Fix mkdocs.yml raw image URLs (#14213)
Signed-off-by: Glenn Jocher <glenn.jocher@ultralytics.com> Co-authored-by: UltralyticsAssistant <web@ultralytics.com> Co-authored-by: Burhan <62214284+Burhan-Q@users.noreply.github.com>
This commit is contained in:
parent
d5db9c916f
commit
5d479c73c2
69 changed files with 4767 additions and 223 deletions
|
|
@ -118,7 +118,7 @@ After creating the AWS CloudFormation Stack, the next step is to deploy YOLOv8.
|
|||
import json
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def output_fn(prediction_output, content_type):
|
||||
def output_fn(prediction_output):
|
||||
"""Formats model outputs as JSON string, extracting attributes like boxes, masks, keypoints."""
|
||||
print("Executing output_fn from inference.py ...")
|
||||
infer = {}
|
||||
|
|
@ -169,3 +169,88 @@ This guide took you step by step through deploying YOLOv8 on Amazon SageMaker En
|
|||
For more technical details, refer to [this article](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/machine-learning/hosting-yolov8-pytorch-model-on-amazon-sagemaker-endpoints/) on the AWS Machine Learning Blog. You can also check out the official [Amazon SageMaker Documentation](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/realtime-endpoints.html) for more insights into various features and functionalities.
|
||||
|
||||
Are you interested in learning more about different YOLOv8 integrations? Visit the [Ultralytics integrations guide page](../integrations/index.md) to discover additional tools and capabilities that can enhance your machine-learning projects.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I deploy the Ultralytics YOLOv8 model on Amazon SageMaker Endpoints?
|
||||
|
||||
To deploy the Ultralytics YOLOv8 model on Amazon SageMaker Endpoints, follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Set Up Your AWS Environment**: Ensure you have an AWS Account, IAM roles with necessary permissions, and the AWS CLI configured. Install AWS CDK if not already done (refer to the [AWS CDK instructions](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cdk/v2/guide/getting_started.html#getting_started_install)).
|
||||
2. **Clone the YOLOv8 SageMaker Repository**:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/aws-samples/host-yolov8-on-sagemaker-endpoint.git
|
||||
cd host-yolov8-on-sagemaker-endpoint/yolov8-pytorch-cdk
|
||||
```
|
||||
3. **Set Up the CDK Environment**: Create a Python virtual environment, activate it, install dependencies, and upgrade AWS CDK library.
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python3 -m venv .venv
|
||||
source .venv/bin/activate
|
||||
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
pip install --upgrade aws-cdk-lib
|
||||
```
|
||||
4. **Deploy using AWS CDK**: Synthesize and deploy the CloudFormation stack, bootstrap the environment.
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cdk synth
|
||||
cdk bootstrap
|
||||
cdk deploy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For further details, review the [documentation section](#step-5-deploy-the-yolov8-model).
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the prerequisites for deploying YOLOv8 on Amazon SageMaker?
|
||||
|
||||
To deploy YOLOv8 on Amazon SageMaker, ensure you have the following prerequisites:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **AWS Account**: Active AWS account ([sign up here](https://aws.amazon.com/)).
|
||||
2. **IAM Roles**: Configured IAM roles with permissions for SageMaker, CloudFormation, and Amazon S3.
|
||||
3. **AWS CLI**: Installed and configured AWS Command Line Interface ([AWS CLI installation guide](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/getting-started-install.html)).
|
||||
4. **AWS CDK**: Installed AWS Cloud Development Kit ([CDK setup guide](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cdk/v2/guide/getting_started.html#getting_started_install)).
|
||||
5. **Service Quotas**: Sufficient quotas for `ml.m5.4xlarge` instances for both endpoint and notebook usage ([request a quota increase](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/servicequotas/latest/userguide/request-quota-increase.html#quota-console-increase)).
|
||||
|
||||
For detailed setup, refer to [this section](#step-1-setup-your-aws-environment).
|
||||
|
||||
### Why should I use Ultralytics YOLOv8 on Amazon SageMaker?
|
||||
|
||||
Using Ultralytics YOLOv8 on Amazon SageMaker offers several advantages:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Scalability and Management**: SageMaker provides a managed environment with features like autoscaling, which helps in real-time inference needs.
|
||||
2. **Integration with AWS Services**: Seamlessly integrate with other AWS services, such as S3 for data storage, CloudFormation for infrastructure as code, and CloudWatch for monitoring.
|
||||
3. **Ease of Deployment**: Simplified setup using AWS CDK scripts and streamlined deployment processes.
|
||||
4. **Performance**: Leverage Amazon SageMaker's high-performance infrastructure for running large scale inference tasks efficiently.
|
||||
|
||||
Explore more about the advantages of using SageMaker in the [introduction section](#amazon-sagemaker).
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I customize the inference logic for YOLOv8 on Amazon SageMaker?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, you can customize the inference logic for YOLOv8 on Amazon SageMaker:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Modify `inference.py`**: Locate and customize the `output_fn` function in the `inference.py` file to tailor output formats.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import json
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def output_fn(prediction_output):
|
||||
"""Formats model outputs as JSON string, extracting attributes like boxes, masks, keypoints."""
|
||||
infer = {}
|
||||
for result in prediction_output:
|
||||
if result.boxes is not None:
|
||||
infer["boxes"] = result.boxes.numpy().data.tolist()
|
||||
# Add more processing logic if necessary
|
||||
return json.dumps(infer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Deploy Updated Model**: Ensure you redeploy the model using Jupyter notebooks provided (`1_DeployEndpoint.ipynb`) to include these changes.
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the [detailed steps](#step-5-deploy-the-yolov8-model) for deploying the modified model.
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I test the deployed YOLOv8 model on Amazon SageMaker?
|
||||
|
||||
To test the deployed YOLOv8 model on Amazon SageMaker:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Open the Test Notebook**: Locate the `2_TestEndpoint.ipynb` notebook in the SageMaker Jupyter environment.
|
||||
2. **Run the Notebook**: Follow the notebook's instructions to send an image to the endpoint, perform inference, and display results.
|
||||
3. **Visualize Results**: Use built-in plotting functionalities to visualize performance metrics, such as bounding boxes around detected objects.
|
||||
|
||||
For comprehensive testing instructions, visit the [testing section](#step-6-testing-your-deployment).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -185,3 +185,62 @@ This guide has led you through the process of integrating ClearML with Ultralyti
|
|||
For further details on usage, visit [ClearML's official documentation](https://clear.ml/docs/latest/docs/integrations/yolov8/).
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, explore more integrations and capabilities of Ultralytics by visiting the [Ultralytics integration guide page](../integrations/index.md), which is a treasure trove of resources and insights.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### What is the process for integrating Ultralytics YOLOv8 with ClearML?
|
||||
|
||||
Integrating Ultralytics YOLOv8 with ClearML involves a series of steps to streamline your MLOps workflow. First, install the necessary packages:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install ultralytics clearml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, initialize the ClearML SDK in your environment using:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
clearml-init
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You then configure ClearML with your credentials from the [ClearML Settings page](https://app.clear.ml/settings/workspace-configuration). Detailed instructions on the entire setup process, including model selection and training configurations, can be found in our [YOLOv8 Model Training guide](../modes/train.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### Why should I use ClearML with Ultralytics YOLOv8 for my machine learning projects?
|
||||
|
||||
Using ClearML with Ultralytics YOLOv8 enhances your machine learning projects by automating experiment tracking, streamlining workflows, and enabling robust model management. ClearML offers real-time metrics tracking, resource utilization monitoring, and a user-friendly interface for comparing experiments. These features help optimize your model's performance and make the development process more efficient. Learn more about the benefits and procedures in our [MLOps Integration guide](../modes/train.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I troubleshoot common issues during YOLOv8 and ClearML integration?
|
||||
|
||||
If you encounter issues during the integration of YOLOv8 with ClearML, consult our [Common Issues guide](../guides/yolo-common-issues.md) for solutions and tips. Typical problems might involve package installation errors, credential setup, or configuration issues. This guide provides step-by-step troubleshooting instructions to resolve these common issues efficiently.
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I set up the ClearML task for YOLOv8 model training?
|
||||
|
||||
Setting up a ClearML task for YOLOv8 training involves initializing a task, selecting the model variant, loading the model, setting up training arguments, and finally, starting the model training. Here's a simplified example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from clearml import Task
|
||||
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Step 1: Creating a ClearML Task
|
||||
task = Task.init(project_name="my_project", task_name="my_yolov8_task")
|
||||
|
||||
# Step 2: Selecting the YOLOv8 Model
|
||||
model_variant = "yolov8n"
|
||||
task.set_parameter("model_variant", model_variant)
|
||||
|
||||
# Step 3: Loading the YOLOv8 Model
|
||||
model = YOLO(f"{model_variant}.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
# Step 4: Setting Up Training Arguments
|
||||
args = dict(data="coco8.yaml", epochs=16)
|
||||
task.connect(args)
|
||||
|
||||
# Step 5: Initiating Model Training
|
||||
results = model.train(**args)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to our [Usage guide](#usage) for a detailed breakdown of these steps.
|
||||
|
||||
### Where can I view the results of my YOLOv8 training in ClearML?
|
||||
|
||||
After running your YOLOv8 training script with ClearML, you can view the results on the ClearML results page. The output will include a URL link to the ClearML dashboard, where you can track metrics, compare experiments, and monitor resource usage. For more details on how to view and interpret the results, check our section on [Viewing the ClearML Results Page](#viewing-the-clearml-results-page).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -176,3 +176,106 @@ Explore [Comet ML's official documentation](https://www.comet.com/docs/v2/integr
|
|||
Furthermore, if you're looking to dive deeper into the practical applications of YOLOv8, specifically for image segmentation tasks, this detailed guide on [fine-tuning YOLOv8 with Comet ML](https://www.comet.com/site/blog/fine-tuning-yolov8-for-image-segmentation-with-comet/) offers valuable insights and step-by-step instructions to enhance your model's performance.
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, to explore other exciting integrations with Ultralytics, check out the [integration guide page](../integrations/index.md), which offers a wealth of resources and information.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I integrate Comet ML with Ultralytics YOLOv8 for training?
|
||||
|
||||
To integrate Comet ML with Ultralytics YOLOv8, follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Install the required packages**:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install ultralytics comet_ml torch torchvision
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Set up your Comet API Key**:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export COMET_API_KEY=<Your API Key>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. **Initialize your Comet project in your Python code**:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import comet_ml
|
||||
|
||||
comet_ml.init(project_name="comet-example-yolov8-coco128")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. **Train your YOLOv8 model and log metrics**:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
results = model.train(
|
||||
data="coco8.yaml", project="comet-example-yolov8-coco128", batch=32, save_period=1, save_json=True, epochs=3
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more detailed instructions, refer to the [Comet ML configuration section](#configuring-comet-ml).
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the benefits of using Comet ML with YOLOv8?
|
||||
|
||||
By integrating Ultralytics YOLOv8 with Comet ML, you can:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Monitor real-time insights**: Get instant feedback on your training results, allowing for quick adjustments.
|
||||
- **Log extensive metrics**: Automatically capture essential metrics such as mAP, loss, hyperparameters, and model checkpoints.
|
||||
- **Track experiments offline**: Log your training runs locally when internet access is unavailable.
|
||||
- **Compare different training runs**: Use the interactive Comet ML dashboard to analyze and compare multiple experiments.
|
||||
|
||||
By leveraging these features, you can optimize your machine learning workflows for better performance and reproducibility. For more information, visit the [Comet ML integration guide](../integrations/index.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I customize the logging behavior of Comet ML during YOLOv8 training?
|
||||
|
||||
Comet ML allows for extensive customization of its logging behavior using environment variables:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Change the number of image predictions logged**:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["COMET_MAX_IMAGE_PREDICTIONS"] = "200"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **Adjust batch logging interval**:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["COMET_EVAL_BATCH_LOGGING_INTERVAL"] = "4"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **Disable confusion matrix logging**:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["COMET_EVAL_LOG_CONFUSION_MATRIX"] = "false"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more customization options, refer to the [Customizing Comet ML Logging](#customizing-comet-ml-logging) section.
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I view detailed metrics and visualizations of my YOLOv8 training on Comet ML?
|
||||
|
||||
Once your YOLOv8 model starts training, you can access a wide range of metrics and visualizations on the Comet ML dashboard. Key features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Experiment Panels**: View different runs and their metrics, including segment mask loss, class loss, and mean average precision.
|
||||
- **Metrics**: Examine metrics in tabular format for detailed analysis.
|
||||
- **Interactive Confusion Matrix**: Assess classification accuracy with an interactive confusion matrix.
|
||||
- **System Metrics**: Monitor GPU and CPU utilization, memory usage, and other system metrics.
|
||||
|
||||
For a detailed overview of these features, visit the [Understanding Your Model's Performance with Comet ML Visualizations](#understanding-your-models-performance-with-comet-ml-visualizations) section.
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I use Comet ML for offline logging when training YOLOv8 models?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, you can enable offline logging in Comet ML by setting the `COMET_MODE` environment variable to "offline":
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["COMET_MODE"] = "offline"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This feature allows you to log your experiment data locally, which can later be uploaded to Comet ML when internet connectivity is available. This is particularly useful when working in environments with limited internet access. For more details, refer to the [Offline Logging](#offline-logging) section.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ CoreML offers various deployment options for machine learning models, including:
|
|||
|
||||
- **Downloaded Models**: These models are fetched from a server as needed. This approach is suitable for larger models or those needing regular updates. It helps keep the app bundle size smaller.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Cloud-Based Deployment**: CoreML models are hosted on servers and accessed by the iOS app through API requests. This scalable and flexible option enables easy model updates without app revisions. It's ideal for complex models or large-scale apps requiring regular updates. However, it does require an internet connection and may pose latency and security issues.
|
||||
- **Cloud-Based Deployment**: CoreML models are hosted on servers and accessed by the iOS app through API requests. This scalable and flexible option enables easy model updates without app revisions. It's ideal for complex models or large-scale apps requiring regular updates. However, it does require an internet connection and may pose latency and security issues.
|
||||
|
||||
## Exporting YOLOv8 Models to CoreML
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -124,3 +124,95 @@ In this guide, we went over how to export Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to CoreML fo
|
|||
For further details on usage, visit the [CoreML official documentation](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/coreml).
|
||||
|
||||
Also, if you'd like to know more about other Ultralytics YOLOv8 integrations, visit our [integration guide page](../integrations/index.md). You'll find plenty of valuable resources and insights there.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I export YOLOv8 models to CoreML format?
|
||||
|
||||
To export your [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) models to CoreML format, you'll first need to ensure you have the `ultralytics` package installed. You can install it using:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Installation"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "CLI"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install ultralytics
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, you can export the model using the following Python or CLI commands:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Usage"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
model.export(format="coreml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "CLI"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
yolo export model=yolov8n.pt format=coreml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For further details, refer to the [Exporting YOLOv8 Models to CoreML](../modes/export.md) section of our documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the benefits of using CoreML for deploying YOLOv8 models?
|
||||
|
||||
CoreML provides numerous advantages for deploying [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) models on Apple devices:
|
||||
|
||||
- **On-device Processing**: Enables local model inference on devices, ensuring data privacy and minimizing latency.
|
||||
- **Performance Optimization**: Leverages the full potential of the device's CPU, GPU, and Neural Engine, optimizing both speed and efficiency.
|
||||
- **Ease of Integration**: Offers a seamless integration experience with Apple's ecosystems, including iOS, macOS, watchOS, and tvOS.
|
||||
- **Versatility**: Supports a wide range of machine learning tasks such as image analysis, audio processing, and natural language processing using the CoreML framework.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details on integrating your CoreML model into an iOS app, check out the guide on [Integrating a Core ML Model into Your App](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/coreml/integrating_a_core_ml_model_into_your_app).
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the deployment options for YOLOv8 models exported to CoreML?
|
||||
|
||||
Once you export your YOLOv8 model to CoreML format, you have multiple deployment options:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **On-Device Deployment**: Directly integrate CoreML models into your app for enhanced privacy and offline functionality. This can be done as:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Embedded Models**: Included in the app bundle, accessible immediately.
|
||||
- **Downloaded Models**: Fetched from a server as needed, keeping the app bundle size smaller.
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Cloud-Based Deployment**: Host CoreML models on servers and access them via API requests. This approach supports easier updates and can handle more complex models.
|
||||
|
||||
For detailed guidance on deploying CoreML models, refer to [CoreML Deployment Options](#coreml-deployment-options).
|
||||
|
||||
### How does CoreML ensure optimized performance for YOLOv8 models?
|
||||
|
||||
CoreML ensures optimized performance for [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) models by utilizing various optimization techniques:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Hardware Acceleration**: Uses the device's CPU, GPU, and Neural Engine for efficient computation.
|
||||
- **Model Compression**: Provides tools for compressing models to reduce their footprint without compromising accuracy.
|
||||
- **Adaptive Inference**: Adjusts inference based on the device's capabilities to maintain a balance between speed and performance.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information on performance optimization, visit the [CoreML official documentation](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/coreml).
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I run inference directly with the exported CoreML model?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, you can run inference directly using the exported CoreML model. Below are the commands for Python and CLI:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Running Inference"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
coreml_model = YOLO("yolov8n.mlpackage")
|
||||
results = coreml_model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "CLI"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
yolo predict model=yolov8n.mlpackage source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For additional information, refer to the [Usage section](#usage) of the CoreML export guide.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -169,3 +169,110 @@ This guide has led you through the process of integrating DVCLive with Ultralyti
|
|||
For further details on usage, visit [DVCLive's official documentation](https://dvc.org/doc/dvclive/ml-frameworks/yolo).
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, explore more integrations and capabilities of Ultralytics by visiting the [Ultralytics integration guide page](../integrations/index.md), which is a collection of great resources and insights.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I integrate DVCLive with Ultralytics YOLOv8 for experiment tracking?
|
||||
|
||||
Integrating DVCLive with Ultralytics YOLOv8 is straightforward. Start by installing the necessary packages:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Installation"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "CLI"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install ultralytics dvclive
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, initialize a Git repository and configure DVCLive in your project:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Initial Environment Setup"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "CLI"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git init -q
|
||||
git config --local user.email "you@example.com"
|
||||
git config --local user.name "Your Name"
|
||||
dvc init -q
|
||||
git commit -m "DVC init"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Follow our [YOLOv8 Installation guide](../quickstart.md) for detailed setup instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why should I use DVCLive for tracking YOLOv8 experiments?
|
||||
|
||||
Using DVCLive with YOLOv8 provides several advantages, such as:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Automated Logging**: DVCLive automatically records key experiment details like model parameters and metrics.
|
||||
- **Easy Comparison**: Facilitates comparison of results across different runs.
|
||||
- **Visualization Tools**: Leverages DVCLive's robust data visualization capabilities for in-depth analysis.
|
||||
|
||||
For further details, refer to our guide on [YOLOv8 Model Training](../modes/train.md) and [YOLO Performance Metrics](../guides/yolo-performance-metrics.md) to maximize your experiment tracking efficiency.
|
||||
|
||||
### How can DVCLive improve my results analysis for YOLOv8 training sessions?
|
||||
|
||||
After completing your YOLOv8 training sessions, DVCLive helps in visualizing and analyzing the results effectively. Example code for loading and displaying experiment data:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import dvc.api
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
|
||||
# Define columns of interest
|
||||
columns = ["Experiment", "epochs", "imgsz", "model", "metrics.mAP50-95(B)"]
|
||||
|
||||
# Retrieve experiment data
|
||||
df = pd.DataFrame(dvc.api.exp_show(), columns=columns)
|
||||
|
||||
# Clean data
|
||||
df.dropna(inplace=True)
|
||||
df.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# Display DataFrame
|
||||
print(df)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To visualize results interactively, use Plotly's parallel coordinates plot:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from plotly.express import parallel_coordinates
|
||||
|
||||
fig = parallel_coordinates(df, columns, color="metrics.mAP50-95(B)")
|
||||
fig.show()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to our guide on [YOLOv8 Training with DVCLive](#yolov8-training-with-dvclive) for more examples and best practices.
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the steps to configure my environment for DVCLive and YOLOv8 integration?
|
||||
|
||||
To configure your environment for a smooth integration of DVCLive and YOLOv8, follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Install Required Packages**: Use `pip install ultralytics dvclive`.
|
||||
2. **Initialize Git Repository**: Run `git init -q`.
|
||||
3. **Setup DVCLive**: Execute `dvc init -q`.
|
||||
4. **Commit to Git**: Use `git commit -m "DVC init"`.
|
||||
|
||||
These steps ensure proper version control and setup for experiment tracking. For in-depth configuration details, visit our [Configuration guide](../quickstart.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I visualize YOLOv8 experiment results using DVCLive?
|
||||
|
||||
DVCLive offers powerful tools to visualize the results of YOLOv8 experiments. Here's how you can generate comparative plots:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Generate Comparative Plots"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "CLI"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
dvc plots diff $(dvc exp list --names-only)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To display these plots in a Jupyter Notebook, use:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from IPython.display import HTML
|
||||
|
||||
# Display plots as HTML
|
||||
HTML(filename="./dvc_plots/index.html")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
These visualizations help identify trends and optimize model performance. Check our detailed guides on [YOLOv8 Experiment Analysis](#analyzing-results) for comprehensive steps and examples.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ Exporting models to TensorFlow Edge TPU makes machine learning tasks fast and ef
|
|||
<img width="100%" src="https://coral.ai/static/docs/images/edgetpu/compile-workflow.png" alt="TFLite Edge TPU">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
The Edge TPU works with quantized models. Quantization makes models smaller and faster without losing much accuracy. It is ideal for the limited resources of edge computing, allowing applications to respond quickly by reducing latency and allowing for quick data processing locally, without cloud dependency. Local processing also keeps user data private and secure since it's not sent to a remote server.
|
||||
The Edge TPU works with quantized models. Quantization makes models smaller and faster without losing much accuracy. It is ideal for the limited resources of edge computing, allowing applications to respond quickly by reducing latency and allowing for quick data processing locally, without cloud dependency. Local processing also keeps user data private and secure since it's not sent to a remote server.
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Features of TFLite Edge TPU
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -116,3 +116,70 @@ In this guide, we've learned how to export Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to TFLite E
|
|||
For further details on usage, visit the [Edge TPU official website](https://cloud.google.com/edge-tpu).
|
||||
|
||||
Also, for more information on other Ultralytics YOLOv8 integrations, please visit our [integration guide page](index.md). There, you'll discover valuable resources and insights.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I export a YOLOv8 model to TFLite Edge TPU format?
|
||||
|
||||
To export a YOLOv8 model to TFLite Edge TPU format, you can follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Usage"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the YOLOv8 model
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
# Export the model to TFLite Edge TPU format
|
||||
model.export(format="edgetpu") # creates 'yolov8n_full_integer_quant_edgetpu.tflite'
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the exported TFLite Edge TPU model
|
||||
edgetpu_model = YOLO("yolov8n_full_integer_quant_edgetpu.tflite")
|
||||
|
||||
# Run inference
|
||||
results = edgetpu_model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "CLI"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Export a YOLOv8n PyTorch model to TFLite Edge TPU format
|
||||
yolo export model=yolov8n.pt format=edgetpu # creates 'yolov8n_full_integer_quant_edgetpu.tflite'
|
||||
|
||||
# Run inference with the exported model
|
||||
yolo predict model=yolov8n_full_integer_quant_edgetpu.tflite source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For complete details on exporting models to other formats, refer to our [export guide](../modes/export.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the benefits of exporting YOLOv8 models to TFLite Edge TPU?
|
||||
|
||||
Exporting YOLOv8 models to TFLite Edge TPU offers several benefits:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Optimized Performance**: Achieve high-speed neural network performance with minimal power consumption.
|
||||
- **Reduced Latency**: Quick local data processing without the need for cloud dependency.
|
||||
- **Enhanced Privacy**: Local processing keeps user data private and secure.
|
||||
|
||||
This makes it ideal for applications in edge computing, where devices have limited power and computational resources. Learn more about [why you should export](#why-should-you-export-to-tflite-edge-tpu).
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I deploy TFLite Edge TPU models on mobile and embedded devices?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, TensorFlow Lite Edge TPU models can be deployed directly on mobile and embedded devices. This deployment approach allows models to execute directly on the hardware, offering faster and more efficient inferencing. For integration examples, check our [guide on deploying Coral Edge TPU on Raspberry Pi](../guides/coral-edge-tpu-on-raspberry-pi.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### What are some common use cases for TFLite Edge TPU models?
|
||||
|
||||
Common use cases for TFLite Edge TPU models include:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Smart Cameras**: Enhancing real-time image and video analysis.
|
||||
- **IoT Devices**: Enabling smart home and industrial automation.
|
||||
- **Healthcare**: Accelerating medical imaging and diagnostics.
|
||||
- **Retail**: Improving inventory management and customer behavior analysis.
|
||||
|
||||
These applications benefit from the high performance and low power consumption of TFLite Edge TPU models. Discover more about [usage scenarios](#deployment-options-with-tflite-edge-tpu).
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I troubleshoot issues while exporting or deploying TFLite Edge TPU models?
|
||||
|
||||
If you encounter issues while exporting or deploying TFLite Edge TPU models, refer to our [Common Issues guide](../guides/yolo-common-issues.md) for troubleshooting tips. This guide covers common problems and solutions to help you ensure smooth operation. For additional support, visit our [Help Center](https://docs.ultralytics.com/help/).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -108,3 +108,44 @@ We've discussed how you can easily experiment with Ultralytics YOLOv8 models on
|
|||
For more details, visit [Google Colab's FAQ page](https://research.google.com/colaboratory/intl/en-GB/faq.html).
|
||||
|
||||
Interested in more YOLOv8 integrations? Visit the [Ultralytics integration guide page](index.md) to explore additional tools and capabilities that can improve your machine-learning projects.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I start training Ultralytics YOLOv8 models on Google Colab?
|
||||
|
||||
To start training Ultralytics YOLOv8 models on Google Colab, sign in to your Google account, then access the [Google Colab YOLOv8 Notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/examples/tutorial.ipynb). This notebook guides you through the setup and training process. After launching the notebook, run the cells step-by-step to train your model. For a full guide, refer to the [YOLOv8 Model Training guide](../modes/train.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the advantages of using Google Colab for training YOLOv8 models?
|
||||
|
||||
Google Colab offers several advantages for training YOLOv8 models:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Zero Setup:** No initial environment setup is required; just log in and start coding.
|
||||
- **Free GPU Access:** Use powerful GPUs or TPUs without the need for expensive hardware.
|
||||
- **Integration with Google Drive:** Easily store and access datasets and models.
|
||||
- **Collaboration:** Share notebooks with others and collaborate in real-time.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information on why you should use Google Colab, explore the [training guide](../modes/train.md) and visit the [Google Colab page](https://colab.google/notebooks/).
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I handle Google Colab session timeouts during YOLOv8 training?
|
||||
|
||||
Google Colab sessions timeout due to inactivity, especially for free users. To handle this:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Stay Active:** Regularly interact with your Colab notebook.
|
||||
2. **Save Progress:** Continuously save your work to Google Drive or GitHub.
|
||||
3. **Colab Pro:** Consider upgrading to Google Colab Pro for longer session durations.
|
||||
|
||||
For more tips on managing your Colab session, visit the [Google Colab FAQ page](https://research.google.com/colaboratory/intl/en-GB/faq.html).
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I use custom datasets for training YOLOv8 models in Google Colab?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, you can use custom datasets to train YOLOv8 models in Google Colab. Upload your dataset to Google Drive and load it directly into your Colab notebook. You can follow Nicolai's YouTube guide, [How to Train YOLOv8 Models on Your Custom Dataset](https://www.youtube.com/embed/LNwODJXcvt4?si=lB9UAc4hatSSEr2a), or refer to the [Custom Dataset Training guide](https://www.ultralytics.com/blog/training-custom-datasets-with-ultralytics-yolov8-in-google-colab) for detailed steps.
|
||||
|
||||
### What should I do if my Google Colab training session is interrupted?
|
||||
|
||||
If your Google Colab training session is interrupted:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Save Regularly:** Avoid losing unsaved progress by regularly saving your work to Google Drive or GitHub.
|
||||
2. **Resume Training:** Restart your session and re-run the cells from where the interruption occurred.
|
||||
3. **Use Checkpoints:** Incorporate checkpointing in your training script to save progress periodically.
|
||||
|
||||
These practices help ensure your progress is secure. Learn more about session management on [Google Colab's FAQ page](https://research.google.com/colaboratory/intl/en-GB/faq.html).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -116,3 +116,84 @@ if __name__ == "__main__":
|
|||
| Image Input | To upload the image for detection. |
|
||||
| Sliders | To adjust confidence and IoU thresholds. |
|
||||
| Image Output | To display the detection results. |
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I use Gradio with Ultralytics YOLOv8 for object detection?
|
||||
|
||||
To use Gradio with Ultralytics YOLOv8 for object detection, you can follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Install Gradio:** Use the command `pip install gradio`.
|
||||
2. **Create Interface:** Write a Python script to initialize the Gradio interface. You can refer to the provided code example in the [documentation](#usage-example) for details.
|
||||
3. **Upload and Adjust:** Upload your image and adjust the confidence and IoU thresholds on the Gradio interface to get real-time object detection results.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's a minimal code snippet for reference:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import gradio as gr
|
||||
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def predict_image(img, conf_threshold, iou_threshold):
|
||||
results = model.predict(
|
||||
source=img,
|
||||
conf=conf_threshold,
|
||||
iou=iou_threshold,
|
||||
show_labels=True,
|
||||
show_conf=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
return results[0].plot() if results else None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
iface = gr.Interface(
|
||||
fn=predict_image,
|
||||
inputs=[
|
||||
gr.Image(type="pil", label="Upload Image"),
|
||||
gr.Slider(minimum=0, maximum=1, value=0.25, label="Confidence threshold"),
|
||||
gr.Slider(minimum=0, maximum=1, value=0.45, label="IoU threshold"),
|
||||
],
|
||||
outputs=gr.Image(type="pil", label="Result"),
|
||||
title="Ultralytics Gradio YOLOv8",
|
||||
description="Upload images for YOLOv8 object detection.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
iface.launch()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the benefits of using Gradio for Ultralytics YOLOv8 object detection?
|
||||
|
||||
Using Gradio for Ultralytics YOLOv8 object detection offers several benefits:
|
||||
|
||||
- **User-Friendly Interface:** Gradio provides an intuitive interface for users to upload images and visualize detection results without any coding effort.
|
||||
- **Real-Time Adjustments:** You can dynamically adjust detection parameters such as confidence and IoU thresholds and see the effects immediately.
|
||||
- **Accessibility:** The web interface is accessible to anyone, making it useful for quick experiments, educational purposes, and demonstrations.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, you can read this [blog post](https://www.ultralytics.com/blog/ai-and-radiology-a-new-era-of-precision-and-efficiency).
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I use Gradio and Ultralytics YOLOv8 together for educational purposes?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, Gradio and Ultralytics YOLOv8 can be utilized together for educational purposes effectively. Gradio's intuitive web interface makes it easy for students and educators to interact with state-of-the-art deep learning models like Ultralytics YOLOv8 without needing advanced programming skills. This setup is ideal for demonstrating key concepts in object detection and computer vision, as Gradio provides immediate visual feedback which helps in understanding the impact of different parameters on the detection performance.
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I adjust the confidence and IoU thresholds in the Gradio interface for YOLOv8?
|
||||
|
||||
In the Gradio interface for YOLOv8, you can adjust the confidence and IoU thresholds using the sliders provided. These thresholds help control the prediction accuracy and object separation:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Confidence Threshold:** Determines the minimum confidence level for detecting objects. Slide to increase or decrease the confidence required.
|
||||
- **IoU Threshold:** Sets the intersection-over-union threshold for distinguishing between overlapping objects. Adjust this value to refine object separation.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information on these parameters, visit the [parameters explanation section](#parameters-explanation).
|
||||
|
||||
### What are some practical applications of using Ultralytics YOLOv8 with Gradio?
|
||||
|
||||
Practical applications of combining Ultralytics YOLOv8 with Gradio include:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Real-Time Object Detection Demonstrations:** Ideal for showcasing how object detection works in real-time.
|
||||
- **Educational Tools:** Useful in academic settings to teach object detection and computer vision concepts.
|
||||
- **Prototype Development:** Efficient for developing and testing prototype object detection applications quickly.
|
||||
- **Community and Collaborations:** Making it easy to share models with the community for feedback and collaboration.
|
||||
|
||||
For examples of similar use cases, check out the [Ultralytics blog](https://www.ultralytics.com/blog/monitoring-animal-behavior-using-ultralytics-yolov8).
|
||||
|
||||
Providing this information within the documentation will help in enhancing the usability and accessibility of Ultralytics YOLOv8, making it more approachable for users at all levels of expertise.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -112,3 +112,27 @@ By writing a guide or tutorial, you can help expand our documentation and provid
|
|||
To contribute, please check out our [Contributing Guide](../help/contributing.md) for instructions on how to submit a Pull Request (PR) 🛠️. We eagerly await your contributions!
|
||||
|
||||
Let's collaborate to make the Ultralytics YOLO ecosystem more expansive and feature-rich 🙏!
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### What is Ultralytics HUB, and how does it streamline the ML workflow?
|
||||
|
||||
Ultralytics HUB is a cloud-based platform designed to make machine learning (ML) workflows for Ultralytics models seamless and efficient. By using this tool, you can easily upload datasets, train models, perform real-time tracking, and deploy YOLOv8 models without needing extensive coding skills. You can explore the key features on the [Ultralytics HUB](https://hub.ultralytics.com) page and get started quickly with our [Quickstart](https://docs.ultralytics.com/hub/quickstart/) guide.
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I integrate Ultralytics YOLO models with Roboflow for dataset management?
|
||||
|
||||
Integrating Ultralytics YOLO models with Roboflow enhances dataset management by providing robust tools for annotation, preprocessing, and augmentation. To get started, follow the steps on the [Roboflow](roboflow.md) integration page. This partnership ensures efficient dataset handling, which is crucial for developing accurate and robust YOLO models.
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I track the performance of my Ultralytics models using MLFlow?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, you can. Integrating MLFlow with Ultralytics models allows you to track experiments, improve reproducibility, and streamline the entire ML lifecycle. Detailed instructions for setting up this integration can be found on the [MLFlow](mlflow.md) integration page. This integration is particularly useful for monitoring model metrics and managing the ML workflow efficiently.
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the benefits of using Neural Magic for YOLOv8 model optimization?
|
||||
|
||||
Neural Magic optimizes YOLOv8 models by leveraging techniques like Quantization Aware Training (QAT) and pruning, resulting in highly efficient, smaller models that perform better on resource-limited hardware. Check out the [Neural Magic](neural-magic.md) integration page to learn how to implement these optimizations for superior performance and leaner models. This is especially beneficial for deployment on edge devices.
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I deploy Ultralytics YOLO models with Gradio for interactive demos?
|
||||
|
||||
To deploy Ultralytics YOLO models with Gradio for interactive object detection demos, you can follow the steps outlined on the [Gradio](gradio.md) integration page. Gradio allows you to create easy-to-use web interfaces for real-time model inference, making it an excellent tool for showcasing your YOLO model's capabilities in a user-friendly format suitable for both developers and end-users.
|
||||
|
||||
By addressing these common questions, we aim to improve user experience and provide valuable insights into the powerful capabilities of Ultralytics products. Incorporating these FAQs will not only enhance the documentation but also drive more organic traffic to the Ultralytics website.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -117,3 +117,91 @@ yolo settings mlflow=False
|
|||
## Conclusion
|
||||
|
||||
MLflow logging integration with Ultralytics YOLO offers a streamlined way to keep track of your machine learning experiments. It empowers you to monitor performance metrics and manage artifacts effectively, thus aiding in robust model development and deployment. For further details please visit the MLflow [official documentation](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/index.html).
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I set up MLflow logging with Ultralytics YOLO?
|
||||
|
||||
To set up MLflow logging with Ultralytics YOLO, you first need to ensure MLflow is installed. You can install it using pip:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install mlflow
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, enable MLflow logging in Ultralytics settings. This can be controlled using the `mlflow` key. For more information, see the [settings guide](../quickstart.md#ultralytics-settings).
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Update Ultralytics MLflow Settings"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import settings
|
||||
|
||||
# Update a setting
|
||||
settings.update({"mlflow": True})
|
||||
|
||||
# Reset settings to default values
|
||||
settings.reset()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "CLI"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Update a setting
|
||||
yolo settings runs_dir='/path/to/runs'
|
||||
|
||||
# Reset settings to default values
|
||||
yolo settings reset
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, start a local MLflow server for tracking:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
mlflow server --backend-store-uri runs/mlflow
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### What metrics and parameters can I log using MLflow with Ultralytics YOLO?
|
||||
|
||||
Ultralytics YOLO with MLflow supports logging various metrics, parameters, and artifacts throughout the training process:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Metrics Logging**: Tracks metrics at the end of each epoch and upon training completion.
|
||||
- **Parameter Logging**: Logs all parameters used in the training process.
|
||||
- **Artifacts Logging**: Saves model artifacts like weights and configuration files after training.
|
||||
|
||||
For more detailed information, visit the [Ultralytics YOLO tracking documentation](#features).
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I disable MLflow logging once it is enabled?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, you can disable MLflow logging for Ultralytics YOLO by updating the settings. Here's how you can do it using the CLI:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
yolo settings mlflow=False
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For further customization and resetting settings, refer to the [settings guide](../quickstart.md#ultralytics-settings).
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I start and stop an MLflow server for Ultralytics YOLO tracking?
|
||||
|
||||
To start an MLflow server for tracking your experiments in Ultralytics YOLO, use the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
mlflow server --backend-store-uri runs/mlflow
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This command starts a local server at http://127.0.0.1:5000 by default. If you need to stop running MLflow server instances, use the following bash command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
ps aux | grep 'mlflow' | grep -v 'grep' | awk '{print $2}' | xargs kill -9
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the [commands section](#commands) for more command options.
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the benefits of integrating MLflow with Ultralytics YOLO for experiment tracking?
|
||||
|
||||
Integrating MLflow with Ultralytics YOLO offers several benefits for managing your machine learning experiments:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Enhanced Experiment Tracking**: Easily track and compare different runs and their outcomes.
|
||||
- **Improved Model Reproducibility**: Ensure that your experiments are reproducible by logging all parameters and artifacts.
|
||||
- **Performance Monitoring**: Visualize performance metrics over time to make data-driven decisions for model improvements.
|
||||
|
||||
For an in-depth look at setting up and leveraging MLflow with Ultralytics YOLO, explore the [MLflow Integration for Ultralytics YOLO](#introduction) documentation.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -118,3 +118,69 @@ In this guide, we've gone over exporting Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to the NCNN f
|
|||
For detailed instructions on usage, please refer to the [official NCNN documentation](https://ncnn.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html).
|
||||
|
||||
Also, if you're interested in exploring other integration options for Ultralytics YOLOv8, be sure to visit our [integration guide page](index.md) for further insights and information.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I export Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to NCNN format?
|
||||
|
||||
To export your Ultralytics YOLOv8 model to NCNN format, follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Python**: Use the `export` function from the YOLO class.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the YOLOv8 model
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
# Export to NCNN format
|
||||
model.export(format="ncnn") # creates '/yolov8n_ncnn_model'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- **CLI**: Use the `yolo` command with the `export` argument.
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
yolo export model=yolov8n.pt format=ncnn # creates '/yolov8n_ncnn_model'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For detailed export options, check the [Export](../modes/export.md) page in the documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the advantages of exporting YOLOv8 models to NCNN?
|
||||
|
||||
Exporting your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to NCNN offers several benefits:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Efficiency**: NCNN models are optimized for mobile and embedded devices, ensuring high performance even with limited computational resources.
|
||||
- **Quantization**: NCNN supports techniques like quantization that improve model speed and reduce memory usage.
|
||||
- **Broad Compatibility**: You can deploy NCNN models on multiple platforms, including Android, iOS, Linux, and macOS.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, see the [Export to NCNN](#why-should-you-export-to-ncnn) section in the documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why should I use NCNN for my mobile AI applications?
|
||||
|
||||
NCNN, developed by Tencent, is specifically optimized for mobile platforms. Key reasons to use NCNN include:
|
||||
|
||||
- **High Performance**: Designed for efficient and fast processing on mobile CPUs.
|
||||
- **Cross-Platform**: Compatible with popular frameworks such as TensorFlow and ONNX, making it easier to convert and deploy models across different platforms.
|
||||
- **Community Support**: Active community support ensures continual improvements and updates.
|
||||
|
||||
To understand more, visit the [NCNN overview](#key-features-of-ncnn-models) in the documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
### What platforms are supported for NCNN model deployment?
|
||||
|
||||
NCNN is versatile and supports various platforms:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Mobile**: Android, iOS.
|
||||
- **Embedded Systems and IoT Devices**: Devices like Raspberry Pi and NVIDIA Jetson.
|
||||
- **Desktop and Servers**: Linux, Windows, and macOS.
|
||||
|
||||
If running models on a Raspberry Pi isn't fast enough, converting to the NCNN format could speed things up as detailed in our [Raspberry Pi Guide](../guides/raspberry-pi.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I deploy Ultralytics YOLOv8 NCNN models on Android?
|
||||
|
||||
To deploy your YOLOv8 models on Android:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Build for Android**: Follow the [NCNN Build for Android](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/wiki/how-to-build#build-for-android) guide.
|
||||
2. **Integrate with Your App**: Use the NCNN Android SDK to integrate the exported model into your application for efficient on-device inference.
|
||||
|
||||
For step-by-step instructions, refer to our guide on [Deploying YOLOv8 NCNN Models](#deploying-exported-yolov8-ncnn-models).
|
||||
|
||||
For more advanced guides and use cases, visit the [Ultralytics documentation page](../guides/model-deployment-options.md).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -160,3 +160,52 @@ This guide explored integrating Ultralytics' YOLOv8 with Neural Magic's DeepSpar
|
|||
For more detailed information and advanced usage, visit [Neural Magic's DeepSparse documentation](https://docs.neuralmagic.com/products/deepsparse/). Also, check out Neural Magic's documentation on the integration with YOLOv8 [here](https://github.com/neuralmagic/deepsparse/tree/main/src/deepsparse/yolov8#yolov8-inference-pipelines) and watch a great session on it [here](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qtJ7bdt52x8).
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, for a broader understanding of various YOLOv8 integrations, visit the [Ultralytics integration guide page](../integrations/index.md), where you can discover a range of other exciting integration possibilities.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### What is Neural Magic's DeepSparse Engine and how does it optimize YOLOv8 performance?
|
||||
|
||||
Neural Magic's DeepSparse Engine is an inference runtime designed to optimize the execution of neural networks on CPUs through advanced techniques such as sparsity, pruning, and quantization. By integrating DeepSparse with YOLOv8, you can achieve GPU-like performance on standard CPUs, significantly enhancing inference speed, model efficiency, and overall performance while maintaining accuracy. For more details, check out the [Neural Magic's DeepSparse section](#neural-magics-deepsparse).
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I install the needed packages to deploy YOLOv8 using Neural Magic's DeepSparse?
|
||||
|
||||
Installing the required packages for deploying YOLOv8 with Neural Magic's DeepSparse is straightforward. You can easily install them using the CLI. Here's the command you need to run:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install deepsparse[yolov8]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once installed, follow the steps provided in the [Installation section](#step-1-installation) to set up your environment and start using DeepSparse with YOLOv8.
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I convert YOLOv8 models to ONNX format for use with DeepSparse?
|
||||
|
||||
To convert YOLOv8 models to the ONNX format, which is required for compatibility with DeepSparse, you can use the following CLI command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
yolo task=detect mode=export model=yolov8n.pt format=onnx opset=13
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This command will export your YOLOv8 model (`yolov8n.pt`) to a format (`yolov8n.onnx`) that can be utilized by the DeepSparse Engine. More information about model export can be found in the [Model Export section](#step-2-exporting-yolov8-to-onnx-format).
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I benchmark YOLOv8 performance on the DeepSparse Engine?
|
||||
|
||||
Benchmarking YOLOv8 performance on DeepSparse helps you analyze throughput and latency to ensure your model is optimized. You can use the following CLI command to run a benchmark:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
deepsparse.benchmark model_path="path/to/yolov8n.onnx" --scenario=sync --input_shapes="[1,3,640,640]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This command will provide you with vital performance metrics. For more details, see the [Benchmarking Performance section](#step-4-benchmarking-performance).
|
||||
|
||||
### Why should I use Neural Magic's DeepSparse with YOLOv8 for object detection tasks?
|
||||
|
||||
Integrating Neural Magic's DeepSparse with YOLOv8 offers several benefits:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Enhanced Inference Speed:** Achieves up to 525 FPS, significantly speeding up YOLOv8's capabilities.
|
||||
- **Optimized Model Efficiency:** Uses sparsity, pruning, and quantization techniques to reduce model size and computational needs while maintaining accuracy.
|
||||
- **High Performance on Standard CPUs:** Offers GPU-like performance on cost-effective CPU hardware.
|
||||
- **Streamlined Integration:** User-friendly tools for easy deployment and integration.
|
||||
- **Flexibility:** Supports both standard and sparsity-optimized YOLOv8 models.
|
||||
- **Cost-Effective:** Reduces operational expenses through efficient resource utilization.
|
||||
|
||||
For a deeper dive into these advantages, visit the [Benefits of Integrating Neural Magic's DeepSparse with YOLOv8 section](#benefits-of-integrating-neural-magics-deepsparse-with-yolov8).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -132,3 +132,82 @@ In this guide, you've learned how to export Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to ONNX fo
|
|||
For further details on usage, visit the [ONNX official documentation](https://onnx.ai/onnx/intro/).
|
||||
|
||||
Also, if you'd like to know more about other Ultralytics YOLOv8 integrations, visit our [integration guide page](../integrations/index.md). You'll find plenty of useful resources and insights there.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I export YOLOv8 models to ONNX format using Ultralytics?
|
||||
|
||||
To export your YOLOv8 models to ONNX format using Ultralytics, follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Usage"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the YOLOv8 model
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
# Export the model to ONNX format
|
||||
model.export(format="onnx") # creates 'yolov8n.onnx'
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the exported ONNX model
|
||||
onnx_model = YOLO("yolov8n.onnx")
|
||||
|
||||
# Run inference
|
||||
results = onnx_model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "CLI"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Export a YOLOv8n PyTorch model to ONNX format
|
||||
yolo export model=yolov8n.pt format=onnx # creates 'yolov8n.onnx'
|
||||
|
||||
# Run inference with the exported model
|
||||
yolo predict model=yolov8n.onnx source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, visit the [export documentation](../modes/export.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the advantages of using ONNX Runtime for deploying YOLOv8 models?
|
||||
|
||||
Using ONNX Runtime for deploying YOLOv8 models offers several advantages:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Cross-platform compatibility**: ONNX Runtime supports various platforms, such as Windows, macOS, and Linux, ensuring your models run smoothly across different environments.
|
||||
- **Hardware acceleration**: ONNX Runtime can leverage hardware-specific optimizations for CPUs, GPUs, and dedicated accelerators, providing high-performance inference.
|
||||
- **Framework interoperability**: Models trained in popular frameworks like PyTorch or TensorFlow can be easily converted to ONNX format and run using ONNX Runtime.
|
||||
|
||||
Learn more by checking the [ONNX Runtime documentation](https://onnxruntime.ai/docs/api/python/api_summary.html).
|
||||
|
||||
### What deployment options are available for YOLOv8 models exported to ONNX?
|
||||
|
||||
YOLOv8 models exported to ONNX can be deployed on various platforms including:
|
||||
|
||||
- **CPUs**: Utilizing ONNX Runtime for optimized CPU inference.
|
||||
- **GPUs**: Leveraging NVIDIA CUDA for high-performance GPU acceleration.
|
||||
- **Edge devices**: Running lightweight models on edge and mobile devices for real-time, on-device inference.
|
||||
- **Web browsers**: Executing models directly within web browsers for interactive web-based applications.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information, explore our guide on [model deployment options](../guides/model-deployment-options.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### Why should I use ONNX format for Ultralytics YOLOv8 models?
|
||||
|
||||
Using ONNX format for Ultralytics YOLOv8 models provides numerous benefits:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Interoperability**: ONNX allows models to be transferred between different machine learning frameworks seamlessly.
|
||||
- **Performance Optimization**: ONNX Runtime can enhance model performance by utilizing hardware-specific optimizations.
|
||||
- **Flexibility**: ONNX supports various deployment environments, enabling you to use the same model on different platforms without modification.
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the comprehensive guide on [exporting YOLOv8 models to ONNX](https://www.ultralytics.com/blog/export-and-optimize-a-yolov8-model-for-inference-on-openvino).
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I troubleshoot issues when exporting YOLOv8 models to ONNX?
|
||||
|
||||
When exporting YOLOv8 models to ONNX, you might encounter common issues such as mismatched dependencies or unsupported operations. To troubleshoot these problems:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Verify that you have the correct version of required dependencies installed.
|
||||
2. Check the official [ONNX documentation](https://onnx.ai/onnx/intro/) for supported operators and features.
|
||||
3. Review the error messages for clues and consult the [Ultralytics Common Issues guide](../guides/yolo-common-issues.md).
|
||||
|
||||
If issues persist, contact Ultralytics support for further assistance.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -284,3 +284,107 @@ For the Intel® Data Center GPU Flex Series, the OpenVINO format was able to del
|
|||
The benchmarks underline the effectiveness of OpenVINO as a tool for deploying deep learning models. By converting models to the OpenVINO format, developers can achieve significant performance improvements, making it easier to deploy these models in real-world applications.
|
||||
|
||||
For more detailed information and instructions on using OpenVINO, refer to the [official OpenVINO documentation](https://docs.openvino.ai/).
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I export YOLOv8 models to OpenVINO format?
|
||||
|
||||
Exporting YOLOv8 models to the OpenVINO format can significantly enhance CPU speed and enable GPU and NPU accelerations on Intel hardware. To export, you can use either Python or CLI as shown below:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Load a YOLOv8n PyTorch model
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
# Export the model
|
||||
model.export(format="openvino") # creates 'yolov8n_openvino_model/'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "CLI"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Export a YOLOv8n PyTorch model to OpenVINO format
|
||||
yolo export model=yolov8n.pt format=openvino # creates 'yolov8n_openvino_model/'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more information, refer to the [export formats documentation](../modes/export.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the benefits of using OpenVINO with YOLOv8 models?
|
||||
|
||||
Using Intel's OpenVINO toolkit with YOLOv8 models offers several benefits:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Performance**: Achieve up to 3x speedup on CPU inference and leverage Intel GPUs and NPUs for acceleration.
|
||||
2. **Model Optimizer**: Convert, optimize, and execute models from popular frameworks like PyTorch, TensorFlow, and ONNX.
|
||||
3. **Ease of Use**: Over 80 tutorial notebooks are available to help users get started, including ones for YOLOv8.
|
||||
4. **Heterogeneous Execution**: Deploy models on various Intel hardware with a unified API.
|
||||
|
||||
For detailed performance comparisons, visit our [benchmarks section](#openvino-yolov8-benchmarks).
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I run inference using a YOLOv8 model exported to OpenVINO?
|
||||
|
||||
After exporting a YOLOv8 model to OpenVINO format, you can run inference using Python or CLI:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the exported OpenVINO model
|
||||
ov_model = YOLO("yolov8n_openvino_model/")
|
||||
|
||||
# Run inference
|
||||
results = ov_model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "CLI"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Run inference with the exported model
|
||||
yolo predict model=yolov8n_openvino_model source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to our [predict mode documentation](../modes/predict.md) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why should I choose Ultralytics YOLOv8 over other models for OpenVINO export?
|
||||
|
||||
Ultralytics YOLOv8 is optimized for real-time object detection with high accuracy and speed. Specifically, when combined with OpenVINO, YOLOv8 provides:
|
||||
|
||||
- Up to 3x speedup on Intel CPUs
|
||||
- Seamless deployment on Intel GPUs and NPUs
|
||||
- Consistent and comparable accuracy across various export formats
|
||||
|
||||
For in-depth performance analysis, check our detailed [YOLOv8 benchmarks](#openvino-yolov8-benchmarks) on different hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I benchmark YOLOv8 models on different formats such as PyTorch, ONNX, and OpenVINO?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, you can benchmark YOLOv8 models in various formats including PyTorch, TorchScript, ONNX, and OpenVINO. Use the following code snippet to run benchmarks on your chosen dataset:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Load a YOLOv8n PyTorch model
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
# Benchmark YOLOv8n speed and accuracy on the COCO8 dataset for all export formats
|
||||
results = model.benchmarks(data="coco8.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "CLI"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Benchmark YOLOv8n speed and accuracy on the COCO8 dataset for all export formats
|
||||
yolo benchmark model=yolov8n.pt data=coco8.yaml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For detailed benchmark results, refer to our [benchmarks section](#openvino-yolov8-benchmarks) and [export formats](../modes/export.md) documentation.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -120,3 +120,83 @@ In this guide, we explored the process of exporting Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to
|
|||
For further details on usage, visit the [PaddlePaddle official documentation](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/en/guides/index_en.html)
|
||||
|
||||
Want to explore more ways to integrate your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models? Our [integration guide page](index.md) explores various options, equipping you with valuable resources and insights.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I export Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to PaddlePaddle format?
|
||||
|
||||
Exporting Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to PaddlePaddle format is straightforward. You can use the `export` method of the YOLO class to perform this exportation. Here is an example using Python:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Usage"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the YOLOv8 model
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
# Export the model to PaddlePaddle format
|
||||
model.export(format="paddle") # creates '/yolov8n_paddle_model'
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the exported PaddlePaddle model
|
||||
paddle_model = YOLO("./yolov8n_paddle_model")
|
||||
|
||||
# Run inference
|
||||
results = paddle_model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "CLI"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Export a YOLOv8n PyTorch model to PaddlePaddle format
|
||||
yolo export model=yolov8n.pt format=paddle # creates '/yolov8n_paddle_model'
|
||||
|
||||
# Run inference with the exported model
|
||||
yolo predict model='./yolov8n_paddle_model' source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more detailed setup and troubleshooting, check the [Ultralytics Installation Guide](../quickstart.md) and [Common Issues Guide](../guides/yolo-common-issues.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the advantages of using PaddlePaddle for model deployment?
|
||||
|
||||
PaddlePaddle offers several key advantages for model deployment:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Performance Optimization**: PaddlePaddle excels in efficient model execution and reduced memory usage.
|
||||
- **Dynamic-to-Static Graph Compilation**: It supports dynamic-to-static compilation, allowing for runtime optimizations.
|
||||
- **Operator Fusion**: By merging compatible operations, it reduces computational overhead.
|
||||
- **Quantization Techniques**: Supports both post-training and quantization-aware training, enabling lower-precision data representations for improved performance.
|
||||
|
||||
You can achieve enhanced results by exporting your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to PaddlePaddle, ensuring flexibility and high performance across various applications and hardware platforms. Learn more about PaddlePaddle's features [here](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/en).
|
||||
|
||||
### Why should I choose PaddlePaddle for deploying my YOLOv8 models?
|
||||
|
||||
PaddlePaddle, developed by Baidu, is optimized for industrial and commercial AI deployments. Its large developer community and robust framework provide extensive tools similar to TensorFlow and PyTorch. By exporting your YOLOv8 models to PaddlePaddle, you leverage:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Enhanced Performance**: Optimal execution speed and reduced memory footprint.
|
||||
- **Flexibility**: Wide compatibility with various devices from smartphones to cloud servers.
|
||||
- **Scalability**: Efficient parallel processing capabilities for distributed environments.
|
||||
|
||||
These features make PaddlePaddle a compelling choice for deploying YOLOv8 models in production settings.
|
||||
|
||||
### How does PaddlePaddle improve model performance over other frameworks?
|
||||
|
||||
PaddlePaddle employs several advanced techniques to optimize model performance:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Dynamic-to-Static Graph**: Converts models into a static computational graph for runtime optimizations.
|
||||
- **Operator Fusion**: Combines compatible operations to minimize memory transfer and increase inference speed.
|
||||
- **Quantization**: Reduces model size and increases efficiency using lower-precision data while maintaining accuracy.
|
||||
|
||||
These techniques prioritize efficient model execution, making PaddlePaddle an excellent option for deploying high-performance YOLOv8 models. For more on optimization, see the [PaddlePaddle official documentation](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/en/guides/index_en.html).
|
||||
|
||||
### What deployment options does PaddlePaddle offer for YOLOv8 models?
|
||||
|
||||
PaddlePaddle provides flexible deployment options:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Paddle Serving**: Deploys models as RESTful APIs, ideal for production with features like model versioning and online A/B testing.
|
||||
- **Paddle Inference API**: Gives low-level control over model execution for custom applications.
|
||||
- **Paddle Lite**: Optimizes models for mobile and embedded devices' limited resources.
|
||||
- **Paddle.js**: Enables deploying models directly within web browsers.
|
||||
|
||||
These options cover a broad range of deployment scenarios, from on-device inference to scalable cloud services. Explore more deployment strategies on the [Ultralytics Model Deployment Options page](../guides/model-deployment-options.md).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -84,3 +84,32 @@ This guide explored the Paperspace Gradient integration for training YOLOv8 mode
|
|||
For further exploration, visit [PaperSpace's official documentation](https://docs.digitalocean.com/products/paperspace/).
|
||||
|
||||
Also, visit the [Ultralytics integration guide page](index.md) to learn more about different YOLOv8 integrations. It's full of insights and tips to take your computer vision projects to the next level.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I train a YOLOv8 model using Paperspace Gradient?
|
||||
|
||||
Training a YOLOv8 model with Paperspace Gradient is straightforward and efficient. First, sign in to the [Paperspace console](https://console.paperspace.com/github/ultralytics/ultralytics). Next, click the “Start Machine” button to initiate a managed GPU environment. Once the environment is ready, you can run the notebook's cells to start training your YOLOv8 model. For detailed instructions, refer to our [YOLOv8 Model Training guide](../modes/train.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the advantages of using Paperspace Gradient for YOLOv8 projects?
|
||||
|
||||
Paperspace Gradient offers several unique advantages for training and deploying YOLOv8 models:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Hardware Flexibility:** Choose from various CPU, GPU, and TPU configurations.
|
||||
- **One-Click Notebooks:** Use pre-configured Jupyter Notebooks for YOLOv8 without worrying about environment setup.
|
||||
- **Experiment Tracking:** Automatic tracking of hyperparameters, metrics, and code changes.
|
||||
- **Dataset Management:** Efficiently manage your datasets within Gradient.
|
||||
- **Model Serving:** Deploy models as REST APIs easily.
|
||||
- **Real-time Monitoring:** Monitor model performance and resource utilization through a dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why should I choose Ultralytics YOLOv8 over other object detection models?
|
||||
|
||||
Ultralytics YOLOv8 stands out for its real-time object detection capabilities and high accuracy. Its seamless integration with platforms like Paperspace Gradient enhances productivity by simplifying the training and deployment process. YOLOv8 supports various use cases, from security systems to retail inventory management. Explore more about YOLOv8's advantages [here](https://www.ultralytics.com/yolo).
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I deploy my YOLOv8 model on edge devices using Paperspace Gradient?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, you can deploy YOLOv8 models on edge devices using Paperspace Gradient. The platform supports various deployment formats like TFLite and Edge TPU, which are optimized for edge devices. After training your model on Gradient, refer to our [export guide](../modes/export.md) for instructions on converting your model to the desired format.
|
||||
|
||||
### How does experiment tracking in Paperspace Gradient help improve YOLOv8 training?
|
||||
|
||||
Experiment tracking in Paperspace Gradient streamlines the model development process by automatically logging hyperparameters, metrics, and code changes. This allows you to easily compare different training runs, identify optimal configurations, and reproduce successful experiments.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -183,3 +183,102 @@ plt.show()
|
|||
In this documentation, we covered common workflows to analyze the results of experiments run with Ray Tune using Ultralytics. The key steps include loading the experiment results from a directory, performing basic experiment-level and trial-level analysis and plotting metrics.
|
||||
|
||||
Explore further by looking into Ray Tune's [Analyze Results](https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/tune/examples/tune_analyze_results.html) docs page to get the most out of your hyperparameter tuning experiments.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I tune the hyperparameters of my YOLOv8 model using Ray Tune?
|
||||
|
||||
To tune the hyperparameters of your Ultralytics YOLOv8 model using Ray Tune, follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Install the required packages:**
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -U ultralytics "ray[tune]"
|
||||
pip install wandb # optional for logging
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Load your YOLOv8 model and start tuning:**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Load a YOLOv8 model
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
# Start tuning with the COCO8 dataset
|
||||
result_grid = model.tune(data="coco8.yaml", use_ray=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This utilizes Ray Tune's advanced search strategies and parallelism to efficiently optimize your model's hyperparameters. For more information, check out the [Ray Tune documentation](https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/tune/index.html).
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the default hyperparameters for YOLOv8 tuning with Ray Tune?
|
||||
|
||||
Ultralytics YOLOv8 uses the following default hyperparameters for tuning with Ray Tune:
|
||||
|
||||
| Parameter | Value Range | Description |
|
||||
| --------------- | -------------------------- | ------------------------------ |
|
||||
| `lr0` | `tune.uniform(1e-5, 1e-1)` | Initial learning rate |
|
||||
| `lrf` | `tune.uniform(0.01, 1.0)` | Final learning rate factor |
|
||||
| `momentum` | `tune.uniform(0.6, 0.98)` | Momentum |
|
||||
| `weight_decay` | `tune.uniform(0.0, 0.001)` | Weight decay |
|
||||
| `warmup_epochs` | `tune.uniform(0.0, 5.0)` | Warmup epochs |
|
||||
| `box` | `tune.uniform(0.02, 0.2)` | Box loss weight |
|
||||
| `cls` | `tune.uniform(0.2, 4.0)` | Class loss weight |
|
||||
| `hsv_h` | `tune.uniform(0.0, 0.1)` | Hue augmentation range |
|
||||
| `translate` | `tune.uniform(0.0, 0.9)` | Translation augmentation range |
|
||||
|
||||
These hyperparameters can be customized to suit your specific needs. For a complete list and more details, refer to the [Hyperparameter Tuning](../guides/hyperparameter-tuning.md) guide.
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I integrate Weights & Biases with my YOLOv8 model tuning?
|
||||
|
||||
To integrate Weights & Biases (W&B) with your Ultralytics YOLOv8 tuning process:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Install W&B:**
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install wandb
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Modify your tuning script:**
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import wandb
|
||||
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
wandb.init(project="YOLO-Tuning", entity="your-entity")
|
||||
|
||||
# Load YOLO model
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
# Tune hyperparameters
|
||||
result_grid = model.tune(data="coco8.yaml", use_ray=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This setup will allow you to monitor the tuning process, track hyperparameter configurations, and visualize results in W&B.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why should I use Ray Tune for hyperparameter optimization with YOLOv8?
|
||||
|
||||
Ray Tune offers numerous advantages for hyperparameter optimization:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Advanced Search Strategies:** Utilizes algorithms like Bayesian Optimization and HyperOpt for efficient parameter search.
|
||||
- **Parallelism:** Supports parallel execution of multiple trials, significantly speeding up the tuning process.
|
||||
- **Early Stopping:** Employs strategies like ASHA to terminate under-performing trials early, saving computational resources.
|
||||
|
||||
Ray Tune seamlessly integrates with Ultralytics YOLOv8, providing an easy-to-use interface for tuning hyperparameters effectively. To get started, check out the [Efficient Hyperparameter Tuning with Ray Tune and YOLOv8](../guides/hyperparameter-tuning.md) guide.
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I define a custom search space for YOLOv8 hyperparameter tuning?
|
||||
|
||||
To define a custom search space for your YOLOv8 hyperparameter tuning with Ray Tune:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ray import tune
|
||||
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
search_space = {"lr0": tune.uniform(1e-5, 1e-1), "momentum": tune.uniform(0.6, 0.98)}
|
||||
result_grid = model.tune(data="coco8.yaml", space=search_space, use_ray=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This customizes the range of hyperparameters like initial learning rate and momentum to be explored during the tuning process. For advanced configurations, refer to the [Custom Search Space Example](#custom-search-space-example) section.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -241,3 +241,29 @@ Below are a few of the many pieces of feedback we have received for using YOLOv8
|
|||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_showcase_2.png" alt="Showcase image" width="500">
|
||||
<img src="https://media.roboflow.com/ultralytics/rf_showcase_3.png" alt="Showcase image" width="500">
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I label data for YOLOv8 models using Roboflow?
|
||||
|
||||
Labeling data for YOLOv8 models using Roboflow is straightforward with Roboflow Annotate. First, create a project on Roboflow and upload your images. After uploading, select the batch of images and click "Start Annotating." You can use the `B` key for bounding boxes or the `P` key for polygons. For faster annotation, use the SAM-based label assistant by clicking the cursor icon in the sidebar. Detailed steps can be found [here](#upload-convert-and-label-data-for-yolov8-format).
|
||||
|
||||
### What services does Roboflow offer for collecting YOLOv8 training data?
|
||||
|
||||
Roboflow provides two key services for collecting YOLOv8 training data: [Universe](https://universe.roboflow.com/?ref=ultralytics) and [Collect](https://roboflow.com/collect?ref=ultralytics). Universe offers access to over 250,000 vision datasets, while Collect helps you gather images using a webcam and automated prompts.
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I manage and analyze my YOLOv8 dataset using Roboflow?
|
||||
|
||||
Roboflow offers robust dataset management tools, including dataset search, tagging, and Health Check. Use the search feature to find images based on text descriptions or tags. Health Check provides insights into dataset quality, showing class balance, image sizes, and annotation heatmaps. This helps optimize dataset performance before training YOLOv8 models. Detailed information can be found [here](#dataset-management-for-yolov8).
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I export my YOLOv8 dataset from Roboflow?
|
||||
|
||||
To export your YOLOv8 dataset from Roboflow, you need to create a dataset version. Click "Versions" in the sidebar, then "Create New Version" and apply any desired augmentations. Once the version is generated, click "Export Dataset" and choose the YOLOv8 format. Follow this process [here](#export-data-in-40-formats-for-model-training).
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I integrate and deploy YOLOv8 models with Roboflow?
|
||||
|
||||
Integrate and deploy YOLOv8 models on Roboflow by uploading your YOLOv8 weights through a few lines of Python code. Use the provided script to authenticate and upload your model, which will create an API for deployment. For details on the script and further instructions, see [this section](#upload-custom-yolov8-model-weights-for-testing-and-deployment).
|
||||
|
||||
### What tools does Roboflow provide for evaluating YOLOv8 models?
|
||||
|
||||
Roboflow offers model evaluation tools, including a confusion matrix and vector analysis plots. Access these tools from the "View Detailed Evaluation" button on your model page. These features help identify model performance issues and find areas for improvement. For more information, refer to [this section](#how-to-evaluate-yolov8-models).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -61,93 +61,180 @@ Before diving into the usage instructions, be sure to check out the range of [YO
|
|||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
rom ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Load a pre-trained model
|
||||
model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
|
||||
Load a pre-trained model
|
||||
odel = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
|
||||
|
||||
# Train the model
|
||||
results = model.train(data='coco8.yaml', epochs=100, imgsz=640)
|
||||
```
|
||||
Train the model
|
||||
esults = model.train(data='coco8.yaml', epochs=100, imgsz=640)
|
||||
``
|
||||
|
||||
Upon running the usage code snippet above, you can expect the following output:
|
||||
ning the usage code snippet above, you can expect the following output:
|
||||
|
||||
```plaintext
|
||||
TensorBoard: Start with 'tensorboard --logdir path_to_your_tensorboard_logs', view at http://localhost:6006/
|
||||
text
|
||||
ard: Start with 'tensorboard --logdir path_to_your_tensorboard_logs', view at http://localhost:6006/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
put indicates that TensorBoard is now actively monitoring your YOLOv8 training session. You can access the TensorBoard dashboard by visiting the provided URL (http://localhost:6006/) to view real-time training metrics and model performance. For users working in Google Colab, the TensorBoard will be displayed in the same cell where you executed the TensorBoard configuration commands.
|
||||
|
||||
information related to the model training process, be sure to check our [YOLOv8 Model Training guide](../modes/train.md). If you are interested in learning more about logging, checkpoints, plotting, and file management, read our [usage guide on configuration](../usage/cfg.md).
|
||||
|
||||
standing Your TensorBoard for YOLOv8 Training
|
||||
|
||||
's focus on understanding the various features and components of TensorBoard in the context of YOLOv8 training. The three key sections of the TensorBoard are Time Series, Scalars, and Graphs.
|
||||
|
||||
Series
|
||||
|
||||
Series feature in the TensorBoard offers a dynamic and detailed perspective of various training metrics over time for YOLOv8 models. It focuses on the progression and trends of metrics across training epochs. Here's an example of what you can expect to see.
|
||||
|
||||
(https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/assets/25847604/20b3e038-0356-465e-a37e-1ea232c68354)
|
||||
|
||||
Features of Time Series in TensorBoard
|
||||
|
||||
er Tags and Pinned Cards**: This functionality allows users to filter specific metrics and pin cards for quick comparison and access. It's particularly useful for focusing on specific aspects of the training process.
|
||||
|
||||
iled Metric Cards**: Time Series divides metrics into different categories like learning rate (lr), training (train), and validation (val) metrics, each represented by individual cards.
|
||||
|
||||
hical Display**: Each card in the Time Series section shows a detailed graph of a specific metric over the course of training. This visual representation aids in identifying trends, patterns, or anomalies in the training process.
|
||||
|
||||
epth Analysis**: Time Series provides an in-depth analysis of each metric. For instance, different learning rate segments are shown, offering insights into how adjustments in learning rate impact the model's learning curve.
|
||||
|
||||
ortance of Time Series in YOLOv8 Training
|
||||
|
||||
Series section is essential for a thorough analysis of the YOLOv8 model's training progress. It lets you track the metrics in real time to promptly identify and solve issues. It also offers a detailed view of each metrics progression, which is crucial for fine-tuning the model and enhancing its performance.
|
||||
|
||||
ars
|
||||
|
||||
in the TensorBoard are crucial for plotting and analyzing simple metrics like loss and accuracy during the training of YOLOv8 models. They offer a clear and concise view of how these metrics evolve with each training epoch, providing insights into the model's learning effectiveness and stability. Here's an example of what you can expect to see.
|
||||
|
||||
(https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/assets/25847604/f9228193-13e9-4768-9edf-8fa15ecd24fa)
|
||||
|
||||
Features of Scalars in TensorBoard
|
||||
|
||||
ning Rate (lr) Tags**: These tags show the variations in the learning rate across different segments (e.g., `pg0`, `pg1`, `pg2`). This helps us understand the impact of learning rate adjustments on the training process.
|
||||
|
||||
ics Tags**: Scalars include performance indicators such as:
|
||||
|
||||
AP50 (B)`: Mean Average Precision at 50% Intersection over Union (IoU), crucial for assessing object detection accuracy.
|
||||
|
||||
AP50-95 (B)`: Mean Average Precision calculated over a range of IoU thresholds, offering a more comprehensive evaluation of accuracy.
|
||||
|
||||
recision (B)`: Indicates the ratio of correctly predicted positive observations, key to understanding prediction accuracy.
|
||||
|
||||
ecall (B)`: Important for models where missing a detection is significant, this metric measures the ability to detect all relevant instances.
|
||||
|
||||
learn more about the different metrics, read our guide on [performance metrics](../guides/yolo-performance-metrics.md).
|
||||
|
||||
ning and Validation Tags (`train`, `val`)**: These tags display metrics specifically for the training and validation datasets, allowing for a comparative analysis of model performance across different data sets.
|
||||
|
||||
ortance of Monitoring Scalars
|
||||
|
||||
g scalar metrics is crucial for fine-tuning the YOLOv8 model. Variations in these metrics, such as spikes or irregular patterns in loss graphs, can highlight potential issues such as overfitting, underfitting, or inappropriate learning rate settings. By closely monitoring these scalars, you can make informed decisions to optimize the training process, ensuring that the model learns effectively and achieves the desired performance.
|
||||
|
||||
erence Between Scalars and Time Series
|
||||
|
||||
th Scalars and Time Series in TensorBoard are used for tracking metrics, they serve slightly different purposes. Scalars focus on plotting simple metrics such as loss and accuracy as scalar values. They provide a high-level overview of how these metrics change with each training epoch. While, the time-series section of the TensorBoard offers a more detailed timeline view of various metrics. It is particularly useful for monitoring the progression and trends of metrics over time, providing a deeper dive into the specifics of the training process.
|
||||
|
||||
hs
|
||||
|
||||
hs section of the TensorBoard visualizes the computational graph of the YOLOv8 model, showing how operations and data flow within the model. It's a powerful tool for understanding the model's structure, ensuring that all layers are connected correctly, and for identifying any potential bottlenecks in data flow. Here's an example of what you can expect to see.
|
||||
|
||||
(https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/assets/25847604/039028e0-4ab3-4170-bfa8-f93ce483f615)
|
||||
|
||||
re particularly useful for debugging the model, especially in complex architectures typical in deep learning models like YOLOv8. They help in verifying layer connections and the overall design of the model.
|
||||
|
||||
ry
|
||||
|
||||
de aims to help you use TensorBoard with YOLOv8 for visualization and analysis of machine learning model training. It focuses on explaining how key TensorBoard features can provide insights into training metrics and model performance during YOLOv8 training sessions.
|
||||
|
||||
re detailed exploration of these features and effective utilization strategies, you can refer to TensorFlow's official [TensorBoard documentation](https://www.tensorflow.org/tensorboard/get_started) and their [GitHub repository](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorboard).
|
||||
|
||||
learn more about the various integrations of Ultralytics? Check out the [Ultralytics integrations guide page](../integrations/index.md) to see what other exciting capabilities are waiting to be discovered!
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
do I integrate YOLOv8 with TensorBoard for real-time visualization?
|
||||
|
||||
ing YOLOv8 with TensorBoard allows for real-time visual insights during model training. First, install the necessary package:
|
||||
|
||||
ple "Installation"
|
||||
|
||||
"CLI"
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Install the required package for YOLOv8 and Tensorboard
|
||||
pip install ultralytics
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, configure TensorBoard to log your training runs, then start TensorBoard:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Configure TensorBoard for Google Colab"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```ipython
|
||||
%load_ext tensorboard
|
||||
%tensorboard --logdir path/to/runs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, during training, YOLOv8 automatically logs metrics like loss and accuracy to TensorBoard. You can monitor these metrics by visiting [http://localhost:6006/](http://localhost:6006/).
|
||||
|
||||
For a comprehensive guide, refer to our [YOLOv8 Model Training guide](../modes/train.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### What benefits does using TensorBoard with YOLOv8 offer?
|
||||
|
||||
Using TensorBoard with YOLOv8 provides several visualization tools essential for efficient model training:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Real-Time Metrics Tracking:** Track key metrics such as loss, accuracy, precision, and recall live.
|
||||
- **Model Graph Visualization:** Understand and debug the model architecture by visualizing computational graphs.
|
||||
- **Embedding Visualization:** Project embeddings to lower-dimensional spaces for better insight.
|
||||
|
||||
These tools enable you to make informed adjustments to enhance your YOLOv8 model's performance. For more details on TensorBoard features, check out the TensorFlow [TensorBoard guide](https://www.tensorflow.org/tensorboard/get_started).
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I monitor training metrics using TensorBoard when training a YOLOv8 model?
|
||||
|
||||
To monitor training metrics while training a YOLOv8 model with TensorBoard, follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Install TensorBoard and YOLOv8:** Run `pip install ultralytics` which includes TensorBoard.
|
||||
2. **Configure TensorBoard Logging:** During the training process, YOLOv8 logs metrics to a specified log directory.
|
||||
3. **Start TensorBoard:** Launch TensorBoard using the command `tensorboard --logdir path/to/your/tensorboard/logs`.
|
||||
|
||||
The TensorBoard dashboard, accessible via [http://localhost:6006/](http://localhost:6006/), provides real-time insights into various training metrics. For a deeper dive into training configurations, visit our [YOLOv8 Configuration guide](../usage/cfg.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### What kind of metrics can I visualize with TensorBoard when training YOLOv8 models?
|
||||
|
||||
When training YOLOv8 models, TensorBoard allows you to visualize an array of important metrics including:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Loss (Training and Validation):** Indicates how well the model is performing during training and validation.
|
||||
- **Accuracy/Precision/Recall:** Key performance metrics to evaluate detection accuracy.
|
||||
- **Learning Rate:** Track learning rate changes to understand its impact on training dynamics.
|
||||
- **mAP (mean Average Precision):** For a comprehensive evaluation of object detection accuracy at various IoU thresholds.
|
||||
|
||||
These visualizations are essential for tracking model performance and making necessary optimizations. For more information on these metrics, refer to our [Performance Metrics guide](../guides/yolo-performance-metrics.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I use TensorBoard in a Google Colab environment for training YOLOv8?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, you can use TensorBoard in a Google Colab environment to train YOLOv8 models. Here's a quick setup:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Configure TensorBoard for Google Colab"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```ipython
|
||||
%load_ext tensorboard
|
||||
%tensorboard --logdir path/to/runs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, run the YOLOv8 training script:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Load a pre-trained model
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
# Train the model
|
||||
results = model.train(data="coco8.yaml", epochs=100, imgsz=640)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This output indicates that TensorBoard is now actively monitoring your YOLOv8 training session. You can access the TensorBoard dashboard by visiting the provided URL (http://localhost:6006/) to view real-time training metrics and model performance. For users working in Google Colab, the TensorBoard will be displayed in the same cell where you executed the TensorBoard configuration commands.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information related to the model training process, be sure to check our [YOLOv8 Model Training guide](../modes/train.md). If you are interested in learning more about logging, checkpoints, plotting, and file management, read our [usage guide on configuration](../usage/cfg.md).
|
||||
|
||||
## Understanding Your TensorBoard for YOLOv8 Training
|
||||
|
||||
Now, let's focus on understanding the various features and components of TensorBoard in the context of YOLOv8 training. The three key sections of the TensorBoard are Time Series, Scalars, and Graphs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Time Series
|
||||
|
||||
The Time Series feature in the TensorBoard offers a dynamic and detailed perspective of various training metrics over time for YOLOv8 models. It focuses on the progression and trends of metrics across training epochs. Here's an example of what you can expect to see.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Key Features of Time Series in TensorBoard
|
||||
|
||||
- **Filter Tags and Pinned Cards**: This functionality allows users to filter specific metrics and pin cards for quick comparison and access. It's particularly useful for focusing on specific aspects of the training process.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Detailed Metric Cards**: Time Series divides metrics into different categories like learning rate (lr), training (train), and validation (val) metrics, each represented by individual cards.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Graphical Display**: Each card in the Time Series section shows a detailed graph of a specific metric over the course of training. This visual representation aids in identifying trends, patterns, or anomalies in the training process.
|
||||
|
||||
- **In-Depth Analysis**: Time Series provides an in-depth analysis of each metric. For instance, different learning rate segments are shown, offering insights into how adjustments in learning rate impact the model's learning curve.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Importance of Time Series in YOLOv8 Training
|
||||
|
||||
The Time Series section is essential for a thorough analysis of the YOLOv8 model's training progress. It lets you track the metrics in real time to promptly identify and solve issues. It also offers a detailed view of each metrics progression, which is crucial for fine-tuning the model and enhancing its performance.
|
||||
|
||||
### Scalars
|
||||
|
||||
Scalars in the TensorBoard are crucial for plotting and analyzing simple metrics like loss and accuracy during the training of YOLOv8 models. They offer a clear and concise view of how these metrics evolve with each training epoch, providing insights into the model's learning effectiveness and stability. Here's an example of what you can expect to see.
|
||||
|
||||
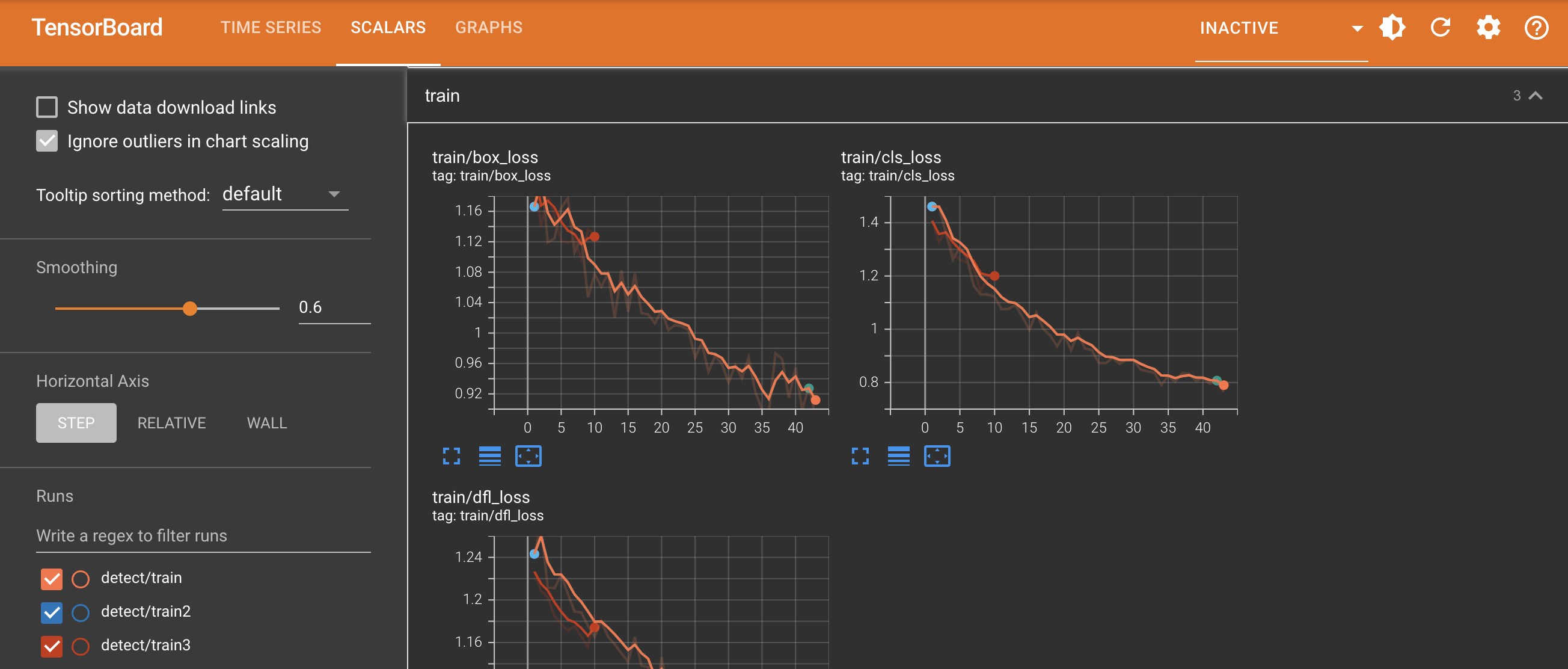
|
||||
|
||||
#### Key Features of Scalars in TensorBoard
|
||||
|
||||
- **Learning Rate (lr) Tags**: These tags show the variations in the learning rate across different segments (e.g., `pg0`, `pg1`, `pg2`). This helps us understand the impact of learning rate adjustments on the training process.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Metrics Tags**: Scalars include performance indicators such as:
|
||||
|
||||
- `mAP50 (B)`: Mean Average Precision at 50% Intersection over Union (IoU), crucial for assessing object detection accuracy.
|
||||
|
||||
- `mAP50-95 (B)`: Mean Average Precision calculated over a range of IoU thresholds, offering a more comprehensive evaluation of accuracy.
|
||||
|
||||
- `Precision (B)`: Indicates the ratio of correctly predicted positive observations, key to understanding prediction accuracy.
|
||||
|
||||
- `Recall (B)`: Important for models where missing a detection is significant, this metric measures the ability to detect all relevant instances.
|
||||
|
||||
- To learn more about the different metrics, read our guide on [performance metrics](../guides/yolo-performance-metrics.md).
|
||||
|
||||
- **Training and Validation Tags (`train`, `val`)**: These tags display metrics specifically for the training and validation datasets, allowing for a comparative analysis of model performance across different data sets.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Importance of Monitoring Scalars
|
||||
|
||||
Observing scalar metrics is crucial for fine-tuning the YOLOv8 model. Variations in these metrics, such as spikes or irregular patterns in loss graphs, can highlight potential issues such as overfitting, underfitting, or inappropriate learning rate settings. By closely monitoring these scalars, you can make informed decisions to optimize the training process, ensuring that the model learns effectively and achieves the desired performance.
|
||||
|
||||
### Difference Between Scalars and Time Series
|
||||
|
||||
While both Scalars and Time Series in TensorBoard are used for tracking metrics, they serve slightly different purposes. Scalars focus on plotting simple metrics such as loss and accuracy as scalar values. They provide a high-level overview of how these metrics change with each training epoch. While, the time-series section of the TensorBoard offers a more detailed timeline view of various metrics. It is particularly useful for monitoring the progression and trends of metrics over time, providing a deeper dive into the specifics of the training process.
|
||||
|
||||
### Graphs
|
||||
|
||||
The Graphs section of the TensorBoard visualizes the computational graph of the YOLOv8 model, showing how operations and data flow within the model. It's a powerful tool for understanding the model's structure, ensuring that all layers are connected correctly, and for identifying any potential bottlenecks in data flow. Here's an example of what you can expect to see.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Graphs are particularly useful for debugging the model, especially in complex architectures typical in deep learning models like YOLOv8. They help in verifying layer connections and the overall design of the model.
|
||||
|
||||
## Summary
|
||||
|
||||
This guide aims to help you use TensorBoard with YOLOv8 for visualization and analysis of machine learning model training. It focuses on explaining how key TensorBoard features can provide insights into training metrics and model performance during YOLOv8 training sessions.
|
||||
|
||||
For a more detailed exploration of these features and effective utilization strategies, you can refer to TensorFlow's official [TensorBoard documentation](https://www.tensorflow.org/tensorboard/get_started) and their [GitHub repository](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorboard).
|
||||
|
||||
Want to learn more about the various integrations of Ultralytics? Check out the [Ultralytics integrations guide page](../integrations/index.md) to see what other exciting capabilities are waiting to be discovered!
|
||||
TensorBoard will visualize the training progress within Colab, providing real-time insights into metrics like loss and accuracy. For additional details on configuring YOLOv8 training, see our detailed [YOLOv8 Installation guide](../quickstart.md).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -453,3 +453,94 @@ In this guide, we focused on converting Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to NVIDIA's Te
|
|||
For more information on usage details, take a look at the [TensorRT official documentation](https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/tensorrt/).
|
||||
|
||||
If you're curious about additional Ultralytics YOLOv8 integrations, our [integration guide page](../integrations/index.md) provides an extensive selection of informative resources and insights.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I convert YOLOv8 models to TensorRT format?
|
||||
|
||||
To convert your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to TensorRT format for optimized NVIDIA GPU inference, follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Install the required package**:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install ultralytics
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Export your YOLOv8 model**:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
model.export(format="engine") # creates 'yolov8n.engine'
|
||||
|
||||
# Run inference
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.engine")
|
||||
results = model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, visit the [YOLOv8 Installation guide](../quickstart.md) and the [export documentation](../modes/export.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the benefits of using TensorRT for YOLOv8 models?
|
||||
|
||||
Using TensorRT to optimize YOLOv8 models offers several benefits:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Faster Inference Speed**: TensorRT optimizes the model layers and uses precision calibration (INT8 and FP16) to speed up inference without significantly sacrificing accuracy.
|
||||
- **Memory Efficiency**: TensorRT manages tensor memory dynamically, reducing overhead and improving GPU memory utilization.
|
||||
- **Layer Fusion**: Combines multiple layers into single operations, reducing computational complexity.
|
||||
- **Kernel Auto-Tuning**: Automatically selects optimized GPU kernels for each model layer, ensuring maximum performance.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information, explore the detailed features of TensorRT [here](https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt) and read our [TensorRT overview section](#tensorrt).
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I use INT8 quantization with TensorRT for YOLOv8 models?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, you can export YOLOv8 models using TensorRT with INT8 quantization. This process involves post-training quantization (PTQ) and calibration:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Export with INT8**:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
model.export(format="engine", batch=8, workspace=4, int8=True, data="coco.yaml")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Run inference**:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.engine", task="detect")
|
||||
result = model.predict("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, refer to the [exporting TensorRT with INT8 quantization section](#exporting-tensorrt-with-int8-quantization).
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I deploy YOLOv8 TensorRT models on an NVIDIA Triton Inference Server?
|
||||
|
||||
Deploying YOLOv8 TensorRT models on an NVIDIA Triton Inference Server can be done using the following resources:
|
||||
|
||||
- **[Deploy Ultralytics YOLOv8 with Triton Server](../guides/triton-inference-server.md)**: Step-by-step guidance on setting up and using Triton Inference Server.
|
||||
- **[NVIDIA Triton Inference Server Documentation](https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/deploying-deep-learning-nvidia-tensorrt/)**: Official NVIDIA documentation for detailed deployment options and configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
These guides will help you integrate YOLOv8 models efficiently in various deployment environments.
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the performance improvements observed with YOLOv8 models exported to TensorRT?
|
||||
|
||||
Performance improvements with TensorRT can vary based on the hardware used. Here are some typical benchmarks:
|
||||
|
||||
- **NVIDIA A100**:
|
||||
|
||||
- **FP32** Inference: ~0.52 ms / image
|
||||
- **FP16** Inference: ~0.34 ms / image
|
||||
- **INT8** Inference: ~0.28 ms / image
|
||||
- Slight reduction in mAP with INT8 precision, but significant improvement in speed.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Consumer GPUs (e.g., RTX 3080)**:
|
||||
- **FP32** Inference: ~1.06 ms / image
|
||||
- **FP16** Inference: ~0.62 ms / image
|
||||
- **INT8** Inference: ~0.52 ms / image
|
||||
|
||||
Detailed performance benchmarks for different hardware configurations can be found in the [performance section](#ultralytics-yolo-tensorrt-export-performance).
|
||||
|
||||
For more comprehensive insights into TensorRT performance, refer to the [Ultralytics documentation](../modes/export.md) and our performance analysis reports.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -124,3 +124,81 @@ In this guide, we explored how to export Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to the TF Gra
|
|||
For further details on usage, visit the [TF GraphDef official documentation](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/Graph).
|
||||
|
||||
For more information on integrating Ultralytics YOLOv8 with other platforms and frameworks, don't forget to check out our [integration guide page](index.md). It has great resources and insights to help you make the most of YOLOv8 in your projects.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I export a YOLOv8 model to TF GraphDef format?
|
||||
|
||||
Ultralytics YOLOv8 models can be exported to TensorFlow GraphDef (TF GraphDef) format seamlessly. This format provides a serialized, platform-independent representation of the model, ideal for deploying in varied environments like mobile and web. To export a YOLOv8 model to TF GraphDef, follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Usage"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the YOLOv8 model
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
# Export the model to TF GraphDef format
|
||||
model.export(format="pb") # creates 'yolov8n.pb'
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the exported TF GraphDef model
|
||||
tf_graphdef_model = YOLO("yolov8n.pb")
|
||||
|
||||
# Run inference
|
||||
results = tf_graphdef_model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "CLI"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Export a YOLOv8n PyTorch model to TF GraphDef format
|
||||
yolo export model="yolov8n.pt" format="pb" # creates 'yolov8n.pb'
|
||||
|
||||
# Run inference with the exported model
|
||||
yolo predict model="yolov8n.pb" source="https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more information on different export options, visit the [Ultralytics documentation on model export](../modes/export.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the benefits of using TF GraphDef for YOLOv8 model deployment?
|
||||
|
||||
Exporting YOLOv8 models to the TF GraphDef format offers multiple advantages, including:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Platform Independence**: TF GraphDef provides a platform-independent format, allowing models to be deployed across various environments including mobile and web browsers.
|
||||
2. **Optimizations**: The format enables several optimizations, such as constant folding, quantization, and graph transformations, which enhance execution efficiency and reduce memory usage.
|
||||
3. **Hardware Acceleration**: Models in TF GraphDef format can leverage hardware accelerators like GPUs, TPUs, and AI chips for performance gains.
|
||||
|
||||
Read more about the benefits in the [TF GraphDef section](#why-should-you-export-to-tf-graphdef) of our documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why should I use Ultralytics YOLOv8 over other object detection models?
|
||||
|
||||
Ultralytics YOLOv8 offers numerous advantages compared to other models like YOLOv5 and YOLOv7. Some key benefits include:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **State-of-the-Art Performance**: YOLOv8 provides exceptional speed and accuracy for real-time object detection, segmentation, and classification.
|
||||
2. **Ease of Use**: Features a user-friendly API for model training, validation, prediction, and export, making it accessible for both beginners and experts.
|
||||
3. **Broad Compatibility**: Supports multiple export formats including ONNX, TensorRT, CoreML, and TensorFlow, for versatile deployment options.
|
||||
|
||||
Explore further details in our [introduction to YOLOv8](https://docs.ultralytics.com/models/yolov8/).
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I deploy a YOLOv8 model on specialized hardware using TF GraphDef?
|
||||
|
||||
Once a YOLOv8 model is exported to TF GraphDef format, you can deploy it across various specialized hardware platforms. Typical deployment scenarios include:
|
||||
|
||||
- **TensorFlow Serving**: Use TensorFlow Serving for scalable model deployment in production environments. It supports model management and efficient serving.
|
||||
- **Mobile Devices**: Convert TF GraphDef models to TensorFlow Lite, optimized for mobile and embedded devices, enabling on-device inference.
|
||||
- **Web Browsers**: Deploy models using TensorFlow.js for client-side inference in web applications.
|
||||
- **AI Accelerators**: Leverage TPUs and custom AI chips for accelerated inference.
|
||||
|
||||
Check the [deployment options](#deployment-options-with-tf-graphdef) section for detailed information.
|
||||
|
||||
### Where can I find solutions for common issues while exporting YOLOv8 models?
|
||||
|
||||
For troubleshooting common issues with exporting YOLOv8 models, Ultralytics provides comprehensive guides and resources. If you encounter problems during installation or model export, refer to:
|
||||
|
||||
- **[Common Issues Guide](../guides/yolo-common-issues.md)**: Offers solutions to frequently faced problems.
|
||||
- **[Installation Guide](../quickstart.md)**: Step-by-step instructions for setting up the required packages.
|
||||
|
||||
These resources should help you resolve most issues related to YOLOv8 model export and deployment.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -118,3 +118,80 @@ In this guide, we explored how to export Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to the TF Sav
|
|||
For further details on usage, visit the [TF SavedModel official documentation](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model).
|
||||
|
||||
For more information on integrating Ultralytics YOLOv8 with other platforms and frameworks, don't forget to check out our [integration guide page](index.md). It's packed with great resources to help you make the most of YOLOv8 in your projects.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I export an Ultralytics YOLO model to TensorFlow SavedModel format?
|
||||
|
||||
Exporting an Ultralytics YOLO model to the TensorFlow SavedModel format is straightforward. You can use either Python or CLI to achieve this:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Exporting YOLOv8 to TF SavedModel"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the YOLOv8 model
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
# Export the model to TF SavedModel format
|
||||
model.export(format="saved_model") # creates '/yolov8n_saved_model'
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the exported TF SavedModel for inference
|
||||
tf_savedmodel_model = YOLO("./yolov8n_saved_model")
|
||||
results = tf_savedmodel_model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "CLI"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Export the YOLOv8 model to TF SavedModel format
|
||||
yolo export model=yolov8n.pt format=saved_model # creates '/yolov8n_saved_model'
|
||||
|
||||
# Run inference with the exported model
|
||||
yolo predict model='./yolov8n_saved_model' source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the [Ultralytics Export documentation](../modes/export.md) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why should I use the TensorFlow SavedModel format?
|
||||
|
||||
The TensorFlow SavedModel format offers several advantages for model deployment:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Portability:** It provides a language-neutral format, making it easy to share and deploy models across different environments.
|
||||
- **Compatibility:** Integrates seamlessly with tools like TensorFlow Serving, TensorFlow Lite, and TensorFlow.js, which are essential for deploying models on various platforms, including web and mobile applications.
|
||||
- **Complete encapsulation:** Encodes the model architecture, weights, and compilation information, allowing for straightforward sharing and training continuation.
|
||||
|
||||
For more benefits and deployment options, check out the [Ultralytics YOLO model deployment options](../guides/model-deployment-options.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the typical deployment scenarios for TF SavedModel?
|
||||
|
||||
TF SavedModel can be deployed in various environments, including:
|
||||
|
||||
- **TensorFlow Serving:** Ideal for production environments requiring scalable and high-performance model serving.
|
||||
- **Cloud Platforms:** Supports major cloud services like Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Microsoft Azure for scalable model deployment.
|
||||
- **Mobile and Embedded Devices:** Using TensorFlow Lite to convert TF SavedModels allows for deployment on mobile devices, IoT devices, and microcontrollers.
|
||||
- **TensorFlow Runtime:** For C++ environments needing low-latency inference with better performance.
|
||||
|
||||
For detailed deployment options, visit the official guides on [deploying TensorFlow models](https://www.tensorflow.org/tfx/guide/serving).
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I install the necessary packages to export YOLOv8 models?
|
||||
|
||||
To export YOLOv8 models, you need to install the `ultralytics` package. Run the following command in your terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install ultralytics
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more detailed installation instructions and best practices, refer to our [Ultralytics Installation guide](../quickstart.md). If you encounter any issues, consult our [Common Issues guide](../guides/yolo-common-issues.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the key features of the TensorFlow SavedModel format?
|
||||
|
||||
TF SavedModel format is beneficial for AI developers due to the following features:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Portability:** Allows sharing and deployment across various environments effortlessly.
|
||||
- **Ease of Deployment:** Encapsulates the computational graph, trained parameters, and metadata into a single package, which simplifies loading and inference.
|
||||
- **Asset Management:** Supports external assets like vocabularies, ensuring they are available when the model loads.
|
||||
|
||||
For further details, explore the [official TensorFlow documentation](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -38,9 +38,9 @@ TF.js provides a range of options to deploy your machine learning models:
|
|||
|
||||
- **In-Browser ML Applications:** You can build web applications that run machine learning models directly in the browser. The need for server-side computation is eliminated and the server load is reduced.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Node.js Applications::** TensorFlow.js also supports deployment in Node.js environments, enabling the development of server-side machine learning applications. It is particularly useful for applications that require the processing power of a server or access to server-side data
|
||||
- **Node.js Applications::** TensorFlow.js also supports deployment in Node.js environments, enabling the development of server-side machine learning applications. It is particularly useful for applications that require the processing power of a server or access to server-side data.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Chrome Extensions:** An interesting deployment scenario is the creation of Chrome extensions with TensorFlow.js. For instance, you can develop an extension that allows users to right-click on an image within any webpage to classify it using a pre-trained ML model. TensorFlow.js can be integrated into everyday web browsing experiences to provide immediate insights or augmentations based on machine learning.
|
||||
- **Chrome Extensions:** An interesting deployment scenario is the creation of Chrome extensions with TensorFlow.js. For instance, you can develop an extension that allows users to right-click on an image within any webpage to classify it using a pre-trained ML model. TensorFlow.js can be integrated into everyday web browsing experiences to provide immediate insights or augmentations based on machine learning.
|
||||
|
||||
## Exporting YOLOv8 Models to TensorFlow.js
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -116,3 +116,79 @@ In this guide, we learned how to export Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to the TensorF
|
|||
For further details on usage, visit the [TensorFlow.js official documentation](https://www.tensorflow.org/js/guide).
|
||||
|
||||
For more information on integrating Ultralytics YOLOv8 with other platforms and frameworks, don't forget to check out our [integration guide page](index.md). It's packed with great resources to help you make the most of YOLOv8 in your projects.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I export Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to TensorFlow.js format?
|
||||
|
||||
Exporting Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to TensorFlow.js (TF.js) format is straightforward. You can follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Usage"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the YOLOv8 model
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
# Export the model to TF.js format
|
||||
model.export(format="tfjs") # creates '/yolov8n_web_model'
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the exported TF.js model
|
||||
tfjs_model = YOLO("./yolov8n_web_model")
|
||||
|
||||
# Run inference
|
||||
results = tfjs_model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "CLI"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Export a YOLOv8n PyTorch model to TF.js format
|
||||
yolo export model=yolov8n.pt format=tfjs # creates '/yolov8n_web_model'
|
||||
|
||||
# Run inference with the exported model
|
||||
yolo predict model='./yolov8n_web_model' source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more details about supported export options, visit the [Ultralytics documentation page on deployment options](../guides/model-deployment-options.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### Why should I export my YOLOv8 models to TensorFlow.js?
|
||||
|
||||
Exporting YOLOv8 models to TensorFlow.js offers several advantages, including:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Local Execution:** Models can run directly in the browser or Node.js, reducing latency and enhancing user experience.
|
||||
2. **Cross-Platform Support:** TF.js supports multiple environments, allowing flexibility in deployment.
|
||||
3. **Offline Capabilities:** Enables applications to function without an internet connection, ensuring reliability and privacy.
|
||||
4. **GPU Acceleration:** Leverages WebGL for GPU acceleration, optimizing performance on devices with limited resources.
|
||||
|
||||
For a comprehensive overview, see our [Integrations with TensorFlow.js](../integrations/tf-graphdef.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### How does TensorFlow.js benefit browser-based machine learning applications?
|
||||
|
||||
TensorFlow.js is specifically designed for efficient execution of ML models in browsers and Node.js environments. Here's how it benefits browser-based applications:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Reduces Latency:** Runs machine learning models locally, providing immediate results without relying on server-side computations.
|
||||
- **Improves Privacy:** Keeps sensitive data on the user's device, minimizing security risks.
|
||||
- **Enables Offline Use:** Models can operate without an internet connection, ensuring consistent functionality.
|
||||
- **Supports Multiple Backends:** Offers flexibility with backends like CPU, WebGL, WebAssembly (WASM), and WebGPU for varying computational needs.
|
||||
|
||||
Interested in learning more about TF.js? Check out the [official TensorFlow.js guide](https://www.tensorflow.org/js/guide).
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the key features of TensorFlow.js for deploying YOLOv8 models?
|
||||
|
||||
Key features of TensorFlow.js include:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Cross-Platform Support:** TF.js can be used in both web browsers and Node.js, providing extensive deployment flexibility.
|
||||
- **Multiple Backends:** Supports CPU, WebGL for GPU acceleration, WebAssembly (WASM), and WebGPU for advanced operations.
|
||||
- **Offline Capabilities:** Models can run directly in the browser without internet connectivity, making it ideal for developing responsive web applications.
|
||||
|
||||
For deployment scenarios and more in-depth information, see our section on [Deployment Options with TensorFlow.js](#deploying-exported-yolov8-tensorflowjs-models).
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I deploy a YOLOv8 model on server-side Node.js applications using TensorFlow.js?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, TensorFlow.js allows the deployment of YOLOv8 models on Node.js environments. This enables server-side machine learning applications that benefit from the processing power of a server and access to server-side data. Typical use cases include real-time data processing and machine learning pipelines on backend servers.
|
||||
|
||||
To get started with Node.js deployment, refer to the [Run TensorFlow.js in Node.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js/guide/nodejs) guide from TensorFlow.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -120,3 +120,74 @@ In this guide, we focused on how to export to TFLite format. By converting your
|
|||
For further details on usage, visit the [TFLite official documentation](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite/guide).
|
||||
|
||||
Also, if you're curious about other Ultralytics YOLOv8 integrations, make sure to check out our [integration guide page](../integrations/index.md). You'll find tons of helpful info and insights waiting for you there.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I export a YOLOv8 model to TFLite format?
|
||||
|
||||
To export a YOLOv8 model to TFLite format, you can use the Ultralytics library. First, install the required package using:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install ultralytics
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, use the following code snippet to export your model:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the YOLOv8 model
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
# Export the model to TFLite format
|
||||
model.export(format="tflite") # creates 'yolov8n_float32.tflite'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For CLI users, you can achieve this with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
yolo export model=yolov8n.pt format=tflite # creates 'yolov8n_float32.tflite'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, visit the [Ultralytics export guide](../modes/export.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the benefits of using TensorFlow Lite for YOLOv8 model deployment?
|
||||
|
||||
TensorFlow Lite (TFLite) is an open-source deep learning framework designed for on-device inference, making it ideal for deploying YOLOv8 models on mobile, embedded, and IoT devices. Key benefits include:
|
||||
|
||||
- **On-device optimization**: Minimize latency and enhance privacy by processing data locally.
|
||||
- **Platform compatibility**: Supports Android, iOS, embedded Linux, and MCU.
|
||||
- **Performance**: Utilizes hardware acceleration to optimize model speed and efficiency.
|
||||
|
||||
To learn more, check out the [TFLite guide](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite/guide).
|
||||
|
||||
### Is it possible to run YOLOv8 TFLite models on Raspberry Pi?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, you can run YOLOv8 TFLite models on Raspberry Pi to improve inference speeds. First, export your model to TFLite format as explained [here](#how-do-i-export-a-yolov8-model-to-tflite-format). Then, use a tool like TensorFlow Lite Interpreter to execute the model on your Raspberry Pi.
|
||||
|
||||
For further optimizations, you might consider using [Coral Edge TPU](https://coral.withgoogle.com/). For detailed steps, refer to our [Raspberry Pi deployment guide](../guides/raspberry-pi.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I use TFLite models on microcontrollers for YOLOv8 predictions?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, TFLite supports deployment on microcontrollers with limited resources. TFLite's core runtime requires only 16 KB of memory on an Arm Cortex M3 and can run basic YOLOv8 models. This makes it suitable for deployment on devices with minimal computational power and memory.
|
||||
|
||||
To get started, visit the [TFLite Micro for Microcontrollers guide](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite/microcontrollers).
|
||||
|
||||
### What platforms are compatible with TFLite exported YOLOv8 models?
|
||||
|
||||
TensorFlow Lite provides extensive platform compatibility, allowing you to deploy YOLOv8 models on a wide range of devices, including:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Android and iOS**: Native support through TFLite Android and iOS libraries.
|
||||
- **Embedded Linux**: Ideal for single-board computers such as Raspberry Pi.
|
||||
- **Microcontrollers**: Suitable for MCUs with constrained resources.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information on deployment options, see our detailed [deployment guide](#deploying-exported-yolov8-tflite-models).
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I troubleshoot common issues during YOLOv8 model export to TFLite?
|
||||
|
||||
If you encounter errors while exporting YOLOv8 models to TFLite, common solutions include:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Check package compatibility**: Ensure you're using compatible versions of Ultralytics and TensorFlow. Refer to our [installation guide](../quickstart.md).
|
||||
- **Model support**: Verify that the specific YOLOv8 model supports TFLite export by checking [here](../modes/export.md).
|
||||
|
||||
For additional troubleshooting tips, visit our [Common Issues guide](../guides/yolo-common-issues.md).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -124,3 +124,81 @@ In this guide, we explored the process of exporting Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to
|
|||
For further details on usage, visit [TorchScript's official documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/jit.html).
|
||||
|
||||
Also, if you'd like to know more about other Ultralytics YOLOv8 integrations, visit our [integration guide page](../integrations/index.md). You'll find plenty of useful resources and insights there.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### What is Ultralytics YOLOv8 model export to TorchScript?
|
||||
|
||||
Exporting an Ultralytics YOLOv8 model to TorchScript allows for flexible, cross-platform deployment. TorchScript, a part of the PyTorch ecosystem, facilitates the serialization of models, which can then be executed in environments that lack Python support. This makes it ideal for deploying models on embedded systems, C++ environments, mobile applications, and even web browsers. Exporting to TorchScript enables efficient performance and wider applicability of your YOLOv8 models across diverse platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I export my YOLOv8 model to TorchScript using Ultralytics?
|
||||
|
||||
To export a YOLOv8 model to TorchScript, you can use the following example code:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Usage"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the YOLOv8 model
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
# Export the model to TorchScript format
|
||||
model.export(format="torchscript") # creates 'yolov8n.torchscript'
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the exported TorchScript model
|
||||
torchscript_model = YOLO("yolov8n.torchscript")
|
||||
|
||||
# Run inference
|
||||
results = torchscript_model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=== "CLI"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Export a YOLOv8n PyTorch model to TorchScript format
|
||||
yolo export model=yolov8n.pt format=torchscript # creates 'yolov8n.torchscript'
|
||||
|
||||
# Run inference with the exported model
|
||||
yolo predict model=yolov8n.torchscript source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more details about the export process, refer to the [Ultralytics documentation on exporting](../modes/export.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### Why should I use TorchScript for deploying YOLOv8 models?
|
||||
|
||||
Using TorchScript for deploying YOLOv8 models offers several advantages:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Portability**: Exported models can run in environments without the need for Python, such as C++ applications, embedded systems, or mobile devices.
|
||||
- **Optimization**: TorchScript supports static graph execution and Just-In-Time (JIT) compilation, which can optimize model performance.
|
||||
- **Cross-Language Integration**: TorchScript models can be integrated into other programming languages, enhancing flexibility and expandability.
|
||||
- **Serialization**: Models can be serialized, allowing for platform-independent loading and inference.
|
||||
|
||||
For more insights into deployment, visit the [PyTorch Mobile Documentation](https://pytorch.org/mobile/home/), [TorchServe Documentation](https://pytorch.org/serve/getting_started.html), and [C++ Deployment Guide](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/advanced/cpp_export.html).
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the installation steps for exporting YOLOv8 models to TorchScript?
|
||||
|
||||
To install the required package for exporting YOLOv8 models, use the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Tip "Installation"
|
||||
|
||||
=== "CLI"
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Install the required package for YOLOv8
|
||||
pip install ultralytics
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For detailed instructions, visit the [Ultralytics Installation guide](../quickstart.md). If any issues arise during installation, consult the [Common Issues guide](../guides/yolo-common-issues.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I deploy my exported TorchScript YOLOv8 models?
|
||||
|
||||
After exporting YOLOv8 models to the TorchScript format, you can deploy them across a variety of platforms:
|
||||
|
||||
- **C++ API**: Ideal for low-overhead, highly efficient production environments.
|
||||
- **Mobile Deployment**: Use [PyTorch Mobile](https://pytorch.org/mobile/home/) for iOS and Android applications.
|
||||
- **Cloud Deployment**: Utilize services like [TorchServe](https://pytorch.org/serve/getting_started.html) for scalable server-side deployment.
|
||||
|
||||
Explore comprehensive guidelines for deploying models in these settings to take full advantage of TorchScript's capabilities.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -63,35 +63,33 @@ Before diving into the usage instructions for YOLOv8 model training with Weights
|
|||
|
||||
=== "Python"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import wandb
|
||||
from wandb.integration.ultralytics import add_wandb_callback
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import wandb
|
||||
from wandb.integration.ultralytics import add_wandb_callback
|
||||
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Step 1: Initialize a Weights & Biases run
|
||||
wandb.init(project="ultralytics", job_type="training")
|
||||
# Initialize a Weights & Biases run
|
||||
wandb.init(project="ultralytics", job_type="training")
|
||||
|
||||
# Step 2: Define the YOLOv8 Model and Dataset
|
||||
model_name = "yolov8n"
|
||||
dataset_name = "coco8.yaml"
|
||||
model = YOLO(f"{model_name}.pt")
|
||||
# Load a YOLO model
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
# Step 3: Add W&B Callback for Ultralytics
|
||||
add_wandb_callback(model, enable_model_checkpointing=True)
|
||||
# Add W&B Callback for Ultralytics
|
||||
add_wandb_callback(model, enable_model_checkpointing=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# Step 4: Train and Fine-Tune the Model
|
||||
model.train(project="ultralytics", data=dataset_name, epochs=5, imgsz=640)
|
||||
# Train and Fine-Tune the Model
|
||||
model.train(project="ultralytics", data="coco8.yaml", epochs=5, imgsz=640)
|
||||
|
||||
# Step 5: Validate the Model
|
||||
model.val()
|
||||
# Validate the Model
|
||||
model.val()
|
||||
|
||||
# Step 6: Perform Inference and Log Results
|
||||
model(["path/to/image1", "path/to/image2"])
|
||||
# Perform Inference and Log Results
|
||||
model(["path/to/image1", "path/to/image2"])
|
||||
|
||||
# Step 7: Finalize the W&B Run
|
||||
wandb.finish()
|
||||
```
|
||||
# Finalize the W&B Run
|
||||
wandb.finish()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Understanding the Code
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -150,3 +148,86 @@ This guide helped you explore Ultralytics' YOLOv8 integration with Weights & Bia
|
|||
For further details on usage, visit [Weights & Biases' official documentation](https://docs.wandb.ai/guides/integrations/ultralytics).
|
||||
|
||||
Also, be sure to check out the [Ultralytics integration guide page](../integrations/index.md), to learn more about different exciting integrations.
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I install the required packages for YOLOv8 and Weights & Biases?
|
||||
|
||||
To install the required packages for YOLOv8 and Weights & Biases, open your command line interface and run:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install --upgrade ultralytics==8.0.186 wandb
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For further guidance on installation steps, refer to our [YOLOv8 Installation guide](../quickstart.md). If you encounter issues, consult the [Common Issues guide](../guides/yolo-common-issues.md) for troubleshooting tips.
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the benefits of integrating Ultralytics YOLOv8 with Weights & Biases?
|
||||
|
||||
Integrating Ultralytics YOLOv8 with Weights & Biases offers several benefits including:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Real-Time Metrics Tracking:** Observe metric changes during training for immediate insights.
|
||||
- **Hyperparameter Optimization:** Improve model performance by fine-tuning learning rate, batch size, etc.
|
||||
- **Comparative Analysis:** Side-by-side comparison of different training runs.
|
||||
- **Resource Monitoring:** Keep track of CPU, GPU, and memory usage.
|
||||
- **Model Artifacts Management:** Easy access and sharing of model checkpoints.
|
||||
|
||||
Explore these features in detail in the Weights & Biases Dashboard section above.
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I configure Weights & Biases for YOLOv8 training?
|
||||
|
||||
To configure Weights & Biases for YOLOv8 training, follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Run the command to initialize Weights & Biases:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
import wandb
|
||||
wandb.login()
|
||||
```
|
||||
2. Retrieve your API key from the Weights & Biases website.
|
||||
3. Use the API key to authenticate your development environment.
|
||||
|
||||
Detailed setup instructions can be found in the Configuring Weights & Biases section above.
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I train a YOLOv8 model using Weights & Biases?
|
||||
|
||||
For training a YOLOv8 model using Weights & Biases, use the following steps in a Python script:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import wandb
|
||||
from wandb.integration.ultralytics import add_wandb_callback
|
||||
|
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize a Weights & Biases run
|
||||
wandb.init(project="ultralytics", job_type="training")
|
||||
|
||||
# Load a YOLO model
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
|
||||
|
||||
# Add W&B Callback for Ultralytics
|
||||
add_wandb_callback(model, enable_model_checkpointing=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# Train and Fine-Tune the Model
|
||||
model.train(project="ultralytics", data="coco8.yaml", epochs=5, imgsz=640)
|
||||
|
||||
# Validate the Model
|
||||
model.val()
|
||||
|
||||
# Perform Inference and Log Results
|
||||
model(["path/to/image1", "path/to/image2"])
|
||||
|
||||
# Finalize the W&B Run
|
||||
wandb.finish()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This script initializes Weights & Biases, sets up the model, trains it, and logs results. For more details, visit the Usage section above.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why should I use Ultralytics YOLOv8 with Weights & Biases over other platforms?
|
||||
|
||||
Ultralytics YOLOv8 integrated with Weights & Biases offers several unique advantages:
|
||||
|
||||
- **High Efficiency:** Real-time tracking of training metrics and performance optimization.
|
||||
- **Scalability:** Easily manage large-scale training jobs with robust resource monitoring and utilization tools.
|
||||
- **Interactivity:** A user-friendly interactive UI for data visualization and model management.
|
||||
- **Community and Support:** Strong integration documentation and community support with flexible customization and enhancement options.
|
||||
|
||||
For comparisons with other platforms like Comet and ClearML, refer to [Ultralytics integrations](../integrations/index.md).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue