 -For a full list of augmentation hyperparameters used in YOLOv8 please refer to the [configurations page](../usage/cfg.md#augmentation).
+For a full list of augmentation hyperparameters used in YOLOv8 please refer to the [configurations page](../usage/cfg.md#augmentation-settings).
### Genetic Evolution and Mutation
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/instance-segmentation-and-tracking.md b/docs/en/guides/instance-segmentation-and-tracking.md
index ac31ac87..558ab57d 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/instance-segmentation-and-tracking.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/instance-segmentation-and-tracking.md
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
---
comments: true
description: Instance Segmentation with Object Tracking using Ultralytics YOLOv8
-keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv8, Instance Segmentation, Object Detection, Object Tracking, Segbbox, Computer Vision, Notebook, IPython Kernel, CLI, Python SDK
+keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv8, Instance Segmentation, Object Detection, Object Tracking, Bounding Box, Computer Vision, Notebook, IPython Kernel, CLI, Python SDK
---
# Instance Segmentation and Tracking using Ultralytics YOLOv8 🚀
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/isolating-segmentation-objects.md b/docs/en/guides/isolating-segmentation-objects.md
index 79d47692..f8e9a7a6 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/isolating-segmentation-objects.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/isolating-segmentation-objects.md
@@ -14,12 +14,12 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
## Recipe Walk Through
-1. Begin with the necessary imports
+1. Begin with the necessary imports
- ```py
+ ```python
from pathlib import Path
- import cv2 as cv
+ import cv2
import numpy as np
from ultralytics import YOLO
```
@@ -30,19 +30,19 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
***
-2. Load a model and run `predict()` method on a source.
+2. Load a model and run `predict()` method on a source.
- ```py
+ ```python
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a model
model = YOLO('yolov8n-seg.pt')
# Run inference
- result = model.predict()
+ results = model.predict()
```
- ??? question "No Prediction Arguments?"
+ !!! question "No Prediction Arguments?"
Without specifying a source, the example images from the library will be used:
@@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
***
-3. Now iterate over the results and the contours. For workflows that want to save an image to file, the source image `base-name` and the detection `class-label` are retrieved for later use (optional).
+3. Now iterate over the results and the contours. For workflows that want to save an image to file, the source image `base-name` and the detection `class-label` are retrieved for later use (optional).
```{ .py .annotate }
# (2) Iterate detection results (helpful for multiple images)
@@ -81,7 +81,7 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
***
-4. Start with generating a binary mask from the source image and then draw a filled contour onto the mask. This will allow the object to be isolated from the other parts of the image. An example from `bus.jpg` for one of the detected `person` class objects is shown on the right.
+4. Start with generating a binary mask from the source image and then draw a filled contour onto the mask. This will allow the object to be isolated from the other parts of the image. An example from `bus.jpg` for one of the detected `person` class objects is shown on the right.
{ width="240", align="right" }
@@ -98,11 +98,11 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
# Draw contour onto mask
- _ = cv.drawContours(b_mask,
+ _ = cv2.drawContours(b_mask,
[contour],
-1,
(255, 255, 255),
- cv.FILLED)
+ cv2.FILLED)
```
@@ -136,7 +136,7 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
- The `tuple` `(255, 255, 255)` represents the color white, which is the desired color for drawing the contour in this binary mask.
- - The addition of `cv.FILLED` will color all pixels enclosed by the contour boundary the same, in this case, all enclosed pixels will be white.
+ - The addition of `cv2.FILLED` will color all pixels enclosed by the contour boundary the same, in this case, all enclosed pixels will be white.
- See [OpenCV Documentation on `drawContours()`](https://docs.opencv.org/4.8.0/d6/d6e/group__imgproc__draw.html#ga746c0625f1781f1ffc9056259103edbc) for more information.
@@ -145,7 +145,7 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
***
-5. Next the there are 2 options for how to move forward with the image from this point and a subsequent option for each.
+5. Next the there are 2 options for how to move forward with the image from this point and a subsequent option for each.
### Object Isolation Options
@@ -155,10 +155,10 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
```py
# Create 3-channel mask
- mask3ch = cv.cvtColor(b_mask, cv.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
+ mask3ch = cv2.cvtColor(b_mask, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
# Isolate object with binary mask
- isolated = cv.bitwise_and(mask3ch, img)
+ isolated = cv2.bitwise_and(mask3ch, img)
```
@@ -258,7 +258,7 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
***
-6. What to do next is entirely left to you as the developer. A basic example of one possible next step (saving the image to file for future use) is shown.
+6. What to do next is entirely left to you as the developer. A basic example of one possible next step (saving the image to file for future use) is shown.
- **NOTE:** this step is optional and can be skipped if not required for your specific use case.
@@ -266,7 +266,7 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
```py
# Save isolated object to file
- _ = cv.imwrite(f'{img_name}_{label}-{ci}.png', iso_crop)
+ _ = cv2.imwrite(f'{img_name}_{label}-{ci}.png', iso_crop)
```
- In this example, the `img_name` is the base-name of the source image file, `label` is the detected class-name, and `ci` is the index of the object detection (in case of multiple instances with the same class name).
@@ -278,7 +278,7 @@ Here, all steps from the previous section are combined into a single block of co
```{ .py .annotate }
from pathlib import Path
-import cv2 as cv
+import cv2
import numpy as np
from ultralytics import YOLO
@@ -298,13 +298,13 @@ for r in res:
# Create contour mask (1)
contour = c.masks.xy.pop().astype(np.int32).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
- _ = cv.drawContours(b_mask, [contour], -1, (255, 255, 255), cv.FILLED)
+ _ = cv2.drawContours(b_mask, [contour], -1, (255, 255, 255), cv2.FILLED)
# Choose one:
# OPTION-1: Isolate object with black background
- mask3ch = cv.cvtColor(b_mask, cv.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
- isolated = cv.bitwise_and(mask3ch, img)
+ mask3ch = cv2.cvtColor(b_mask, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
+ isolated = cv2.bitwise_and(mask3ch, img)
# OPTION-2: Isolate object with transparent background (when saved as PNG)
isolated = np.dstack([img, b_mask])
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md b/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md
index 67728e96..c00fbe19 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md
@@ -175,8 +175,8 @@ Object counting with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|-----------------------|-------------|----------------------------|-----------------------------------------------|
| `view_img` | `bool` | `False` | Display frames with counts |
-| `view_in_counts` | `bool` | `True` | Display incounts only on video frame |
-| `view_out_counts` | `bool` | `True` | Display outcounts only on video frame |
+| `view_in_counts` | `bool` | `True` | Display in-counts only on video frame |
+| `view_out_counts` | `bool` | `True` | Display out-counts only on video frame |
| `line_thickness` | `int` | `2` | Increase bounding boxes thickness |
| `reg_pts` | `list` | `[(20, 400), (1260, 400)]` | Points defining the Region Area |
| `classes_names` | `dict` | `model.model.names` | Dictionary of Class Names |
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md b/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md
index 126d3df2..240230a8 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md
@@ -16,7 +16,6 @@ Object cropping with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly
- **Reduced Data Volume**: By extracting only relevant objects, object cropping helps in minimizing data size, making it efficient for storage, transmission, or subsequent computational tasks.
