Add Docs glossary links (#16448)
Signed-off-by: UltralyticsAssistant <web@ultralytics.com> Co-authored-by: UltralyticsAssistant <web@ultralytics.com>
This commit is contained in:
parent
8b8c25f216
commit
443fbce194
193 changed files with 1124 additions and 1124 deletions
|
|
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ Unlike many other datasets, the Caltech-101 dataset is not formally split into t
|
|||
|
||||
## Applications
|
||||
|
||||
The Caltech-101 dataset is extensively used for training and evaluating deep learning models in object recognition tasks, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Support Vector Machines (SVMs), and various other machine learning algorithms. Its wide variety of categories and high-quality images make it an excellent dataset for research and development in the field of machine learning and computer vision.
|
||||
The Caltech-101 dataset is extensively used for training and evaluating [deep learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/deep-learning-dl) models in object recognition tasks, such as [Convolutional Neural Networks](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/convolutional-neural-network-cnn) (CNNs), Support Vector Machines (SVMs), and various other machine learning algorithms. Its wide variety of categories and high-quality images make it an excellent dataset for research and development in the field of machine learning and [computer vision](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/computer-vision-cv).
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -84,11 +84,11 @@ We would like to acknowledge Li Fei-Fei, Rob Fergus, and Pietro Perona for creat
|
|||
|
||||
### What is the Caltech-101 dataset used for in machine learning?
|
||||
|
||||
The [Caltech-101](https://data.caltech.edu/records/mzrjq-6wc02) dataset is widely used in machine learning for object recognition tasks. It contains around 9,000 images across 101 categories, providing a challenging benchmark for evaluating object recognition algorithms. Researchers leverage it to train and test models, especially Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Support Vector Machines (SVMs), in computer vision.
|
||||
The [Caltech-101](https://data.caltech.edu/records/mzrjq-6wc02) dataset is widely used in machine learning for object recognition tasks. It contains around 9,000 images across 101 categories, providing a challenging benchmark for evaluating object recognition algorithms. Researchers leverage it to train and test models, especially Convolutional [Neural Networks](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/neural-network-nn) (CNNs) and [Support Vector Machines](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/support-vector-machine-svm) (SVMs), in computer vision.
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I train an Ultralytics YOLO model on the Caltech-101 dataset?
|
||||
|
||||
To train an Ultralytics YOLO model on the Caltech-101 dataset, you can use the provided code snippets. For example, to train for 100 epochs:
|
||||
To train an Ultralytics YOLO model on the Caltech-101 dataset, you can use the provided code snippets. For example, to train for 100 [epochs](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/epoch):
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "Train Example"
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -122,7 +122,7 @@ The Caltech-101 dataset includes:
|
|||
- Variable number of images per category, typically between 40 and 800.
|
||||
- Variable image sizes, with most being medium resolution.
|
||||
|
||||
These features make it an excellent choice for training and evaluating object recognition models in machine learning and computer vision.
|
||||
These features make it an excellent choice for training and evaluating object recognition models in [machine learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/machine-learning-ml) and computer vision.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why should I cite the Caltech-101 dataset in my research?
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ The [Caltech-256](https://data.caltech.edu/records/nyy15-4j048) dataset is an ex
|
|||
allowfullscreen>
|
||||
</iframe>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<strong>Watch:</strong> How to Train Image Classification Model using Caltech-256 Dataset with Ultralytics HUB
|
||||
<strong>Watch:</strong> How to Train [Image Classification](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/image-classification) Model using Caltech-256 Dataset with Ultralytics HUB
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Features
|
||||
|
|
@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ Like Caltech-101, the Caltech-256 dataset does not have a formal split between t
|
|||
|
||||
## Applications
|
||||
|
||||
The Caltech-256 dataset is extensively used for training and evaluating deep learning models in object recognition tasks, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Support Vector Machines (SVMs), and various other machine learning algorithms. Its diverse set of categories and high-quality images make it an invaluable dataset for research and development in the field of machine learning and computer vision.
|
||||
The Caltech-256 dataset is extensively used for training and evaluating [deep learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/deep-learning-dl) models in object recognition tasks, such as [Convolutional Neural Networks](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/convolutional-neural-network-cnn) (CNNs), Support Vector Machines (SVMs), and various other machine learning algorithms. Its diverse set of categories and high-quality images make it an invaluable dataset for research and development in the field of machine learning and [computer vision](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/computer-vision-cv).
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -84,7 +84,7 @@ If you use the Caltech-256 dataset in your research or development work, please
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We would like to acknowledge Gregory Griffin, Alex Holub, and Pietro Perona for creating and maintaining the Caltech-256 dataset as a valuable resource for the machine learning and computer vision research community. For more information about the
|
||||
We would like to acknowledge Gregory Griffin, Alex Holub, and Pietro Perona for creating and maintaining the Caltech-256 dataset as a valuable resource for the [machine learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/machine-learning-ml) and computer vision research community. For more information about the
|
||||
|
||||
Caltech-256 dataset and its creators, visit the [Caltech-256 dataset website](https://data.caltech.edu/records/nyy15-4j048).
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -96,7 +96,7 @@ The [Caltech-256](https://data.caltech.edu/records/nyy15-4j048) dataset is a lar
|
|||
|
||||
### How can I train a YOLO model on the Caltech-256 dataset using Python or CLI?
|
||||
|
||||
To train a YOLO model on the Caltech-256 dataset for 100 epochs, you can use the following code snippets. Refer to the model [Training](../../modes/train.md) page for additional options.
|
||||
To train a YOLO model on the Caltech-256 dataset for 100 [epochs](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/epoch), you can use the following code snippets. Refer to the model [Training](../../modes/train.md) page for additional options.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "Train Example"
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -123,10 +123,10 @@ To train a YOLO model on the Caltech-256 dataset for 100 epochs, you can use the
|
|||
|
||||
The Caltech-256 dataset is widely used for various object recognition tasks such as:
|
||||
|
||||
- Training Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
|
||||
- Evaluating the performance of Support Vector Machines (SVMs)
|
||||
- Training Convolutional [Neural Networks](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/neural-network-nn) (CNNs)
|
||||
- Evaluating the performance of [Support Vector Machines](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/support-vector-machine-svm) (SVMs)
|
||||
- Benchmarking new deep learning algorithms
|
||||
- Developing object detection models using frameworks like Ultralytics YOLO
|
||||
- Developing [object detection](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/object-detection) models using frameworks like Ultralytics YOLO
|
||||
|
||||
Its diversity and comprehensive annotations make it ideal for research and development in machine learning and computer vision.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -141,6 +141,6 @@ Ultralytics YOLO models offer several advantages for training on the Caltech-256
|
|||
- **High Accuracy**: YOLO models are known for their state-of-the-art performance in object detection tasks.
|
||||
- **Speed**: They provide real-time inference capabilities, making them suitable for applications requiring quick predictions.
|
||||
- **Ease of Use**: With Ultralytics HUB, users can train, validate, and deploy models without extensive coding.
|
||||
- **Pretrained Models**: Starting from pretrained models, like `yolov8n-cls.pt`, can significantly reduce training time and improve model accuracy.
|
||||
- **Pretrained Models**: Starting from pretrained models, like `yolov8n-cls.pt`, can significantly reduce training time and improve model [accuracy](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/accuracy).
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, explore our [comprehensive training guide](../../modes/train.md).
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: CIFAR-10, dataset, machine learning, computer vision, image classifica
|
|||
|
||||
# CIFAR-10 Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
The [CIFAR-10](https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html) (Canadian Institute For Advanced Research) dataset is a collection of images used widely for machine learning and computer vision algorithms. It was developed by researchers at the CIFAR institute and consists of 60,000 32x32 color images in 10 different classes.
|
||||
The [CIFAR-10](https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html) (Canadian Institute For Advanced Research) dataset is a collection of images used widely for [machine learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/machine-learning-ml) and computer vision algorithms. It was developed by researchers at the CIFAR institute and consists of 60,000 32x32 color images in 10 different classes.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
|
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ The [CIFAR-10](https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html) (Canadian Institute
|
|||
allowfullscreen>
|
||||
</iframe>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<strong>Watch:</strong> How to Train an Image Classification Model with CIFAR-10 Dataset using Ultralytics YOLOv8
|
||||
<strong>Watch:</strong> How to Train an [Image Classification](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/image-classification) Model with CIFAR-10 Dataset using Ultralytics YOLOv8
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Features
|
||||
|
|
@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ The CIFAR-10 dataset is split into two subsets:
|
|||
|
||||
## Applications
|
||||
|
||||
The CIFAR-10 dataset is widely used for training and evaluating deep learning models in image classification tasks, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Support Vector Machines (SVMs), and various other machine learning algorithms. The diversity of the dataset in terms of classes and the presence of color images make it a well-rounded dataset for research and development in the field of machine learning and computer vision.
|
||||
The CIFAR-10 dataset is widely used for training and evaluating [deep learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/deep-learning-dl) models in image classification tasks, such as [Convolutional Neural Networks](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/convolutional-neural-network-cnn) (CNNs), Support Vector Machines (SVMs), and various other machine learning algorithms. The diversity of the dataset in terms of classes and the presence of color images make it a well-rounded dataset for research and development in the field of machine learning and computer vision.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -88,13 +88,13 @@ If you use the CIFAR-10 dataset in your research or development work, please cit
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We would like to acknowledge Alex Krizhevsky for creating and maintaining the CIFAR-10 dataset as a valuable resource for the machine learning and computer vision research community. For more information about the CIFAR-10 dataset and its creator, visit the [CIFAR-10 dataset website](https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html).
|
||||
We would like to acknowledge Alex Krizhevsky for creating and maintaining the CIFAR-10 dataset as a valuable resource for the machine learning and [computer vision](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/computer-vision-cv) research community. For more information about the CIFAR-10 dataset and its creator, visit the [CIFAR-10 dataset website](https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html).
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I train a YOLO model on the CIFAR-10 dataset?
|
||||
|
||||
To train a YOLO model on the CIFAR-10 dataset using Ultralytics, you can follow the examples provided for both Python and CLI. Here is a basic example to train your model for 100 epochs with an image size of 32x32 pixels:
|
||||
To train a YOLO model on the CIFAR-10 dataset using Ultralytics, you can follow the examples provided for both Python and CLI. Here is a basic example to train your model for 100 [epochs](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/epoch) with an image size of 32x32 pixels:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -138,7 +138,7 @@ This diverse dataset is essential for training image classification models in fi
|
|||
|
||||
### Why use the CIFAR-10 dataset for image classification tasks?
|
||||
|
||||
The CIFAR-10 dataset is an excellent benchmark for image classification due to its diversity and structure. It contains a balanced mix of 60,000 labeled images across 10 different categories, which helps in training robust and generalized models. It is widely used for evaluating deep learning models, including Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and other machine learning algorithms. The dataset is relatively small, making it suitable for quick experimentation and algorithm development. Explore its numerous applications in the [applications](#applications) section.
