matrix.tags }} yolo benchmark model=yolov8n.pt imgsz=160 verbose=0.26
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 6a307906..d016bcbe 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -192,6 +192,8 @@ See [Pose Docs](https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/pose) for usage examples with
## Integrations
+Our key integrations with leading AI platforms extend the functionality of Ultralytics' offerings, enhancing tasks like dataset labeling, training, visualization, and model management. Discover how Ultralytics, in collaboration with [Roboflow](https://roboflow.com/?ref=ultralytics), ClearML, [Comet](https://bit.ly/yolov8-readme-comet), Neural Magic and [OpenVINO](https://docs.ultralytics.com/integrations/openvino), can optimize your AI workflow.
+
 diff --git a/README.zh-CN.md b/README.zh-CN.md
index e71f57e7..29fdc0a5 100644
--- a/README.zh-CN.md
+++ b/README.zh-CN.md
@@ -191,6 +191,8 @@ success = model.export(format="onnx") # 将模型导出为 ONNX 格式
##
diff --git a/README.zh-CN.md b/README.zh-CN.md
index e71f57e7..29fdc0a5 100644
--- a/README.zh-CN.md
+++ b/README.zh-CN.md
@@ -191,6 +191,8 @@ success = model.export(format="onnx") # 将模型导出为 ONNX 格式
## 集成
+我们与领先的AI平台的关键整合扩展了Ultralytics产品的功能,增强了数据集标签化、训练、可视化和模型管理等任务。探索Ultralytics如何与[Roboflow](https://roboflow.com/?ref=ultralytics)、ClearML、[Comet](https://bit.ly/yolov8-readme-comet)、Neural Magic以及[OpenVINO](https://docs.ultralytics.com/integrations/openvino)合作,优化您的AI工作流程。
+
 diff --git a/docs/integrations/index.md b/docs/integrations/index.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..89e5964f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/integrations/index.md
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+---
+comments: true
+description: Explore Ultralytics integrations with tools for dataset management, model optimization, ML workflows automation, experiment tracking, version control, and more. Learn about our support for various model export formats for deployment.
+keywords: Ultralytics integrations, Roboflow, Neural Magic, ClearML, Comet ML, DVC, Ultralytics HUB, MLFlow, Neptune, Ray Tune, TensorBoard, W&B, model export formats, PyTorch, TorchScript, ONNX, OpenVINO, TensorRT, CoreML, TF SavedModel, TF GraphDef, TF Lite, TF Edge TPU, TF.js, PaddlePaddle, NCNN
+---
+
+# Ultralytics Integrations
+
+Welcome to the Ultralytics Integrations page! This page provides an overview of our partnerships with various tools and platforms, designed to streamline your machine learning workflows, enhance dataset management, simplify model training, and facilitate efficient deployment.
+
+
diff --git a/docs/integrations/index.md b/docs/integrations/index.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..89e5964f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/integrations/index.md
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+---
+comments: true
+description: Explore Ultralytics integrations with tools for dataset management, model optimization, ML workflows automation, experiment tracking, version control, and more. Learn about our support for various model export formats for deployment.
+keywords: Ultralytics integrations, Roboflow, Neural Magic, ClearML, Comet ML, DVC, Ultralytics HUB, MLFlow, Neptune, Ray Tune, TensorBoard, W&B, model export formats, PyTorch, TorchScript, ONNX, OpenVINO, TensorRT, CoreML, TF SavedModel, TF GraphDef, TF Lite, TF Edge TPU, TF.js, PaddlePaddle, NCNN
+---
+
+# Ultralytics Integrations
+
+Welcome to the Ultralytics Integrations page! This page provides an overview of our partnerships with various tools and platforms, designed to streamline your machine learning workflows, enhance dataset management, simplify model training, and facilitate efficient deployment.
+
+ +
+## Datasets Integrations
+
+- [Roboflow](https://roboflow.com/): Facilitate seamless dataset management for Ultralytics models, offering robust annotation, preprocessing, and augmentation capabilities.
+
+## Training Integrations
+
+- [Comet ML](https://www.comet.ml/): Enhance your model development with Ultralytics by tracking, comparing, and optimizing your machine learning experiments.
+
+- [ClearML](https://clear.ml/): Automate your Ultralytics ML workflows, monitor experiments, and foster team collaboration.
+
+- [DVC](https://dvc.org/): Implement version control for your Ultralytics machine learning projects, synchronizing data, code, and models effectively.
+
+- [Ultralytics HUB](https://hub.ultralytics.com): Access and contribute to a community of pre-trained Ultralytics models.
+
+- [MLFlow](https://mlflow.org/): Streamline the entire ML lifecycle of Ultralytics models, from experimentation and reproducibility to deployment.
+
+- [Neptune](https://neptune.ai/): Maintain a comprehensive log of your ML experiments with Ultralytics in this metadata store designed for MLOps.
+
+- [Ray Tune](ray-tune.md): Optimize the hyperparameters of your Ultralytics models at any scale.
+
+- [TensorBoard](https://tensorboard.dev/): Visualize your Ultralytics ML workflows, monitor model metrics, and foster team collaboration.
+
+- [Weights & Biases (W&B)](https://wandb.ai/site): Monitor experiments, visualize metrics, and foster reproducibility and collaboration on Ultralytics projects.
+
+## Deployment Integrations
+
+- [Neural Magic](https://neuralmagic.com/): Leverage Quantization Aware Training (QAT) and pruning techniques to optimize Ultralytics models for superior performance and leaner size.
+
+### Export Formats
+
+We also support a variety of model export formats for deployment in different environments. Here are the available formats:
+
+| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
+|--------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|----------|-----------------------------------------------------|
+| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - |
+| [TorchScript](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/jit.html) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize` |
+| [ONNX](https://onnx.ai/) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset` |
+| [OpenVINO](/integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` |
+| [TensorRT](https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace` |
+| [CoreML](https://github.com/apple/coremltools) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlmodel` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms` |
+| [TF SavedModel](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras` |
+| [TF GraphDef](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/Graph) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz` |
+| [TF Lite](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8` |
+| [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [NCNN](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` |
+
+Explore the links to learn more about each integration and how to get the most out of them with Ultralytics.
diff --git a/docs/integrations/openvino.md b/docs/integrations/openvino.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0cc1468e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/integrations/openvino.md
@@ -0,0 +1,271 @@
+---
+comments: true
+description: Discover the power of deploying your Ultralytics YOLOv8 model using OpenVINO format for up to 10x speedup vs PyTorch.
+keywords: ultralytics docs, YOLOv8, export YOLOv8, YOLOv8 model deployment, exporting YOLOv8, OpenVINO, OpenVINO format
+---
+
+
+
+## Datasets Integrations
+
+- [Roboflow](https://roboflow.com/): Facilitate seamless dataset management for Ultralytics models, offering robust annotation, preprocessing, and augmentation capabilities.
+
+## Training Integrations
+
+- [Comet ML](https://www.comet.ml/): Enhance your model development with Ultralytics by tracking, comparing, and optimizing your machine learning experiments.
+
+- [ClearML](https://clear.ml/): Automate your Ultralytics ML workflows, monitor experiments, and foster team collaboration.
+
+- [DVC](https://dvc.org/): Implement version control for your Ultralytics machine learning projects, synchronizing data, code, and models effectively.
+
+- [Ultralytics HUB](https://hub.ultralytics.com): Access and contribute to a community of pre-trained Ultralytics models.
+
+- [MLFlow](https://mlflow.org/): Streamline the entire ML lifecycle of Ultralytics models, from experimentation and reproducibility to deployment.
+
+- [Neptune](https://neptune.ai/): Maintain a comprehensive log of your ML experiments with Ultralytics in this metadata store designed for MLOps.
+
+- [Ray Tune](ray-tune.md): Optimize the hyperparameters of your Ultralytics models at any scale.
+
+- [TensorBoard](https://tensorboard.dev/): Visualize your Ultralytics ML workflows, monitor model metrics, and foster team collaboration.
+
+- [Weights & Biases (W&B)](https://wandb.ai/site): Monitor experiments, visualize metrics, and foster reproducibility and collaboration on Ultralytics projects.
+
+## Deployment Integrations
+
+- [Neural Magic](https://neuralmagic.com/): Leverage Quantization Aware Training (QAT) and pruning techniques to optimize Ultralytics models for superior performance and leaner size.
+
+### Export Formats
+
+We also support a variety of model export formats for deployment in different environments. Here are the available formats:
+
+| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
+|--------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|----------|-----------------------------------------------------|
+| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - |
+| [TorchScript](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/jit.html) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize` |
+| [ONNX](https://onnx.ai/) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset` |
+| [OpenVINO](/integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` |
+| [TensorRT](https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace` |
+| [CoreML](https://github.com/apple/coremltools) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlmodel` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms` |
+| [TF SavedModel](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras` |
+| [TF GraphDef](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/Graph) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz` |
+| [TF Lite](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8` |
+| [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [NCNN](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` |
+
+Explore the links to learn more about each integration and how to get the most out of them with Ultralytics.
diff --git a/docs/integrations/openvino.md b/docs/integrations/openvino.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0cc1468e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/integrations/openvino.md
@@ -0,0 +1,271 @@
+---
+comments: true
+description: Discover the power of deploying your Ultralytics YOLOv8 model using OpenVINO format for up to 10x speedup vs PyTorch.
+keywords: ultralytics docs, YOLOv8, export YOLOv8, YOLOv8 model deployment, exporting YOLOv8, OpenVINO, OpenVINO format
+---
+
+ +
+**Export mode** is used for exporting a YOLOv8 model to a format that can be used for deployment. In this guide, we specifically cover exporting to OpenVINO, which can provide up to 3x [CPU](https://docs.openvino.ai/2023.0/openvino_docs_OV_UG_supported_plugins_CPU.html) speedup as well as accelerating on other Intel hardware ([iGPU](https://docs.openvino.ai/2023.0/openvino_docs_OV_UG_supported_plugins_GPU.html), [dGPU](https://docs.openvino.ai/2023.0/openvino_docs_OV_UG_supported_plugins_GPU.html), [VPU](https://docs.openvino.ai/2022.3/openvino_docs_OV_UG_supported_plugins_VPU.html), etc.).
+
+OpenVINO, short for Open Visual Inference & Neural Network Optimization toolkit, is a comprehensive toolkit for optimizing and deploying AI inference models. Even though the name contains Visual, OpenVINO also supports various additional tasks including language, audio, time series, etc.
+
+## Usage Examples
+
+Export a YOLOv8n model to OpenVINO format and run inference with the exported model.
+
+!!! example ""
+
+ === "Python"
+
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a YOLOv8n PyTorch model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Export the model
+ model.export(format='openvino') # creates 'yolov8n_openvino_model/'
+
+ # Load the exported OpenVINO model
+ ov_model = YOLO('yolov8n_openvino_model/')
+
+ # Run inference
+ results = ov_model('https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg')
+ ```
+ === "CLI"
+
+ ```bash
+ # Export a YOLOv8n PyTorch model to OpenVINO format
+ yolo export model=yolov8n.pt format=openvino # creates 'yolov8n_openvino_model/'
+
+ # Run inference with the exported model
+ yolo predict model=yolov8n_openvino_model source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
+ ```
+
+## Arguments
+
+| Key | Value | Description |
+|----------|--------------|------------------------------------------------------|
+| `format` | `'openvino'` | format to export to |
+| `imgsz` | `640` | image size as scalar or (h, w) list, i.e. (640, 480) |
+| `half` | `False` | FP16 quantization |
+
+## Benefits of OpenVINO
+
+1. **Performance**: OpenVINO delivers high-performance inference by utilizing the power of Intel CPUs, integrated and discrete GPUs, and FPGAs.
+2. **Support for Heterogeneous Execution**: OpenVINO provides an API to write once and deploy on any supported Intel hardware (CPU, GPU, FPGA, VPU, etc.).
+3. **Model Optimizer**: OpenVINO provides a Model Optimizer that imports, converts, and optimizes models from popular deep learning frameworks such as PyTorch, TensorFlow, TensorFlow Lite, Keras, ONNX, PaddlePaddle, and Caffe.
+4. **Ease of Use**: The toolkit comes with more than [80 tutorial notebooks](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks) (including [YOLOv8 optimization](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/tree/main/notebooks/230-yolov8-optimization)) teaching different aspects of the toolkit.
+
+## OpenVINO Export Structure
+
+When you export a model to OpenVINO format, it results in a directory containing the following:
+
+1. **XML file**: Describes the network topology.
+2. **BIN file**: Contains the weights and biases binary data.
+3. **Mapping file**: Holds mapping of original model output tensors to OpenVINO tensor names.
+
+You can use these files to run inference with the OpenVINO Inference Engine.
+
+## Using OpenVINO Export in Deployment
+
+Once you have the OpenVINO files, you can use the OpenVINO Runtime to run the model. The Runtime provides a unified API to inference across all supported Intel hardware. It also provides advanced capabilities like load balancing across Intel hardware and asynchronous execution. For more information on running the inference, refer to the [Inference with OpenVINO Runtime Guide](https://docs.openvino.ai/2023.0/openvino_docs_OV_UG_OV_Runtime_User_Guide.html).
+
+Remember, you'll need the XML and BIN files as well as any application-specific settings like input size, scale factor for normalization, etc., to correctly set up and use the model with the Runtime.
+
+In your deployment application, you would typically do the following steps:
+
+1. Initialize OpenVINO by creating `core = Core()`.
+2. Load the model using the `core.read_model()` method.
+3. Compile the model using the `core.compile_model()` function.
+4. Prepare the input (image, text, audio, etc.).
+5. Run inference using `compiled_model(input_data)`.
+
+For more detailed steps and code snippets, refer to the [OpenVINO documentation](https://docs.openvino.ai/) or [API tutorial](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/blob/main/notebooks/002-openvino-api/002-openvino-api.ipynb).
+
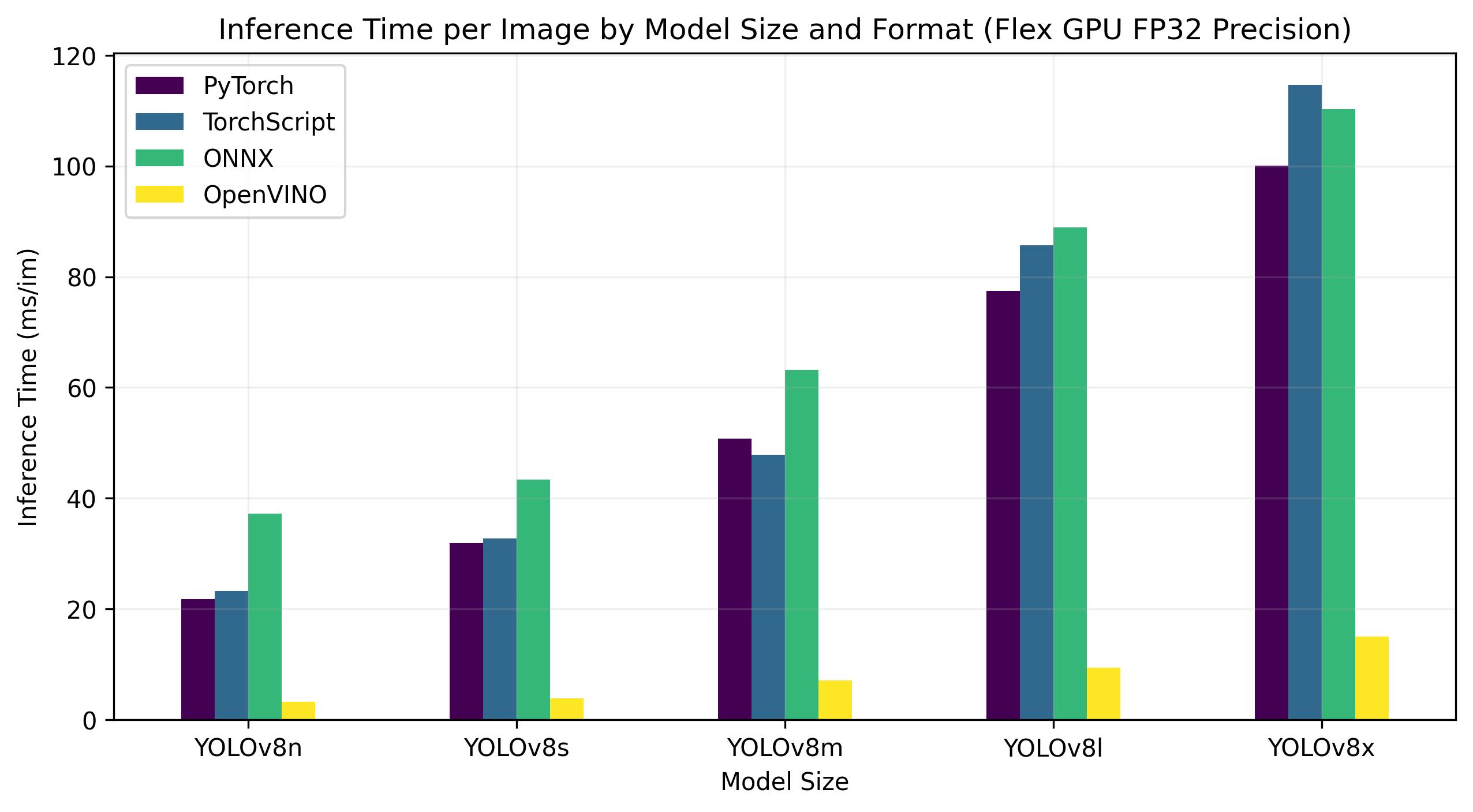
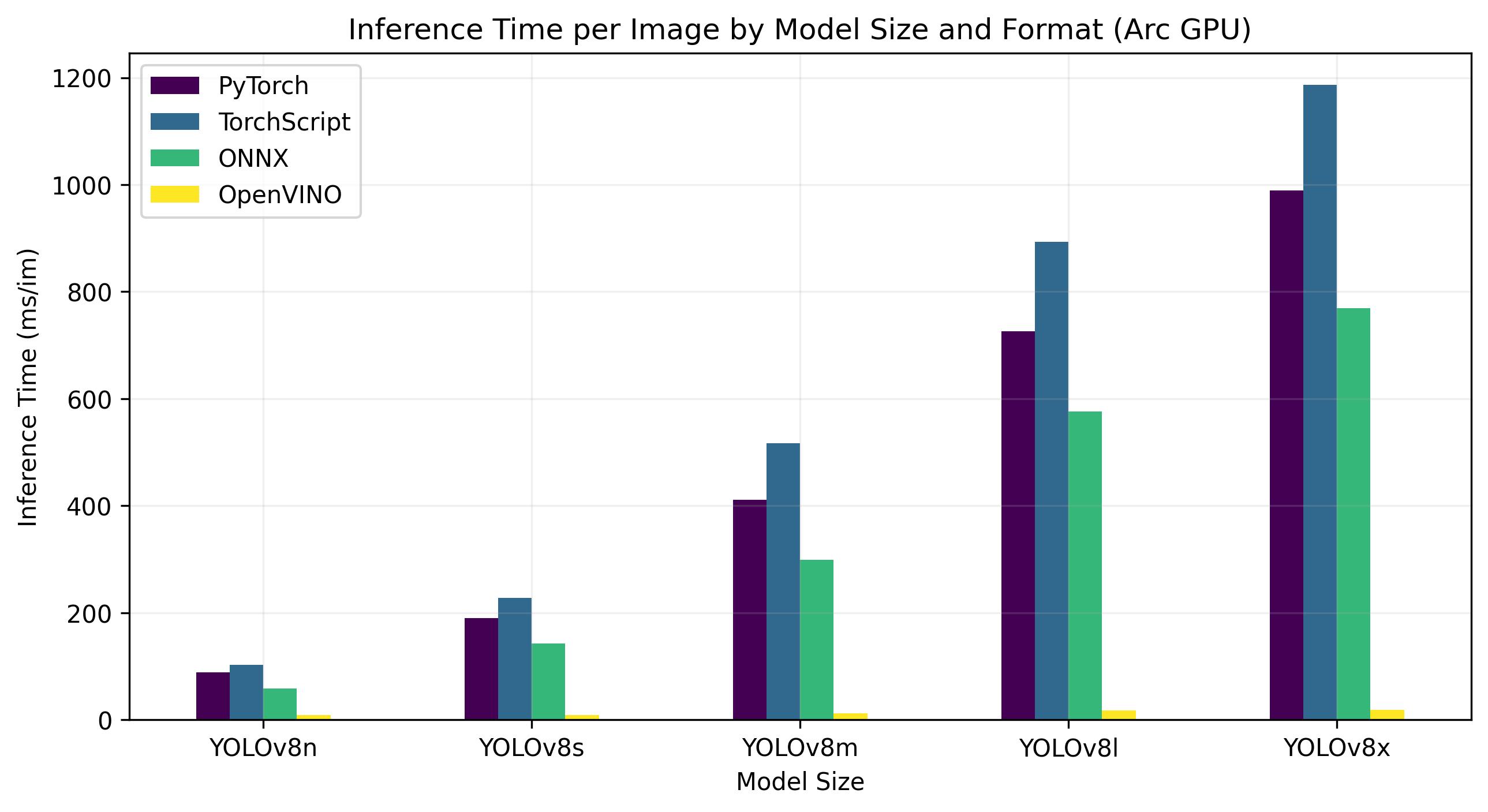
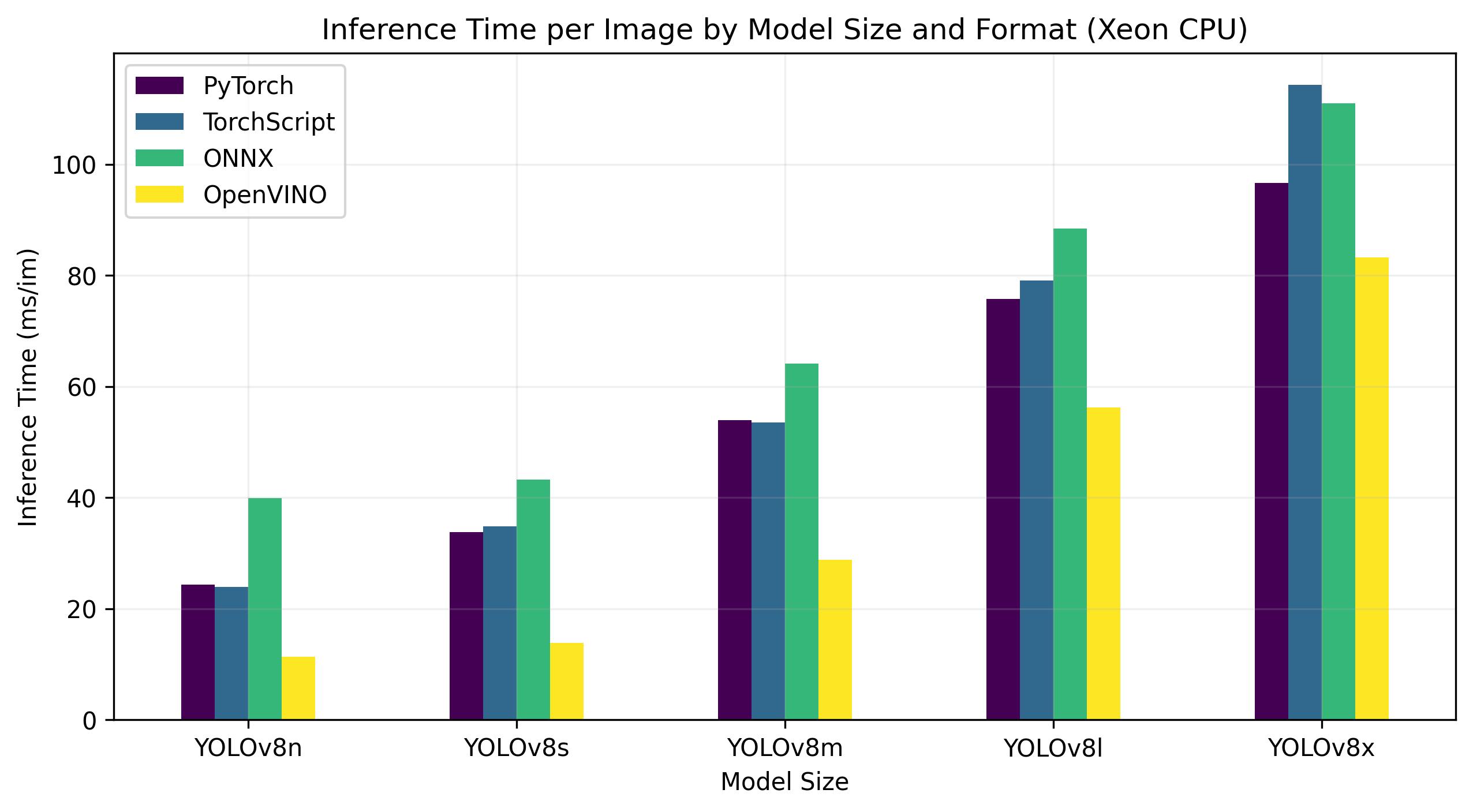
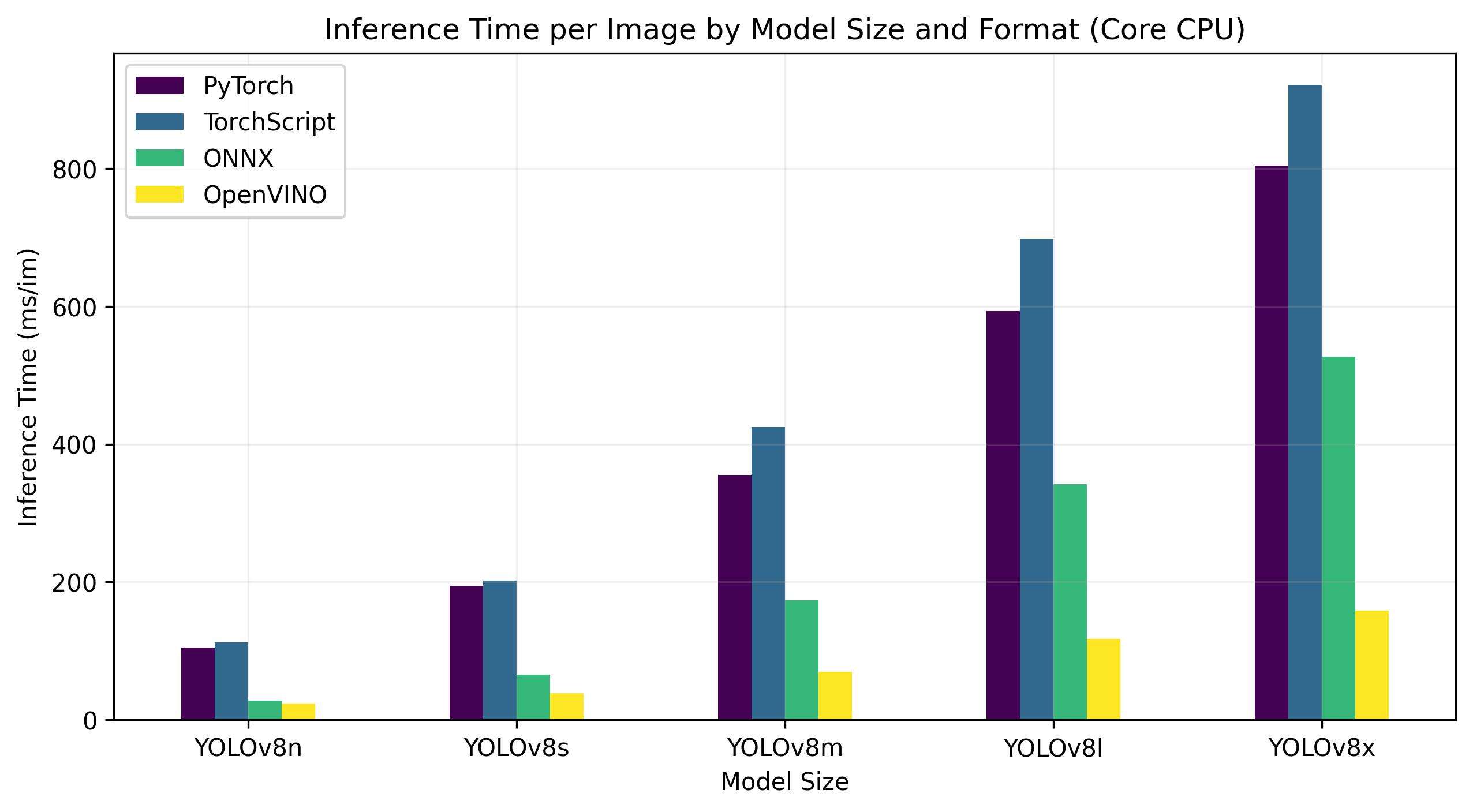
+## OpenVINO YOLOv8 Benchmarks
+
+YOLOv8 benchmarks below were run by the Ultralytics team on 4 different model formats measuring speed and accuracy: PyTorch, TorchScript, ONNX and OpenVINO. Benchmarks were run on Intel Flex and Arc GPUs, and on Intel Xeon CPUs at FP32 precision (with the `half=False` argument).
+
+!!! note
+
+ The benchmarking results below are for reference and might vary based on the exact hardware and software configuration of a system, as well as the current workload of the system at the time the benchmarks are run.
+
+ All benchmarks run with `openvino` python package version [2023.0.1](https://pypi.org/project/openvino/2023.0.1/).
+
+### Intel Flex GPU
+
+The Intel® Data Center GPU Flex Series is a versatile and robust solution designed for the intelligent visual cloud. This GPU supports a wide array of workloads including media streaming, cloud gaming, AI visual inference, and virtual desktop Infrastructure workloads. It stands out for its open architecture and built-in support for the AV1 encode, providing a standards-based software stack for high-performance, cross-architecture applications. The Flex Series GPU is optimized for density and quality, offering high reliability, availability, and scalability.
+
+Benchmarks below run on Intel® Data Center GPU Flex 170 at FP32 precision.
+
+
+
+**Export mode** is used for exporting a YOLOv8 model to a format that can be used for deployment. In this guide, we specifically cover exporting to OpenVINO, which can provide up to 3x [CPU](https://docs.openvino.ai/2023.0/openvino_docs_OV_UG_supported_plugins_CPU.html) speedup as well as accelerating on other Intel hardware ([iGPU](https://docs.openvino.ai/2023.0/openvino_docs_OV_UG_supported_plugins_GPU.html), [dGPU](https://docs.openvino.ai/2023.0/openvino_docs_OV_UG_supported_plugins_GPU.html), [VPU](https://docs.openvino.ai/2022.3/openvino_docs_OV_UG_supported_plugins_VPU.html), etc.).
+
+OpenVINO, short for Open Visual Inference & Neural Network Optimization toolkit, is a comprehensive toolkit for optimizing and deploying AI inference models. Even though the name contains Visual, OpenVINO also supports various additional tasks including language, audio, time series, etc.
+
+## Usage Examples
+
+Export a YOLOv8n model to OpenVINO format and run inference with the exported model.
+
+!!! example ""
+
+ === "Python"
+
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a YOLOv8n PyTorch model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Export the model
+ model.export(format='openvino') # creates 'yolov8n_openvino_model/'
+
+ # Load the exported OpenVINO model
+ ov_model = YOLO('yolov8n_openvino_model/')
+
+ # Run inference
+ results = ov_model('https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg')
+ ```
+ === "CLI"
+
+ ```bash
+ # Export a YOLOv8n PyTorch model to OpenVINO format
+ yolo export model=yolov8n.pt format=openvino # creates 'yolov8n_openvino_model/'
+
+ # Run inference with the exported model
+ yolo predict model=yolov8n_openvino_model source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
+ ```
+
+## Arguments
+
+| Key | Value | Description |
+|----------|--------------|------------------------------------------------------|
+| `format` | `'openvino'` | format to export to |
+| `imgsz` | `640` | image size as scalar or (h, w) list, i.e. (640, 480) |
+| `half` | `False` | FP16 quantization |
+
+## Benefits of OpenVINO
+
+1. **Performance**: OpenVINO delivers high-performance inference by utilizing the power of Intel CPUs, integrated and discrete GPUs, and FPGAs.
+2. **Support for Heterogeneous Execution**: OpenVINO provides an API to write once and deploy on any supported Intel hardware (CPU, GPU, FPGA, VPU, etc.).
+3. **Model Optimizer**: OpenVINO provides a Model Optimizer that imports, converts, and optimizes models from popular deep learning frameworks such as PyTorch, TensorFlow, TensorFlow Lite, Keras, ONNX, PaddlePaddle, and Caffe.
+4. **Ease of Use**: The toolkit comes with more than [80 tutorial notebooks](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks) (including [YOLOv8 optimization](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/tree/main/notebooks/230-yolov8-optimization)) teaching different aspects of the toolkit.
+
+## OpenVINO Export Structure
+
+When you export a model to OpenVINO format, it results in a directory containing the following:
+
+1. **XML file**: Describes the network topology.
+2. **BIN file**: Contains the weights and biases binary data.
+3. **Mapping file**: Holds mapping of original model output tensors to OpenVINO tensor names.
+
+You can use these files to run inference with the OpenVINO Inference Engine.
+
+## Using OpenVINO Export in Deployment
+
+Once you have the OpenVINO files, you can use the OpenVINO Runtime to run the model. The Runtime provides a unified API to inference across all supported Intel hardware. It also provides advanced capabilities like load balancing across Intel hardware and asynchronous execution. For more information on running the inference, refer to the [Inference with OpenVINO Runtime Guide](https://docs.openvino.ai/2023.0/openvino_docs_OV_UG_OV_Runtime_User_Guide.html).
+
+Remember, you'll need the XML and BIN files as well as any application-specific settings like input size, scale factor for normalization, etc., to correctly set up and use the model with the Runtime.
+
+In your deployment application, you would typically do the following steps:
+
+1. Initialize OpenVINO by creating `core = Core()`.
+2. Load the model using the `core.read_model()` method.
+3. Compile the model using the `core.compile_model()` function.
+4. Prepare the input (image, text, audio, etc.).
+5. Run inference using `compiled_model(input_data)`.
+
+For more detailed steps and code snippets, refer to the [OpenVINO documentation](https://docs.openvino.ai/) or [API tutorial](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/blob/main/notebooks/002-openvino-api/002-openvino-api.ipynb).
+
+## OpenVINO YOLOv8 Benchmarks
+
+YOLOv8 benchmarks below were run by the Ultralytics team on 4 different model formats measuring speed and accuracy: PyTorch, TorchScript, ONNX and OpenVINO. Benchmarks were run on Intel Flex and Arc GPUs, and on Intel Xeon CPUs at FP32 precision (with the `half=False` argument).
+
+!!! note
+
+ The benchmarking results below are for reference and might vary based on the exact hardware and software configuration of a system, as well as the current workload of the system at the time the benchmarks are run.
+
+ All benchmarks run with `openvino` python package version [2023.0.1](https://pypi.org/project/openvino/2023.0.1/).
+
+### Intel Flex GPU
+
+The Intel® Data Center GPU Flex Series is a versatile and robust solution designed for the intelligent visual cloud. This GPU supports a wide array of workloads including media streaming, cloud gaming, AI visual inference, and virtual desktop Infrastructure workloads. It stands out for its open architecture and built-in support for the AV1 encode, providing a standards-based software stack for high-performance, cross-architecture applications. The Flex Series GPU is optimized for density and quality, offering high reliability, availability, and scalability.
+
+Benchmarks below run on Intel® Data Center GPU Flex 170 at FP32 precision.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
 +
+ diff --git a/README.zh-CN.md b/README.zh-CN.md
index e71f57e7..29fdc0a5 100644
--- a/README.zh-CN.md
+++ b/README.zh-CN.md
@@ -191,6 +191,8 @@ success = model.export(format="onnx") # 将模型导出为 ONNX 格式
##
diff --git a/README.zh-CN.md b/README.zh-CN.md
index e71f57e7..29fdc0a5 100644
--- a/README.zh-CN.md
+++ b/README.zh-CN.md
@@ -191,6 +191,8 @@ success = model.export(format="onnx") # 将模型导出为 ONNX 格式
##  diff --git a/docs/integrations/index.md b/docs/integrations/index.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..89e5964f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/integrations/index.md
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+---
+comments: true
+description: Explore Ultralytics integrations with tools for dataset management, model optimization, ML workflows automation, experiment tracking, version control, and more. Learn about our support for various model export formats for deployment.
+keywords: Ultralytics integrations, Roboflow, Neural Magic, ClearML, Comet ML, DVC, Ultralytics HUB, MLFlow, Neptune, Ray Tune, TensorBoard, W&B, model export formats, PyTorch, TorchScript, ONNX, OpenVINO, TensorRT, CoreML, TF SavedModel, TF GraphDef, TF Lite, TF Edge TPU, TF.js, PaddlePaddle, NCNN
+---
+
+# Ultralytics Integrations
+
+Welcome to the Ultralytics Integrations page! This page provides an overview of our partnerships with various tools and platforms, designed to streamline your machine learning workflows, enhance dataset management, simplify model training, and facilitate efficient deployment.
+
+
diff --git a/docs/integrations/index.md b/docs/integrations/index.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..89e5964f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/integrations/index.md
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+---
+comments: true
+description: Explore Ultralytics integrations with tools for dataset management, model optimization, ML workflows automation, experiment tracking, version control, and more. Learn about our support for various model export formats for deployment.
+keywords: Ultralytics integrations, Roboflow, Neural Magic, ClearML, Comet ML, DVC, Ultralytics HUB, MLFlow, Neptune, Ray Tune, TensorBoard, W&B, model export formats, PyTorch, TorchScript, ONNX, OpenVINO, TensorRT, CoreML, TF SavedModel, TF GraphDef, TF Lite, TF Edge TPU, TF.js, PaddlePaddle, NCNN
+---
+
+# Ultralytics Integrations
+
+Welcome to the Ultralytics Integrations page! This page provides an overview of our partnerships with various tools and platforms, designed to streamline your machine learning workflows, enhance dataset management, simplify model training, and facilitate efficient deployment.
+
+ +
+## Datasets Integrations
+
+- [Roboflow](https://roboflow.com/): Facilitate seamless dataset management for Ultralytics models, offering robust annotation, preprocessing, and augmentation capabilities.
+
+## Training Integrations
+
+- [Comet ML](https://www.comet.ml/): Enhance your model development with Ultralytics by tracking, comparing, and optimizing your machine learning experiments.
+
+- [ClearML](https://clear.ml/): Automate your Ultralytics ML workflows, monitor experiments, and foster team collaboration.
+
+- [DVC](https://dvc.org/): Implement version control for your Ultralytics machine learning projects, synchronizing data, code, and models effectively.
+
+- [Ultralytics HUB](https://hub.ultralytics.com): Access and contribute to a community of pre-trained Ultralytics models.
+
+- [MLFlow](https://mlflow.org/): Streamline the entire ML lifecycle of Ultralytics models, from experimentation and reproducibility to deployment.
+
+- [Neptune](https://neptune.ai/): Maintain a comprehensive log of your ML experiments with Ultralytics in this metadata store designed for MLOps.
+
+- [Ray Tune](ray-tune.md): Optimize the hyperparameters of your Ultralytics models at any scale.
+
+- [TensorBoard](https://tensorboard.dev/): Visualize your Ultralytics ML workflows, monitor model metrics, and foster team collaboration.
+
+- [Weights & Biases (W&B)](https://wandb.ai/site): Monitor experiments, visualize metrics, and foster reproducibility and collaboration on Ultralytics projects.
+
+## Deployment Integrations
+
+- [Neural Magic](https://neuralmagic.com/): Leverage Quantization Aware Training (QAT) and pruning techniques to optimize Ultralytics models for superior performance and leaner size.
+
+### Export Formats
+
+We also support a variety of model export formats for deployment in different environments. Here are the available formats:
+
+| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
+|--------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|----------|-----------------------------------------------------|
+| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - |
+| [TorchScript](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/jit.html) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize` |
+| [ONNX](https://onnx.ai/) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset` |
+| [OpenVINO](/integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` |
+| [TensorRT](https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace` |
+| [CoreML](https://github.com/apple/coremltools) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlmodel` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms` |
+| [TF SavedModel](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras` |
+| [TF GraphDef](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/Graph) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz` |
+| [TF Lite](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8` |
+| [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [NCNN](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` |
+
+Explore the links to learn more about each integration and how to get the most out of them with Ultralytics.
diff --git a/docs/integrations/openvino.md b/docs/integrations/openvino.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0cc1468e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/integrations/openvino.md
@@ -0,0 +1,271 @@
+---
+comments: true
+description: Discover the power of deploying your Ultralytics YOLOv8 model using OpenVINO format for up to 10x speedup vs PyTorch.
+keywords: ultralytics docs, YOLOv8, export YOLOv8, YOLOv8 model deployment, exporting YOLOv8, OpenVINO, OpenVINO format
+---
+
+
+
+## Datasets Integrations
+
+- [Roboflow](https://roboflow.com/): Facilitate seamless dataset management for Ultralytics models, offering robust annotation, preprocessing, and augmentation capabilities.
+
+## Training Integrations
+
+- [Comet ML](https://www.comet.ml/): Enhance your model development with Ultralytics by tracking, comparing, and optimizing your machine learning experiments.
+
+- [ClearML](https://clear.ml/): Automate your Ultralytics ML workflows, monitor experiments, and foster team collaboration.
+
+- [DVC](https://dvc.org/): Implement version control for your Ultralytics machine learning projects, synchronizing data, code, and models effectively.
+
+- [Ultralytics HUB](https://hub.ultralytics.com): Access and contribute to a community of pre-trained Ultralytics models.
+
+- [MLFlow](https://mlflow.org/): Streamline the entire ML lifecycle of Ultralytics models, from experimentation and reproducibility to deployment.
+
+- [Neptune](https://neptune.ai/): Maintain a comprehensive log of your ML experiments with Ultralytics in this metadata store designed for MLOps.
+
+- [Ray Tune](ray-tune.md): Optimize the hyperparameters of your Ultralytics models at any scale.
+
+- [TensorBoard](https://tensorboard.dev/): Visualize your Ultralytics ML workflows, monitor model metrics, and foster team collaboration.
+
+- [Weights & Biases (W&B)](https://wandb.ai/site): Monitor experiments, visualize metrics, and foster reproducibility and collaboration on Ultralytics projects.
+
+## Deployment Integrations
+
+- [Neural Magic](https://neuralmagic.com/): Leverage Quantization Aware Training (QAT) and pruning techniques to optimize Ultralytics models for superior performance and leaner size.
+
+### Export Formats
+
+We also support a variety of model export formats for deployment in different environments. Here are the available formats:
+
+| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
+|--------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|----------|-----------------------------------------------------|
+| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - |
+| [TorchScript](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/jit.html) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize` |
+| [ONNX](https://onnx.ai/) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset` |
+| [OpenVINO](/integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` |
+| [TensorRT](https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace` |
+| [CoreML](https://github.com/apple/coremltools) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlmodel` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms` |
+| [TF SavedModel](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras` |
+| [TF GraphDef](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/Graph) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz` |
+| [TF Lite](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8` |
+| [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [NCNN](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` |
+
+Explore the links to learn more about each integration and how to get the most out of them with Ultralytics.
diff --git a/docs/integrations/openvino.md b/docs/integrations/openvino.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..0cc1468e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/integrations/openvino.md
@@ -0,0 +1,271 @@
+---
+comments: true
+description: Discover the power of deploying your Ultralytics YOLOv8 model using OpenVINO format for up to 10x speedup vs PyTorch.
+keywords: ultralytics docs, YOLOv8, export YOLOv8, YOLOv8 model deployment, exporting YOLOv8, OpenVINO, OpenVINO format
+---
+
+ +
+**Export mode** is used for exporting a YOLOv8 model to a format that can be used for deployment. In this guide, we specifically cover exporting to OpenVINO, which can provide up to 3x [CPU](https://docs.openvino.ai/2023.0/openvino_docs_OV_UG_supported_plugins_CPU.html) speedup as well as accelerating on other Intel hardware ([iGPU](https://docs.openvino.ai/2023.0/openvino_docs_OV_UG_supported_plugins_GPU.html), [dGPU](https://docs.openvino.ai/2023.0/openvino_docs_OV_UG_supported_plugins_GPU.html), [VPU](https://docs.openvino.ai/2022.3/openvino_docs_OV_UG_supported_plugins_VPU.html), etc.).
+
+OpenVINO, short for Open Visual Inference & Neural Network Optimization toolkit, is a comprehensive toolkit for optimizing and deploying AI inference models. Even though the name contains Visual, OpenVINO also supports various additional tasks including language, audio, time series, etc.
+
+## Usage Examples
+
+Export a YOLOv8n model to OpenVINO format and run inference with the exported model.
+
+!!! example ""
+
+ === "Python"
+
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a YOLOv8n PyTorch model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Export the model
+ model.export(format='openvino') # creates 'yolov8n_openvino_model/'
+
+ # Load the exported OpenVINO model
+ ov_model = YOLO('yolov8n_openvino_model/')
+
+ # Run inference
+ results = ov_model('https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg')
+ ```
+ === "CLI"
+
+ ```bash
+ # Export a YOLOv8n PyTorch model to OpenVINO format
+ yolo export model=yolov8n.pt format=openvino # creates 'yolov8n_openvino_model/'
+
+ # Run inference with the exported model
+ yolo predict model=yolov8n_openvino_model source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
+ ```
+
+## Arguments
+
+| Key | Value | Description |
+|----------|--------------|------------------------------------------------------|
+| `format` | `'openvino'` | format to export to |
+| `imgsz` | `640` | image size as scalar or (h, w) list, i.e. (640, 480) |
+| `half` | `False` | FP16 quantization |
+
+## Benefits of OpenVINO
+
+1. **Performance**: OpenVINO delivers high-performance inference by utilizing the power of Intel CPUs, integrated and discrete GPUs, and FPGAs.
+2. **Support for Heterogeneous Execution**: OpenVINO provides an API to write once and deploy on any supported Intel hardware (CPU, GPU, FPGA, VPU, etc.).
+3. **Model Optimizer**: OpenVINO provides a Model Optimizer that imports, converts, and optimizes models from popular deep learning frameworks such as PyTorch, TensorFlow, TensorFlow Lite, Keras, ONNX, PaddlePaddle, and Caffe.
+4. **Ease of Use**: The toolkit comes with more than [80 tutorial notebooks](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks) (including [YOLOv8 optimization](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/tree/main/notebooks/230-yolov8-optimization)) teaching different aspects of the toolkit.
+
+## OpenVINO Export Structure
+
+When you export a model to OpenVINO format, it results in a directory containing the following:
+
+1. **XML file**: Describes the network topology.
+2. **BIN file**: Contains the weights and biases binary data.
+3. **Mapping file**: Holds mapping of original model output tensors to OpenVINO tensor names.
+
+You can use these files to run inference with the OpenVINO Inference Engine.
+
+## Using OpenVINO Export in Deployment
+
+Once you have the OpenVINO files, you can use the OpenVINO Runtime to run the model. The Runtime provides a unified API to inference across all supported Intel hardware. It also provides advanced capabilities like load balancing across Intel hardware and asynchronous execution. For more information on running the inference, refer to the [Inference with OpenVINO Runtime Guide](https://docs.openvino.ai/2023.0/openvino_docs_OV_UG_OV_Runtime_User_Guide.html).
+
+Remember, you'll need the XML and BIN files as well as any application-specific settings like input size, scale factor for normalization, etc., to correctly set up and use the model with the Runtime.
+
+In your deployment application, you would typically do the following steps:
+
+1. Initialize OpenVINO by creating `core = Core()`.
+2. Load the model using the `core.read_model()` method.
+3. Compile the model using the `core.compile_model()` function.
+4. Prepare the input (image, text, audio, etc.).
+5. Run inference using `compiled_model(input_data)`.
+
+For more detailed steps and code snippets, refer to the [OpenVINO documentation](https://docs.openvino.ai/) or [API tutorial](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/blob/main/notebooks/002-openvino-api/002-openvino-api.ipynb).
+
+## OpenVINO YOLOv8 Benchmarks
+
+YOLOv8 benchmarks below were run by the Ultralytics team on 4 different model formats measuring speed and accuracy: PyTorch, TorchScript, ONNX and OpenVINO. Benchmarks were run on Intel Flex and Arc GPUs, and on Intel Xeon CPUs at FP32 precision (with the `half=False` argument).
+
+!!! note
+
+ The benchmarking results below are for reference and might vary based on the exact hardware and software configuration of a system, as well as the current workload of the system at the time the benchmarks are run.
+
+ All benchmarks run with `openvino` python package version [2023.0.1](https://pypi.org/project/openvino/2023.0.1/).
+
+### Intel Flex GPU
+
+The Intel® Data Center GPU Flex Series is a versatile and robust solution designed for the intelligent visual cloud. This GPU supports a wide array of workloads including media streaming, cloud gaming, AI visual inference, and virtual desktop Infrastructure workloads. It stands out for its open architecture and built-in support for the AV1 encode, providing a standards-based software stack for high-performance, cross-architecture applications. The Flex Series GPU is optimized for density and quality, offering high reliability, availability, and scalability.
+
+Benchmarks below run on Intel® Data Center GPU Flex 170 at FP32 precision.
+
+
+
+**Export mode** is used for exporting a YOLOv8 model to a format that can be used for deployment. In this guide, we specifically cover exporting to OpenVINO, which can provide up to 3x [CPU](https://docs.openvino.ai/2023.0/openvino_docs_OV_UG_supported_plugins_CPU.html) speedup as well as accelerating on other Intel hardware ([iGPU](https://docs.openvino.ai/2023.0/openvino_docs_OV_UG_supported_plugins_GPU.html), [dGPU](https://docs.openvino.ai/2023.0/openvino_docs_OV_UG_supported_plugins_GPU.html), [VPU](https://docs.openvino.ai/2022.3/openvino_docs_OV_UG_supported_plugins_VPU.html), etc.).
+
+OpenVINO, short for Open Visual Inference & Neural Network Optimization toolkit, is a comprehensive toolkit for optimizing and deploying AI inference models. Even though the name contains Visual, OpenVINO also supports various additional tasks including language, audio, time series, etc.
+
+## Usage Examples
+
+Export a YOLOv8n model to OpenVINO format and run inference with the exported model.
+
+!!! example ""
+
+ === "Python"
+
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a YOLOv8n PyTorch model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Export the model
+ model.export(format='openvino') # creates 'yolov8n_openvino_model/'
+
+ # Load the exported OpenVINO model
+ ov_model = YOLO('yolov8n_openvino_model/')
+
+ # Run inference
+ results = ov_model('https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg')
+ ```
+ === "CLI"
+
+ ```bash
+ # Export a YOLOv8n PyTorch model to OpenVINO format
+ yolo export model=yolov8n.pt format=openvino # creates 'yolov8n_openvino_model/'
+
+ # Run inference with the exported model
+ yolo predict model=yolov8n_openvino_model source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
+ ```
+
+## Arguments
+
+| Key | Value | Description |
+|----------|--------------|------------------------------------------------------|
+| `format` | `'openvino'` | format to export to |
+| `imgsz` | `640` | image size as scalar or (h, w) list, i.e. (640, 480) |
+| `half` | `False` | FP16 quantization |
+
+## Benefits of OpenVINO
+
+1. **Performance**: OpenVINO delivers high-performance inference by utilizing the power of Intel CPUs, integrated and discrete GPUs, and FPGAs.
+2. **Support for Heterogeneous Execution**: OpenVINO provides an API to write once and deploy on any supported Intel hardware (CPU, GPU, FPGA, VPU, etc.).
+3. **Model Optimizer**: OpenVINO provides a Model Optimizer that imports, converts, and optimizes models from popular deep learning frameworks such as PyTorch, TensorFlow, TensorFlow Lite, Keras, ONNX, PaddlePaddle, and Caffe.
+4. **Ease of Use**: The toolkit comes with more than [80 tutorial notebooks](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks) (including [YOLOv8 optimization](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/tree/main/notebooks/230-yolov8-optimization)) teaching different aspects of the toolkit.
+
+## OpenVINO Export Structure
+
+When you export a model to OpenVINO format, it results in a directory containing the following:
+
+1. **XML file**: Describes the network topology.
+2. **BIN file**: Contains the weights and biases binary data.
+3. **Mapping file**: Holds mapping of original model output tensors to OpenVINO tensor names.
+
+You can use these files to run inference with the OpenVINO Inference Engine.
+
+## Using OpenVINO Export in Deployment
+
+Once you have the OpenVINO files, you can use the OpenVINO Runtime to run the model. The Runtime provides a unified API to inference across all supported Intel hardware. It also provides advanced capabilities like load balancing across Intel hardware and asynchronous execution. For more information on running the inference, refer to the [Inference with OpenVINO Runtime Guide](https://docs.openvino.ai/2023.0/openvino_docs_OV_UG_OV_Runtime_User_Guide.html).
+
+Remember, you'll need the XML and BIN files as well as any application-specific settings like input size, scale factor for normalization, etc., to correctly set up and use the model with the Runtime.
+
+In your deployment application, you would typically do the following steps:
+
+1. Initialize OpenVINO by creating `core = Core()`.
+2. Load the model using the `core.read_model()` method.
+3. Compile the model using the `core.compile_model()` function.
+4. Prepare the input (image, text, audio, etc.).
+5. Run inference using `compiled_model(input_data)`.
+
+For more detailed steps and code snippets, refer to the [OpenVINO documentation](https://docs.openvino.ai/) or [API tutorial](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino_notebooks/blob/main/notebooks/002-openvino-api/002-openvino-api.ipynb).
+
+## OpenVINO YOLOv8 Benchmarks
+
+YOLOv8 benchmarks below were run by the Ultralytics team on 4 different model formats measuring speed and accuracy: PyTorch, TorchScript, ONNX and OpenVINO. Benchmarks were run on Intel Flex and Arc GPUs, and on Intel Xeon CPUs at FP32 precision (with the `half=False` argument).
+
+!!! note
+
+ The benchmarking results below are for reference and might vary based on the exact hardware and software configuration of a system, as well as the current workload of the system at the time the benchmarks are run.
+
+ All benchmarks run with `openvino` python package version [2023.0.1](https://pypi.org/project/openvino/2023.0.1/).
+
+### Intel Flex GPU
+
+The Intel® Data Center GPU Flex Series is a versatile and robust solution designed for the intelligent visual cloud. This GPU supports a wide array of workloads including media streaming, cloud gaming, AI visual inference, and virtual desktop Infrastructure workloads. It stands out for its open architecture and built-in support for the AV1 encode, providing a standards-based software stack for high-performance, cross-architecture applications. The Flex Series GPU is optimized for density and quality, offering high reliability, availability, and scalability.
+
+Benchmarks below run on Intel® Data Center GPU Flex 170 at FP32 precision.
+
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+