- **Enhanced Precision**: YOLOv8's object detection accuracy ensures that the cropped objects maintain their spatial relationships, preserving the integrity of the visual information for detailed analysis.
-
## Visuals
| Airport Luggage |
@@ -24,7 +23,6 @@ Object cropping with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly
| 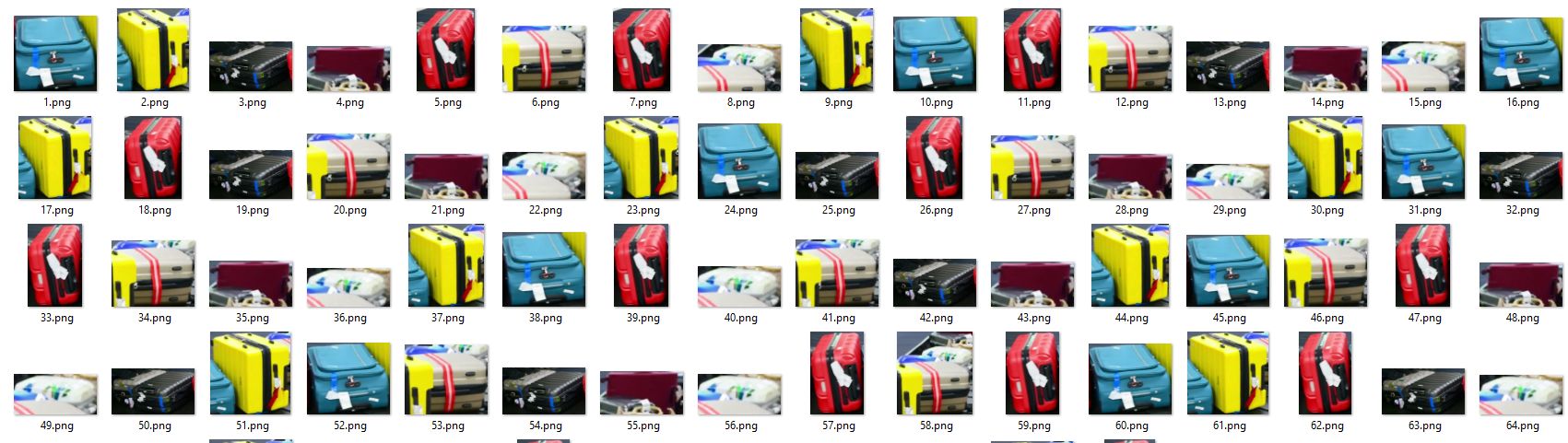 |
| Suitcases Cropping at airport conveyor belt using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
-
!!! Example "Object Cropping using YOLOv8 Example"
=== "Object Cropping"
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/workouts-monitoring.md b/docs/en/guides/workouts-monitoring.md
index b2297803..fd4d7e0f 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/workouts-monitoring.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/workouts-monitoring.md
@@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ Monitoring workouts through pose estimation with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://gi
- **Optimized Performance:** Tailoring workouts based on monitoring data for better results.
- **Goal Achievement:** Track and adjust fitness goals for measurable progress.
- **Personalization:** Customized workout plans based on individual data for effectiveness.
-- **Health Awareness:** Early detection of patterns indicating health issues or overtraining.
+- **Health Awareness:** Early detection of patterns indicating health issues or over-training.
- **Informed Decisions:** Data-driven decisions for adjusting routines and setting realistic goals.
## Real World Applications
@@ -109,7 +109,7 @@ Monitoring workouts through pose estimation with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://gi
| `kpts_to_check` | `list` | `None` | List of three keypoints index, for counting specific workout, followed by keypoint Map |
| `view_img` | `bool` | `False` | Display the frame with counts |
| `line_thickness` | `int` | `2` | Increase the thickness of count value |
-| `pose_type` | `str` | `pushup` | Pose that need to be monitored, "pullup" and "abworkout" also supported |
+| `pose_type` | `str` | `pushup` | Pose that need to be monitored, `pullup` and `abworkout` also supported |
| `pose_up_angle` | `int` | `145` | Pose Up Angle value |
| `pose_down_angle` | `int` | `90` | Pose Down Angle value |
diff --git a/docs/en/hub/cloud-training.md b/docs/en/hub/cloud-training.md
index 91178ea2..f774475a 100644
--- a/docs/en/hub/cloud-training.md
+++ b/docs/en/hub/cloud-training.md
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, HUB Models, AI model training, model creation, model trai
# Cloud Training
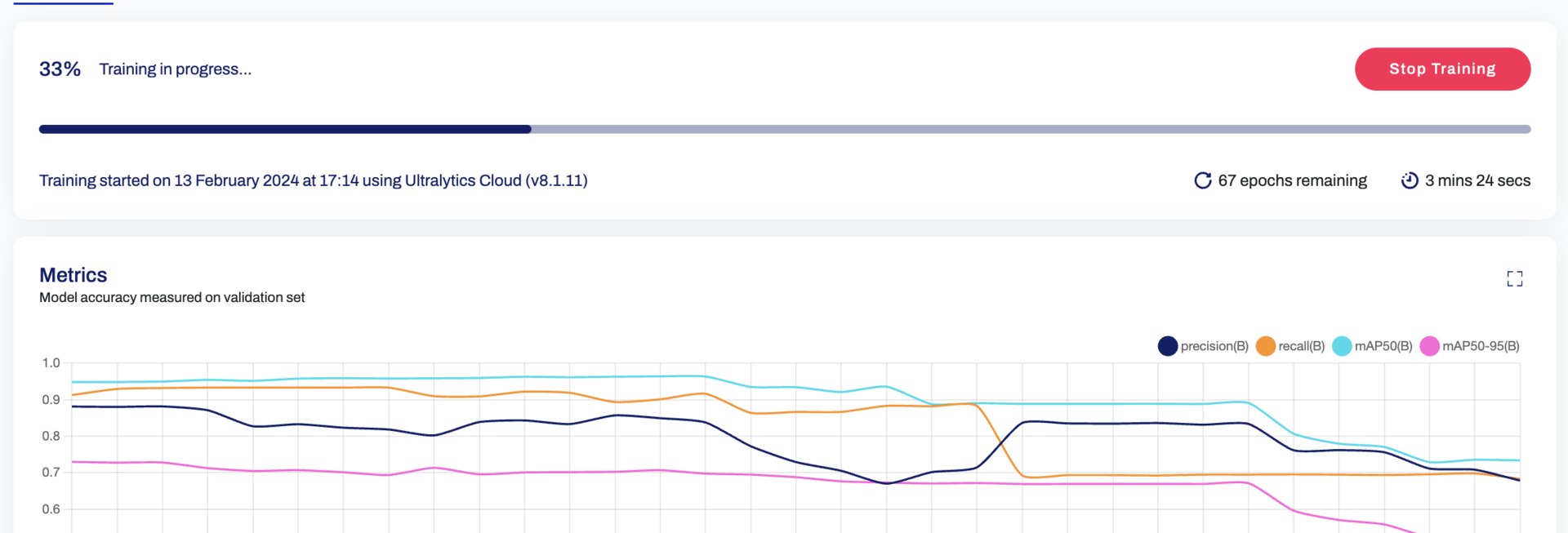
-[Ultralytics HUB](https://hub.ultralytics.com/) provides a powerful and user-friendly cloud platform to train custom object detection models. Easily select your dataset and the desired training method, then kick off the process with just a few clicks. Ultralytics HUB offers pre-built options and various model architectures to streamline your workflow.
+[Ultralytics HUB](https://hub.ultralytics.com/) provides a powerful and user-friendly cloud platform to train custom object detection models. Easily select your dataset and the desired training method, then kick off the process with just a few clicks. Ultralytics HUB offers pre-built options and various model architectures to streamline your workflow.
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/amazon-sagemaker.md b/docs/en/integrations/amazon-sagemaker.md
index 55fd4c76..f57fc2ee 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/amazon-sagemaker.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/amazon-sagemaker.md
@@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ First, ensure you have the following prerequisites in place:
- AWS CDK: If not already installed, install the AWS Cloud Development Kit (CDK), which will be used for scripting the deployment. Follow [the AWS CDK instructions](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cdk/v2/guide/getting_started.html#getting_started_install) for installation.
-- Adequate Service Quota: Confirm that you have sufficient quotas for two separate resources in Amazon SageMaker: one for ml.m5.4xlarge for endpoint usage and another for ml.m5.4xlarge for notebook instance usage. Each of these requires a minimum of one quota value. If your current quotas are below this requirement, it's important to request an increase for each. You can request a quota increase by following the detailed instructions in the [AWS Service Quotas documentation](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/servicequotas/latest/userguide/request-quota-increase.html#quota-console-increase).
+- Adequate Service Quota: Confirm that you have sufficient quotas for two separate resources in Amazon SageMaker: one for `ml.m5.4xlarge` for endpoint usage and another for `ml.m5.4xlarge` for notebook instance usage. Each of these requires a minimum of one quota value. If your current quotas are below this requirement, it's important to request an increase for each. You can request a quota increase by following the detailed instructions in the [AWS Service Quotas documentation](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/servicequotas/latest/userguide/request-quota-increase.html#quota-console-increase).
### Step 2: Clone the YOLOv8 SageMaker Repository
@@ -115,17 +115,21 @@ After creating the AWS CloudFormation Stack, the next step is to deploy YOLOv8.
- Access and Modify inference.py: After opening the SageMaker notebook instance in Jupyter, locate the inference.py file. Edit the output_fn function in inference.py as shown below and save your changes to the script, ensuring that there are no syntax errors.
```python
+import json
+
def output_fn(prediction_output, content_type):
print("Executing output_fn from inference.py ...")
infer = {}
for result in prediction_output:
- if 'boxes' in result._keys and result.boxes is not None:
+ if result.boxes is not None:
infer['boxes'] = result.boxes.numpy().data.tolist()
- if 'masks' in result._keys and result.masks is not None:
+ if result.masks is not None:
infer['masks'] = result.masks.numpy().data.tolist()
- if 'keypoints' in result._keys and result.keypoints is not None:
+ if result.keypoints is not None:
infer['keypoints'] = result.keypoints.numpy().data.tolist()
- if 'probs' in result._keys and result.probs is not None:
+ if result.obb is not None:
+ infer['obb'] = result.obb.numpy().data.tolist()
+ if result.probs is not None:
infer['probs'] = result.probs.numpy().data.tolist()
return json.dumps(infer)
```
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/coreml.md b/docs/en/integrations/coreml.md
index cbcff691..5533da57 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/coreml.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/coreml.md
@@ -18,9 +18,10 @@ The CoreML export format allows you to optimize your [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https:
[CoreML](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/coreml) is Apple's foundational machine learning framework that builds upon Accelerate, BNNS, and Metal Performance Shaders. It provides a machine-learning model format that seamlessly integrates into iOS applications and supports tasks such as image analysis, natural language processing, audio-to-text conversion, and sound analysis.
-Applications can take advantage of Core ML without the need to have a network connection or API calls because the Core ML framework works using on-device computing. This means model inferencing can be performed locally on the user's device.
+Applications can take advantage of Core ML without the need to have a network connection or API calls because the Core ML framework works using on-device computing. This means model inference can be performed locally on the user's device.
## Key Features of CoreML Models
+
Apple's CoreML framework offers robust features for on-device machine learning. Here are the key features that make CoreML a powerful tool for developers:
- **Comprehensive Model Support**: Converts and runs models from popular frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, scikit-learn, XGBoost, and LibSVM.
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/index.md b/docs/en/integrations/index.md
index b52f3db9..77a723dc 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/index.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/index.md
@@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ Welcome to the Ultralytics Integrations page! This page provides an overview of
- [CoreML](coreml.md): CoreML, developed by [Apple](https://www.apple.com/), is a framework designed for efficiently integrating machine learning models into applications across iOS, macOS, watchOS, and tvOS, using Apple's hardware for effective and secure model deployment.
- [TFLite](tflite.md): Developed by [Google](https://www.google.com), TFLite is a lightweight framework for deploying machine learning models on mobile and edge devices, ensuring fast, efficient inference with minimal memory footprint.
-
+
- [NCNN](ncnn.md): Developed by [Tencent](http://www.tencent.com/), NCNN is an efficient neural network inference framework tailored for mobile devices. It enables direct deployment of AI models into apps, optimizing performance across various mobile platforms.
### Export Formats
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/ncnn.md b/docs/en/integrations/ncnn.md
index eadc9813..835f8fcd 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/ncnn.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/ncnn.md
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv8, NCNN Export, Export YOLOv8, Model Deployment
# How to Export to NCNN from YOLOv8 for Smooth Deployment
-Deploying computer vision models on devices with limited computational power, such as mobile or embedded systems, can be tricky. You need to make sure you use a format optimized for optimal performance. This makes sure that even devices with limited processing power can handle advanced computer vision tasks well.
+Deploying computer vision models on devices with limited computational power, such as mobile or embedded systems, can be tricky. You need to make sure you use a format optimized for optimal performance. This makes sure that even devices with limited processing power can handle advanced computer vision tasks well.
The export to NCNN format feature allows you to optimize your [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) models for lightweight device-based applications. In this guide, we'll walk you through how to convert your models to the NCNN format, making it easier for your models to perform well on various mobile and embedded devices.
@@ -18,19 +18,19 @@ The export to NCNN format feature allows you to optimize your [Ultralytics YOLOv
The [NCNN](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) framework, developed by Tencent, is a high-performance neural network inference computing framework optimized specifically for mobile platforms, including mobile phones, embedded devices, and IoT devices. NCNN is compatible with a wide range of platforms, including Linux, Android, iOS, and macOS.
-NCNN is known for its fast processing speed on mobile CPUs and enables rapid deployment of deep learning models to mobile platforms. This makes it easier to build smart apps, putting the power of AI right at your fingertips.
+NCNN is known for its fast processing speed on mobile CPUs and enables rapid deployment of deep learning models to mobile platforms. This makes it easier to build smart apps, putting the power of AI right at your fingertips.
## Key Features of NCNN Models
NCNN models offer a wide range of key features that enable on-device machine learning by helping developers run their models on mobile, embedded, and edge devices:
- - **Efficient and High-Performance**: NCNN models are made to be efficient and lightweight, optimized for running on mobile and embedded devices like Raspberry Pi with limited resources. They can also achieve high performance with high accuracy on various computer vision-based tasks.
+- **Efficient and High-Performance**: NCNN models are made to be efficient and lightweight, optimized for running on mobile and embedded devices like Raspberry Pi with limited resources. They can also achieve high performance with high accuracy on various computer vision-based tasks.
- - **Quantization**: NCNN models often support quantization which is a technique that reduces the precision of the model's weights and activations. This leads to further improvements in performance and reduces memory footprint.
+- **Quantization**: NCNN models often support quantization which is a technique that reduces the precision of the model's weights and activations. This leads to further improvements in performance and reduces memory footprint.
- - **Compatibility**: NCNN models are compatible with popular deep learning frameworks like [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/), [Caffe](https://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/), and [ONNX](https://onnx.ai/). This compatibility allows developers to use existing models and workflows easily.
+- **Compatibility**: NCNN models are compatible with popular deep learning frameworks like [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/), [Caffe](https://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/), and [ONNX](https://onnx.ai/). This compatibility allows developers to use existing models and workflows easily.
- - **Easy to Use**: NCNN models are designed for easy integration into various applications, thanks to their compatibility with popular deep learning frameworks. Additionally, NCNN offers user-friendly tools for converting models between different formats, ensuring smooth interoperability across the development landscape.
+- **Easy to Use**: NCNN models are designed for easy integration into various applications, thanks to their compatibility with popular deep learning frameworks. Additionally, NCNN offers user-friendly tools for converting models between different formats, ensuring smooth interoperability across the development landscape.
## Deployment Options with NCNN
@@ -65,7 +65,7 @@ For detailed instructions and best practices related to the installation process
### Usage
-Before diving into the usage instructions, it's important to note that while all [Ultralytics YOLOv8 models]((../models/index.md)) are available for exporting, you can ensure that the model you select supports export functionality [here](../modes/export.md).
+Before diving into the usage instructions, it's important to note that while all [Ultralytics YOLOv8 models](../models/index.md) are available for exporting, you can ensure that the model you select supports export functionality [here](../modes/export.md).
!!! Example "Usage"
@@ -103,13 +103,13 @@ For more details about supported export options, visit the [Ultralytics document
After successfully exporting your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to NCNN format, you can now deploy them. The primary and recommended first step for running a NCNN model is to utilize the YOLO("./model_ncnn_model") method, as outlined in the previous usage code snippet. However, for in-depth instructions on deploying your NCNN models in various other settings, take a look at the following resources:
-- **[Android](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/wiki/how-to-build#build-for-android)**: This blog explains how to use NCNN models for performing tasks like object detection through Android applications.
+- **[Android](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/wiki/how-to-build#build-for-android)**: This blog explains how to use NCNN models for performing tasks like object detection through Android applications.
- - **[macOS](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/wiki/how-to-build#build-for-macos)**: Understand how to use NCNN models for performing tasks through macOS.
+- **[macOS](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/wiki/how-to-build#build-for-macos)**: Understand how to use NCNN models for performing tasks through macOS.
- - **[Linux](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/wiki/how-to-build#build-for-linux)**: Explore this page to learn how to deploy NCNN models on limited resource devices like Raspberry Pi and other similar devices.
+- **[Linux](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/wiki/how-to-build#build-for-linux)**: Explore this page to learn how to deploy NCNN models on limited resource devices like Raspberry Pi and other similar devices.
- - **[Windows x64 using VS2017](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/wiki/how-to-build#build-for-windows-x64-using-visual-studio-community-2017)**: Explore this blog to learn how to deploy NCNN models on windows x64 using Visual Studio Community 2017.
+- **[Windows x64 using VS2017](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/wiki/how-to-build#build-for-windows-x64-using-visual-studio-community-2017)**: Explore this blog to learn how to deploy NCNN models on windows x64 using Visual Studio Community 2017.
## Summary
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/neural-magic.md b/docs/en/integrations/neural-magic.md
index 90e90dbe..53910972 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/neural-magic.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/neural-magic.md
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: YOLOv8, DeepSparse Engine, Ultralytics, CPU Inference, Neural Network
# Optimizing YOLOv8 Inferences with Neural Magic’s DeepSparse Engine
-When deploying object detection models like [Ultralytics’ YOLOv8](https://ultralytics.com) on various hardware, you can bump into unique issues like optimization. This is where YOLOv8’s integration with Neural Magic’s DeepSparse Engine steps in. It transforms the way YOLOv8 models are executed and enables GPU-level performance directly on CPUs.
+When deploying object detection models like [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://ultralytics.com) on various hardware, you can bump into unique issues like optimization. This is where YOLOv8’s integration with Neural Magic’s DeepSparse Engine steps in. It transforms the way YOLOv8 models are executed and enables GPU-level performance directly on CPUs.
This guide shows you how to deploy YOLOv8 using Neural Magic's DeepSparse, how to run inferences, and also how to benchmark performance to ensure it is optimized.
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/tensorboard.md b/docs/en/integrations/tensorboard.md
index f462416a..5e0cbf12 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/tensorboard.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/tensorboard.md
@@ -102,7 +102,7 @@ The Time Series feature in the TensorBoard offers a dynamic and detailed perspec
#### Importance of Time Series in YOLOv8 Training
-The Time Series section is essential for a thorough analysis of the YOLOv8 model's training progress. It lets you track the metrics in real time so you can promptly identify and solve issues. It also offers a detailed view of each metric's progression, which is crucial for fine-tuning the model and enhancing its performance.
+The Time Series section is essential for a thorough analysis of the YOLOv8 model's training progress. It lets you track the metrics in real time to promptly identify and solve issues. It also offers a detailed view of each metric's progression, which is crucial for fine-tuning the model and enhancing its performance.
### Scalars
@@ -146,7 +146,7 @@ Graphs are particularly useful for debugging the model, especially in complex ar
## Summary
-This guide aims to help you use TensorBoard with YOLOv8 for visualization and analysis of machine learning model training. It focuses on explaining how key TensorBoard features can provides insights into training metrics and model performance during YOLOv8 training sessions.
+This guide aims to help you use TensorBoard with YOLOv8 for visualization and analysis of machine learning model training. It focuses on explaining how key TensorBoard features can provide insights into training metrics and model performance during YOLOv8 training sessions.
For a more detailed exploration of these features and effective utilization strategies, you can refer to TensorFlow’s official [TensorBoard documentation](https://www.tensorflow.org/tensorboard/get_started) and their [GitHub repository](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorboard).
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/tensorrt.md b/docs/en/integrations/tensorrt.md
index 88b3bf46..aa896752 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/tensorrt.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/tensorrt.md
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ By using the TensorRT export format, you can enhance your [Ultralytics YOLOv8](h
-For a full list of augmentation hyperparameters used in YOLOv8 please refer to the [configurations page](../usage/cfg.md#augmentation).
+For a full list of augmentation hyperparameters used in YOLOv8 please refer to the [configurations page](../usage/cfg.md#augmentation-settings).
### Genetic Evolution and Mutation
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/instance-segmentation-and-tracking.md b/docs/en/guides/instance-segmentation-and-tracking.md
index ac31ac87..558ab57d 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/instance-segmentation-and-tracking.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/instance-segmentation-and-tracking.md
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
---
comments: true
description: Instance Segmentation with Object Tracking using Ultralytics YOLOv8
-keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv8, Instance Segmentation, Object Detection, Object Tracking, Segbbox, Computer Vision, Notebook, IPython Kernel, CLI, Python SDK
+keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv8, Instance Segmentation, Object Detection, Object Tracking, Bounding Box, Computer Vision, Notebook, IPython Kernel, CLI, Python SDK
---
# Instance Segmentation and Tracking using Ultralytics YOLOv8 🚀
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/isolating-segmentation-objects.md b/docs/en/guides/isolating-segmentation-objects.md
index 79d47692..f8e9a7a6 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/isolating-segmentation-objects.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/isolating-segmentation-objects.md
@@ -14,12 +14,12 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
## Recipe Walk Through
-1. Begin with the necessary imports
+1. Begin with the necessary imports
- ```py
+ ```python
from pathlib import Path
- import cv2 as cv
+ import cv2
import numpy as np
from ultralytics import YOLO
```
@@ -30,19 +30,19 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
***
-2. Load a model and run `predict()` method on a source.
+2. Load a model and run `predict()` method on a source.
- ```py
+ ```python
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a model
model = YOLO('yolov8n-seg.pt')
# Run inference
- result = model.predict()
+ results = model.predict()
```
- ??? question "No Prediction Arguments?"
+ !!! question "No Prediction Arguments?"
Without specifying a source, the example images from the library will be used:
@@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
***
-3. Now iterate over the results and the contours. For workflows that want to save an image to file, the source image `base-name` and the detection `class-label` are retrieved for later use (optional).
+3. Now iterate over the results and the contours. For workflows that want to save an image to file, the source image `base-name` and the detection `class-label` are retrieved for later use (optional).
```{ .py .annotate }
# (2) Iterate detection results (helpful for multiple images)
@@ -81,7 +81,7 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
***
-4. Start with generating a binary mask from the source image and then draw a filled contour onto the mask. This will allow the object to be isolated from the other parts of the image. An example from `bus.jpg` for one of the detected `person` class objects is shown on the right.
+4. Start with generating a binary mask from the source image and then draw a filled contour onto the mask. This will allow the object to be isolated from the other parts of the image. An example from `bus.jpg` for one of the detected `person` class objects is shown on the right.
{ width="240", align="right" }
@@ -98,11 +98,11 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
# Draw contour onto mask
- _ = cv.drawContours(b_mask,
+ _ = cv2.drawContours(b_mask,
[contour],
-1,
(255, 255, 255),
- cv.FILLED)
+ cv2.FILLED)
```
@@ -136,7 +136,7 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
- The `tuple` `(255, 255, 255)` represents the color white, which is the desired color for drawing the contour in this binary mask.
- - The addition of `cv.FILLED` will color all pixels enclosed by the contour boundary the same, in this case, all enclosed pixels will be white.
+ - The addition of `cv2.FILLED` will color all pixels enclosed by the contour boundary the same, in this case, all enclosed pixels will be white.
- See [OpenCV Documentation on `drawContours()`](https://docs.opencv.org/4.8.0/d6/d6e/group__imgproc__draw.html#ga746c0625f1781f1ffc9056259103edbc) for more information.
@@ -145,7 +145,7 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
***
-5. Next the there are 2 options for how to move forward with the image from this point and a subsequent option for each.
+5. Next the there are 2 options for how to move forward with the image from this point and a subsequent option for each.
### Object Isolation Options
@@ -155,10 +155,10 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
```py
# Create 3-channel mask
- mask3ch = cv.cvtColor(b_mask, cv.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
+ mask3ch = cv2.cvtColor(b_mask, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
# Isolate object with binary mask
- isolated = cv.bitwise_and(mask3ch, img)
+ isolated = cv2.bitwise_and(mask3ch, img)
```
@@ -258,7 +258,7 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
***
-6. What to do next is entirely left to you as the developer. A basic example of one possible next step (saving the image to file for future use) is shown.
+6. What to do next is entirely left to you as the developer. A basic example of one possible next step (saving the image to file for future use) is shown.
- **NOTE:** this step is optional and can be skipped if not required for your specific use case.
@@ -266,7 +266,7 @@ After performing the [Segment Task](../tasks/segment.md), it's sometimes desirab
```py
# Save isolated object to file
- _ = cv.imwrite(f'{img_name}_{label}-{ci}.png', iso_crop)
+ _ = cv2.imwrite(f'{img_name}_{label}-{ci}.png', iso_crop)
```
- In this example, the `img_name` is the base-name of the source image file, `label` is the detected class-name, and `ci` is the index of the object detection (in case of multiple instances with the same class name).
@@ -278,7 +278,7 @@ Here, all steps from the previous section are combined into a single block of co
```{ .py .annotate }
from pathlib import Path
-import cv2 as cv
+import cv2
import numpy as np
from ultralytics import YOLO
@@ -298,13 +298,13 @@ for r in res:
# Create contour mask (1)
contour = c.masks.xy.pop().astype(np.int32).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
- _ = cv.drawContours(b_mask, [contour], -1, (255, 255, 255), cv.FILLED)
+ _ = cv2.drawContours(b_mask, [contour], -1, (255, 255, 255), cv2.FILLED)
# Choose one:
# OPTION-1: Isolate object with black background
- mask3ch = cv.cvtColor(b_mask, cv.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
- isolated = cv.bitwise_and(mask3ch, img)
+ mask3ch = cv2.cvtColor(b_mask, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
+ isolated = cv2.bitwise_and(mask3ch, img)
# OPTION-2: Isolate object with transparent background (when saved as PNG)
isolated = np.dstack([img, b_mask])
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md b/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md
index 67728e96..c00fbe19 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/object-counting.md
@@ -175,8 +175,8 @@ Object counting with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|-----------------------|-------------|----------------------------|-----------------------------------------------|
| `view_img` | `bool` | `False` | Display frames with counts |
-| `view_in_counts` | `bool` | `True` | Display incounts only on video frame |
-| `view_out_counts` | `bool` | `True` | Display outcounts only on video frame |
+| `view_in_counts` | `bool` | `True` | Display in-counts only on video frame |
+| `view_out_counts` | `bool` | `True` | Display out-counts only on video frame |
| `line_thickness` | `int` | `2` | Increase bounding boxes thickness |
| `reg_pts` | `list` | `[(20, 400), (1260, 400)]` | Points defining the Region Area |
| `classes_names` | `dict` | `model.model.names` | Dictionary of Class Names |
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md b/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md
index 126d3df2..240230a8 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/object-cropping.md
@@ -16,7 +16,6 @@ Object cropping with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly
- **Reduced Data Volume**: By extracting only relevant objects, object cropping helps in minimizing data size, making it efficient for storage, transmission, or subsequent computational tasks.
- **Enhanced Precision**: YOLOv8's object detection accuracy ensures that the cropped objects maintain their spatial relationships, preserving the integrity of the visual information for detailed analysis.
-
## Visuals
| Airport Luggage |
@@ -24,7 +23,6 @@ Object cropping with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly
|  |
| Suitcases Cropping at airport conveyor belt using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
-
!!! Example "Object Cropping using YOLOv8 Example"
=== "Object Cropping"
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/workouts-monitoring.md b/docs/en/guides/workouts-monitoring.md
index b2297803..fd4d7e0f 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/workouts-monitoring.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/workouts-monitoring.md
@@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ Monitoring workouts through pose estimation with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://gi
- **Optimized Performance:** Tailoring workouts based on monitoring data for better results.
- **Goal Achievement:** Track and adjust fitness goals for measurable progress.
- **Personalization:** Customized workout plans based on individual data for effectiveness.
-- **Health Awareness:** Early detection of patterns indicating health issues or overtraining.
+- **Health Awareness:** Early detection of patterns indicating health issues or over-training.
- **Informed Decisions:** Data-driven decisions for adjusting routines and setting realistic goals.
## Real World Applications
@@ -109,7 +109,7 @@ Monitoring workouts through pose estimation with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://gi
| `kpts_to_check` | `list` | `None` | List of three keypoints index, for counting specific workout, followed by keypoint Map |
| `view_img` | `bool` | `False` | Display the frame with counts |
| `line_thickness` | `int` | `2` | Increase the thickness of count value |
-| `pose_type` | `str` | `pushup` | Pose that need to be monitored, "pullup" and "abworkout" also supported |
+| `pose_type` | `str` | `pushup` | Pose that need to be monitored, `pullup` and `abworkout` also supported |
| `pose_up_angle` | `int` | `145` | Pose Up Angle value |
| `pose_down_angle` | `int` | `90` | Pose Down Angle value |
diff --git a/docs/en/hub/cloud-training.md b/docs/en/hub/cloud-training.md
index 91178ea2..f774475a 100644
--- a/docs/en/hub/cloud-training.md
+++ b/docs/en/hub/cloud-training.md
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, HUB Models, AI model training, model creation, model trai
# Cloud Training
-[Ultralytics HUB](https://hub.ultralytics.com/) provides a powerful and user-friendly cloud platform to train custom object detection models. Easily select your dataset and the desired training method, then kick off the process with just a few clicks. Ultralytics HUB offers pre-built options and various model architectures to streamline your workflow.
+[Ultralytics HUB](https://hub.ultralytics.com/) provides a powerful and user-friendly cloud platform to train custom object detection models. Easily select your dataset and the desired training method, then kick off the process with just a few clicks. Ultralytics HUB offers pre-built options and various model architectures to streamline your workflow.

diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/amazon-sagemaker.md b/docs/en/integrations/amazon-sagemaker.md
index 55fd4c76..f57fc2ee 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/amazon-sagemaker.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/amazon-sagemaker.md
@@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ First, ensure you have the following prerequisites in place:
- AWS CDK: If not already installed, install the AWS Cloud Development Kit (CDK), which will be used for scripting the deployment. Follow [the AWS CDK instructions](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cdk/v2/guide/getting_started.html#getting_started_install) for installation.
-- Adequate Service Quota: Confirm that you have sufficient quotas for two separate resources in Amazon SageMaker: one for ml.m5.4xlarge for endpoint usage and another for ml.m5.4xlarge for notebook instance usage. Each of these requires a minimum of one quota value. If your current quotas are below this requirement, it's important to request an increase for each. You can request a quota increase by following the detailed instructions in the [AWS Service Quotas documentation](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/servicequotas/latest/userguide/request-quota-increase.html#quota-console-increase).
+- Adequate Service Quota: Confirm that you have sufficient quotas for two separate resources in Amazon SageMaker: one for `ml.m5.4xlarge` for endpoint usage and another for `ml.m5.4xlarge` for notebook instance usage. Each of these requires a minimum of one quota value. If your current quotas are below this requirement, it's important to request an increase for each. You can request a quota increase by following the detailed instructions in the [AWS Service Quotas documentation](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/servicequotas/latest/userguide/request-quota-increase.html#quota-console-increase).
### Step 2: Clone the YOLOv8 SageMaker Repository
@@ -115,17 +115,21 @@ After creating the AWS CloudFormation Stack, the next step is to deploy YOLOv8.
- Access and Modify inference.py: After opening the SageMaker notebook instance in Jupyter, locate the inference.py file. Edit the output_fn function in inference.py as shown below and save your changes to the script, ensuring that there are no syntax errors.
```python
+import json
+
def output_fn(prediction_output, content_type):
print("Executing output_fn from inference.py ...")
infer = {}
for result in prediction_output:
- if 'boxes' in result._keys and result.boxes is not None:
+ if result.boxes is not None:
infer['boxes'] = result.boxes.numpy().data.tolist()
- if 'masks' in result._keys and result.masks is not None:
+ if result.masks is not None:
infer['masks'] = result.masks.numpy().data.tolist()
- if 'keypoints' in result._keys and result.keypoints is not None:
+ if result.keypoints is not None:
infer['keypoints'] = result.keypoints.numpy().data.tolist()
- if 'probs' in result._keys and result.probs is not None:
+ if result.obb is not None:
+ infer['obb'] = result.obb.numpy().data.tolist()
+ if result.probs is not None:
infer['probs'] = result.probs.numpy().data.tolist()
return json.dumps(infer)
```
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/coreml.md b/docs/en/integrations/coreml.md
index cbcff691..5533da57 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/coreml.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/coreml.md
@@ -18,9 +18,10 @@ The CoreML export format allows you to optimize your [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https:
[CoreML](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/coreml) is Apple's foundational machine learning framework that builds upon Accelerate, BNNS, and Metal Performance Shaders. It provides a machine-learning model format that seamlessly integrates into iOS applications and supports tasks such as image analysis, natural language processing, audio-to-text conversion, and sound analysis.
-Applications can take advantage of Core ML without the need to have a network connection or API calls because the Core ML framework works using on-device computing. This means model inferencing can be performed locally on the user's device.
+Applications can take advantage of Core ML without the need to have a network connection or API calls because the Core ML framework works using on-device computing. This means model inference can be performed locally on the user's device.
## Key Features of CoreML Models
+
Apple's CoreML framework offers robust features for on-device machine learning. Here are the key features that make CoreML a powerful tool for developers:
- **Comprehensive Model Support**: Converts and runs models from popular frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, scikit-learn, XGBoost, and LibSVM.
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/index.md b/docs/en/integrations/index.md
index b52f3db9..77a723dc 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/index.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/index.md
@@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ Welcome to the Ultralytics Integrations page! This page provides an overview of
- [CoreML](coreml.md): CoreML, developed by [Apple](https://www.apple.com/), is a framework designed for efficiently integrating machine learning models into applications across iOS, macOS, watchOS, and tvOS, using Apple's hardware for effective and secure model deployment.
- [TFLite](tflite.md): Developed by [Google](https://www.google.com), TFLite is a lightweight framework for deploying machine learning models on mobile and edge devices, ensuring fast, efficient inference with minimal memory footprint.
-
+
- [NCNN](ncnn.md): Developed by [Tencent](http://www.tencent.com/), NCNN is an efficient neural network inference framework tailored for mobile devices. It enables direct deployment of AI models into apps, optimizing performance across various mobile platforms.
### Export Formats
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/ncnn.md b/docs/en/integrations/ncnn.md
index eadc9813..835f8fcd 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/ncnn.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/ncnn.md
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv8, NCNN Export, Export YOLOv8, Model Deployment
# How to Export to NCNN from YOLOv8 for Smooth Deployment
-Deploying computer vision models on devices with limited computational power, such as mobile or embedded systems, can be tricky. You need to make sure you use a format optimized for optimal performance. This makes sure that even devices with limited processing power can handle advanced computer vision tasks well.
+Deploying computer vision models on devices with limited computational power, such as mobile or embedded systems, can be tricky. You need to make sure you use a format optimized for optimal performance. This makes sure that even devices with limited processing power can handle advanced computer vision tasks well.
The export to NCNN format feature allows you to optimize your [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) models for lightweight device-based applications. In this guide, we'll walk you through how to convert your models to the NCNN format, making it easier for your models to perform well on various mobile and embedded devices.
@@ -18,19 +18,19 @@ The export to NCNN format feature allows you to optimize your [Ultralytics YOLOv
The [NCNN](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) framework, developed by Tencent, is a high-performance neural network inference computing framework optimized specifically for mobile platforms, including mobile phones, embedded devices, and IoT devices. NCNN is compatible with a wide range of platforms, including Linux, Android, iOS, and macOS.
-NCNN is known for its fast processing speed on mobile CPUs and enables rapid deployment of deep learning models to mobile platforms. This makes it easier to build smart apps, putting the power of AI right at your fingertips.
+NCNN is known for its fast processing speed on mobile CPUs and enables rapid deployment of deep learning models to mobile platforms. This makes it easier to build smart apps, putting the power of AI right at your fingertips.
## Key Features of NCNN Models
NCNN models offer a wide range of key features that enable on-device machine learning by helping developers run their models on mobile, embedded, and edge devices:
- - **Efficient and High-Performance**: NCNN models are made to be efficient and lightweight, optimized for running on mobile and embedded devices like Raspberry Pi with limited resources. They can also achieve high performance with high accuracy on various computer vision-based tasks.
+- **Efficient and High-Performance**: NCNN models are made to be efficient and lightweight, optimized for running on mobile and embedded devices like Raspberry Pi with limited resources. They can also achieve high performance with high accuracy on various computer vision-based tasks.
- - **Quantization**: NCNN models often support quantization which is a technique that reduces the precision of the model's weights and activations. This leads to further improvements in performance and reduces memory footprint.
+- **Quantization**: NCNN models often support quantization which is a technique that reduces the precision of the model's weights and activations. This leads to further improvements in performance and reduces memory footprint.
- - **Compatibility**: NCNN models are compatible with popular deep learning frameworks like [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/), [Caffe](https://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/), and [ONNX](https://onnx.ai/). This compatibility allows developers to use existing models and workflows easily.
+- **Compatibility**: NCNN models are compatible with popular deep learning frameworks like [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/), [Caffe](https://caffe.berkeleyvision.org/), and [ONNX](https://onnx.ai/). This compatibility allows developers to use existing models and workflows easily.
- - **Easy to Use**: NCNN models are designed for easy integration into various applications, thanks to their compatibility with popular deep learning frameworks. Additionally, NCNN offers user-friendly tools for converting models between different formats, ensuring smooth interoperability across the development landscape.
+- **Easy to Use**: NCNN models are designed for easy integration into various applications, thanks to their compatibility with popular deep learning frameworks. Additionally, NCNN offers user-friendly tools for converting models between different formats, ensuring smooth interoperability across the development landscape.
## Deployment Options with NCNN
@@ -65,7 +65,7 @@ For detailed instructions and best practices related to the installation process
### Usage
-Before diving into the usage instructions, it's important to note that while all [Ultralytics YOLOv8 models]((../models/index.md)) are available for exporting, you can ensure that the model you select supports export functionality [here](../modes/export.md).
+Before diving into the usage instructions, it's important to note that while all [Ultralytics YOLOv8 models](../models/index.md) are available for exporting, you can ensure that the model you select supports export functionality [here](../modes/export.md).
!!! Example "Usage"
@@ -103,13 +103,13 @@ For more details about supported export options, visit the [Ultralytics document
After successfully exporting your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to NCNN format, you can now deploy them. The primary and recommended first step for running a NCNN model is to utilize the YOLO("./model_ncnn_model") method, as outlined in the previous usage code snippet. However, for in-depth instructions on deploying your NCNN models in various other settings, take a look at the following resources:
-- **[Android](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/wiki/how-to-build#build-for-android)**: This blog explains how to use NCNN models for performing tasks like object detection through Android applications.
+- **[Android](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/wiki/how-to-build#build-for-android)**: This blog explains how to use NCNN models for performing tasks like object detection through Android applications.
- - **[macOS](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/wiki/how-to-build#build-for-macos)**: Understand how to use NCNN models for performing tasks through macOS.
+- **[macOS](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/wiki/how-to-build#build-for-macos)**: Understand how to use NCNN models for performing tasks through macOS.
- - **[Linux](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/wiki/how-to-build#build-for-linux)**: Explore this page to learn how to deploy NCNN models on limited resource devices like Raspberry Pi and other similar devices.
+- **[Linux](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/wiki/how-to-build#build-for-linux)**: Explore this page to learn how to deploy NCNN models on limited resource devices like Raspberry Pi and other similar devices.
- - **[Windows x64 using VS2017](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/wiki/how-to-build#build-for-windows-x64-using-visual-studio-community-2017)**: Explore this blog to learn how to deploy NCNN models on windows x64 using Visual Studio Community 2017.
+- **[Windows x64 using VS2017](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn/wiki/how-to-build#build-for-windows-x64-using-visual-studio-community-2017)**: Explore this blog to learn how to deploy NCNN models on windows x64 using Visual Studio Community 2017.
## Summary
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/neural-magic.md b/docs/en/integrations/neural-magic.md
index 90e90dbe..53910972 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/neural-magic.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/neural-magic.md
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: YOLOv8, DeepSparse Engine, Ultralytics, CPU Inference, Neural Network
# Optimizing YOLOv8 Inferences with Neural Magic’s DeepSparse Engine
-When deploying object detection models like [Ultralytics’ YOLOv8](https://ultralytics.com) on various hardware, you can bump into unique issues like optimization. This is where YOLOv8’s integration with Neural Magic’s DeepSparse Engine steps in. It transforms the way YOLOv8 models are executed and enables GPU-level performance directly on CPUs.
+When deploying object detection models like [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://ultralytics.com) on various hardware, you can bump into unique issues like optimization. This is where YOLOv8’s integration with Neural Magic’s DeepSparse Engine steps in. It transforms the way YOLOv8 models are executed and enables GPU-level performance directly on CPUs.
This guide shows you how to deploy YOLOv8 using Neural Magic's DeepSparse, how to run inferences, and also how to benchmark performance to ensure it is optimized.
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/tensorboard.md b/docs/en/integrations/tensorboard.md
index f462416a..5e0cbf12 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/tensorboard.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/tensorboard.md
@@ -102,7 +102,7 @@ The Time Series feature in the TensorBoard offers a dynamic and detailed perspec
#### Importance of Time Series in YOLOv8 Training
-The Time Series section is essential for a thorough analysis of the YOLOv8 model's training progress. It lets you track the metrics in real time so you can promptly identify and solve issues. It also offers a detailed view of each metric's progression, which is crucial for fine-tuning the model and enhancing its performance.
+The Time Series section is essential for a thorough analysis of the YOLOv8 model's training progress. It lets you track the metrics in real time to promptly identify and solve issues. It also offers a detailed view of each metric's progression, which is crucial for fine-tuning the model and enhancing its performance.
### Scalars
@@ -146,7 +146,7 @@ Graphs are particularly useful for debugging the model, especially in complex ar
## Summary
-This guide aims to help you use TensorBoard with YOLOv8 for visualization and analysis of machine learning model training. It focuses on explaining how key TensorBoard features can provides insights into training metrics and model performance during YOLOv8 training sessions.
+This guide aims to help you use TensorBoard with YOLOv8 for visualization and analysis of machine learning model training. It focuses on explaining how key TensorBoard features can provide insights into training metrics and model performance during YOLOv8 training sessions.
For a more detailed exploration of these features and effective utilization strategies, you can refer to TensorFlow’s official [TensorBoard documentation](https://www.tensorflow.org/tensorboard/get_started) and their [GitHub repository](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorboard).
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/tensorrt.md b/docs/en/integrations/tensorrt.md
index 88b3bf46..aa896752 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/tensorrt.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/tensorrt.md
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ By using the TensorRT export format, you can enhance your [Ultralytics YOLOv8](h
 -[TensorRT](https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt#:~:text=NVIDIA%20TensorRT%2DLLM%20is%20an,knowledge%20of%20C%2B%2B%20or%20CUDA.), developed by NVIDIA, is an advanced software development kit (SDK) designed for high-speed deep learning inference. It’s well-suited for real-time applications like object detection.
+[TensorRT](https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt), developed by NVIDIA, is an advanced software development kit (SDK) designed for high-speed deep learning inference. It’s well-suited for real-time applications like object detection.
This toolkit optimizes deep learning models for NVIDIA GPUs and results in faster and more efficient operations. TensorRT models undergo TensorRT optimization, which includes techniques like layer fusion, precision calibration (INT8 and FP16), dynamic tensor memory management, and kernel auto-tuning. Converting deep learning models into the TensorRT format allows developers to realize the potential of NVIDIA GPUs fully.
@@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ TensorRT models offer a range of key features that contribute to their efficienc
## Deployment Options in TensorRT
-Before we look at the code for exporting YOLOv8 models to the TensorRT format, let’s understand where TensorRT models are normally used.
+Before we look at the code for exporting YOLOv8 models to the TensorRT format, let’s understand where TensorRT models are normally used.
TensorRT offers several deployment options, and each option balances ease of integration, performance optimization, and flexibility differently:
@@ -52,7 +52,7 @@ TensorRT offers several deployment options, and each option balances ease of int
- **Standalone TensorRT Runtime API**: Offers granular control, ideal for performance-critical applications. It's more complex but allows for custom implementation of unsupported operators.
-- **NVIDIA Triton Inference Server**: An option that supports models from various frameworks. Particularly suited for cloud or edge inferencing, it provides features like concurrent model execution and model analysis.
+- **NVIDIA Triton Inference Server**: An option that supports models from various frameworks. Particularly suited for cloud or edge inference, it provides features like concurrent model execution and model analysis.
## Exporting YOLOv8 Models to TensorRT
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/tflite.md b/docs/en/integrations/tflite.md
index 805e8a33..03fe1565 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/tflite.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/tflite.md
@@ -6,17 +6,17 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv8, TFLite Export, Export YOLOv8, Model Deployment
# A Guide on YOLOv8 Model Export to TFLite for Deployment
+
-[TensorRT](https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt#:~:text=NVIDIA%20TensorRT%2DLLM%20is%20an,knowledge%20of%20C%2B%2B%20or%20CUDA.), developed by NVIDIA, is an advanced software development kit (SDK) designed for high-speed deep learning inference. It’s well-suited for real-time applications like object detection.
+[TensorRT](https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt), developed by NVIDIA, is an advanced software development kit (SDK) designed for high-speed deep learning inference. It’s well-suited for real-time applications like object detection.
This toolkit optimizes deep learning models for NVIDIA GPUs and results in faster and more efficient operations. TensorRT models undergo TensorRT optimization, which includes techniques like layer fusion, precision calibration (INT8 and FP16), dynamic tensor memory management, and kernel auto-tuning. Converting deep learning models into the TensorRT format allows developers to realize the potential of NVIDIA GPUs fully.
@@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ TensorRT models offer a range of key features that contribute to their efficienc
## Deployment Options in TensorRT
-Before we look at the code for exporting YOLOv8 models to the TensorRT format, let’s understand where TensorRT models are normally used.
+Before we look at the code for exporting YOLOv8 models to the TensorRT format, let’s understand where TensorRT models are normally used.
TensorRT offers several deployment options, and each option balances ease of integration, performance optimization, and flexibility differently:
@@ -52,7 +52,7 @@ TensorRT offers several deployment options, and each option balances ease of int
- **Standalone TensorRT Runtime API**: Offers granular control, ideal for performance-critical applications. It's more complex but allows for custom implementation of unsupported operators.
-- **NVIDIA Triton Inference Server**: An option that supports models from various frameworks. Particularly suited for cloud or edge inferencing, it provides features like concurrent model execution and model analysis.
+- **NVIDIA Triton Inference Server**: An option that supports models from various frameworks. Particularly suited for cloud or edge inference, it provides features like concurrent model execution and model analysis.
## Exporting YOLOv8 Models to TensorRT
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/tflite.md b/docs/en/integrations/tflite.md
index 805e8a33..03fe1565 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/tflite.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/tflite.md
@@ -6,17 +6,17 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv8, TFLite Export, Export YOLOv8, Model Deployment
# A Guide on YOLOv8 Model Export to TFLite for Deployment
+
+
+
-  -
-
-  +
+ 