|
||||
The CIFAR-10 dataset is an excellent benchmark for image classification due to its diversity and structure. It contains a balanced mix of 60,000 labeled images across 10 different categories, which helps in training robust and generalized models. It is widely used for evaluating deep learning models, including Convolutional [Neural Networks](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/neural-network-nn) (CNNs) and other machine learning algorithms. The dataset is relatively small, making it suitable for quick experimentation and algorithm development. Explore its numerous applications in the [applications](#applications) section.
|
||||
|
||||
### How is the CIFAR-10 dataset structured?
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -170,4 +170,4 @@ Acknowledging the dataset's creators helps support continued research and develo
|
|||
|
||||
### What are some practical examples of using the CIFAR-10 dataset?
|
||||
|
||||
The CIFAR-10 dataset is often used for training image classification models, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Support Vector Machines (SVMs). These models can be employed in various computer vision tasks including object detection, image recognition, and automated tagging. To see some practical examples, check the code snippets in the [usage](#usage) section.
|
||||
The CIFAR-10 dataset is often used for training image classification models, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and [Support Vector Machines](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/support-vector-machine-svm) (SVMs). These models can be employed in various computer vision tasks including [object detection](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/object-detection), [image recognition](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/image-recognition), and automated tagging. To see some practical examples, check the code snippets in the [usage](#usage) section.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: CIFAR-100, dataset, machine learning, computer vision, image classific
|
|||
|
||||
# CIFAR-100 Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
The [CIFAR-100](https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html) (Canadian Institute For Advanced Research) dataset is a significant extension of the CIFAR-10 dataset, composed of 60,000 32x32 color images in 100 different classes. It was developed by researchers at the CIFAR institute, offering a more challenging dataset for more complex machine learning and computer vision tasks.
|
||||
The [CIFAR-100](https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html) (Canadian Institute For Advanced Research) dataset is a significant extension of the CIFAR-10 dataset, composed of 60,000 32x32 color images in 100 different classes. It was developed by researchers at the CIFAR institute, offering a more challenging dataset for more complex machine learning and [computer vision](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/computer-vision-cv) tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Features
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -25,11 +25,11 @@ The CIFAR-100 dataset is split into two subsets:
|
|||
|
||||
## Applications
|
||||
|
||||
The CIFAR-100 dataset is extensively used for training and evaluating deep learning models in image classification tasks, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Support Vector Machines (SVMs), and various other machine learning algorithms. The diversity of the dataset in terms of classes and the presence of color images make it a more challenging and comprehensive dataset for research and development in the field of machine learning and computer vision.
|
||||
The CIFAR-100 dataset is extensively used for training and evaluating deep learning models in image classification tasks, such as [Convolutional Neural Networks](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/convolutional-neural-network-cnn) (CNNs), Support Vector Machines (SVMs), and various other machine learning algorithms. The diversity of the dataset in terms of classes and the presence of color images make it a more challenging and comprehensive dataset for research and development in the field of machine learning and computer vision.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
To train a YOLO model on the CIFAR-100 dataset for 100 epochs with an image size of 32x32, you can use the following code snippets. For a comprehensive list of available arguments, refer to the model [Training](../../modes/train.md) page.
|
||||
To train a YOLO model on the CIFAR-100 dataset for 100 [epochs](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/epoch) with an image size of 32x32, you can use the following code snippets. For a comprehensive list of available arguments, refer to the model [Training](../../modes/train.md) page.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "Train Example"
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ To train a YOLO model on the CIFAR-100 dataset for 100 epochs with an image size
|
|||
|
||||
## Sample Images and Annotations
|
||||
|
||||
The CIFAR-100 dataset contains color images of various objects, providing a well-structured dataset for image classification tasks. Here are some examples of images from the dataset:
|
||||
The CIFAR-100 dataset contains color images of various objects, providing a well-structured dataset for [image classification](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/image-classification) tasks. Here are some examples of images from the dataset:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -77,13 +77,13 @@ If you use the CIFAR-100 dataset in your research or development work, please ci
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We would like to acknowledge Alex Krizhevsky for creating and maintaining the CIFAR-100 dataset as a valuable resource for the machine learning and computer vision research community. For more information about the CIFAR-100 dataset and its creator, visit the [CIFAR-100 dataset website](https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html).
|
||||
We would like to acknowledge Alex Krizhevsky for creating and maintaining the CIFAR-100 dataset as a valuable resource for the [machine learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/machine-learning-ml) and computer vision research community. For more information about the CIFAR-100 dataset and its creator, visit the [CIFAR-100 dataset website](https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html).
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
### What is the CIFAR-100 dataset and why is it significant?
|
||||
|
||||
The [CIFAR-100 dataset](https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html) is a large collection of 60,000 32x32 color images classified into 100 classes. Developed by the Canadian Institute For Advanced Research (CIFAR), it provides a challenging dataset ideal for complex machine learning and computer vision tasks. Its significance lies in the diversity of classes and the small size of the images, making it a valuable resource for training and testing deep learning models, like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), using frameworks such as Ultralytics YOLO.
|
||||
The [CIFAR-100 dataset](https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html) is a large collection of 60,000 32x32 color images classified into 100 classes. Developed by the Canadian Institute For Advanced Research (CIFAR), it provides a challenging dataset ideal for complex machine learning and computer vision tasks. Its significance lies in the diversity of classes and the small size of the images, making it a valuable resource for training and testing deep learning models, like Convolutional [Neural Networks](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/neural-network-nn) (CNNs), using frameworks such as Ultralytics YOLO.
|
||||
|
||||
### How do I train a YOLO model on the CIFAR-100 dataset?
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -114,7 +114,7 @@ For a comprehensive list of available arguments, please refer to the model [Trai
|
|||
|
||||
### What are the primary applications of the CIFAR-100 dataset?
|
||||
|
||||
The CIFAR-100 dataset is extensively used in training and evaluating deep learning models for image classification. Its diverse set of 100 classes, grouped into 20 coarse categories, provides a challenging environment for testing algorithms such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Support Vector Machines (SVMs), and various other machine learning approaches. This dataset is a key resource in research and development within machine learning and computer vision fields.
|
||||
The CIFAR-100 dataset is extensively used in training and evaluating [deep learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/deep-learning-dl) models for image classification. Its diverse set of 100 classes, grouped into 20 coarse categories, provides a challenging environment for testing algorithms such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), [Support Vector Machines](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/support-vector-machine-svm) (SVMs), and various other machine learning approaches. This dataset is a key resource in research and development within machine learning and computer vision fields.
|
||||
|
||||
### How is the CIFAR-100 dataset structured?
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: Fashion-MNIST, image classification, Zalando dataset, machine learning
|
|||
|
||||
# Fashion-MNIST Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
The [Fashion-MNIST](https://github.com/zalandoresearch/fashion-mnist) dataset is a database of Zalando's article images—consisting of a training set of 60,000 examples and a test set of 10,000 examples. Each example is a 28x28 grayscale image, associated with a label from 10 classes. Fashion-MNIST is intended to serve as a direct drop-in replacement for the original MNIST dataset for benchmarking machine learning algorithms.
|
||||
The [Fashion-MNIST](https://github.com/zalandoresearch/fashion-mnist) dataset is a database of Zalando's article images—consisting of a training set of 60,000 examples and a test set of 10,000 examples. Each example is a 28x28 grayscale image, associated with a label from 10 classes. Fashion-MNIST is intended to serve as a direct drop-in replacement for the original MNIST dataset for benchmarking [machine learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/machine-learning-ml) algorithms.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
|
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ The [Fashion-MNIST](https://github.com/zalandoresearch/fashion-mnist) dataset is
|
|||
allowfullscreen>
|
||||
</iframe>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<strong>Watch:</strong> How to do Image Classification on Fashion MNIST Dataset using Ultralytics YOLOv8
|
||||
<strong>Watch:</strong> How to do [Image Classification](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/image-classification) on Fashion MNIST Dataset using Ultralytics YOLOv8
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Features
|
||||
|
|
@ -50,11 +50,11 @@ Each training and test example is assigned to one of the following labels:
|
|||
|
||||
## Applications
|
||||
|
||||
The Fashion-MNIST dataset is widely used for training and evaluating deep learning models in image classification tasks, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Support Vector Machines (SVMs), and various other machine learning algorithms. The dataset's simple and well-structured format makes it an essential resource for researchers and practitioners in the field of machine learning and computer vision.
|
||||
The Fashion-MNIST dataset is widely used for training and evaluating deep learning models in image classification tasks, such as [Convolutional Neural Networks](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/convolutional-neural-network-cnn) (CNNs), [Support Vector Machines](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/support-vector-machine-svm) (SVMs), and various other machine learning algorithms. The dataset's simple and well-structured format makes it an essential resource for researchers and practitioners in the field of machine learning and computer vision.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
To train a CNN model on the Fashion-MNIST dataset for 100 epochs with an image size of 28x28, you can use the following code snippets. For a comprehensive list of available arguments, refer to the model [Training](../../modes/train.md) page.
|
||||
To train a CNN model on the Fashion-MNIST dataset for 100 [epochs](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/epoch) with an image size of 28x28, you can use the following code snippets. For a comprehensive list of available arguments, refer to the model [Training](../../modes/train.md) page.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "Train Example"
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -124,7 +124,7 @@ For more detailed training parameters, refer to the [Training page](../../modes/
|
|||
|
||||
### Why should I use the Fashion-MNIST dataset for benchmarking my machine learning models?
|
||||
|
||||
The [Fashion-MNIST](https://github.com/zalandoresearch/fashion-mnist) dataset is widely recognized in the deep learning community as a robust alternative to MNIST. It offers a more complex and varied set of images, making it an excellent choice for benchmarking image classification models. The dataset's structure, comprising 60,000 training images and 10,000 testing images, each labeled with one of 10 classes, makes it ideal for evaluating the performance of different machine learning algorithms in a more challenging context.
|
||||
The [Fashion-MNIST](https://github.com/zalandoresearch/fashion-mnist) dataset is widely recognized in the [deep learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/deep-learning-dl) community as a robust alternative to MNIST. It offers a more complex and varied set of images, making it an excellent choice for benchmarking image classification models. The dataset's structure, comprising 60,000 training images and 10,000 testing images, each labeled with one of 10 classes, makes it ideal for evaluating the performance of different machine learning algorithms in a more challenging context.
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I use Ultralytics YOLO for image classification tasks like Fashion-MNIST?
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -132,7 +132,7 @@ Yes, Ultralytics YOLO models can be used for image classification tasks, includi
|
|||
|
||||
### What are the key features and structure of the Fashion-MNIST dataset?
|
||||
|
||||
The Fashion-MNIST dataset is divided into two main subsets: 60,000 training images and 10,000 testing images. Each image is a 28x28-pixel grayscale picture representing one of 10 fashion-related classes. The simplicity and well-structured format make it ideal for training and evaluating models in machine learning and computer vision tasks. For more details on the dataset structure, see the [Dataset Structure section](#dataset-structure).
|
||||
The Fashion-MNIST dataset is divided into two main subsets: 60,000 training images and 10,000 testing images. Each image is a 28x28-pixel grayscale picture representing one of 10 fashion-related classes. The simplicity and well-structured format make it ideal for training and evaluating models in machine learning and [computer vision](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/computer-vision-cv) tasks. For more details on the dataset structure, see the [Dataset Structure section](#dataset-structure).
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I acknowledge the use of the Fashion-MNIST dataset in my research?
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: ImageNet, deep learning, visual recognition, computer vision, pretrain
|
|||
|
||||
# ImageNet Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
[ImageNet](https://www.image-net.org/) is a large-scale database of annotated images designed for use in visual object recognition research. It contains over 14 million images, with each image annotated using WordNet synsets, making it one of the most extensive resources available for training deep learning models in computer vision tasks.
|
||||
[ImageNet](https://www.image-net.org/) is a large-scale database of annotated images designed for use in visual object recognition research. It contains over 14 million images, with each image annotated using WordNet synsets, making it one of the most extensive resources available for training [deep learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/deep-learning-dl) models in [computer vision](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/computer-vision-cv) tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
## ImageNet Pretrained Models
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ keywords: ImageNet, deep learning, visual recognition, computer vision, pretrain
|
|||
|
||||
- ImageNet contains over 14 million high-resolution images spanning thousands of object categories.
|
||||
- The dataset is organized according to the WordNet hierarchy, with each synset representing a category.
|
||||
- ImageNet is widely used for training and benchmarking in the field of computer vision, particularly for image classification and object detection tasks.
|
||||
- ImageNet is widely used for training and benchmarking in the field of computer vision, particularly for [image classification](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/image-classification) and [object detection](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/object-detection) tasks.
|
||||
- The annual ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC) has been instrumental in advancing computer vision research.
|
||||
|
||||
## Dataset Structure
|
||||
|
|
@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ The ImageNet dataset is widely used for training and evaluating deep learning mo
|
|||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
To train a deep learning model on the ImageNet dataset for 100 epochs with an image size of 224x224, you can use the following code snippets. For a comprehensive list of available arguments, refer to the model [Training](../../modes/train.md) page.
|
||||
To train a deep learning model on the ImageNet dataset for 100 [epochs](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/epoch) with an image size of 224x224, you can use the following code snippets. For a comprehensive list of available arguments, refer to the model [Training](../../modes/train.md) page.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "Train Example"
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -90,7 +90,7 @@ If you use the ImageNet dataset in your research or development work, please cit
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We would like to acknowledge the ImageNet team, led by Olga Russakovsky, Jia Deng, and Li Fei-Fei, for creating and maintaining the ImageNet dataset as a valuable resource for the machine learning and computer vision research community. For more information about the ImageNet dataset and its creators, visit the [ImageNet website](https://www.image-net.org/).
|
||||
We would like to acknowledge the ImageNet team, led by Olga Russakovsky, Jia Deng, and Li Fei-Fei, for creating and maintaining the ImageNet dataset as a valuable resource for the [machine learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/machine-learning-ml) and computer vision research community. For more information about the ImageNet dataset and its creators, visit the [ImageNet website](https://www.image-net.org/).
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -127,7 +127,7 @@ For more in-depth training instruction, refer to our [Training page](../../modes
|
|||
|
||||
### Why should I use the Ultralytics YOLOv8 pretrained models for my ImageNet dataset projects?
|
||||
|
||||
Ultralytics YOLOv8 pretrained models offer state-of-the-art performance in terms of speed and accuracy for various computer vision tasks. For example, the YOLOv8n-cls model, with a top-1 accuracy of 69.0% and a top-5 accuracy of 88.3%, is optimized for real-time applications. Pretrained models reduce the computational resources required for training from scratch and accelerate development cycles. Learn more about the performance metrics of YOLOv8 models in the [ImageNet Pretrained Models section](#imagenet-pretrained-models).
|
||||
Ultralytics YOLOv8 pretrained models offer state-of-the-art performance in terms of speed and [accuracy](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/accuracy) for various computer vision tasks. For example, the YOLOv8n-cls model, with a top-1 accuracy of 69.0% and a top-5 accuracy of 88.3%, is optimized for real-time applications. Pretrained models reduce the computational resources required for training from scratch and accelerate development cycles. Learn more about the performance metrics of YOLOv8 models in the [ImageNet Pretrained Models section](#imagenet-pretrained-models).
|
||||
|
||||
### How is the ImageNet dataset structured, and why is it important?
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -135,4 +135,4 @@ The ImageNet dataset is organized using the WordNet hierarchy, where each node i
|
|||
|
||||
### What role does the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC) play in computer vision?
|
||||
|
||||
The annual [ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC)](https://image-net.org/challenges/LSVRC/) has been pivotal in driving advancements in computer vision by providing a competitive platform for evaluating algorithms on a large-scale, standardized dataset. It offers standardized evaluation metrics, fostering innovation and development in areas such as image classification, object detection, and image segmentation. The challenge has continuously pushed the boundaries of what is possible with deep learning and computer vision technologies.
|
||||
The annual [ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC)](https://image-net.org/challenges/LSVRC/) has been pivotal in driving advancements in computer vision by providing a competitive platform for evaluating algorithms on a large-scale, standardized dataset. It offers standardized evaluation metrics, fostering innovation and development in areas such as image classification, object detection, and [image segmentation](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/image-segmentation). The challenge has continuously pushed the boundaries of what is possible with deep learning and computer vision technologies.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ The [ImageNet10](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v0.0.0/
|
|||
|
||||
- ImageNet10 is a compact version of ImageNet, with 20 images representing the first 10 classes of the original dataset.
|
||||
- The dataset is organized according to the WordNet hierarchy, mirroring the structure of the full ImageNet dataset.
|
||||
- It is ideally suited for CI tests, sanity checks, and rapid testing of training pipelines in computer vision tasks.
|
||||
- It is ideally suited for CI tests, sanity checks, and rapid testing of training pipelines in [computer vision](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/computer-vision-cv) tasks.
|
||||
- Although not designed for model benchmarking, it can provide a quick indication of a model's basic functionality and correctness.
|
||||
|
||||
## Dataset Structure
|
||||
|
|
@ -74,7 +74,7 @@ If you use the ImageNet10 dataset in your research or development work, please c
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We would like to acknowledge the ImageNet team, led by Olga Russakovsky, Jia Deng, and Li Fei-Fei, for creating and maintaining the ImageNet dataset. The ImageNet10 dataset, while a compact subset, is a valuable resource for quick testing and debugging in the machine learning and computer vision research community. For more information about the ImageNet dataset and its creators, visit the [ImageNet website](https://www.image-net.org/).
|
||||
We would like to acknowledge the ImageNet team, led by Olga Russakovsky, Jia Deng, and Li Fei-Fei, for creating and maintaining the ImageNet dataset. The ImageNet10 dataset, while a compact subset, is a valuable resource for quick testing and debugging in the [machine learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/machine-learning-ml) and computer vision research community. For more information about the ImageNet dataset and its creators, visit the [ImageNet website](https://www.image-net.org/).
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -111,7 +111,7 @@ Refer to the [Training](../../modes/train.md) page for a comprehensive list of a
|
|||
|
||||
### Why should I use the ImageNet10 dataset for CI tests and sanity checks?
|
||||
|
||||
The ImageNet10 dataset is designed specifically for CI tests, sanity checks, and quick evaluations in deep learning pipelines. Its small size allows for rapid iteration and testing, making it perfect for continuous integration processes where speed is crucial. By maintaining the structural complexity and diversity of the original ImageNet dataset, ImageNet10 provides a reliable indication of a model's basic functionality and correctness without the overhead of processing a large dataset.
|
||||
The ImageNet10 dataset is designed specifically for CI tests, sanity checks, and quick evaluations in [deep learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/deep-learning-dl) pipelines. Its small size allows for rapid iteration and testing, making it perfect for continuous integration processes where speed is crucial. By maintaining the structural complexity and diversity of the original ImageNet dataset, ImageNet10 provides a reliable indication of a model's basic functionality and correctness without the overhead of processing a large dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
### What are the main features of the ImageNet10 dataset?
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ The ImageNette dataset is split into two subsets:
|
|||
|
||||
## Applications
|
||||
|
||||
The ImageNette dataset is widely used for training and evaluating deep learning models in image classification tasks, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), and various other machine learning algorithms. The dataset's straightforward format and well-chosen classes make it a handy resource for both beginner and experienced practitioners in the field of machine learning and computer vision.
|
||||
The ImageNette dataset is widely used for training and evaluating [deep learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/deep-learning-dl) models in image classification tasks, such as [Convolutional Neural Networks](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/convolutional-neural-network-cnn) (CNNs), and various other machine learning algorithms. The dataset's straightforward format and well-chosen classes make it a handy resource for both beginner and experienced practitioners in the field of machine learning and computer vision.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -52,7 +52,7 @@ To train a model on the ImageNette dataset for 100 epochs with a standard image
|
|||
|
||||
## Sample Images and Annotations
|
||||
|
||||
The ImageNette dataset contains colored images of various objects and scenes, providing a diverse dataset for image classification tasks. Here are some examples of images from the dataset:
|
||||
The ImageNette dataset contains colored images of various objects and scenes, providing a diverse dataset for [image classification](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/image-classification) tasks. Here are some examples of images from the dataset:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -116,11 +116,11 @@ If you use the ImageNette dataset in your research or development work, please a
|
|||
|
||||
### What is the ImageNette dataset?
|
||||
|
||||
The [ImageNette dataset](https://github.com/fastai/imagenette) is a simplified subset of the larger [ImageNet dataset](https://www.image-net.org/), featuring only 10 easily distinguishable classes such as tench, English springer, and French horn. It was created to offer a more manageable dataset for efficient training and evaluation of image classification models. This dataset is particularly useful for quick software development and educational purposes in machine learning and computer vision.
|
||||
The [ImageNette dataset](https://github.com/fastai/imagenette) is a simplified subset of the larger [ImageNet dataset](https://www.image-net.org/), featuring only 10 easily distinguishable classes such as tench, English springer, and French horn. It was created to offer a more manageable dataset for efficient training and evaluation of image classification models. This dataset is particularly useful for quick software development and educational purposes in [machine learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/machine-learning-ml) and computer vision.
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I use the ImageNette dataset for training a YOLO model?
|
||||
|
||||
To train a YOLO model on the ImageNette dataset for 100 epochs, you can use the following commands. Make sure to have the Ultralytics YOLO environment set up.
|
||||
To train a YOLO model on the ImageNette dataset for 100 [epochs](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/epoch), you can use the following commands. Make sure to have the Ultralytics YOLO environment set up.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "Train Example"
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -186,8 +186,8 @@ For more information, refer to [Training with ImageNette160 and ImageNette320](#
|
|||
|
||||
The ImageNette dataset is extensively used in:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Educational Settings**: To educate beginners in machine learning and computer vision.
|
||||
- **Educational Settings**: To educate beginners in machine learning and [computer vision](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/computer-vision-cv).
|
||||
- **Software Development**: For rapid prototyping and development of image classification models.
|
||||
- **Deep Learning Research**: To evaluate and benchmark the performance of various deep learning models, especially Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs).
|
||||
- **Deep Learning Research**: To evaluate and benchmark the performance of various deep learning models, especially Convolutional [Neural Networks](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/neural-network-nn) (CNNs).
|
||||
|
||||
Explore the [Applications](#applications) section for detailed use cases.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: ImageWoof dataset, ImageNet subset, dog breeds, image classification,
|
|||
|
||||
# ImageWoof Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
The [ImageWoof](https://github.com/fastai/imagenette) dataset is a subset of the ImageNet consisting of 10 classes that are challenging to classify, since they're all dog breeds. It was created as a more difficult task for image classification algorithms to solve, aiming at encouraging development of more advanced models.
|
||||
The [ImageWoof](https://github.com/fastai/imagenette) dataset is a subset of the ImageNet consisting of 10 classes that are challenging to classify, since they're all dog breeds. It was created as a more difficult task for [image classification](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/image-classification) algorithms to solve, aiming at encouraging development of more advanced models.
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Features
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ The ImageWoof dataset is widely used for training and evaluating deep learning m
|
|||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
To train a CNN model on the ImageWoof dataset for 100 epochs with an image size of 224x224, you can use the following code snippets. For a comprehensive list of available arguments, refer to the model [Training](../../modes/train.md) page.
|
||||
To train a CNN model on the ImageWoof dataset for 100 [epochs](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/epoch) with an image size of 224x224, you can use the following code snippets. For a comprehensive list of available arguments, refer to the model [Training](../../modes/train.md) page.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "Train Example"
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -97,7 +97,7 @@ The example showcases the subtle differences and similarities among the differen
|
|||
|
||||
If you use the ImageWoof dataset in your research or development work, please make sure to acknowledge the creators of the dataset by linking to the [official dataset repository](https://github.com/fastai/imagenette).
|
||||
|
||||
We would like to acknowledge the FastAI team for creating and maintaining the ImageWoof dataset as a valuable resource for the machine learning and computer vision research community. For more information about the ImageWoof dataset, visit the [ImageWoof dataset repository](https://github.com/fastai/imagenette).
|
||||
We would like to acknowledge the FastAI team for creating and maintaining the ImageWoof dataset as a valuable resource for the [machine learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/machine-learning-ml) and [computer vision](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/computer-vision-cv) research community. For more information about the ImageWoof dataset, visit the [ImageWoof dataset repository](https://github.com/fastai/imagenette).
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -107,7 +107,7 @@ The [ImageWoof](https://github.com/fastai/imagenette) dataset is a challenging s
|
|||
|
||||
### How can I train a model using the ImageWoof dataset with Ultralytics YOLO?
|
||||
|
||||
To train a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model on the ImageWoof dataset using Ultralytics YOLO for 100 epochs at an image size of 224x224, you can use the following code:
|
||||
To train a [Convolutional Neural Network](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/convolutional-neural-network-cnn) (CNN) model on the ImageWoof dataset using Ultralytics YOLO for 100 epochs at an image size of 224x224, you can use the following code:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "Train Example"
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -137,7 +137,7 @@ The ImageWoof dataset comes in three sizes:
|
|||
2. **Medium Size (imagewoof320)**: Resized images with a maximum edge length of 320 pixels, suited for faster training.
|
||||
3. **Small Size (imagewoof160)**: Resized images with a maximum edge length of 160 pixels, perfect for rapid prototyping.
|
||||
|
||||
Use these versions by replacing 'imagewoof' in the dataset argument accordingly. Note, however, that smaller images may yield lower classification accuracy but can be useful for quicker iterations.
|
||||
Use these versions by replacing 'imagewoof' in the dataset argument accordingly. Note, however, that smaller images may yield lower classification [accuracy](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/accuracy) but can be useful for quicker iterations.
|
||||
|
||||
### How do noisy labels in the ImageWoof dataset benefit training?
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -145,4 +145,4 @@ Noisy labels in the ImageWoof dataset simulate real-world conditions where label
|
|||
|
||||
### What are the key challenges of using the ImageWoof dataset?
|
||||
|
||||
The primary challenge of the ImageWoof dataset lies in the subtle differences among the dog breeds it includes. Since it focuses on 10 closely related breeds, distinguishing between them requires more advanced and fine-tuned image classification models. This makes ImageWoof an excellent benchmark to test the capabilities and improvements of deep learning models.
|
||||
The primary challenge of the ImageWoof dataset lies in the subtle differences among the dog breeds it includes. Since it focuses on 10 closely related breeds, distinguishing between them requires more advanced and fine-tuned image classification models. This makes ImageWoof an excellent benchmark to test the capabilities and improvements of [deep learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/deep-learning-dl) models.
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -103,12 +103,12 @@ This structured approach ensures that the model can effectively learn from well-
|
|||
|
||||
Ultralytics supports the following datasets with automatic download:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Caltech 101](caltech101.md): A dataset containing images of 101 object categories for image classification tasks.
|
||||
- [Caltech 101](caltech101.md): A dataset containing images of 101 object categories for [image classification](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/image-classification) tasks.
|
||||
- [Caltech 256](caltech256.md): An extended version of Caltech 101 with 256 object categories and more challenging images.
|
||||
- [CIFAR-10](cifar10.md): A dataset of 60K 32x32 color images in 10 classes, with 6K images per class.
|
||||
- [CIFAR-100](cifar100.md): An extended version of CIFAR-10 with 100 object categories and 600 images per class.
|
||||
- [Fashion-MNIST](fashion-mnist.md): A dataset consisting of 70,000 grayscale images of 10 fashion categories for image classification tasks.
|
||||
- [ImageNet](imagenet.md): A large-scale dataset for object detection and image classification with over 14 million images and 20,000 categories.
|
||||
- [ImageNet](imagenet.md): A large-scale dataset for [object detection](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/object-detection) and image classification with over 14 million images and 20,000 categories.
|
||||
- [ImageNet-10](imagenet10.md): A smaller subset of ImageNet with 10 categories for faster experimentation and testing.
|
||||
- [Imagenette](imagenette.md): A smaller subset of ImageNet that contains 10 easily distinguishable classes for quicker training and testing.
|
||||
- [Imagewoof](imagewoof.md): A more challenging subset of ImageNet containing 10 dog breed categories for image classification tasks.
|
||||
|
|
@ -184,7 +184,7 @@ Ultralytics YOLO offers several benefits for image classification, including:
|
|||
|
||||
- **Pretrained Models**: Load pretrained models like `yolov8n-cls.pt` to jump-start your training process.
|
||||
- **Ease of Use**: Simple API and CLI commands for training and evaluation.
|
||||
- **High Performance**: State-of-the-art accuracy and speed, ideal for real-time applications.
|
||||
- **High Performance**: State-of-the-art [accuracy](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/accuracy) and speed, ideal for real-time applications.
|
||||
- **Support for Multiple Datasets**: Seamless integration with various popular datasets like CIFAR-10, ImageNet, and more.
|
||||
- **Community and Support**: Access to extensive documentation and an active community for troubleshooting and improvements.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ The [MNIST](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/) (Modified National Institute of S
|
|||
|
||||
- MNIST contains 60,000 training images and 10,000 testing images of handwritten digits.
|
||||
- The dataset comprises grayscale images of size 28x28 pixels.
|
||||
- The images are normalized to fit into a 28x28 pixel bounding box and anti-aliased, introducing grayscale levels.
|
||||
- The images are normalized to fit into a 28x28 pixel [bounding box](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/bounding-box) and anti-aliased, introducing grayscale levels.
|
||||
- MNIST is widely used for training and testing in the field of machine learning, especially for image classification tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
## Dataset Structure
|
||||
|
|
@ -28,11 +28,11 @@ Extended MNIST (EMNIST) is a newer dataset developed and released by NIST to be
|
|||
|
||||
## Applications
|
||||
|
||||
The MNIST dataset is widely used for training and evaluating deep learning models in image classification tasks, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Support Vector Machines (SVMs), and various other machine learning algorithms. The dataset's simple and well-structured format makes it an essential resource for researchers and practitioners in the field of machine learning and computer vision.
|
||||
The MNIST dataset is widely used for training and evaluating [deep learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/deep-learning-dl) models in image classification tasks, such as [Convolutional Neural Networks](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/convolutional-neural-network-cnn) (CNNs), [Support Vector Machines](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/support-vector-machine-svm) (SVMs), and various other machine learning algorithms. The dataset's simple and well-structured format makes it an essential resource for researchers and practitioners in the field of machine learning and computer vision.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
To train a CNN model on the MNIST dataset for 100 epochs with an image size of 32x32, you can use the following code snippets. For a comprehensive list of available arguments, refer to the model [Training](../../modes/train.md) page.
|
||||
To train a CNN model on the MNIST dataset for 100 [epochs](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/epoch) with an image size of 32x32, you can use the following code snippets. For a comprehensive list of available arguments, refer to the model [Training](../../modes/train.md) page.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "Train Example"
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ To train a CNN model on the MNIST dataset for 100 epochs with an image size of 3
|
|||
|
||||
## Sample Images and Annotations
|
||||
|
||||
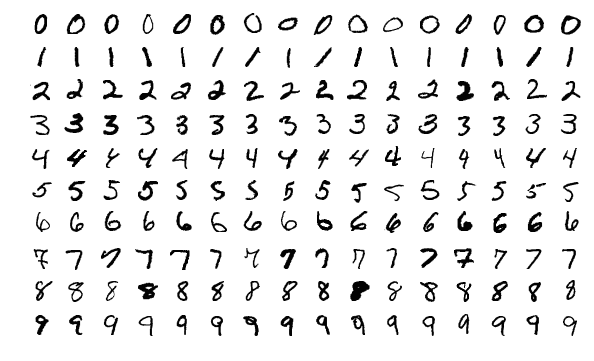
The MNIST dataset contains grayscale images of handwritten digits, providing a well-structured dataset for image classification tasks. Here are some examples of images from the dataset:
|
||||
The MNIST dataset contains grayscale images of handwritten digits, providing a well-structured dataset for [image classification](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/image-classification) tasks. Here are some examples of images from the dataset:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -83,7 +83,7 @@ research or development work, please cite the following paper:
|
|||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We would like to acknowledge Yann LeCun, Corinna Cortes, and Christopher J.C. Burges for creating and maintaining the MNIST dataset as a valuable resource for the machine learning and computer vision research community. For more information about the MNIST dataset and its creators, visit the [MNIST dataset website](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/).
|
||||
We would like to acknowledge Yann LeCun, Corinna Cortes, and Christopher J.C. Burges for creating and maintaining the MNIST dataset as a valuable resource for the [machine learning](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/machine-learning-ml) and [computer vision](https://www.ultralytics.com/glossary/computer-vision-cv) research community. For more information about the MNIST dataset and its creators, visit the [MNIST dataset website](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/).
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue