Docs cleanup and Google-style tracker docstrings (#6751)
Signed-off-by: Glenn Jocher <glenn.jocher@ultralytics.com> Co-authored-by: pre-commit-ci[bot] <66853113+pre-commit-ci[bot]@users.noreply.github.com>
This commit is contained in:
parent
60041014a8
commit
80802be1e5
44 changed files with 740 additions and 529 deletions
|
|
@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ YOLOv5 introduces some minor changes compared to its predecessors:
|
|||
|
||||
To test the speed of `SPP` and `SPPF`, the following code can be used:
|
||||
|
||||
<details markdown>
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>SPP vs SPPF speed profiling example (click to open)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ description: Learn how to optimize YOLOv5 with hyperparameter evolution using Ge
|
|||
keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv5, Hyperparameter Optimization, Genetic Algorithm, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, AI, Object Detection, Image Classification, Python
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
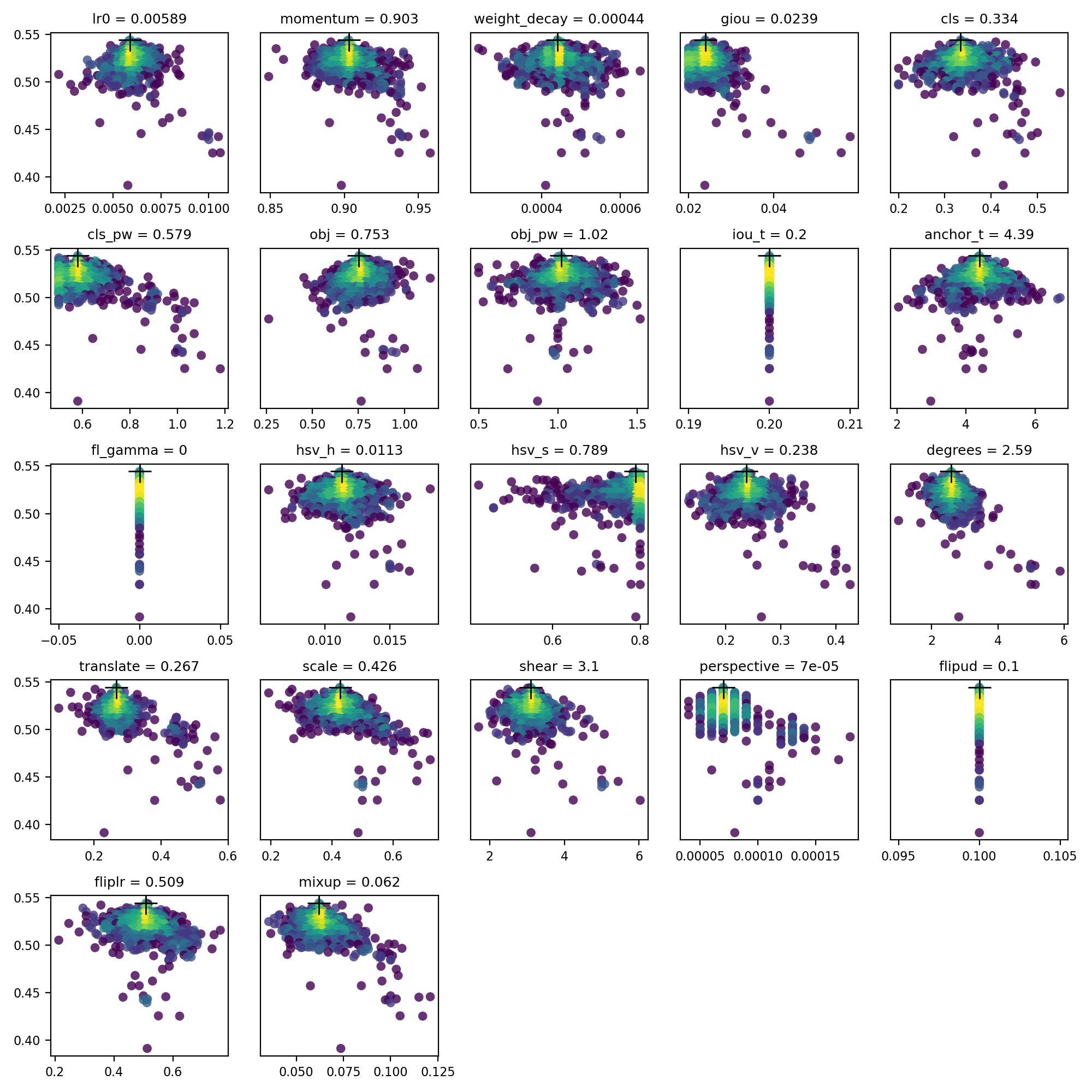
📚 This guide explains **hyperparameter evolution** for YOLOv5 🚀. Hyperparameter evolution is a method of [Hyperparameter Optimization](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperparameter_optimization) using a [Genetic Algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genetic_algorithm) (GA) for optimization. UPDATED 25 September 2022.
|
||||
📚 This guide explains **hyperparameter evolution** for YOLOv5 🚀. Hyperparameter evolution is a method of [Hyperparameter Optimization](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyperparameter_optimization) using a [Genetic Algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genetic_algorithm) (GA) for optimization.
|
||||
|
||||
Hyperparameters in ML control various aspects of training, and finding optimal values for them can be a challenge. Traditional methods like grid searches can quickly become intractable due to 1) the high dimensional search space 2) unknown correlations among the dimensions, and 3) expensive nature of evaluating the fitness at each point, making GA a suitable candidate for hyperparameter searches.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -149,17 +149,18 @@ We recommend a minimum of 300 generations of evolution for best results. Note th
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Environments
|
||||
## Supported Environments
|
||||
|
||||
YOLOv5 is designed to be run in the following up-to-date verified environments (with all dependencies including [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda)/[CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/) and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) preinstalled):
|
||||
Ultralytics provides a range of ready-to-use environments, each pre-installed with essential dependencies such as [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda), [CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/), and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), to kickstart your projects.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Notebooks** with free GPU: <a href="https://bit.ly/yolov5-paperspace-notebook"><img src="https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg" alt="Run on Gradient"></a> <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>
|
||||
- **Google Cloud** Deep Learning VM. See [GCP Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial/)
|
||||
- **Amazon** Deep Learning AMI. See [AWS Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial/)
|
||||
- **Docker Image**. See [Docker Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/docker_image_quickstart_tutorial/) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>
|
||||
- **Free GPU Notebooks**: <a href="https://bit.ly/yolov5-paperspace-notebook"><img src="https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg" alt="Run on Gradient"></a> <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>
|
||||
- **Google Cloud**: [GCP Quickstart Guide](../environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Amazon**: [AWS Quickstart Guide](../environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Azure**: [AzureML Quickstart Guide](../environments/azureml_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Docker**: [Docker Quickstart Guide](../environments/docker_image_quickstart_tutorial.md) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Status
|
||||
## Project Status
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml"><img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml/badge.svg" alt="YOLOv5 CI"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
If this badge is green, all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are currently passing. CI tests verify correct operation of YOLOv5 [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py) and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py) on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu every 24 hours and on every commit.
|
||||
This badge indicates that all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are successfully passing. These CI tests rigorously check the functionality and performance of YOLOv5 across various key aspects: [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py), and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py). They ensure consistent and reliable operation on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu, with tests conducted every 24 hours and upon each new commit.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ description: Learn how to ensemble YOLOv5 models for improved mAP and Recall! Cl
|
|||
keywords: YOLOv5, object detection, ensemble learning, mAP, Recall
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to use YOLOv5 🚀 **model ensembling** during testing and inference for improved mAP and Recall. UPDATED 25 September 2022.
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to use YOLOv5 🚀 **model ensembling** during testing and inference for improved mAP and Recall.
|
||||
|
||||
From [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ensemble_learning](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ensemble_learning):
|
||||
> Ensemble modeling is a process where multiple diverse models are created to predict an outcome, either by using many different modeling algorithms or using different training data sets. The ensemble model then aggregates the prediction of each base model and results in once final prediction for the unseen data. The motivation for using ensemble models is to reduce the generalization error of the prediction. As long as the base models are diverse and independent, the prediction error of the model decreases when the ensemble approach is used. The approach seeks the wisdom of crowds in making a prediction. Even though the ensemble model has multiple base models within the model, it acts and performs as a single model.
|
||||
|
|
@ -129,17 +129,18 @@ Done. (0.223s)
|
|||
|
||||
<img src="https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/26833433/124489091-ea4f9a00-ddb0-11eb-8ef1-d6f335c97f6f.jpg" width="500" alt="YOLO inference result">
|
||||
|
||||
## Environments
|
||||
## Supported Environments
|
||||
|
||||
YOLOv5 is designed to be run in the following up-to-date verified environments (with all dependencies including [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda)/[CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/) and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) preinstalled):
|
||||
Ultralytics provides a range of ready-to-use environments, each pre-installed with essential dependencies such as [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda), [CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/), and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), to kickstart your projects.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Notebooks** with free GPU: <a href="https://bit.ly/yolov5-paperspace-notebook"><img src="https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg" alt="Run on Gradient"></a> <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>
|
||||
- **Google Cloud** Deep Learning VM. See [GCP Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial/)
|
||||
- **Amazon** Deep Learning AMI. See [AWS Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial/)
|
||||
- **Docker Image**. See [Docker Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/docker_image_quickstart_tutorial/) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>
|
||||
- **Free GPU Notebooks**: <a href="https://bit.ly/yolov5-paperspace-notebook"><img src="https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg" alt="Run on Gradient"></a> <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>
|
||||
- **Google Cloud**: [GCP Quickstart Guide](../environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Amazon**: [AWS Quickstart Guide](../environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Azure**: [AzureML Quickstart Guide](../environments/azureml_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Docker**: [Docker Quickstart Guide](../environments/docker_image_quickstart_tutorial.md) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Status
|
||||
## Project Status
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml"><img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml/badge.svg" alt="YOLOv5 CI"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
If this badge is green, all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are currently passing. CI tests verify correct operation of YOLOv5 [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py) and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py) on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu every 24 hours and on every commit.
|
||||
This badge indicates that all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are successfully passing. These CI tests rigorously check the functionality and performance of YOLOv5 across various key aspects: [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py), and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py). They ensure consistent and reliable operation on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu, with tests conducted every 24 hours and upon each new commit.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv5, model export, PyTorch, TorchScript, ONNX, OpenVIN
|
|||
|
||||
# TFLite, ONNX, CoreML, TensorRT Export
|
||||
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to export a trained YOLOv5 🚀 model from PyTorch to ONNX and TorchScript formats. UPDATED 8 December 2022.
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to export a trained YOLOv5 🚀 model from PyTorch to ONNX and TorchScript formats.
|
||||
|
||||
## Before You Start
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -228,17 +228,18 @@ YOLOv5 OpenVINO C++ inference examples:
|
|||
|
||||
- [https://aukerul-shuvo.github.io/YOLOv5_TensorFlow-JS/](https://aukerul-shuvo.github.io/YOLOv5_TensorFlow-JS/)
|
||||
|
||||
## Environments
|
||||
## Supported Environments
|
||||
|
||||
YOLOv5 is designed to be run in the following up-to-date verified environments (with all dependencies including [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda)/[CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/) and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) preinstalled):
|
||||
Ultralytics provides a range of ready-to-use environments, each pre-installed with essential dependencies such as [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda), [CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/), and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), to kickstart your projects.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Notebooks** with free GPU: <a href="https://bit.ly/yolov5-paperspace-notebook"><img src="https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg" alt="Run on Gradient"></a> <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>
|
||||
- **Google Cloud** Deep Learning VM. See [GCP Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial/)
|
||||
- **Amazon** Deep Learning AMI. See [AWS Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial/)
|
||||
- **Docker Image**. See [Docker Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/docker_image_quickstart_tutorial/) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>
|
||||
- **Free GPU Notebooks**: <a href="https://bit.ly/yolov5-paperspace-notebook"><img src="https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg" alt="Run on Gradient"></a> <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>
|
||||
- **Google Cloud**: [GCP Quickstart Guide](../environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Amazon**: [AWS Quickstart Guide](../environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Azure**: [AzureML Quickstart Guide](../environments/azureml_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Docker**: [Docker Quickstart Guide](../environments/docker_image_quickstart_tutorial.md) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Status
|
||||
## Project Status
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml"><img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml/badge.svg" alt="YOLOv5 CI"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
If this badge is green, all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are currently passing. CI tests verify correct operation of YOLOv5 [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py) and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py) on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu every 24 hours and on every commit.
|
||||
This badge indicates that all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are successfully passing. These CI tests rigorously check the functionality and performance of YOLOv5 across various key aspects: [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py), and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py). They ensure consistent and reliable operation on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu, with tests conducted every 24 hours and upon each new commit.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ description: Improve YOLOv5 model efficiency by pruning with Ultralytics. Unders
|
|||
keywords: YOLOv5, YOLO, Ultralytics, model pruning, PyTorch, machine learning, deep learning, computer vision, object detection
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to apply **pruning** to YOLOv5 🚀 models. UPDATED 25 September 2022.
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to apply **pruning** to YOLOv5 🚀 models.
|
||||
|
||||
## Before You Start
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -93,17 +93,18 @@ Results saved to runs/val/exp3
|
|||
|
||||
In the results we can observe that we have achieved a **sparsity of 30%** in our model after pruning, which means that 30% of the model's weight parameters in `nn.Conv2d` layers are equal to 0. **Inference time is essentially unchanged**, while the model's **AP and AR scores a slightly reduced**.
|
||||
|
||||
## Environments
|
||||
## Supported Environments
|
||||
|
||||
YOLOv5 is designed to be run in the following up-to-date verified environments (with all dependencies including [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda)/[CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/) and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) preinstalled):
|
||||
Ultralytics provides a range of ready-to-use environments, each pre-installed with essential dependencies such as [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda), [CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/), and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), to kickstart your projects.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Notebooks** with free GPU: <a href="https://bit.ly/yolov5-paperspace-notebook"><img src="https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg" alt="Run on Gradient"></a> <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>
|
||||
- **Google Cloud** Deep Learning VM. See [GCP Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial/)
|
||||
- **Amazon** Deep Learning AMI. See [AWS Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial/)
|
||||
- **Docker Image**. See [Docker Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/docker_image_quickstart_tutorial/) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>
|
||||
- **Free GPU Notebooks**: <a href="https://bit.ly/yolov5-paperspace-notebook"><img src="https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg" alt="Run on Gradient"></a> <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>
|
||||
- **Google Cloud**: [GCP Quickstart Guide](../environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Amazon**: [AWS Quickstart Guide](../environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Azure**: [AzureML Quickstart Guide](../environments/azureml_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Docker**: [Docker Quickstart Guide](../environments/docker_image_quickstart_tutorial.md) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Status
|
||||
## Project Status
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml"><img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml/badge.svg" alt="YOLOv5 CI"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
If this badge is green, all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are currently passing. CI tests verify correct operation of YOLOv5 [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py) and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py) on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu every 24 hours and on every commit.
|
||||
This badge indicates that all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are successfully passing. These CI tests rigorously check the functionality and performance of YOLOv5 across various key aspects: [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py), and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py). They ensure consistent and reliable operation on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu, with tests conducted every 24 hours and upon each new commit.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ description: Learn how to train datasets on single or multiple GPUs using YOLOv5
|
|||
keywords: YOLOv5, multi-GPU Training, YOLOv5 training, deep learning, machine learning, object detection, Ultralytics
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to properly use **multiple** GPUs to train a dataset with YOLOv5 🚀 on single or multiple machine(s). UPDATED 25 December 2022.
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to properly use **multiple** GPUs to train a dataset with YOLOv5 🚀 on single or multiple machine(s).
|
||||
|
||||
## Before You Start
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -55,7 +55,7 @@ python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node 2 train.py --batch 64 --data co
|
|||
|
||||
The code above will use GPUs `0... (N-1)`.
|
||||
|
||||
<details markdown>
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>Use specific GPUs (click to expand)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
You can do so by simply passing `--device` followed by your specific GPUs. For example, in the code below, we will use GPUs `2,3`.
|
||||
|
|
@ -66,7 +66,7 @@ python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node 2 train.py --batch 64 --data co
|
|||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details markdown>
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>Use SyncBatchNorm (click to expand)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
[SyncBatchNorm](https://pytorch.org/docs/master/generated/torch.nn.SyncBatchNorm.html) could increase accuracy for multiple gpu training, however, it will slow down training by a significant factor. It is **only** available for Multiple GPU DistributedDataParallel training.
|
||||
|
|
@ -81,12 +81,12 @@ python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node 2 train.py --batch 64 --data co
|
|||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details markdown>
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>Use Multiple machines (click to expand)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
This is **only** available for Multiple GPU DistributedDataParallel training.
|
||||
|
||||
Before we continue, make sure the files on all machines are the same, dataset, codebase, etc. Afterwards, make sure the machines can communicate to each other.
|
||||
Before we continue, make sure the files on all machines are the same, dataset, codebase, etc. Afterward, make sure the machines can communicate to each other.
|
||||
|
||||
You will have to choose a master machine(the machine that the others will talk to). Note down its address(`master_addr`) and choose a port(`master_port`). I will use `master_addr = 192.168.1.1` and `master_port = 1234` for the example below.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -123,7 +123,7 @@ python -m torch.distributed.run --master_port 1234 --nproc_per_node 2 ...
|
|||
|
||||
DDP profiling results on an [AWS EC2 P4d instance](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial/) with 8x A100 SXM4-40GB for YOLOv5l for 1 COCO epoch.
|
||||
|
||||
<details markdown>
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>Profiling code</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
|
|
@ -153,12 +153,12 @@ python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node 8 train.py --batch-size 128 --d
|
|||
|
||||
If an error occurs, please read the checklist below first! (It could save your time)
|
||||
|
||||
<details markdown>
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>Checklist (click to expand) </summary>
|
||||
|
||||
<ul>
|
||||
<li>Have you properly read this post? </li>
|
||||
<li>Have you tried to reclone the codebase? The code changes <b>daily</b>.</li>
|
||||
<li>Have you tried to re-clone the codebase? The code changes <b>daily</b>.</li>
|
||||
<li>Have you tried to search for your error? Someone may have already encountered it in this repo or in another and have the solution. </li>
|
||||
<li>Have you installed all the requirements listed on top (including the correct Python and Pytorch versions)? </li>
|
||||
<li>Have you tried in other environments listed in the "Environments" section below? </li>
|
||||
|
|
@ -169,21 +169,22 @@ If you went through all the above, feel free to raise an Issue by giving as much
|
|||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
## Environments
|
||||
## Supported Environments
|
||||
|
||||
YOLOv5 is designed to be run in the following up-to-date verified environments (with all dependencies including [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda)/[CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/) and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) preinstalled):
|
||||
Ultralytics provides a range of ready-to-use environments, each pre-installed with essential dependencies such as [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda), [CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/), and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), to kickstart your projects.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Notebooks** with free GPU: <a href="https://bit.ly/yolov5-paperspace-notebook"><img src="https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg" alt="Run on Gradient"></a> <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>
|
||||
- **Google Cloud** Deep Learning VM. See [GCP Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial/)
|
||||
- **Amazon** Deep Learning AMI. See [AWS Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial/)
|
||||
- **Docker Image**. See [Docker Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/docker_image_quickstart_tutorial/) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>
|
||||
- **Free GPU Notebooks**: <a href="https://bit.ly/yolov5-paperspace-notebook"><img src="https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg" alt="Run on Gradient"></a> <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>
|
||||
- **Google Cloud**: [GCP Quickstart Guide](../environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Amazon**: [AWS Quickstart Guide](../environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Azure**: [AzureML Quickstart Guide](../environments/azureml_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Docker**: [Docker Quickstart Guide](../environments/docker_image_quickstart_tutorial.md) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Status
|
||||
## Project Status
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml"><img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml/badge.svg" alt="YOLOv5 CI"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
If this badge is green, all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are currently passing. CI tests verify correct operation of YOLOv5 [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py) and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py) on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu every 24 hours and on every commit.
|
||||
This badge indicates that all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are successfully passing. These CI tests rigorously check the functionality and performance of YOLOv5 across various key aspects: [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py), and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py). They ensure consistent and reliable operation on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu, with tests conducted every 24 hours and upon each new commit.
|
||||
|
||||
## Credits
|
||||
|
||||
I would like to thank @MagicFrogSJTU, who did all the heavy lifting, and @glenn-jocher for guiding us along the way.
|
||||
We would like to thank @MagicFrogSJTU, who did all the heavy lifting, and @glenn-jocher for guiding us along the way.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -146,7 +146,7 @@ url = 'http://0.0.0.0:5543/predict/from_files'
|
|||
resp = requests.post(url=url, files=files)
|
||||
|
||||
# response is returned in JSON
|
||||
annotations = json.loads(resp.text) # dictionary of annotation results
|
||||
annotations = json.loads(resp.text) # dictionary of annotation results
|
||||
bounding_boxes = annotations["boxes"]
|
||||
labels = annotations["labels"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ description: Detailed guide on loading YOLOv5 from PyTorch Hub. Includes example
|
|||
keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv5, PyTorch, loading YOLOv5, PyTorch Hub, inference, multi-GPU inference, training
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to load YOLOv5 🚀 from PyTorch Hub at [https://pytorch.org/hub/ultralytics_yolov5](https://pytorch.org/hub/ultralytics_yolov5). UPDATED 26 March 2023.
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to load YOLOv5 🚀 from PyTorch Hub at [https://pytorch.org/hub/ultralytics_yolov5](https://pytorch.org/hub/ultralytics_yolov5).
|
||||
|
||||
## Before You Start
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ im1 = Image.open('zidane.jpg') # PIL image
|
|||
im2 = cv2.imread('bus.jpg')[..., ::-1] # OpenCV image (BGR to RGB)
|
||||
|
||||
# Inference
|
||||
results = model([im1, im2], size=640) # batch of images
|
||||
results = model([im1, im2], size=640) # batch of images
|
||||
|
||||
# Results
|
||||
results.print()
|
||||
|
|
@ -87,12 +87,12 @@ YOLOv5 models contain various inference attributes such as **confidence threshol
|
|||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model.conf = 0.25 # NMS confidence threshold
|
||||
iou = 0.45 # NMS IoU threshold
|
||||
agnostic = False # NMS class-agnostic
|
||||
multi_label = False # NMS multiple labels per box
|
||||
classes = None # (optional list) filter by class, i.e. = [0, 15, 16] for COCO persons, cats and dogs
|
||||
max_det = 1000 # maximum number of detections per image
|
||||
amp = False # Automatic Mixed Precision (AMP) inference
|
||||
iou = 0.45 # NMS IoU threshold
|
||||
agnostic = False # NMS class-agnostic
|
||||
multi_label = False # NMS multiple labels per box
|
||||
classes = None # (optional list) filter by class, i.e. = [0, 15, 16] for COCO persons, cats and dogs
|
||||
max_det = 1000 # maximum number of detections per image
|
||||
amp = False # Automatic Mixed Precision (AMP) inference
|
||||
|
||||
results = model(im, size=320) # custom inference size
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -177,9 +177,11 @@ YOLOv5 models can be loaded to multiple GPUs in parallel with threaded inference
|
|||
import torch
|
||||
import threading
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def run(model, im):
|
||||
results = model(im)
|
||||
results.save()
|
||||
results = model(im)
|
||||
results.save()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Models
|
||||
model0 = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', device=0)
|
||||
|
|
@ -195,6 +197,8 @@ threading.Thread(target=run, args=[model1, 'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.j
|
|||
To load a YOLOv5 model for training rather than inference, set `autoshape=False`. To load a model with randomly initialized weights (to train from scratch) use `pretrained=False`. You must provide your own training script in this case. Alternatively see our YOLOv5 [Train Custom Data Tutorial](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/tutorials/train_custom_data) for model training.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', autoshape=False) # load pretrained
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'yolov5s', autoshape=False, pretrained=False) # load scratch
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -206,7 +210,7 @@ For use with API services. See https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/2291 a
|
|||
```python
|
||||
results = model(im) # inference
|
||||
|
||||
results.ims # array of original images (as np array) passed to model for inference
|
||||
results.ims # array of original images (as np array) passed to model for inference
|
||||
results.render() # updates results.ims with boxes and labels
|
||||
for im in results.ims:
|
||||
buffered = BytesIO()
|
||||
|
|
@ -233,7 +237,7 @@ results = model(im) # inference
|
|||
results.pandas().xyxy[0] # Pandas DataFrame
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<details markdown>
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>Pandas Output (click to expand)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
|
@ -274,15 +278,47 @@ results = model(ims) # inference
|
|||
results.pandas().xyxy[0].to_json(orient="records") # JSON img1 predictions
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<details markdown>
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>JSON Output (click to expand)</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
[
|
||||
{"xmin":749.5,"ymin":43.5,"xmax":1148.0,"ymax":704.5,"confidence":0.8740234375,"class":0,"name":"person"},
|
||||
{"xmin":433.5,"ymin":433.5,"xmax":517.5,"ymax":714.5,"confidence":0.6879882812,"class":27,"name":"tie"},
|
||||
{"xmin":115.25,"ymin":195.75,"xmax":1096.0,"ymax":708.0,"confidence":0.6254882812,"class":0,"name":"person"},
|
||||
{"xmin":986.0,"ymin":304.0,"xmax":1028.0,"ymax":420.0,"confidence":0.2873535156,"class":27,"name":"tie"}
|
||||
{
|
||||
"xmin": 749.5,
|
||||
"ymin": 43.5,
|
||||
"xmax": 1148.0,
|
||||
"ymax": 704.5,
|
||||
"confidence": 0.8740234375,
|
||||
"class": 0,
|
||||
"name": "person"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"xmin": 433.5,
|
||||
"ymin": 433.5,
|
||||
"xmax": 517.5,
|
||||
"ymax": 714.5,
|
||||
"confidence": 0.6879882812,
|
||||
"class": 27,
|
||||
"name": "tie"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"xmin": 115.25,
|
||||
"ymin": 195.75,
|
||||
"xmax": 1096.0,
|
||||
"ymax": 708.0,
|
||||
"confidence": 0.6254882812,
|
||||
"class": 0,
|
||||
"name": "person"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"xmin": 986.0,
|
||||
"ymin": 304.0,
|
||||
"xmax": 1028.0,
|
||||
"ymax": 420.0,
|
||||
"confidence": 0.2873535156,
|
||||
"class": 27,
|
||||
"name": "tie"
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -293,6 +329,8 @@ results.pandas().xyxy[0].to_json(orient="records") # JSON img1 predictions
|
|||
This example loads a custom 20-class [VOC](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/data/VOC.yaml)-trained YOLOv5s model `'best.pt'` with PyTorch Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'custom', path='path/to/best.pt') # local model
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('path/to/yolov5', 'custom', path='path/to/best.pt', source='local') # local repo
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
|
@ -305,27 +343,30 @@ PyTorch Hub supports inference on most YOLOv5 export formats, including custom t
|
|||
💡 ProTip: **ONNX** and **OpenVINO** may be up to 2-3X faster than PyTorch on [**CPU benchmarks**](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/6613)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'custom', path='yolov5s.pt') # PyTorch
|
||||
'yolov5s.torchscript') # TorchScript
|
||||
'yolov5s.onnx') # ONNX
|
||||
'yolov5s_openvino_model/') # OpenVINO
|
||||
'yolov5s.engine') # TensorRT
|
||||
'yolov5s.mlmodel') # CoreML (macOS-only)
|
||||
'yolov5s.tflite') # TFLite
|
||||
'yolov5s_paddle_model/') # PaddlePaddle
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'custom', path='yolov5s.torchscript') # TorchScript
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'custom', path='yolov5s.onnx') # ONNX
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'custom', path='yolov5s_openvino_model/') # OpenVINO
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'custom', path='yolov5s.engine') # TensorRT
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'custom', path='yolov5s.mlmodel') # CoreML (macOS-only)
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'custom', path='yolov5s.tflite') # TFLite
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('ultralytics/yolov5', 'custom', path='yolov5s_paddle_model/') # PaddlePaddle
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Environments
|
||||
## Supported Environments
|
||||
|
||||
YOLOv5 is designed to be run in the following up-to-date verified environments (with all dependencies including [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda)/[CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/) and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) preinstalled):
|
||||
Ultralytics provides a range of ready-to-use environments, each pre-installed with essential dependencies such as [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda), [CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/), and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), to kickstart your projects.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Notebooks** with free GPU: <a href="https://bit.ly/yolov5-paperspace-notebook"><img src="https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg" alt="Run on Gradient"></a> <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>
|
||||
- **Google Cloud** Deep Learning VM. See [GCP Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial/)
|
||||
- **Amazon** Deep Learning AMI. See [AWS Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial/)
|
||||
- **Docker Image**. See [Docker Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/docker_image_quickstart_tutorial/) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>
|
||||
- **Free GPU Notebooks**: <a href="https://bit.ly/yolov5-paperspace-notebook"><img src="https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg" alt="Run on Gradient"></a> <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>
|
||||
- **Google Cloud**: [GCP Quickstart Guide](../environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Amazon**: [AWS Quickstart Guide](../environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Azure**: [AzureML Quickstart Guide](../environments/azureml_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Docker**: [Docker Quickstart Guide](../environments/docker_image_quickstart_tutorial.md) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Status
|
||||
## Project Status
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml"><img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml/badge.svg" alt="YOLOv5 CI"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
If this badge is green, all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are currently passing. CI tests verify correct operation of YOLOv5 [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py) and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py) on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu every 24 hours and on every commit.
|
||||
This badge indicates that all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are successfully passing. These CI tests rigorously check the functionality and performance of YOLOv5 across various key aspects: [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py), and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py). They ensure consistent and reliable operation on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu, with tests conducted every 24 hours and upon each new commit.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv5, Roboflow, data organization, data labelling, data
|
|||
|
||||
# Roboflow Datasets
|
||||
|
||||
You can now use Roboflow to organize, label, prepare, version, and host your datasets for training YOLOv5 🚀 models. Roboflow is free to use with YOLOv5 if you make your workspace public. UPDATED 7 June 2023.
|
||||
You can now use Roboflow to organize, label, prepare, version, and host your datasets for training YOLOv5 🚀 models. Roboflow is free to use with YOLOv5 if you make your workspace public.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Warning
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ After uploading data to Roboflow, you can label your data and review previous la
|
|||
|
||||
## Versioning
|
||||
|
||||
You can make versions of your dataset with different preprocessing and offline augmentation options. YOLOv5 does online augmentations natively, so be intentional when layering Roboflow's offline augs on top.
|
||||
You can make versions of your dataset with different preprocessing and offline augmentation options. YOLOv5 does online augmentations natively, so be intentional when layering Roboflow's offline augmentations on top.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -50,3 +50,19 @@ We have released a custom training tutorial demonstrating all of the above capab
|
|||
The real world is messy and your model will invariably encounter situations your dataset didn't anticipate. Using [active learning](https://blog.roboflow.com/what-is-active-learning/) is an important strategy to iteratively improve your dataset and model. With the Roboflow and YOLOv5 integration, you can quickly make improvements on your model deployments by using a battle tested machine learning pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align=""><a href="https://roboflow.com/?ref=ultralytics"><img width="1000" src="https://uploads-ssl.webflow.com/5f6bc60e665f54545a1e52a5/615627e5824c9c6195abfda9_computer-vision-cycle.png" alt="Roboflow active learning"></a></p>
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported Environments
|
||||
|
||||
Ultralytics provides a range of ready-to-use environments, each pre-installed with essential dependencies such as [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda), [CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/), and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), to kickstart your projects.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Free GPU Notebooks**: <a href="https://bit.ly/yolov5-paperspace-notebook"><img src="https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg" alt="Run on Gradient"></a> <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>
|
||||
- **Google Cloud**: [GCP Quickstart Guide](../environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Amazon**: [AWS Quickstart Guide](../environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Azure**: [AzureML Quickstart Guide](../environments/azureml_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Docker**: [Docker Quickstart Guide](../environments/docker_image_quickstart_tutorial.md) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Project Status
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml"><img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml/badge.svg" alt="YOLOv5 CI"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
This badge indicates that all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are successfully passing. These CI tests rigorously check the functionality and performance of YOLOv5 across various key aspects: [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py), and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py). They ensure consistent and reliable operation on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu, with tests conducted every 24 hours and upon each new commit.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: TensorRT, NVIDIA Jetson, DeepStream SDK, deployment, Ultralytics, YOLO
|
|||
|
||||
# Deploy on NVIDIA Jetson using TensorRT and DeepStream SDK
|
||||
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to deploy a trained model into NVIDIA Jetson Platform and perform inference using TensorRT and DeepStream SDK. Here we use TensorRT to maximize the inference performance on the Jetson platform. UPDATED 18 November 2022.
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to deploy a trained model into NVIDIA Jetson Platform and perform inference using TensorRT and DeepStream SDK. Here we use TensorRT to maximize the inference performance on the Jetson platform.
|
||||
|
||||
## Hardware Verification
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: YOLOv5, Ultralytics, Test-Time Augmentation, TTA, mAP, Recall, model p
|
|||
|
||||
# Test-Time Augmentation (TTA)
|
||||
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to use Test Time Augmentation (TTA) during testing and inference for improved mAP and Recall with YOLOv5 🚀. UPDATED 25 September 2022.
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to use Test Time Augmentation (TTA) during testing and inference for improved mAP and Recall with YOLOv5 🚀.
|
||||
|
||||
## Before You Start
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -147,17 +147,18 @@ results.print() # or .show(), .save(), .crop(), .pandas(), etc.
|
|||
|
||||
You can customize the TTA ops applied in the YOLOv5 `forward_augment()` method [here](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/8c6f9e15bfc0000d18b976a95b9d7c17d407ec91/models/yolo.py#L125-L137).
|
||||
|
||||
## Environments
|
||||
## Supported Environments
|
||||
|
||||
YOLOv5 is designed to be run in the following up-to-date verified environments (with all dependencies including [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda)/[CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/) and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) preinstalled):
|
||||
Ultralytics provides a range of ready-to-use environments, each pre-installed with essential dependencies such as [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda), [CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/), and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), to kickstart your projects.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Notebooks** with free GPU: <a href="https://bit.ly/yolov5-paperspace-notebook"><img src="https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg" alt="Run on Gradient"></a> <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>
|
||||
- **Google Cloud** Deep Learning VM. See [GCP Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial/)
|
||||
- **Amazon** Deep Learning AMI. See [AWS Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial/)
|
||||
- **Docker Image**. See [Docker Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/docker_image_quickstart_tutorial/) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>
|
||||
- **Free GPU Notebooks**: <a href="https://bit.ly/yolov5-paperspace-notebook"><img src="https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg" alt="Run on Gradient"></a> <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>
|
||||
- **Google Cloud**: [GCP Quickstart Guide](../environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Amazon**: [AWS Quickstart Guide](../environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Azure**: [AzureML Quickstart Guide](../environments/azureml_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Docker**: [Docker Quickstart Guide](../environments/docker_image_quickstart_tutorial.md) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Status
|
||||
## Project Status
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml"><img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml/badge.svg" alt="YOLOv5 CI"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
If this badge is green, all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are currently passing. CI tests verify correct operation of YOLOv5 [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py) and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py) on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu every 24 hours and on every commit.
|
||||
This badge indicates that all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are successfully passing. These CI tests rigorously check the functionality and performance of YOLOv5 across various key aspects: [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py), and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py). They ensure consistent and reliable operation on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu, with tests conducted every 24 hours and upon each new commit.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ description: Our comprehensive guide provides insights on how to train your YOLO
|
|||
keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv5, Training guide, dataset preparation, model selection, training settings, mAP results, Machine Learning, Object Detection
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to produce the best mAP and training results with YOLOv5 🚀. UPDATED 25 May 2022.
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to produce the best mAP and training results with YOLOv5 🚀.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of the time good results can be obtained with no changes to the models or training settings, **provided your dataset is sufficiently large and well labelled**. If at first you don't get good results, there are steps you might be able to take to improve, but we always recommend users **first train with all default settings** before considering any changes. This helps establish a performance baseline and spot areas for improvement.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ python train.py --data custom.yaml --weights '' --cfg yolov5s.yaml
|
|||
|
||||
Before modifying anything, **first train with default settings to establish a performance baseline**. A full list of train.py settings can be found in the [train.py](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py) argparser.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Epochs.** Start with 300 epochs. If this overfits early then you can reduce epochs. If overfitting does not occur after 300 epochs, train longer, i.e. 600, 1200 etc epochs.
|
||||
- **Epochs.** Start with 300 epochs. If this overfits early then you can reduce epochs. If overfitting does not occur after 300 epochs, train longer, i.e. 600, 1200 etc. epochs.
|
||||
- **Image size.** COCO trains at native resolution of `--img 640`, though due to the high amount of small objects in the dataset it can benefit from training at higher resolutions such as `--img 1280`. If there are many small objects then custom datasets will benefit from training at native or higher resolution. Best inference results are obtained at the same `--img` as the training was run at, i.e. if you train at `--img 1280` you should also test and detect at `--img 1280`.
|
||||
- **Batch size.** Use the largest `--batch-size` that your hardware allows for. Small batch sizes produce poor batchnorm statistics and should be avoided.
|
||||
- **Hyperparameters.** Default hyperparameters are in [hyp.scratch-low.yaml](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/data/hyps/hyp.scratch-low.yaml). We recommend you train with default hyperparameters first before thinking of modifying any. In general, increasing augmentation hyperparameters will reduce and delay overfitting, allowing for longer trainings and higher final mAP. Reduction in loss component gain hyperparameters like `hyp['obj']` will help reduce overfitting in those specific loss components. For an automated method of optimizing these hyperparameters, see our [Hyperparameter Evolution Tutorial](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/tutorials/hyperparameter_evolution).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ description: Learn how to train your data on custom datasets using YOLOv5. Simpl
|
|||
keywords: YOLOv5, train on custom dataset, image collection, model training, object detection, image labelling, Ultralytics, PyTorch, machine learning
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to train your own **custom dataset** with [YOLOv5](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5) 🚀. UPDATED 7 June 2023.
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to train your own **custom dataset** with [YOLOv5](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5) 🚀.
|
||||
|
||||
## Before You Start
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ Creating a custom model to detect your objects is an iterative process of collec
|
|||
|
||||
YOLOv5 models must be trained on labelled data in order to learn classes of objects in that data. There are two options for creating your dataset before you start training:
|
||||
|
||||
<details open markdown>
|
||||
<details open>
|
||||
<summary>Use <a href="https://roboflow.com/?ref=ultralytics">Roboflow</a> to create your dataset in YOLO format 🌟</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Warning
|
||||
|
|
@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ Export in `YOLOv5 Pytorch` format, then copy the snippet into your training scri
|
|||
Now continue with `2. Select a Model`.
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details markdown>
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>Or manually prepare your dataset</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.1 Create dataset.yaml
|
||||
|
|
@ -94,7 +94,7 @@ names:
|
|||
0: person
|
||||
1: bicycle
|
||||
2: car
|
||||
...
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
77: teddy bear
|
||||
78: hair drier
|
||||
79: toothbrush
|
||||
|
|
@ -212,17 +212,18 @@ Once your model is trained you can use your best checkpoint `best.pt` to:
|
|||
* [Evolve](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/tutorials/hyperparameter_evolution) hyperparameters to improve performance
|
||||
* [Improve](https://docs.roboflow.com/adding-data/upload-api?ref=ultralytics) your model by sampling real-world images and adding them to your dataset
|
||||
|
||||
## Environments
|
||||
## Supported Environments
|
||||
|
||||
YOLOv5 is designed to be run in the following up-to-date verified environments (with all dependencies including [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda)/[CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/) and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) preinstalled):
|
||||
Ultralytics provides a range of ready-to-use environments, each pre-installed with essential dependencies such as [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda), [CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/), and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), to kickstart your projects.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Notebooks** with free GPU: <a href="https://bit.ly/yolov5-paperspace-notebook"><img src="https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg" alt="Run on Gradient"></a> <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>
|
||||
- **Google Cloud** Deep Learning VM. See [GCP Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial/)
|
||||
- **Amazon** Deep Learning AMI. See [AWS Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial/)
|
||||
- **Docker Image**. See [Docker Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/docker_image_quickstart_tutorial/) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>
|
||||
- **Free GPU Notebooks**: <a href="https://bit.ly/yolov5-paperspace-notebook"><img src="https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg" alt="Run on Gradient"></a> <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>
|
||||
- **Google Cloud**: [GCP Quickstart Guide](../environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Amazon**: [AWS Quickstart Guide](../environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Azure**: [AzureML Quickstart Guide](../environments/azureml_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Docker**: [Docker Quickstart Guide](../environments/docker_image_quickstart_tutorial.md) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Status
|
||||
## Project Status
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml"><img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml/badge.svg" alt="YOLOv5 CI"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
If this badge is green, all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are currently passing. CI tests verify correct operation of YOLOv5 [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py) and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py) on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu every 24 hours and on every commit.
|
||||
This badge indicates that all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are successfully passing. These CI tests rigorously check the functionality and performance of YOLOv5 across various key aspects: [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py), and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py). They ensure consistent and reliable operation on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu, with tests conducted every 24 hours and upon each new commit.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ description: Learn to freeze YOLOv5 layers for efficient transfer learning. Opti
|
|||
keywords: YOLOv5, freeze layers, transfer learning, model retraining, Ultralytics
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to **freeze** YOLOv5 🚀 layers when **transfer learning**. Transfer learning is a useful way to quickly retrain a model on new data without having to retrain the entire network. Instead, part of the initial weights are frozen in place, and the rest of the weights are used to compute loss and are updated by the optimizer. This requires less resources than normal training and allows for faster training times, though it may also result in reductions to final trained accuracy. UPDATED 25 September 2022.
|
||||
📚 This guide explains how to **freeze** YOLOv5 🚀 layers when **transfer learning**. Transfer learning is a useful way to quickly retrain a model on new data without having to retrain the entire network. Instead, part of the initial weights are frozen in place, and the rest of the weights are used to compute loss and are updated by the optimizer. This requires less resources than normal training and allows for faster training times, though it may also result in reductions to final trained accuracy.
|
||||
|
||||
## Before You Start
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -21,13 +21,13 @@ pip install -r requirements.txt # install
|
|||
All layers that match the train.py `freeze` list in train.py will be frozen by setting their gradients to zero before training starts.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Freeze
|
||||
freeze = [f'model.{x}.' for x in range(freeze)] # layers to freeze
|
||||
for k, v in model.named_parameters():
|
||||
v.requires_grad = True # train all layers
|
||||
if any(x in k for x in freeze):
|
||||
print(f'freezing {k}')
|
||||
v.requires_grad = False
|
||||
# Freeze
|
||||
freeze = [f'model.{x}.' for x in range(freeze)] # layers to freeze
|
||||
for k, v in model.named_parameters():
|
||||
v.requires_grad = True # train all layers
|
||||
if any(x in k for x in freeze):
|
||||
print(f'freezing {k}')
|
||||
v.requires_grad = False
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To see a list of module names:
|
||||
|
|
@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ To see a list of module names:
|
|||
for k, v in model.named_parameters():
|
||||
print(k)
|
||||
|
||||
# Output
|
||||
"""Output:
|
||||
model.0.conv.conv.weight
|
||||
model.0.conv.bn.weight
|
||||
model.0.conv.bn.bias
|
||||
|
|
@ -54,48 +54,49 @@ model.24.m.1.weight
|
|||
model.24.m.1.bias
|
||||
model.24.m.2.weight
|
||||
model.24.m.2.bias
|
||||
"""
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Looking at the model architecture we can see that the model backbone is layers 0-9:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
# YOLOv5 backbone
|
||||
backbone:
|
||||
# [from, number, module, args]
|
||||
[[-1, 1, Focus, [64, 3]], # 0-P1/2
|
||||
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
|
||||
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [128]],
|
||||
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
|
||||
[-1, 9, BottleneckCSP, [256]],
|
||||
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
|
||||
[-1, 9, BottleneckCSP, [512]],
|
||||
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
|
||||
[-1, 1, SPP, [1024, [5, 9, 13]]],
|
||||
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [1024, False]], # 9
|
||||
]
|
||||
backbone:
|
||||
# [from, number, module, args]
|
||||
[[-1, 1, Focus, [64, 3]], # 0-P1/2
|
||||
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
|
||||
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [128]],
|
||||
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
|
||||
[-1, 9, BottleneckCSP, [256]],
|
||||
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
|
||||
[-1, 9, BottleneckCSP, [512]],
|
||||
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
|
||||
[-1, 1, SPP, [1024, [5, 9, 13]]],
|
||||
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [1024, False]], # 9
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
# YOLOv5 head
|
||||
head:
|
||||
[[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
|
||||
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
|
||||
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
|
||||
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [512, False]], # 13
|
||||
# YOLOv5 head
|
||||
head:
|
||||
[[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
|
||||
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
|
||||
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
|
||||
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [512, False]], # 13
|
||||
|
||||
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
|
||||
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
|
||||
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
|
||||
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [256, False]], # 17 (P3/8-small)
|
||||
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
|
||||
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
|
||||
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
|
||||
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [256, False]], # 17 (P3/8-small)
|
||||
|
||||
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
|
||||
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
|
||||
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [512, False]], # 20 (P4/16-medium)
|
||||
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
|
||||
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
|
||||
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [512, False]], # 20 (P4/16-medium)
|
||||
|
||||
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
|
||||
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
|
||||
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [1024, False]], # 23 (P5/32-large)
|
||||
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
|
||||
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
|
||||
[-1, 3, BottleneckCSP, [1024, False]], # 23 (P5/32-large)
|
||||
|
||||
[[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
|
||||
]
|
||||
[[17, 20, 23], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
so we can define the freeze list to contain all modules with 'model.0.' - 'model.9.' in their names:
|
||||
|
|
@ -116,7 +117,7 @@ python train.py --freeze 24
|
|||
|
||||
We train YOLOv5m on VOC on both of the above scenarios, along with a default model (no freezing), starting from the official COCO pretrained `--weights yolov5m.pt`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
train.py --batch 48 --weights yolov5m.pt --data voc.yaml --epochs 50 --cache --img 512 --hyp hyp.finetune.yaml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -138,17 +139,18 @@ Interestingly, the more modules are frozen the less GPU memory is required to tr
|
|||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Environments
|
||||
## Supported Environments
|
||||
|
||||
YOLOv5 is designed to be run in the following up-to-date verified environments (with all dependencies including [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda)/[CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/) and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) preinstalled):
|
||||
Ultralytics provides a range of ready-to-use environments, each pre-installed with essential dependencies such as [CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda), [CUDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn), [Python](https://www.python.org/), and [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), to kickstart your projects.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Notebooks** with free GPU: <a href="https://bit.ly/yolov5-paperspace-notebook"><img src="https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg" alt="Run on Gradient"></a> <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>
|
||||
- **Google Cloud** Deep Learning VM. See [GCP Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial/)
|
||||
- **Amazon** Deep Learning AMI. See [AWS Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial/)
|
||||
- **Docker Image**. See [Docker Quickstart Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/docker_image_quickstart_tutorial/) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>
|
||||
- **Free GPU Notebooks**: <a href="https://bit.ly/yolov5-paperspace-notebook"><img src="https://assets.paperspace.io/img/gradient-badge.svg" alt="Run on Gradient"></a> <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>
|
||||
- **Google Cloud**: [GCP Quickstart Guide](../environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Amazon**: [AWS Quickstart Guide](../environments/aws_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Azure**: [AzureML Quickstart Guide](../environments/azureml_quickstart_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- **Docker**: [Docker Quickstart Guide](../environments/docker_image_quickstart_tutorial.md) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Status
|
||||
## Project Status
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml"><img src="https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml/badge.svg" alt="YOLOv5 CI"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
If this badge is green, all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are currently passing. CI tests verify correct operation of YOLOv5 [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py) and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py) on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu every 24 hours and on every commit.
|
||||
This badge indicates that all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions) Continuous Integration (CI) tests are successfully passing. These CI tests rigorously check the functionality and performance of YOLOv5 across various key aspects: [training](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/train.py), [validation](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/val.py), [inference](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/detect.py), [export](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/export.py), and [benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/benchmarks.py). They ensure consistent and reliable operation on macOS, Windows, and Ubuntu, with tests conducted every 24 hours and upon each new commit.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue