Docs cleanup and Google-style tracker docstrings (#6751)
Signed-off-by: Glenn Jocher <glenn.jocher@ultralytics.com> Co-authored-by: pre-commit-ci[bot] <66853113+pre-commit-ci[bot]@users.noreply.github.com>
This commit is contained in:
parent
60041014a8
commit
80802be1e5
44 changed files with 740 additions and 529 deletions
|
|
@ -1,88 +1,95 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
comments: true
|
||||
description: Step-by-step guide to run YOLOv5 on AWS Deep Learning instance. Learn how to create an instance, connect to it and train, validate and deploy models.
|
||||
keywords: AWS, YOLOv5, instance, deep learning, Ultralytics, guide, training, deployment, object detection
|
||||
description: Follow this comprehensive guide to set up and operate YOLOv5 on an AWS Deep Learning instance for object detection tasks. Get started with model training and deployment.
|
||||
keywords: YOLOv5, AWS Deep Learning AMIs, object detection, machine learning, AI, model training, instance setup, Ultralytics
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# YOLOv5 🚀 on AWS Deep Learning Instance: A Comprehensive Guide
|
||||
# YOLOv5 🚀 on AWS Deep Learning Instance: Your Complete Guide
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will help new users run YOLOv5 on an Amazon Web Services (AWS) Deep Learning instance. AWS offers a [Free Tier](https://aws.amazon.com/free/) and a [credit program](https://aws.amazon.com/activate/) for a quick and affordable start.
|
||||
Setting up a high-performance deep learning environment can be daunting for newcomers, but fear not! 🛠️ With this guide, we'll walk you through the process of getting YOLOv5 up and running on an AWS Deep Learning instance. By leveraging the power of Amazon Web Services (AWS), even those new to machine learning can get started quickly and cost-effectively. The AWS platform's scalability is perfect for both experimentation and production deployment.
|
||||
|
||||
Other quickstart options for YOLOv5 include our [Colab Notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb) <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>, [GCP Deep Learning VM](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial), and our Docker image at [Docker Hub](https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>. *Updated: 21 April 2023*.
|
||||
Other quickstart options for YOLOv5 include our [Colab Notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb) <a href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/master/tutorial.ipynb"><img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"></a> <a href="https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"></a>, [GCP Deep Learning VM](https://docs.ultralytics.com/yolov5/environments/google_cloud_quickstart_tutorial), and our Docker image at [Docker Hub](https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5) <a href="https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/yolov5"><img src="https://img.shields.io/docker/pulls/ultralytics/yolov5?logo=docker" alt="Docker Pulls"></a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. AWS Console Sign-in
|
||||
## Step 1: AWS Console Sign-In
|
||||
|
||||
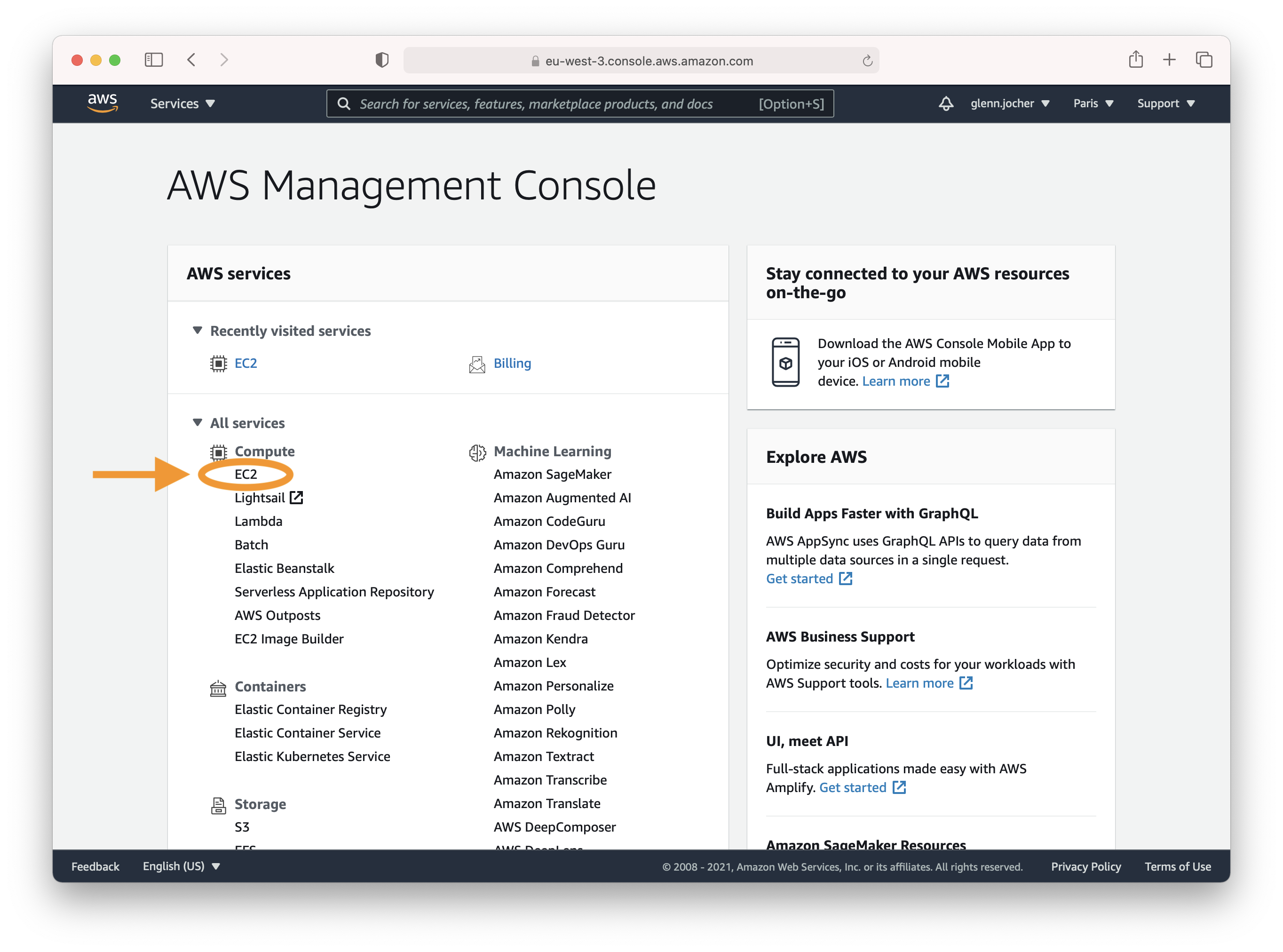
Create an account or sign in to the AWS console at [https://aws.amazon.com/console/](https://aws.amazon.com/console/) and select the **EC2** service.
|
||||
Start by creating an account or signing in to the AWS console at [https://aws.amazon.com/console/](https://aws.amazon.com/console/). Once logged in, select the **EC2** service to manage and set up your instances.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. Launch Instance
|
||||
## Step 2: Launch Your Instance
|
||||
|
||||
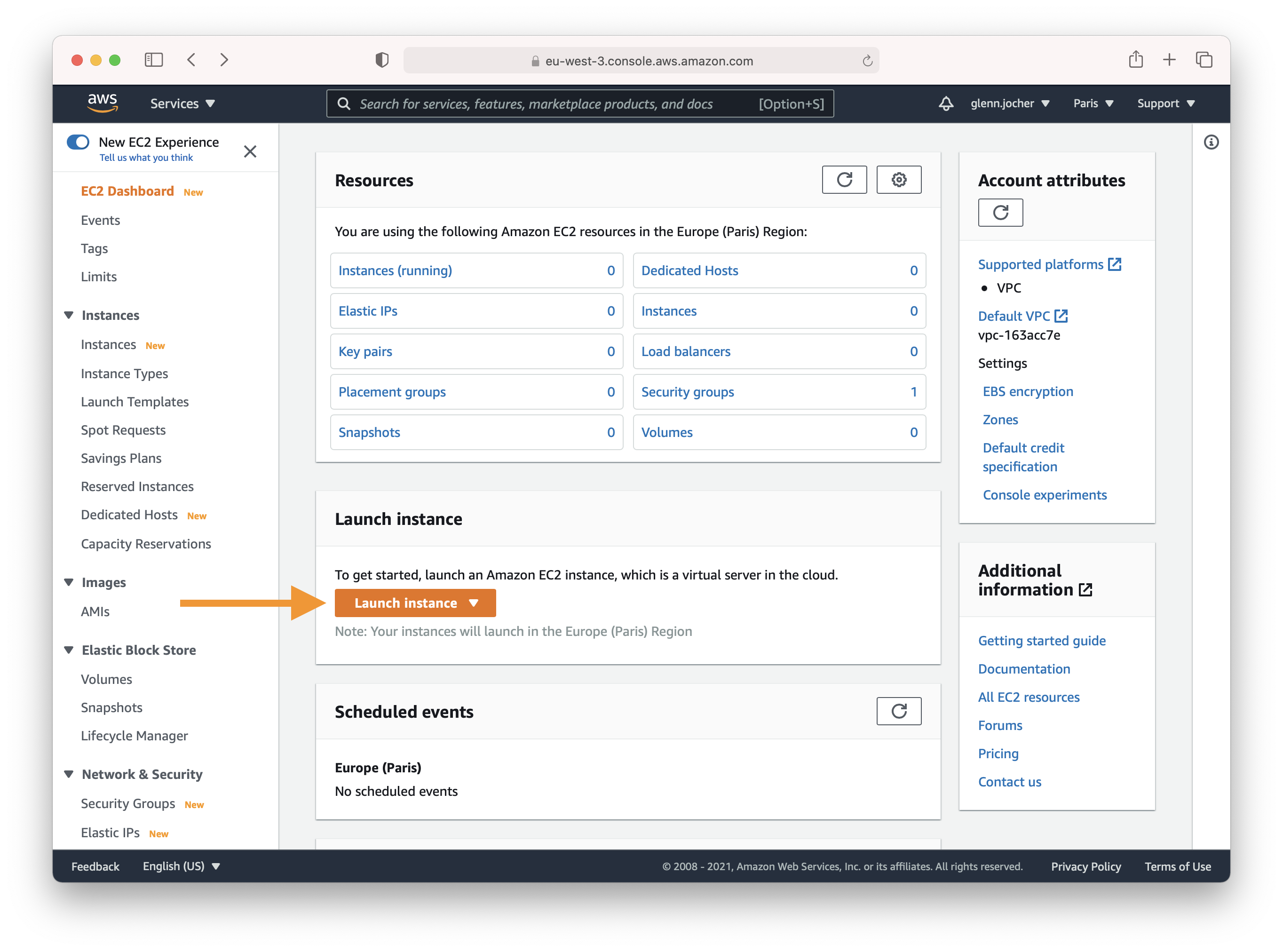
In the EC2 section of the AWS console, click the **Launch instance** button.
|
||||
In the EC2 dashboard, you'll find the **Launch Instance** button which is your gateway to creating a new virtual server.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Choose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
|
||||
### Selecting the Right Amazon Machine Image (AMI)
|
||||
|
||||
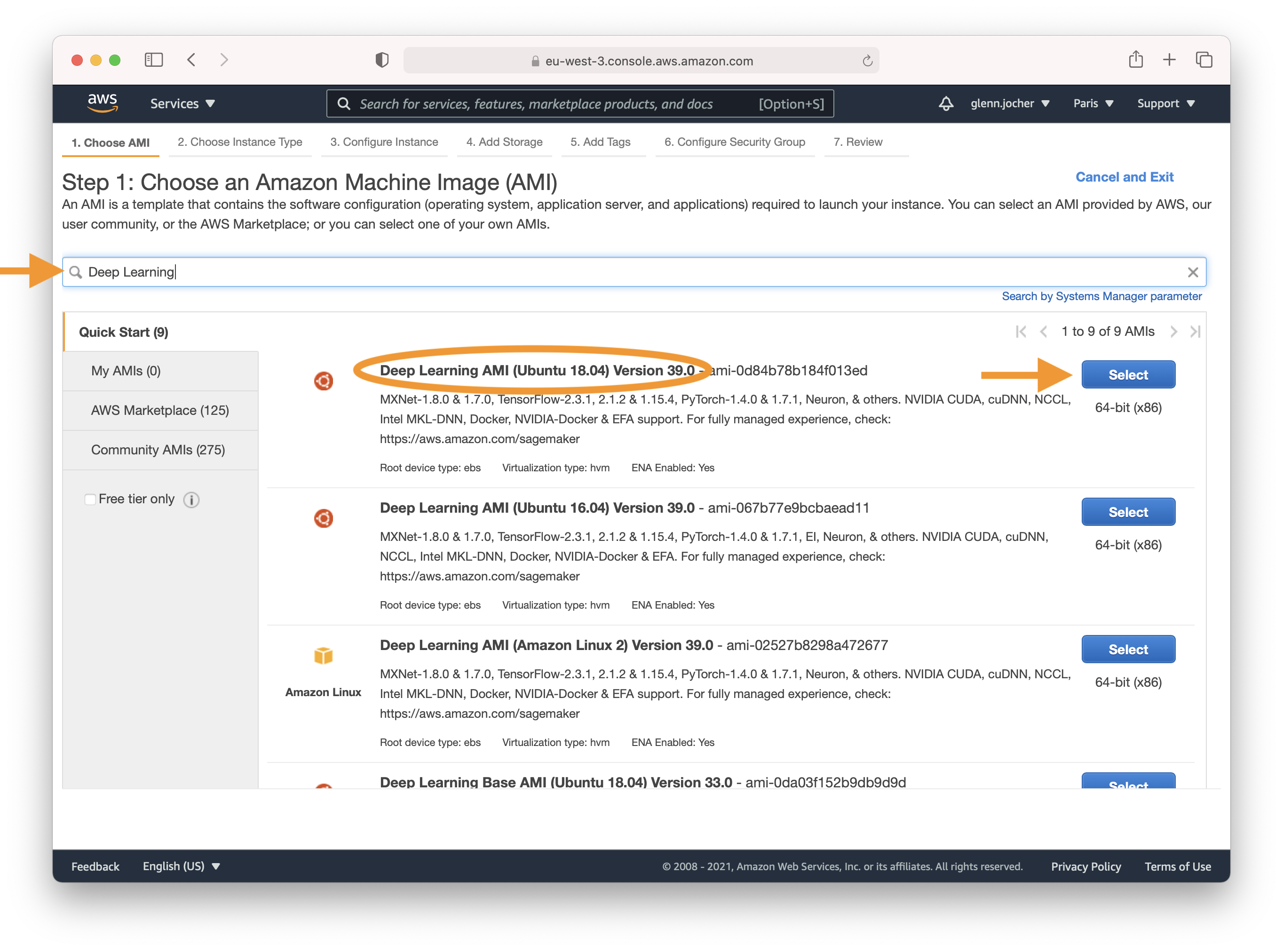
Enter 'Deep Learning' in the search field and select the most recent Ubuntu Deep Learning AMI (recommended), or an alternative Deep Learning AMI. For more information on selecting an AMI, see [Choosing Your DLAMI](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/dlami/latest/devguide/options.html).
|
||||
Here's where you choose the operating system and software stack for your instance. Type 'Deep Learning' into the search field and select the latest Ubuntu-based Deep Learning AMI, unless your needs dictate otherwise. Amazon's Deep Learning AMIs come pre-installed with popular frameworks and GPU drivers to streamline your setup process.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Select an Instance Type
|
||||
### Picking an Instance Type
|
||||
|
||||
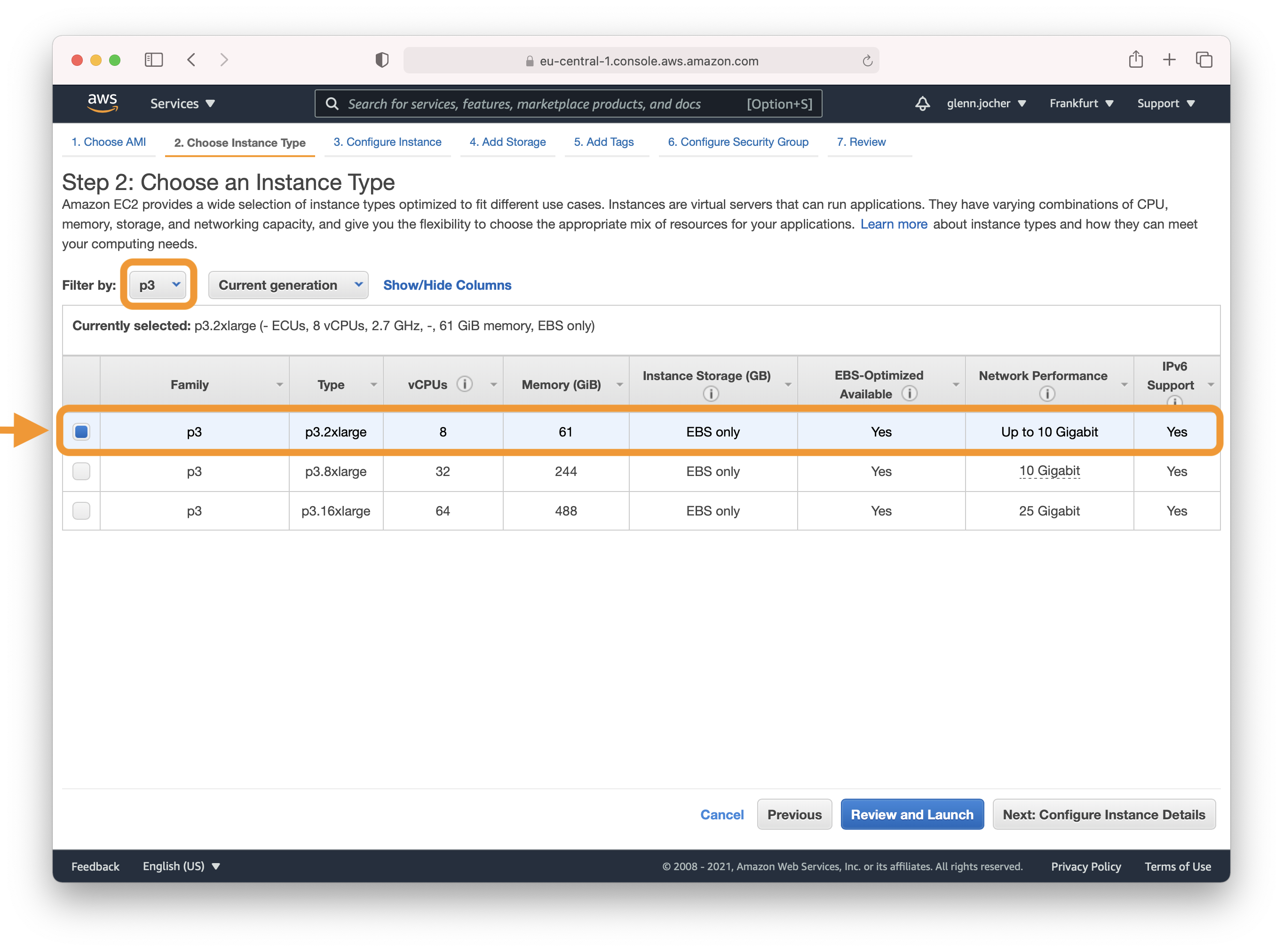
A GPU instance is recommended for most deep learning purposes. Training new models will be faster on a GPU instance than a CPU instance. Multi-GPU instances or distributed training across multiple instances with GPUs can offer sub-linear scaling. To set up distributed training, see [Distributed Training](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/dlami/latest/devguide/distributed-training.html).
|
||||
For deep learning tasks, selecting a GPU instance type is generally recommended as it can vastly accelerate model training. For instance size considerations, remember that the model's memory requirements should never exceed what your instance can provide.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** The size of your model should be a factor in selecting an instance. If your model exceeds an instance's available RAM, select a different instance type with enough memory for your application.
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to [EC2 Instance Types](https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/instance-types/) and choose Accelerated Computing to see the different GPU instance options.
|
||||
For a list of available GPU instance types, visit [EC2 Instance Types](https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/instance-types/), specifically under Accelerated Computing.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For more information on GPU monitoring and optimization, see [GPU Monitoring and Optimization](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/dlami/latest/devguide/tutorial-gpu.html). For pricing, see [On-Demand Pricing](https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/pricing/on-demand/) and [Spot Pricing](https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/spot/pricing/).
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure Instance Details
|
||||
### Configuring Your Instance
|
||||
|
||||
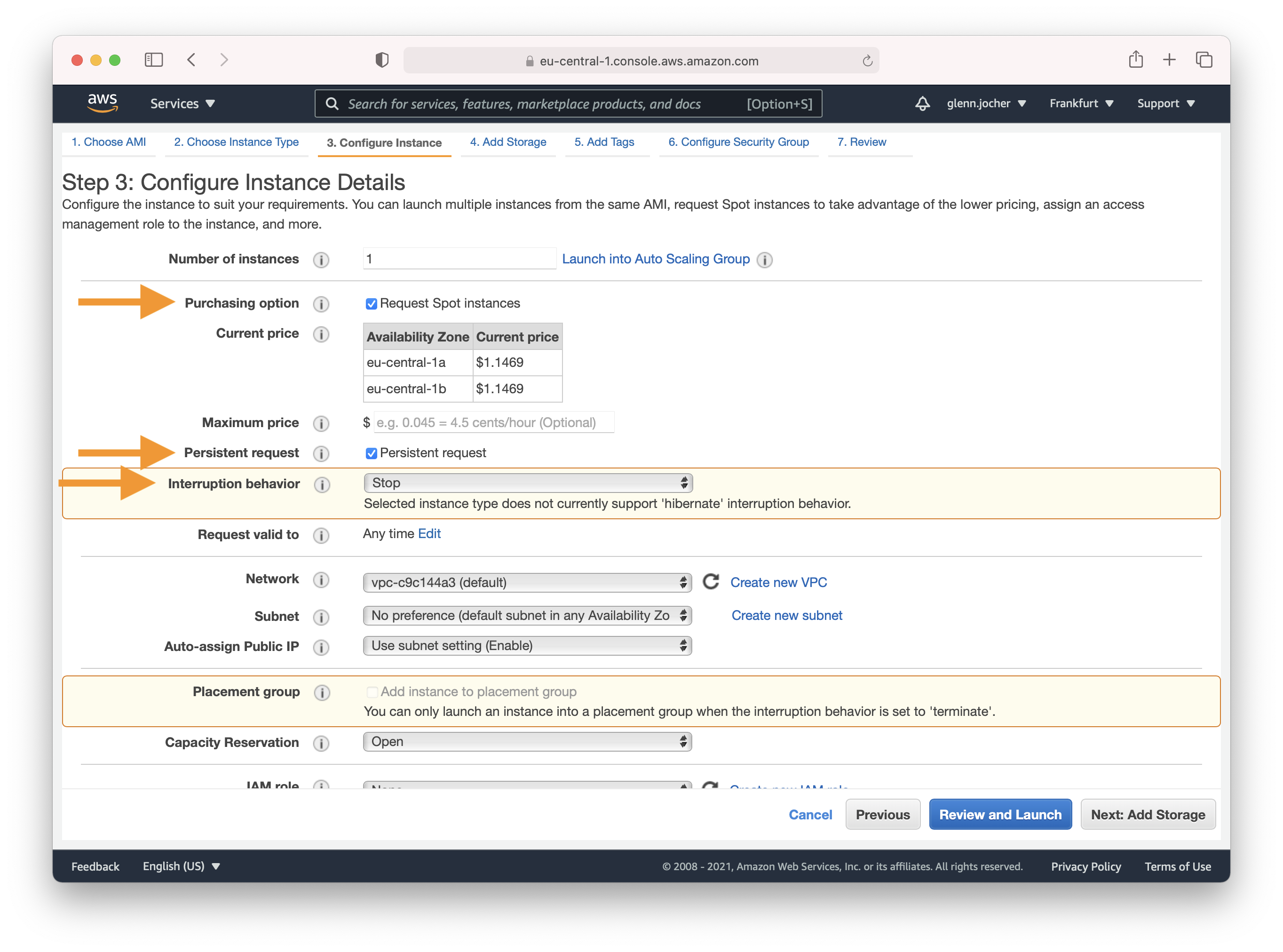
Amazon EC2 Spot Instances let you take advantage of unused EC2 capacity in the AWS cloud. Spot Instances are available at up to a 70% discount compared to On-Demand prices. We recommend a persistent spot instance, which will save your data and restart automatically when spot instance availability returns after spot instance termination. For full-price On-Demand instances, leave these settings at their default values.
|
||||
Amazon EC2 Spot Instances offer a cost-effective way to run applications as they allow you to bid for unused capacity at a fraction of the standard cost. For a persistent experience that retains data even when the Spot Instance goes down, opt for a persistent request.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Complete Steps 4-7 to finalize your instance hardware and security settings, and then launch the instance.
|
||||
Remember to adjust the rest of your instance settings and security configurations as needed in Steps 4-7 before launching.
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. Connect to Instance
|
||||
## Step 3: Connect to Your Instance
|
||||
|
||||
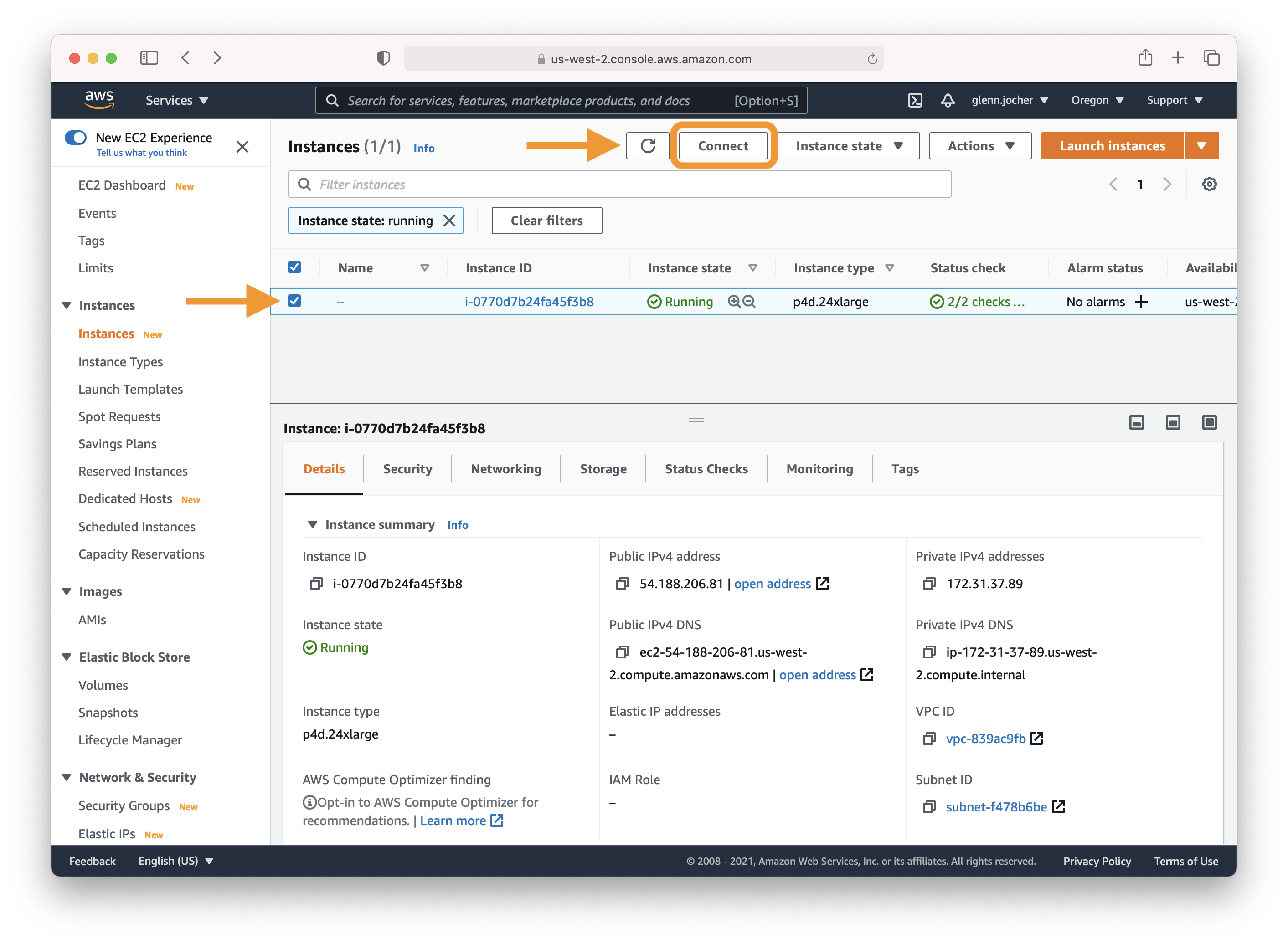
Select the checkbox next to your running instance, and then click Connect. Copy and paste the SSH terminal command into a terminal of your choice to connect to your instance.
|
||||
Once your instance is running, select its checkbox and click Connect to access the SSH information. Use the displayed SSH command in your preferred terminal to establish a connection to your instance.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 4. Run YOLOv5
|
||||
## Step 4: Running YOLOv5
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have logged in to your instance, clone the repository and install the dependencies in a [**Python>=3.8.0**](https://www.python.org/) environment, including [**PyTorch>=1.8**](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/). [Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/tree/master/models) and [datasets](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/tree/master/data) download automatically from the latest YOLOv5 [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases).
|
||||
Logged into your instance, you're now ready to clone the YOLOv5 repository and install dependencies within a Python 3.8 or later environment. YOLOv5's models and datasets will automatically download from the latest [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases).
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 # clone
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 # clone repository
|
||||
cd yolov5
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt # install
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt # install dependencies
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, start training, testing, detecting, and exporting YOLOv5 models:
|
||||
With your environment set up, you can begin training, validating, performing inference, and exporting your YOLOv5 models:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python train.py # train a model
|
||||
python val.py --weights yolov5s.pt # validate a model for Precision, Recall, and mAP
|
||||
python detect.py --weights yolov5s.pt --source path/to/images # run inference on images and videos
|
||||
python export.py --weights yolov5s.pt --include onnx coreml tflite # export models to other formats
|
||||
# Train a model on your data
|
||||
python train.py
|
||||
|
||||
# Validate the trained model for Precision, Recall, and mAP
|
||||
python val.py --weights yolov5s.pt
|
||||
|
||||
# Run inference using the trained model on your images or videos
|
||||
python detect.py --weights yolov5s.pt --source path/to/images
|
||||
|
||||
# Export the trained model to other formats for deployment
|
||||
python export.py --weights yolov5s.pt --include onnx coreml tflite
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Optional Extras
|
||||
|
||||
Add 64GB of swap memory (to `--cache` large datasets):
|
||||
To add more swap memory, which can be a savior for large datasets, run:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
sudo fallocate -l 64G /swapfile
|
||||
sudo chmod 600 /swapfile
|
||||
sudo mkswap /swapfile
|
||||
sudo swapon /swapfile
|
||||
free -h # check memory
|
||||
sudo fallocate -l 64G /swapfile # allocate 64GB swap file
|
||||
sudo chmod 600 /swapfile # modify permissions
|
||||
sudo mkswap /swapfile # set up a Linux swap area
|
||||
sudo swapon /swapfile # activate swap file
|
||||
free -h # verify swap memory
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you have successfully set up and run YOLOv5 on an AWS Deep Learning instance. Enjoy training, testing, and deploying your object detection models!
|
||||
And that's it! 🎉 You've successfully created an AWS Deep Learning instance and run YOLOv5. Whether you're just starting with object detection or scaling up for production, this setup can help you achieve your machine learning goals. Happy training, validating, and deploying! If you encounter any hiccups along the way, the robust AWS documentation and the active Ultralytics community are here to support you.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue