Add Docs languages zh, es, ru, pt, fr, de, ja, ko (#6316)
Signed-off-by: Glenn Jocher <glenn.jocher@ultralytics.com> Co-authored-by: pre-commit-ci[bot] <66853113+pre-commit-ci[bot]@users.noreply.github.com>
This commit is contained in:
parent
e3a538bbde
commit
48e70f0921
144 changed files with 17632 additions and 76 deletions
|
|
@ -72,16 +72,16 @@ Here's how you can use these formats to train your model:
|
|||
|
||||
Here is a list of the supported datasets and a brief description for each:
|
||||
|
||||
- [**Argoverse**](./argoverse.md): A collection of sensor data collected from autonomous vehicles. It contains 3D tracking annotations for car objects.
|
||||
- [**COCO**](./coco.md): Common Objects in Context (COCO) is a large-scale object detection, segmentation, and captioning dataset with 80 object categories.
|
||||
- [**COCO8**](./coco8.md): A smaller subset of the COCO dataset, COCO8 is more lightweight and faster to train.
|
||||
- [**GlobalWheat2020**](./globalwheat2020.md): A dataset containing images of wheat heads for the Global Wheat Challenge 2020.
|
||||
- [**Objects365**](./objects365.md): A large-scale object detection dataset with 365 object categories and 600k images, aimed at advancing object detection research.
|
||||
- [**OpenImagesV7**](./open-images-v7.md): A comprehensive dataset by Google with 1.7M train images and 42k validation images.
|
||||
- [**SKU-110K**](./sku-110k.md): A dataset containing images of densely packed retail products, intended for retail environment object detection.
|
||||
- [**VisDrone**](./visdrone.md): A dataset focusing on drone-based images, containing various object categories like cars, pedestrians, and cyclists.
|
||||
- [**VOC**](./voc.md): PASCAL VOC is a popular object detection dataset with 20 object categories including vehicles, animals, and furniture.
|
||||
- [**xView**](./xview.md): A dataset containing high-resolution satellite imagery, designed for the detection of various object classes in overhead views.
|
||||
- [**Argoverse**](argoverse.md): A collection of sensor data collected from autonomous vehicles. It contains 3D tracking annotations for car objects.
|
||||
- [**COCO**](coco.md): Common Objects in Context (COCO) is a large-scale object detection, segmentation, and captioning dataset with 80 object categories.
|
||||
- [**COCO8**](coco8.md): A smaller subset of the COCO dataset, COCO8 is more lightweight and faster to train.
|
||||
- [**GlobalWheat2020**](globalwheat2020.md): A dataset containing images of wheat heads for the Global Wheat Challenge 2020.
|
||||
- [**Objects365**](objects365.md): A large-scale object detection dataset with 365 object categories and 600k images, aimed at advancing object detection research.
|
||||
- [**OpenImagesV7**](open-images-v7.md): A comprehensive dataset by Google with 1.7M train images and 42k validation images.
|
||||
- [**SKU-110K**](sku-110k.md): A dataset containing images of densely packed retail products, intended for retail environment object detection.
|
||||
- [**VisDrone**](visdrone.md): A dataset focusing on drone-based images, containing various object categories like cars, pedestrians, and cyclists.
|
||||
- [**VOC**](voc.md): PASCAL VOC is a popular object detection dataset with 20 object categories including vehicles, animals, and furniture.
|
||||
- [**xView**](xview.md): A dataset containing high-resolution satellite imagery, designed for the detection of various object classes in overhead views.
|
||||
|
||||
### Adding your own dataset
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ To train a model using these OBB formats:
|
|||
|
||||
Currently, the following datasets with Oriented Bounding Boxes are supported:
|
||||
|
||||
- [**DOTA v2**](./dota-v2.md): DOTA (A Large-scale Dataset for Object Detection in Aerial Images) version 2, emphasizes detection from aerial perspectives and contains oriented bounding boxes with 1.7 million instances and 11,268 images.
|
||||
- [**DOTA v2**](dota-v2.md): DOTA (A Large-scale Dataset for Object Detection in Aerial Images) version 2, emphasizes detection from aerial perspectives and contains oriented bounding boxes with 1.7 million instances and 11,268 images.
|
||||
|
||||
### Incorporating your own OBB dataset
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -96,7 +96,7 @@ This section outlines the datasets that are compatible with Ultralytics YOLO for
|
|||
- **Keypoints**: 17 keypoints including nose, eyes, ears, shoulders, elbows, wrists, hips, knees, and ankles.
|
||||
- **Usage**: Suitable for training human pose estimation models.
|
||||
- **Additional Notes**: The dataset is rich and diverse, containing over 200k labeled images.
|
||||
- [Read more about COCO-Pose](./coco.md)
|
||||
- [Read more about COCO-Pose](coco.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### COCO8-Pose
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -106,7 +106,7 @@ This section outlines the datasets that are compatible with Ultralytics YOLO for
|
|||
- **Keypoints**: 17 keypoints including nose, eyes, ears, shoulders, elbows, wrists, hips, knees, and ankles.
|
||||
- **Usage**: Suitable for testing and debugging object detection models, or for experimenting with new detection approaches.
|
||||
- **Additional Notes**: COCO8-Pose is ideal for sanity checks and CI checks.
|
||||
- [Read more about COCO8-Pose](./coco8-pose.md)
|
||||
- [Read more about COCO8-Pose](coco8-pose.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Tiger-Pose
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -115,7 +115,7 @@ This section outlines the datasets that are compatible with Ultralytics YOLO for
|
|||
- **Number of Classes**: 1 (Tiger).
|
||||
- **Keypoints**: 12 keypoints.
|
||||
- **Usage**: Great for animal pose or any other pose that is not human-based.
|
||||
- [Read more about Tiger-Pose](./tiger-pose.md)
|
||||
- [Read more about Tiger-Pose](tiger-pose.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Adding your own dataset
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -143,6 +143,6 @@ Certainly, here is the table updated with code snippets:
|
|||
| `device` | `str, optional` | Device to run the models on. Defaults to an empty string (CPU or GPU, if available). | `''` |
|
||||
| `output_dir` | `str or None, optional` | Directory to save the annotated results. Defaults to a `'labels'` folder in the same directory as `'data'`. | `None` |
|
||||
|
||||
The `auto_annotate` function takes the path to your images, along with optional arguments for specifying the pre-trained detection and [SAM segmentation models](https://docs.ultralytics.com/models/sam), the device to run the models on, and the output directory for saving the annotated results.
|
||||
The `auto_annotate` function takes the path to your images, along with optional arguments for specifying the pre-trained detection and [SAM segmentation models](../../models/sam.md), the device to run the models on, and the output directory for saving the annotated results.
|
||||
|
||||
By leveraging the power of pre-trained models, auto-annotation can significantly reduce the time and effort required for creating high-quality segmentation datasets. This feature is particularly useful for researchers and developers working with large image collections, as it allows them to focus on model development and evaluation rather than manual annotation.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -262,21 +262,21 @@ ncnn is a high-performance neural network inference framework optimized for the
|
|||
|
||||
The following table provides a snapshot of the various deployment options available for YOLOv8 models, helping you to assess which may best fit your project needs based on several critical criteria. For an in-depth look at each deployment option's format, please see the [Ultralytics documentation page on export formats](https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/export/#export-formats).
|
||||
|
||||
| Deployment Option | Performance Benchmarks | Compatibility and Integration | Community Support and Ecosystem | Case Studies | Maintenance and Updates | Security Considerations | Hardware Acceleration |
|
||||
|--------------------|------------------------|-------------------------------|--------------------------------|--------------|------------------------|-------------------------|-----------------------|
|
||||
| PyTorch | Good flexibility; may trade off raw performance | Excellent with Python libraries | Extensive resources and community | Research and prototypes | Regular, active development | Dependent on deployment environment | CUDA support for GPU acceleration |
|
||||
| TorchScript | Better for production than PyTorch | Smooth transition from PyTorch to C++ | Specialized but narrower than PyTorch | Industry where Python is a bottleneck | Consistent updates with PyTorch | Improved security without full Python | Inherits CUDA support from PyTorch |
|
||||
| ONNX | Variable depending on runtime | High across different frameworks | Broad ecosystem, supported by many orgs | Flexibility across ML frameworks | Regular updates for new operations | Ensure secure conversion and deployment practices | Various hardware optimizations |
|
||||
| OpenVINO | Optimized for Intel hardware | Best within Intel ecosystem | Solid in computer vision domain | IoT and edge with Intel hardware | Regular updates for Intel hardware | Robust features for sensitive applications | Tailored for Intel hardware |
|
||||
| TensorRT | Top-tier on NVIDIA GPUs | Best for NVIDIA hardware | Strong network through NVIDIA | Real-time video and image inference | Frequent updates for new GPUs | Emphasis on security | Designed for NVIDIA GPUs |
|
||||
| CoreML | Optimized for on-device Apple hardware | Exclusive to Apple ecosystem | Strong Apple and developer support | On-device ML on Apple products | Regular Apple updates | Focus on privacy and security | Apple neural engine and GPU |
|
||||
| TF SavedModel | Scalable in server environments | Wide compatibility in TensorFlow ecosystem | Large support due to TensorFlow popularity | Serving models at scale | Regular updates by Google and community | Robust features for enterprise | Various hardware accelerations |
|
||||
| TF GraphDef | Stable for static computation graphs | Integrates well with TensorFlow infrastructure | Resources for optimizing static graphs | Scenarios requiring static graphs | Updates alongside TensorFlow core | Established TensorFlow security practices | TensorFlow acceleration options |
|
||||
| TF Lite | Speed and efficiency on mobile/embedded | Wide range of device support | Robust community, Google backed | Mobile applications with minimal footprint | Latest features for mobile | Secure environment on end-user devices | GPU and DSP among others |
|
||||
| TF Edge TPU | Optimized for Google's Edge TPU hardware | Exclusive to Edge TPU devices | Growing with Google and third-party resources | IoT devices requiring real-time processing | Improvements for new Edge TPU hardware | Google's robust IoT security | Custom-designed for Google Coral |
|
||||
| TF.js | Reasonable in-browser performance | High with web technologies | Web and Node.js developers support | Interactive web applications | TensorFlow team and community contributions | Web platform security model | Enhanced with WebGL and other APIs |
|
||||
| PaddlePaddle | Competitive, easy to use and scalable | Baidu ecosystem, wide application support | Rapidly growing, especially in China | Chinese market and language processing | Focus on Chinese AI applications | Emphasizes data privacy and security | Including Baidu's Kunlun chips |
|
||||
| ncnn | Optimized for mobile ARM-based devices | Mobile and embedded ARM systems | Niche but active mobile/embedded ML community | Android and ARM systems efficiency | High performance maintenance on ARM | On-device security advantages | ARM CPUs and GPUs optimizations |
|
||||
| Deployment Option | Performance Benchmarks | Compatibility and Integration | Community Support and Ecosystem | Case Studies | Maintenance and Updates | Security Considerations | Hardware Acceleration |
|
||||
|-------------------|-------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------|
|
||||
| PyTorch | Good flexibility; may trade off raw performance | Excellent with Python libraries | Extensive resources and community | Research and prototypes | Regular, active development | Dependent on deployment environment | CUDA support for GPU acceleration |
|
||||
| TorchScript | Better for production than PyTorch | Smooth transition from PyTorch to C++ | Specialized but narrower than PyTorch | Industry where Python is a bottleneck | Consistent updates with PyTorch | Improved security without full Python | Inherits CUDA support from PyTorch |
|
||||
| ONNX | Variable depending on runtime | High across different frameworks | Broad ecosystem, supported by many orgs | Flexibility across ML frameworks | Regular updates for new operations | Ensure secure conversion and deployment practices | Various hardware optimizations |
|
||||
| OpenVINO | Optimized for Intel hardware | Best within Intel ecosystem | Solid in computer vision domain | IoT and edge with Intel hardware | Regular updates for Intel hardware | Robust features for sensitive applications | Tailored for Intel hardware |
|
||||
| TensorRT | Top-tier on NVIDIA GPUs | Best for NVIDIA hardware | Strong network through NVIDIA | Real-time video and image inference | Frequent updates for new GPUs | Emphasis on security | Designed for NVIDIA GPUs |
|
||||
| CoreML | Optimized for on-device Apple hardware | Exclusive to Apple ecosystem | Strong Apple and developer support | On-device ML on Apple products | Regular Apple updates | Focus on privacy and security | Apple neural engine and GPU |
|
||||
| TF SavedModel | Scalable in server environments | Wide compatibility in TensorFlow ecosystem | Large support due to TensorFlow popularity | Serving models at scale | Regular updates by Google and community | Robust features for enterprise | Various hardware accelerations |
|
||||
| TF GraphDef | Stable for static computation graphs | Integrates well with TensorFlow infrastructure | Resources for optimizing static graphs | Scenarios requiring static graphs | Updates alongside TensorFlow core | Established TensorFlow security practices | TensorFlow acceleration options |
|
||||
| TF Lite | Speed and efficiency on mobile/embedded | Wide range of device support | Robust community, Google backed | Mobile applications with minimal footprint | Latest features for mobile | Secure environment on end-user devices | GPU and DSP among others |
|
||||
| TF Edge TPU | Optimized for Google's Edge TPU hardware | Exclusive to Edge TPU devices | Growing with Google and third-party resources | IoT devices requiring real-time processing | Improvements for new Edge TPU hardware | Google's robust IoT security | Custom-designed for Google Coral |
|
||||
| TF.js | Reasonable in-browser performance | High with web technologies | Web and Node.js developers support | Interactive web applications | TensorFlow team and community contributions | Web platform security model | Enhanced with WebGL and other APIs |
|
||||
| PaddlePaddle | Competitive, easy to use and scalable | Baidu ecosystem, wide application support | Rapidly growing, especially in China | Chinese market and language processing | Focus on Chinese AI applications | Emphasizes data privacy and security | Including Baidu's Kunlun chips |
|
||||
| ncnn | Optimized for mobile ARM-based devices | Mobile and embedded ARM systems | Niche but active mobile/embedded ML community | Android and ARM systems efficiency | High performance maintenance on ARM | On-device security advantages | ARM CPUs and GPUs optimizations |
|
||||
|
||||
This comparative analysis gives you a high-level overview. For deployment, it's essential to consider the specific requirements and constraints of your project, and consult the detailed documentation and resources available for each option.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ Welcome to the Ultralytics HUB App! We are excited to introduce this powerful mo
|
|||
|
||||
## App Documentation
|
||||
|
||||
- [**iOS**](./ios.md): Learn about YOLO CoreML models accelerated on Apple's Neural Engine for iPhones and iPads.
|
||||
- [**Android**](./android.md): Explore TFLite acceleration on Android mobile devices.
|
||||
- [**iOS**](ios.md): Learn about YOLO CoreML models accelerated on Apple's Neural Engine for iPhones and iPads.
|
||||
- [**Android**](android.md): Explore TFLite acceleration on Android mobile devices.
|
||||
|
||||
Get started today by downloading the Ultralytics HUB App on your mobile device and unlock the potential of YOLOv5 and YOLOv8 models on-the-go. Don't forget to check out our comprehensive [HUB Docs](../index.md) for more information on training, deploying, and using your custom models with the Ultralytics HUB platform.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -50,12 +50,12 @@ HUB is designed to be user-friendly and intuitive, with a drag-and-drop interfac
|
|||
|
||||
We hope that the resources here will help you get the most out of HUB. Please browse the HUB <a href="https://docs.ultralytics.com/hub">Docs</a> for details, raise an issue on <a href="https://github.com/ultralytics/hub/issues/new/choose">GitHub</a> for support, and join our <a href="https://ultralytics.com/discord">Discord</a> community for questions and discussions!
|
||||
|
||||
- [**Quickstart**](./quickstart.md). Start training and deploying YOLO models with HUB in seconds.
|
||||
- [**Datasets: Preparing and Uploading**](./datasets.md). Learn how to prepare and upload your datasets to HUB in YOLO format.
|
||||
- [**Projects: Creating and Managing**](./projects.md). Group your models into projects for improved organization.
|
||||
- [**Models: Training and Exporting**](./models.md). Train YOLOv5 and YOLOv8 models on your custom datasets and export them to various formats for deployment.
|
||||
- [**Integrations: Options**](./integrations.md). Explore different integration options for your trained models, such as TensorFlow, ONNX, OpenVINO, CoreML, and PaddlePaddle.
|
||||
- [**Ultralytics HUB App**](./app/index.md). Learn about the Ultralytics App for iOS and Android, which allows you to run models directly on your mobile device.
|
||||
* [**iOS**](./app/ios.md). Learn about YOLO CoreML models accelerated on Apple's Neural Engine on iPhones and iPads.
|
||||
* [**Android**](./app/android.md). Explore TFLite acceleration on mobile devices.
|
||||
- [**Inference API**](./inference_api.md). Understand how to use the Inference API for running your trained models in the cloud to generate predictions.
|
||||
- [**Quickstart**](quickstart.md). Start training and deploying YOLO models with HUB in seconds.
|
||||
- [**Datasets: Preparing and Uploading**](datasets.md). Learn how to prepare and upload your datasets to HUB in YOLO format.
|
||||
- [**Projects: Creating and Managing**](projects.md). Group your models into projects for improved organization.
|
||||
- [**Models: Training and Exporting**](models.md). Train YOLOv5 and YOLOv8 models on your custom datasets and export them to various formats for deployment.
|
||||
- [**Integrations: Options**](integrations.md). Explore different integration options for your trained models, such as TensorFlow, ONNX, OpenVINO, CoreML, and PaddlePaddle.
|
||||
- [**Ultralytics HUB App**](app/index.md). Learn about the Ultralytics App for iOS and Android, which allows you to run models directly on your mobile device.
|
||||
* [**iOS**](app/ios.md). Learn about YOLO CoreML models accelerated on Apple's Neural Engine on iPhones and iPads.
|
||||
* [**Android**](app/android.md). Explore TFLite acceleration on mobile devices.
|
||||
- [**Inference API**](inference_api.md). Understand how to use the Inference API for running your trained models in the cloud to generate predictions.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -128,7 +128,7 @@ You can also use our Ultralytics Cloud API to effortlessly [run inference](https
|
|||
|
||||
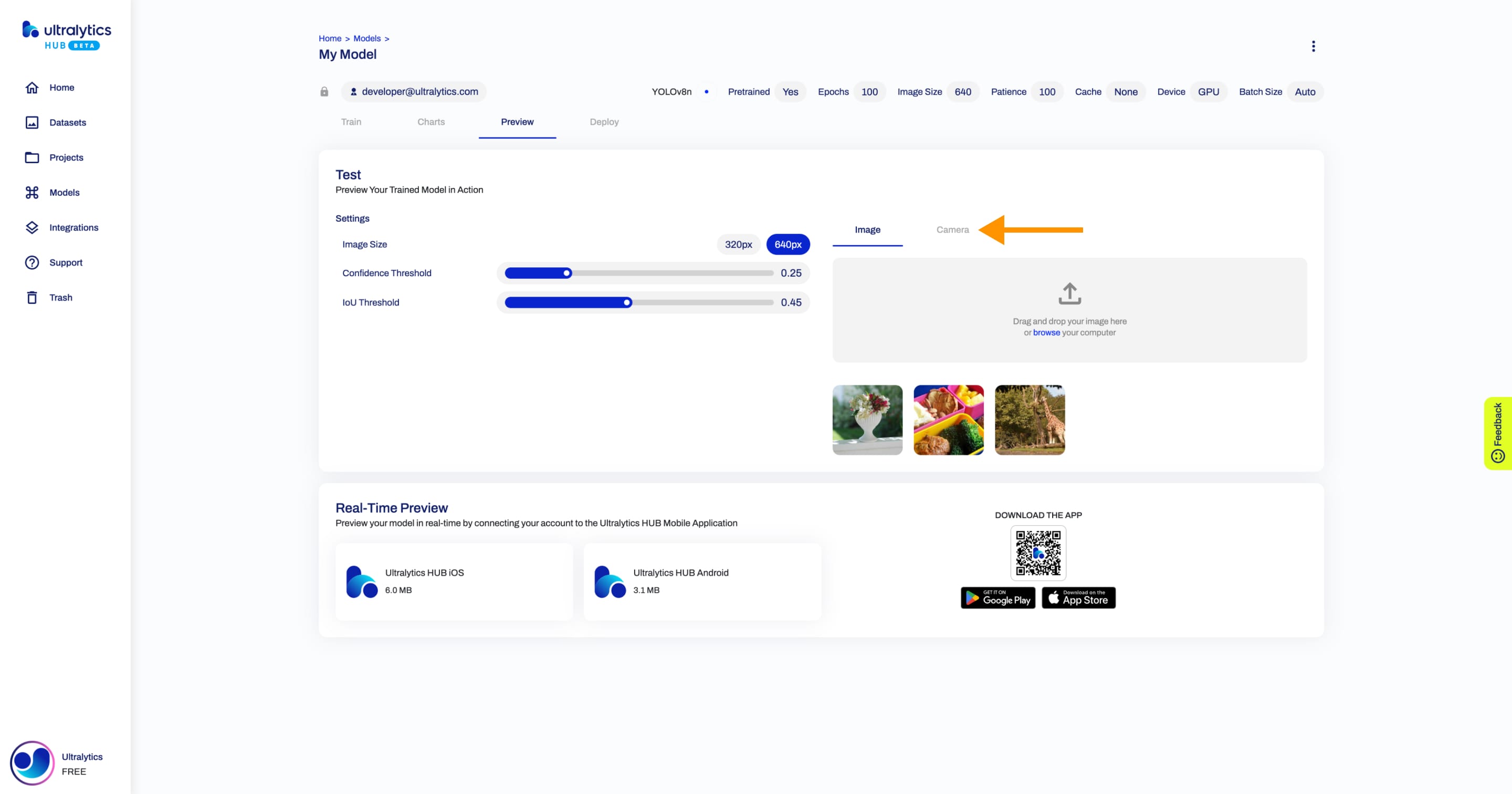
|
||||
|
||||
Furthermore, you can preview your model in real-time directly on your [iOS](https://apps.apple.com/xk/app/ultralytics/id1583935240) or [Android](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.ultralytics.ultralytics_app) mobile device by [downloading](https://ultralytics.com/app_install) our [Ultralytics HUB Mobile Application](./app/index.md).
|
||||
Furthermore, you can preview your model in real-time directly on your [iOS](https://apps.apple.com/xk/app/ultralytics/id1583935240) or [Android](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.ultralytics.ultralytics_app) mobile device by [downloading](https://ultralytics.com/app_install) our [Ultralytics HUB Mobile Application](app/index.md).
|
||||
|
||||
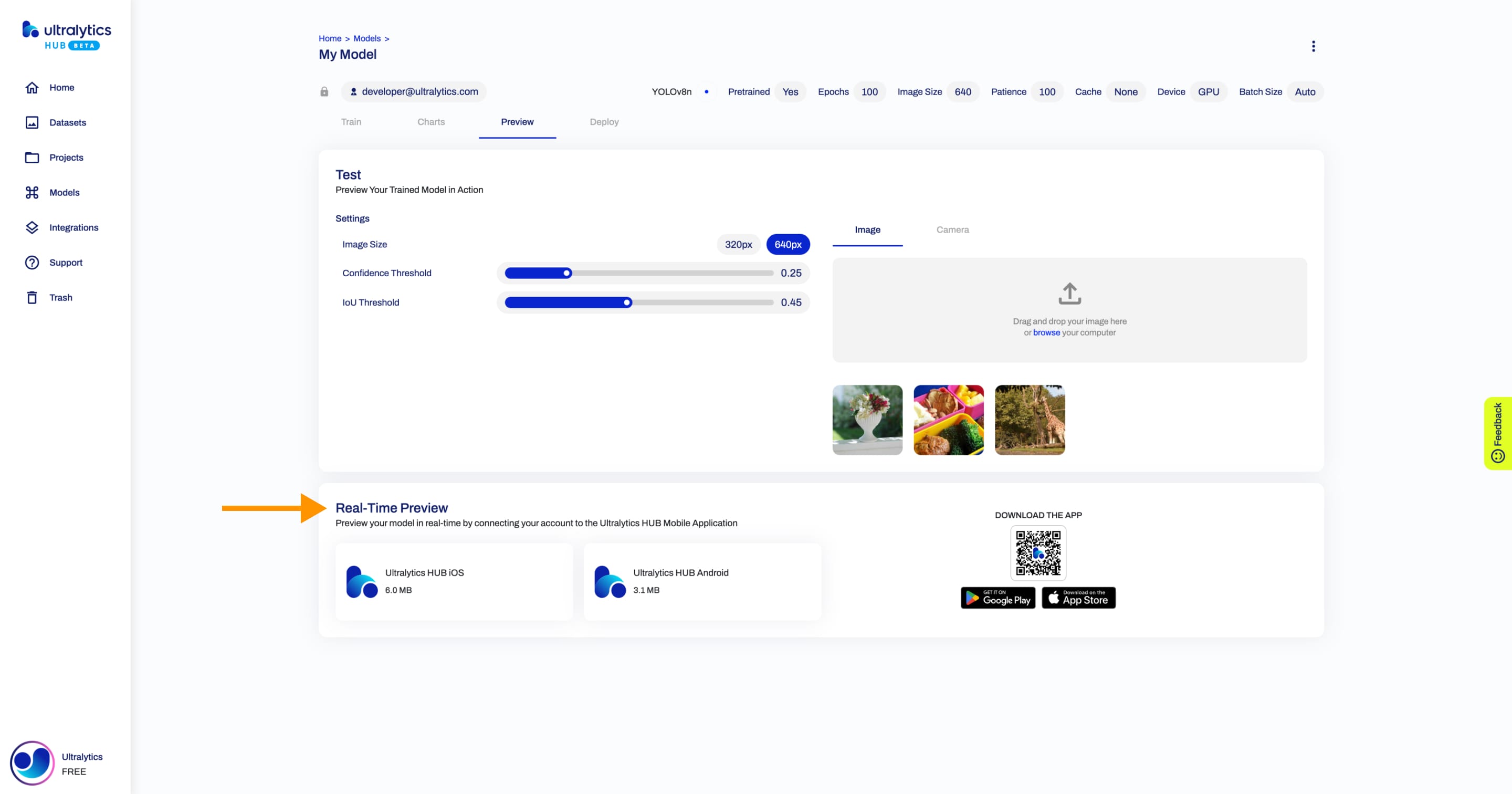
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -12,17 +12,17 @@ Welcome to Ultralytics' model documentation! We offer support for a wide range o
|
|||
|
||||
Here are some of the key models supported:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **[YOLOv3](./yolov3.md)**: The third iteration of the YOLO model family, originally by Joseph Redmon, known for its efficient real-time object detection capabilities.
|
||||
2. **[YOLOv4](./yolov4.md)**: A darknet-native update to YOLOv3, released by Alexey Bochkovskiy in 2020.
|
||||
3. **[YOLOv5](./yolov5.md)**: An improved version of the YOLO architecture by Ultralytics, offering better performance and speed trade-offs compared to previous versions.
|
||||
4. **[YOLOv6](./yolov6.md)**: Released by [Meituan](https://about.meituan.com/) in 2022, and in use in many of the company's autonomous delivery robots.
|
||||
5. **[YOLOv7](./yolov7.md)**: Updated YOLO models released in 2022 by the authors of YOLOv4.
|
||||
6. **[YOLOv8](./yolov8.md)**: The latest version of the YOLO family, featuring enhanced capabilities such as instance segmentation, pose/keypoints estimation, and classification.
|
||||
7. **[Segment Anything Model (SAM)](./sam.md)**: Meta's Segment Anything Model (SAM).
|
||||
8. **[Mobile Segment Anything Model (MobileSAM)](./mobile-sam.md)**: MobileSAM for mobile applications, by Kyung Hee University.
|
||||
9. **[Fast Segment Anything Model (FastSAM)](./fast-sam.md)**: FastSAM by Image & Video Analysis Group, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
|
||||
10. **[YOLO-NAS](./yolo-nas.md)**: YOLO Neural Architecture Search (NAS) Models.
|
||||
11. **[Realtime Detection Transformers (RT-DETR)](./rtdetr.md)**: Baidu's PaddlePaddle Realtime Detection Transformer (RT-DETR) models.
|
||||
1. **[YOLOv3](yolov3.md)**: The third iteration of the YOLO model family, originally by Joseph Redmon, known for its efficient real-time object detection capabilities.
|
||||
2. **[YOLOv4](yolov4.md)**: A darknet-native update to YOLOv3, released by Alexey Bochkovskiy in 2020.
|
||||
3. **[YOLOv5](yolov5.md)**: An improved version of the YOLO architecture by Ultralytics, offering better performance and speed trade-offs compared to previous versions.
|
||||
4. **[YOLOv6](yolov6.md)**: Released by [Meituan](https://about.meituan.com/) in 2022, and in use in many of the company's autonomous delivery robots.
|
||||
5. **[YOLOv7](yolov7.md)**: Updated YOLO models released in 2022 by the authors of YOLOv4.
|
||||
6. **[YOLOv8](yolov8.md)**: The latest version of the YOLO family, featuring enhanced capabilities such as instance segmentation, pose/keypoints estimation, and classification.
|
||||
7. **[Segment Anything Model (SAM)](sam.md)**: Meta's Segment Anything Model (SAM).
|
||||
8. **[Mobile Segment Anything Model (MobileSAM)](mobile-sam.md)**: MobileSAM for mobile applications, by Kyung Hee University.
|
||||
9. **[Fast Segment Anything Model (FastSAM)](fast-sam.md)**: FastSAM by Image & Video Analysis Group, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
|
||||
10. **[YOLO-NAS](yolo-nas.md)**: YOLO Neural Architecture Search (NAS) Models.
|
||||
11. **[Realtime Detection Transformers (RT-DETR)](rtdetr.md)**: Baidu's PaddlePaddle Realtime Detection Transformer (RT-DETR) models.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -89,7 +89,7 @@ You can download the model [here](https://github.com/ChaoningZhang/MobileSAM/blo
|
|||
model.predict('ultralytics/assets/zidane.jpg', bboxes=[439, 437, 524, 709])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We have implemented `MobileSAM` and `SAM` using the same API. For more usage information, please see the [SAM page](./sam.md).
|
||||
We have implemented `MobileSAM` and `SAM` using the same API. For more usage information, please see the [SAM page](sam.md).
|
||||
|
||||
## Citations and Acknowledgements
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ Welcome to the Ultralytics documentation page for YOLOv4, a state-of-the-art, re
|
|||
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
YOLOv4 stands for You Only Look Once version 4. It is a real-time object detection model developed to address the limitations of previous YOLO versions like [YOLOv3](./yolov3.md) and other object detection models. Unlike other convolutional neural network (CNN) based object detectors, YOLOv4 is not only applicable for recommendation systems but also for standalone process management and human input reduction. Its operation on conventional graphics processing units (GPUs) allows for mass usage at an affordable price, and it is designed to work in real-time on a conventional GPU while requiring only one such GPU for training.
|
||||
YOLOv4 stands for You Only Look Once version 4. It is a real-time object detection model developed to address the limitations of previous YOLO versions like [YOLOv3](yolov3.md) and other object detection models. Unlike other convolutional neural network (CNN) based object detectors, YOLOv4 is not only applicable for recommendation systems but also for standalone process management and human input reduction. Its operation on conventional graphics processing units (GPUs) allows for mass usage at an affordable price, and it is designed to work in real-time on a conventional GPU while requiring only one such GPU for training.
|
||||
|
||||
## Architecture
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ keywords: YOLOv5u, object detection, pre-trained models, Ultralytics, Inference,
|
|||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
YOLOv5u represents an advancement in object detection methodologies. Originating from the foundational architecture of the [YOLOv5](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5) model developed by Ultralytics, YOLOv5u integrates the anchor-free, objectness-free split head, a feature previously introduced in the [YOLOv8](./yolov8.md) models. This adaptation refines the model's architecture, leading to an improved accuracy-speed tradeoff in object detection tasks. Given the empirical results and its derived features, YOLOv5u provides an efficient alternative for those seeking robust solutions in both research and practical applications.
|
||||
YOLOv5u represents an advancement in object detection methodologies. Originating from the foundational architecture of the [YOLOv5](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5) model developed by Ultralytics, YOLOv5u integrates the anchor-free, objectness-free split head, a feature previously introduced in the [YOLOv8](yolov8.md) models. This adaptation refines the model's architecture, leading to an improved accuracy-speed tradeoff in object detection tasks. Given the empirical results and its derived features, YOLOv5u provides an efficient alternative for those seeking robust solutions in both research and practical applications.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,3 +1,10 @@
|
|||
User-agent: *
|
||||
Sitemap: http://docs.ultralytics.com/sitemap.xml
|
||||
Sitemap: http://docs.ultralytics.com/de/sitemap.xml
|
||||
Sitemap: http://docs.ultralytics.com/es/sitemap.xml
|
||||
Sitemap: http://docs.ultralytics.com/fr/sitemap.xml
|
||||
Sitemap: http://docs.ultralytics.com/ja/sitemap.xml
|
||||
Sitemap: http://docs.ultralytics.com/ko/sitemap.xml
|
||||
Sitemap: http://docs.ultralytics.com/pt/sitemap.xml
|
||||
Sitemap: http://docs.ultralytics.com/ru/sitemap.xml
|
||||
Sitemap: http://docs.ultralytics.com/zh/sitemap.xml
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ The YOLO command line interface (CLI) allows for simple single-line commands wit
|
|||
MODE (required) is one of [train, val, predict, export, track]
|
||||
ARGS (optional) are any number of custom 'arg=value' pairs like 'imgsz=320' that override defaults.
|
||||
```
|
||||
See all ARGS in the full [Configuration Guide](./cfg.md) or with `yolo cfg`
|
||||
See all ARGS in the full [Configuration Guide](cfg.md) or with `yolo cfg`
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Train"
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue