diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/detect/african-wildlife.md b/docs/en/datasets/detect/african-wildlife.md
index 3970ffa5..586df884 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/detect/african-wildlife.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/detect/african-wildlife.md
@@ -75,7 +75,6 @@ To train a YOLOv8n model on the African wildlife dataset for 100 epochs with an
# Start prediction with a finetuned *.pt model
yolo detect predict model='path/to/best.pt' imgsz=640 source="https://ultralytics.com/assets/african-wildlife-sample.jpg"
```
-
## Sample Images and Annotations
@@ -89,4 +88,4 @@ This example illustrates the variety and complexity of images in the African wil
## Citations and Acknowledgments
-The dataset has been released available under the [AGPL-3.0 License](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/LICENSE).
\ No newline at end of file
+The dataset has been released available under the [AGPL-3.0 License](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/LICENSE).
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/detect/brain-tumor.md b/docs/en/datasets/detect/brain-tumor.md
index 1507e747..81723239 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/detect/brain-tumor.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/detect/brain-tumor.md
@@ -74,7 +74,6 @@ To train a YOLOv8n model on the brain tumor dataset for 100 epochs with an image
# Start prediction with a finetuned *.pt model
yolo detect predict model='path/to/best.pt' imgsz=640 source="https://ultralytics.com/assets/brain-tumor-sample.jpg"
```
-
## Sample Images and Annotations
@@ -88,4 +87,4 @@ This example highlights the diversity and intricacy of images within the brain t
## Citations and Acknowledgments
-The dataset has been released available under the [AGPL-3.0 License](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/LICENSE).
\ No newline at end of file
+The dataset has been released available under the [AGPL-3.0 License](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/LICENSE).
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/detect/lvis.md b/docs/en/datasets/detect/lvis.md
index ccb29794..2ddf49d9 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/detect/lvis.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/detect/lvis.md
@@ -29,7 +29,6 @@ The LVIS dataset is split into three subsets:
3. **Minival**: This subset is exactly the same as COCO val2017 set which has 5k images used for validation purposes during model training.
4. **Test**: This subset consists of 20k images used for testing and benchmarking the trained models. Ground truth annotations for this subset are not publicly available, and the results are submitted to the [LVIS evaluation server](https://eval.ai/web/challenges/challenge-page/675/overview) for performance evaluation.
-
## Applications
The LVIS dataset is widely used for training and evaluating deep learning models in object detection (such as YOLO, Faster R-CNN, and SSD), instance segmentation (such as Mask R-CNN). The dataset's diverse set of object categories, large number of annotated images, and standardized evaluation metrics make it an essential resource for computer vision researchers and practitioners.
diff --git a/docs/en/datasets/index.md b/docs/en/datasets/index.md
index 1ac05fc8..db27ba82 100644
--- a/docs/en/datasets/index.md
+++ b/docs/en/datasets/index.md
@@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ Bounding box object detection is a computer vision technique that involves detec
- [Argoverse](detect/argoverse.md): A dataset containing 3D tracking and motion forecasting data from urban environments with rich annotations.
- [COCO](detect/coco.md): A large-scale dataset designed for object detection, segmentation, and captioning with over 200K labeled images.
-- [LVIS](lvis.md): A large-scale object detection, segmentation, and captioning dataset with 1203 object categories.
+- [LVIS](detect/lvis.md): A large-scale object detection, segmentation, and captioning dataset with 1203 object categories.
- [COCO8](detect/coco8.md): Contains the first 4 images from COCO train and COCO val, suitable for quick tests.
- [Global Wheat 2020](detect/globalwheat2020.md): A dataset of wheat head images collected from around the world for object detection and localization tasks.
- [Objects365](detect/objects365.md): A high-quality, large-scale dataset for object detection with 365 object categories and over 600K annotated images.
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/nvidia-jetson.md b/docs/en/guides/nvidia-jetson.md
index 5e2597cd..b8d90dff 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/nvidia-jetson.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/nvidia-jetson.md
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ This comprehensive guide provides a detailed walkthrough for deploying Ultralyti
## What is NVIDIA Jetson?
-NVIDIA Jetson is a series of embedded computing boards designed to bring accelerated AI (artificial intelligence) computing to edge devices. These compact and powerful devices are built around NVIDIA's GPU architecture and are capable of running complex AI algorithms and deep learning models directly on the device, without needing to rely on cloud computing resources. Jetson boards are often used in robotics, autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and other applications where AI inference needs to be performed locally with low latency and high efficiency. Additionally these boards are based on the ARM64 architecture and runs on lower power compared to traditional GPU computing devices.
+NVIDIA Jetson is a series of embedded computing boards designed to bring accelerated AI (artificial intelligence) computing to edge devices. These compact and powerful devices are built around NVIDIA's GPU architecture and are capable of running complex AI algorithms and deep learning models directly on the device, without needing to rely on cloud computing resources. Jetson boards are often used in robotics, autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and other applications where AI inference needs to be performed locally with low latency and high efficiency. Additionally, these boards are based on the ARM64 architecture and runs on lower power compared to traditional GPU computing devices.
## NVIDIA Jetson Series Comparison
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ NVIDIA Jetson is a series of embedded computing boards designed to bring acceler
| | Jetson AGX Orin 64GB | Jetson Orin NX 16GB | Jetson Orin Nano 8GB | Jetson AGX Xavier | Jetson Xavier NX | Jetson Nano |
|-------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------|
-| AI Performance | 275 TOPS | 100 TOPS | 40 TOPs | 32 TOPS | 21 TOPS | 472 GFLOPS |
+| AI Performance | 275 TOPS | 100 TOPS | 40 TOPs | 32 TOPS | 21 TOPS | 472 GFLOPS |
| GPU | 2048-core NVIDIA Ampere architecture GPU with 64 Tensor Cores | 1024-core NVIDIA Ampere architecture GPU with 32 Tensor Cores | 1024-core NVIDIA Ampere architecture GPU with 32 Tensor Cores | 512-core NVIDIA Volta architecture GPU with 64 Tensor Cores | 384-core NVIDIA Volta™ architecture GPU with 48 Tensor Cores | 128-core NVIDIA Maxwell™ architecture GPU |
| GPU Max Frequency | 1.3 GHz | 918 MHz | 625 MHz | 1377 MHz | 1100 MHz | 921MHz |
| CPU | 12-core NVIDIA Arm® Cortex A78AE v8.2 64-bit CPU 3MB L2 + 6MB L3 | 8-core NVIDIA Arm® Cortex A78AE v8.2 64-bit CPU 2MB L2 + 4MB L3 | 6-core Arm® Cortex®-A78AE v8.2 64-bit CPU 1.5MB L2 + 4MB L3 | 8-core NVIDIA Carmel Arm®v8.2 64-bit CPU 8MB L2 + 4MB L3 | 6-core NVIDIA Carmel Arm®v8.2 64-bit CPU 6MB L2 + 4MB L3 | Quad-Core Arm® Cortex®-A57 MPCore processor |
@@ -67,6 +67,7 @@ t=ultralytics/ultralytics:latest-jetson && sudo docker pull $t && sudo docker ru
Here we will install ultralyics package on the Jetson with optional dependencies so that we can export the PyTorch models to other different formats. We will mainly focus on [NVIDIA TensorRT exports](https://docs.ultralytics.com/integrations/tensorrt) because TensoRT will make sure we can get the maximum performance out of the Jetson devices.
1. Update packages list, install pip and upgrade to latest
+
```sh
sudo apt update
sudo apt install python3-pip -y
@@ -74,25 +75,29 @@ pip install -U pip
```
2. Install `ultralytics` pip package with optional dependencies
+
```sh
pip install ultralytics[export]
```
3. Reboot the device
+
```sh
sudo reboot
```
### Install PyTorch and Torchvision
-The above ultralytics installation will install Torch and Torchvision. However, these 2 packages installed via pip are not compatible to run on Jetson platform which is based on ARM64 architecture. Therefore we need to manually install pre-built PyTorch pip wheel and compile/ install Torchvision from source.
+The above ultralytics installation will install Torch and Torchvision. However, these 2 packages installed via pip are not compatible to run on Jetson platform which is based on ARM64 architecture. Therefore, we need to manually install pre-built PyTorch pip wheel and compile/ install Torchvision from source.
1. Uninstall currently installed PyTorch and Torchvision
+
```sh
pip uninstall torch torchvision
```
2. Install PyTorch 2.1.0 according to JP5.1.3
+
```sh
sudo apt-get install -y libopenblas-base libopenmpi-dev
wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/redist/jp/v512/pytorch/torch-2.1.0a0+41361538.nv23.06-cp38-cp38-linux_aarch64.whl -O torch-2.1.0a0+41361538.nv23.06-cp38-cp38-linux_aarch64.whl
@@ -100,6 +105,7 @@ pip install torch-2.1.0a0+41361538.nv23.06-cp38-cp38-linux_aarch64.whl
```
3. Install Torchvision v0.16.2 according to PyTorch v2.1.0
+
```sh
sudo apt install -y libjpeg-dev zlib1g-dev
git clone https://github.com/pytorch/vision torchvision
@@ -149,13 +155,13 @@ The YOLOv8n model in PyTorch format is converted to TensorRT to run inference wi
## Arguments
-| Key | Value | Description |
-|----------|--------------|------------------------------------------------------|
+| Key | Value | Description |
+|----------|------------|------------------------------------------------------|
| `format` | `'engine'` | format to export to |
-| `imgsz` | `640` | image size as scalar or (h, w) list, i.e. (640, 480) |
-| `half` | `False` | FP16 quantization |
+| `imgsz` | `640` | image size as scalar or (h, w) list, i.e. (640, 480) |
+| `half` | `False` | FP16 quantization |
-## NVIDIA Jetson Orin YOLOv8 Benchmarks
+## NVIDIA Jetson Orin YOLOv8 Benchmarks
YOLOv8 benchmarks below were run by the Ultralytics team on 3 different model formats measuring speed and accuracy: PyTorch, TorchScript and TensorRT. Benchmarks were run on Seeed Studio reComputer J4012 powered by Jetson Orin NX 16GB device at FP32 precision with default input image size of 640.
@@ -185,7 +191,6 @@ This table represents the benchmark results for five different models (YOLOv8n,
Visit [this link](https://www.seeedstudio.com/blog/2023/03/30/yolov8-performance-benchmarks-on-nvidia-jetson-devices) to explore more benchmarking efforts by Seeed Studio running on different versions of NVIDIA Jetson hardware.
-
## Reproduce Our Results
To reproduce the above Ultralytics benchmarks on all export [formats](../modes/export.md) run this code:
@@ -212,7 +217,6 @@ To reproduce the above Ultralytics benchmarks on all export [formats](../modes/e
Note that benchmarking results might vary based on the exact hardware and software configuration of a system, as well as the current workload of the system at the time the benchmarks are run. For the most reliable results use a dataset with a large number of images, i.e. `data='coco128.yaml' (128 val images), or `data='coco.yaml'` (5000 val images).
-
!!! Note
Currently only PyTorch, Torchscript and TensorRT are working with the benchmarking tools. We will update it to support other exports in the future.
@@ -237,7 +241,7 @@ When using NVIDIA Jetson, there are a couple of best practices to follow in orde
3. Install Jetson Stats Application
- We can use jetson stats application to monitor the temperatures of the system components and check other system details such as view CPU, GPU, RAM utilizations, change power modes, set to max clocks, check JetPack information
+ We can use jetson stats application to monitor the temperatures of the system components and check other system details such as view CPU, GPU, RAM utilization, change power modes, set to max clocks, check JetPack information
```sh
sudo apt update
sudo pip install jetson-stats
@@ -249,4 +253,4 @@ When using NVIDIA Jetson, there are a couple of best practices to follow in orde
## Next Steps
-Congratulations on successfully setting up YOLOv8 on your NVIDIA Jetson! For further learning and support, visit more guide at [Ultralytics YOLOv8 Docs](../)!
\ No newline at end of file
+Congratulations on successfully setting up YOLOv8 on your NVIDIA Jetson! For further learning and support, visit more guide at [Ultralytics YOLOv8 Docs](../index.md)!
diff --git a/docs/en/guides/queue-management.md b/docs/en/guides/queue-management.md
index 9e72fd25..e02da630 100644
--- a/docs/en/guides/queue-management.md
+++ b/docs/en/guides/queue-management.md
@@ -10,7 +10,6 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv8, Queue Management, Object Counting, Object Trackin
Queue management using [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/) involves organizing and controlling lines of people or vehicles to reduce wait times and enhance efficiency. It's about optimizing queues to improve customer satisfaction and system performance in various settings like retail, banks, airports, and healthcare facilities.
-
## Advantages of Queue Management?
- **Reduced Waiting Times:** Queue management systems efficiently organize queues, minimizing wait times for customers. This leads to improved satisfaction levels as customers spend less time waiting and more time engaging with products or services.
@@ -23,7 +22,6 @@ Queue management using [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultra
| 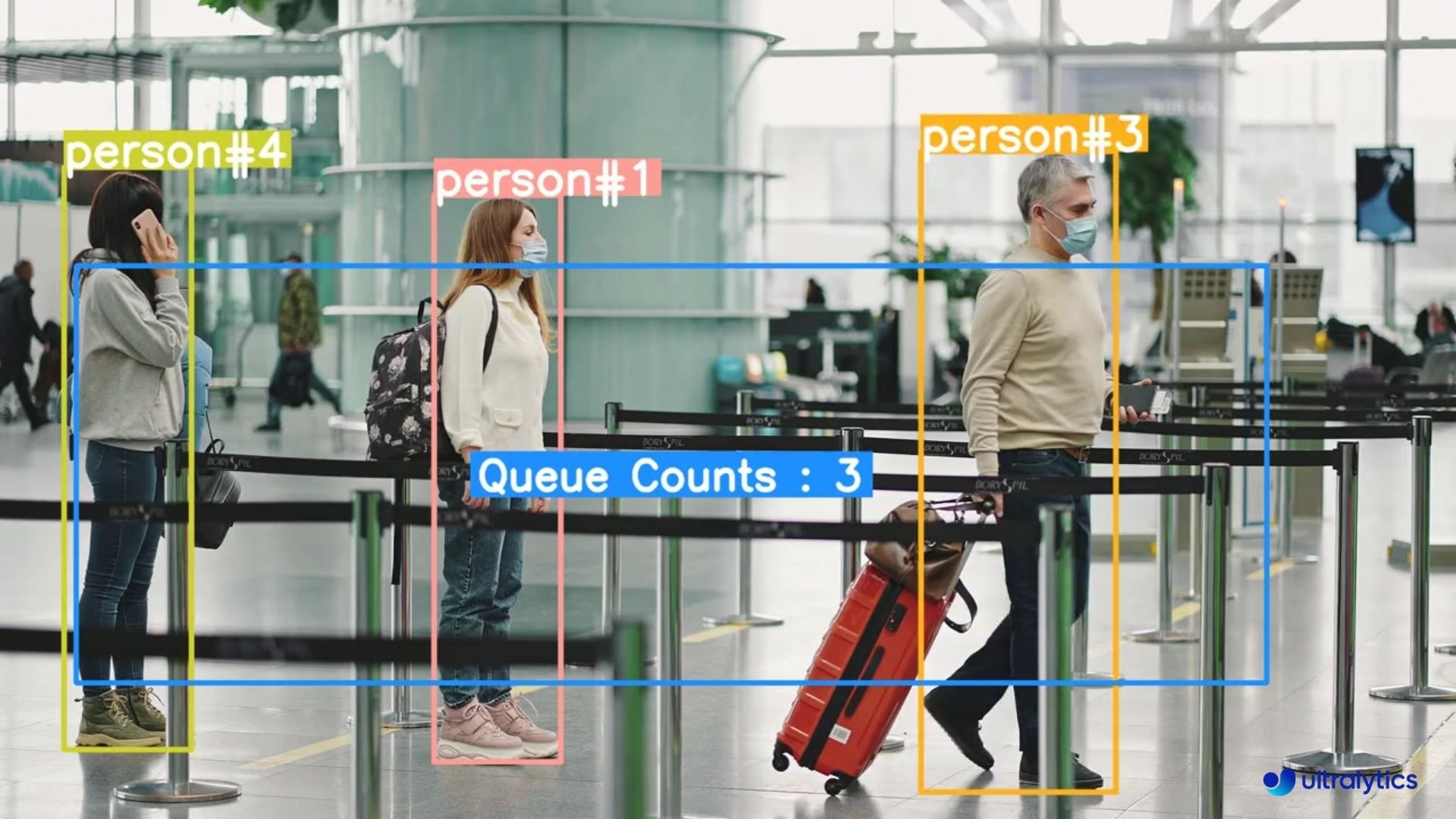 | 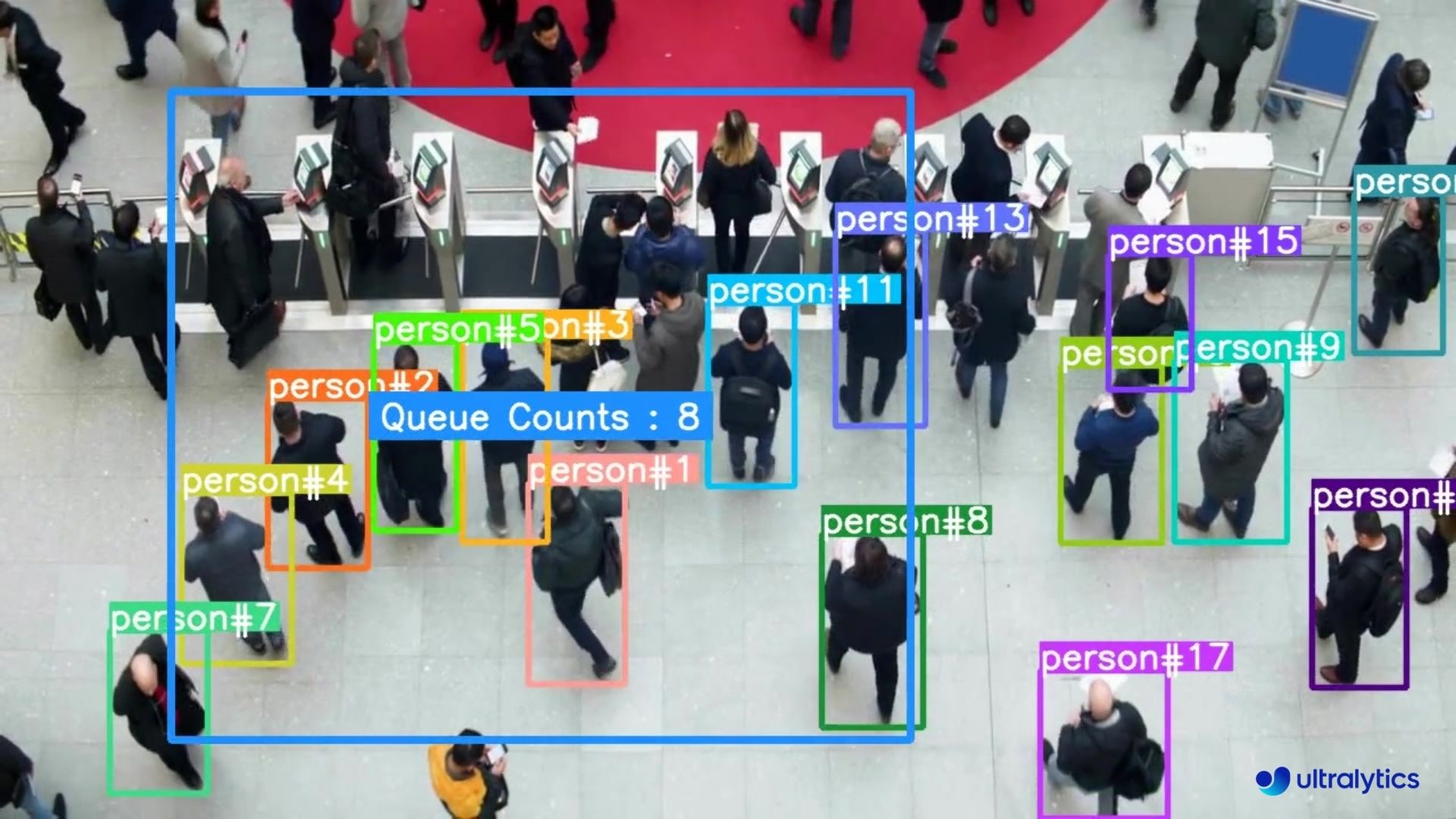 |
| Queue management at airport ticket counter Using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Queue monitoring in crowd Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
-
!!! Example "Queue Management using YOLOv8 Example"
=== "Queue Manager"
@@ -126,20 +124,20 @@ Queue management using [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultra
### Optional Arguments `set_args`
-| Name | Type | Default | Description |
-|-----------------------|-------------|----------------------------|---------------------------------------------|
-| `view_img` | `bool` | `False` | Display frames with counts |
-| `view_queue_counts` | `bool` | `True` | Display Queue counts only on video frame |
-| `line_thickness` | `int` | `2` | Increase bounding boxes thickness |
-| `reg_pts` | `list` | `[(20, 400), (1260, 400)]` | Points defining the Region Area |
-| `classes_names` | `dict` | `model.model.names` | Dictionary of Class Names |
-| `region_color` | `RGB Color` | `(255, 0, 255)` | Color of the Object counting Region or Line |
-| `track_thickness` | `int` | `2` | Thickness of Tracking Lines |
-| `draw_tracks` | `bool` | `False` | Enable drawing Track lines |
-| `track_color` | `RGB Color` | `(0, 255, 0)` | Color for each track line |
-| `count_txt_color` | `RGB Color` | `(255, 255, 255)` | Foreground color for Object counts text |
-| `region_thickness` | `int` | `5` | Thickness for object counter region or line |
-| `fontsize` | `float` | `0.6` | Font size of counting text |
+| Name | Type | Default | Description |
+|---------------------|-------------|----------------------------|---------------------------------------------|
+| `view_img` | `bool` | `False` | Display frames with counts |
+| `view_queue_counts` | `bool` | `True` | Display Queue counts only on video frame |
+| `line_thickness` | `int` | `2` | Increase bounding boxes thickness |
+| `reg_pts` | `list` | `[(20, 400), (1260, 400)]` | Points defining the Region Area |
+| `classes_names` | `dict` | `model.model.names` | Dictionary of Class Names |
+| `region_color` | `RGB Color` | `(255, 0, 255)` | Color of the Object counting Region or Line |
+| `track_thickness` | `int` | `2` | Thickness of Tracking Lines |
+| `draw_tracks` | `bool` | `False` | Enable drawing Track lines |
+| `track_color` | `RGB Color` | `(0, 255, 0)` | Color for each track line |
+| `count_txt_color` | `RGB Color` | `(255, 255, 255)` | Foreground color for Object counts text |
+| `region_thickness` | `int` | `5` | Thickness for object counter region or line |
+| `fontsize` | `float` | `0.6` | Font size of counting text |
### Arguments `model.track`
diff --git a/docs/en/help/CI.md b/docs/en/help/CI.md
index 033cf717..62c8d3a8 100644
--- a/docs/en/help/CI.md
+++ b/docs/en/help/CI.md
@@ -22,13 +22,13 @@ Here's a brief description of our CI actions:
Below is the table showing the status of these CI tests for our main repositories:
-| Repository | CI | Docker Deployment | Broken Links | CodeQL | PyPi and Docs Publishing |
-|-----------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
-| [yolov3](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/actions/workflows/docker.yml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/actions/workflows/links.yml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/actions/workflows/codeql-analysis.yml) | |
-| [yolov5](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/docker.yml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/links.yml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/codeql-analysis.yml) | |
-| [ultralytics](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/actions/workflows/ci.yaml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/actions/workflows/docker.yaml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/actions/workflows/links.yml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/actions/workflows/codeql.yaml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/actions/workflows/publish.yml) |
-| [hub](https://github.com/ultralytics/hub) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/hub/actions/workflows/ci.yaml) | | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/hub/actions/workflows/links.yml) | | |
-| [docs](https://github.com/ultralytics/docs) | | | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/actions/workflows/links.yml)[](https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/actions/workflows/check_domains.yml) | | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/actions/workflows/pages/pages-build-deployment) |
+| Repository | CI | Docker Deployment | Broken Links | CodeQL | PyPi and Docs Publishing |
+|-----------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| [yolov3](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/actions/workflows/docker.yml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/actions/workflows/links.yml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/actions/workflows/codeql-analysis.yml) | |
+| [yolov5](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/ci-testing.yml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/docker.yml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/links.yml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/actions/workflows/codeql-analysis.yml) | |
+| [ultralytics](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/actions/workflows/ci.yaml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/actions/workflows/docker.yaml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/actions/workflows/links.yml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/actions/workflows/codeql.yaml) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/actions/workflows/publish.yml) |
+| [hub](https://github.com/ultralytics/hub) | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/hub/actions/workflows/ci.yaml) | | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/hub/actions/workflows/links.yml) | | |
+| [docs](https://github.com/ultralytics/docs) | | | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/actions/workflows/links.yml)[](https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/actions/workflows/check_domains.yml) | | [](https://github.com/ultralytics/docs/actions/workflows/pages/pages-build-deployment) |
Each badge shows the status of the last run of the corresponding CI test on the `main` branch of the respective repository. If a test fails, the badge will display a "failing" status, and if it passes, it will display a "passing" status.
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/edge-tpu.md b/docs/en/integrations/edge-tpu.md
index aa83c449..ec2ec4a8 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/edge-tpu.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/edge-tpu.md
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ The Edge TPU works with quantized models. Quantization makes models smaller and
Here are the key features that make TFLite Edge TPU a great model format choice for developers:
-- **Optimized Performance on Edge Devices**: The TFLite Edge TPU achieves high-speed neural networking performance through quantization, model optimization, hardware acceleration, and compiler optimization. Its minimalistic architecture contributes to its smaller size and cost-efficiency.
+- **Optimized Performance on Edge Devices**: The TFLite Edge TPU achieves high-speed neural networking performance through quantization, model optimization, hardware acceleration, and compiler optimization. Its minimalistic architecture contributes to its smaller size and cost-efficiency.
- **High Computational Throughput**: TFLite Edge TPU combines specialized hardware acceleration and efficient runtime execution to achieve high computational throughput. It is well-suited for deploying machine learning models with stringent performance requirements on edge devices.
@@ -38,9 +38,9 @@ TFLite Edge TPU offers various deployment options for machine learning models, i
- **On-Device Deployment**: TensorFlow Edge TPU models can be directly deployed on mobile and embedded devices. On-device deployment allows the models to execute directly on the hardware, eliminating the need for cloud connectivity.
-- **Edge Computing with Cloud TensorFlow TPUs**: In scenarios where edge devices have limited processing capabilities, TensorFlow Edge TPUs can offload inference tasks to cloud servers equipped with TPUs.
+- **Edge Computing with Cloud TensorFlow TPUs**: In scenarios where edge devices have limited processing capabilities, TensorFlow Edge TPUs can offload inference tasks to cloud servers equipped with TPUs.
-- **Hybrid Deployment**: A hybrid approach combines on-device and cloud deployment and offers a versatile and scalable solution for deploying machine learning models. Advantages include on-device processing for quick responses and cloud computing for more complex computations.
+- **Hybrid Deployment**: A hybrid approach combines on-device and cloud deployment and offers a versatile and scalable solution for deploying machine learning models. Advantages include on-device processing for quick responses and cloud computing for more complex computations.
## Exporting YOLOv8 Models to TFLite Edge TPU
@@ -99,7 +99,7 @@ For more details about supported export options, visit the [Ultralytics document
## Deploying Exported YOLOv8 TFLite Edge TPU Models
-After successfully exporting your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to TFLite Edge TPU format, you can now deploy them. The primary and recommended first step for running a TFLite Edge TPU model is to use the YOLO("model_edgetpu.tflite") method, as outlined in the previous usage code snippet.
+After successfully exporting your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to TFLite Edge TPU format, you can now deploy them. The primary and recommended first step for running a TFLite Edge TPU model is to use the YOLO("model_edgetpu.tflite") method, as outlined in the previous usage code snippet.
However, for in-depth instructions on deploying your TFLite Edge TPU models, take a look at the following resources:
@@ -111,7 +111,7 @@ However, for in-depth instructions on deploying your TFLite Edge TPU models, tak
## Summary
-In this guide, we’ve learned how to export Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to TFLite Edge TPU format. By following the steps mentioned above, you can increase the speed and power of your computer vision applications.
+In this guide, we’ve learned how to export Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to TFLite Edge TPU format. By following the steps mentioned above, you can increase the speed and power of your computer vision applications.
For further details on usage, visit the [Edge TPU official website](https://cloud.google.com/edge-tpu).
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/index.md b/docs/en/integrations/index.md
index c16a10ec..cc8fb7a0 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/index.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/index.md
@@ -64,7 +64,7 @@ Welcome to the Ultralytics Integrations page! This page provides an overview of
- [CoreML](coreml.md): CoreML, developed by [Apple](https://www.apple.com/), is a framework designed for efficiently integrating machine learning models into applications across iOS, macOS, watchOS, and tvOS, using Apple's hardware for effective and secure model deployment.
- [TF SavedModel](tf-savedmodel.md): Developed by [Google](https://www.google.com), TF SavedModel is a universal serialization format for TensorFlow models, enabling easy sharing and deployment across a wide range of platforms, from servers to edge devices.
-
+
- [TF GraphDef](tf-graphdef.md): Developed by [Google](https://www.google.com), GraphDef is TensorFlow's format for representing computation graphs, enabling optimized execution of machine learning models across diverse hardware.
- [TFLite](tflite.md): Developed by [Google](https://www.google.com), TFLite is a lightweight framework for deploying machine learning models on mobile and edge devices, ensuring fast, efficient inference with minimal memory footprint.
@@ -72,7 +72,7 @@ Welcome to the Ultralytics Integrations page! This page provides an overview of
- [TFLite Edge TPU](edge-tpu.md): Developed by [Google](https://www.google.com) for optimizing TensorFlow Lite models on Edge TPUs, this model format ensures high-speed, efficient edge computing.
- [PaddlePaddle](paddlepaddle.md): An open-source deep learning platform by [Baidu](https://www.baidu.com/), PaddlePaddle enables the efficient deployment of AI models and focuses on the scalability of industrial applications.
-
+
- [NCNN](ncnn.md): Developed by [Tencent](http://www.tencent.com/), NCNN is an efficient neural network inference framework tailored for mobile devices. It enables direct deployment of AI models into apps, optimizing performance across various mobile platforms.
### Export Formats
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/paddlepaddle.md b/docs/en/integrations/paddlepaddle.md
index f41116fb..bc8ccead 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/paddlepaddle.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/paddlepaddle.md
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ The ability to export to PaddlePaddle model format allows you to optimize your [
 -Developed by Baidu, [PaddlePaddle](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/en) (**PA**rallel **D**istributed **D**eep **LE**arning) is China's first open-source deep learning platform. Unlike some frameworks built mainly for research, PaddlePaddle prioritizes ease of use and smooth integration across industries.
+Developed by Baidu, [PaddlePaddle](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/en) (**PA**rallel **D**istributed **D**eep **LE**arning) is China's first open-source deep learning platform. Unlike some frameworks built mainly for research, PaddlePaddle prioritizes ease of use and smooth integration across industries.
It offers tools and resources similar to popular frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch, making it accessible for developers of all experience levels. From farming and factories to service businesses, PaddlePaddle's large developer community of over 4.77 million is helping create and deploy AI applications.
@@ -26,11 +26,11 @@ By exporting your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to PaddlePaddle format, you can tap
PaddlePaddle models offer a range of key features that contribute to their flexibility, performance, and scalability across diverse deployment scenarios:
- - **Dynamic-to-Static Graph**: PaddlePaddle supports [dynamic-to-static compilation](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/en/guides/jit/index_en.html), where models can be translated into a static computational graph. This enables optimizations that reduce runtime overhead and boost inference performance.
+- **Dynamic-to-Static Graph**: PaddlePaddle supports [dynamic-to-static compilation](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/en/guides/jit/index_en.html), where models can be translated into a static computational graph. This enables optimizations that reduce runtime overhead and boost inference performance.
- - **Operator Fusion**: PaddlePaddle, like TensorRT, uses [operator fusion](https://developer.nvidia.com/gtc/2020/video/s21436-vid) to streamline computation and reduce overhead. The framework minimizes memory transfers and computational steps by merging compatible operations, resulting in faster inference.
+- **Operator Fusion**: PaddlePaddle, like TensorRT, uses [operator fusion](https://developer.nvidia.com/gtc/2020/video/s21436-vid) to streamline computation and reduce overhead. The framework minimizes memory transfers and computational steps by merging compatible operations, resulting in faster inference.
- - **Quantization**: PaddlePaddle supports [quantization techniques](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/en/api/paddle/quantization/PTQ_en.html), including post-training quantization and quantization-aware training. These techniques allow for the use of lower-precision data representations, effectively boosting performance and reducing model size.
+- **Quantization**: PaddlePaddle supports [quantization techniques](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/en/api/paddle/quantization/PTQ_en.html), including post-training quantization and quantization-aware training. These techniques allow for the use of lower-precision data representations, effectively boosting performance and reducing model size.
## Deployment Options in PaddlePaddle
@@ -103,7 +103,7 @@ For more details about supported export options, visit the [Ultralytics document
## Deploying Exported YOLOv8 PaddlePaddle Models
-After successfully exporting your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to PaddlePaddle format, you can now deploy them. The primary and recommended first step for running a PaddlePaddle model is to use the YOLO("./model_paddle_model") method, as outlined in the previous usage code snippet.
+After successfully exporting your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to PaddlePaddle format, you can now deploy them. The primary and recommended first step for running a PaddlePaddle model is to use the YOLO("./model_paddle_model") method, as outlined in the previous usage code snippet.
However, for in-depth instructions on deploying your PaddlePaddle models in various other settings, take a look at the following resources:
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/tf-graphdef.md b/docs/en/integrations/tf-graphdef.md
index cd167272..f7d3fdb6 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/tf-graphdef.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/tf-graphdef.md
@@ -20,17 +20,17 @@ GraphDef models can use hardware accelerators such as GPUs, TPUs, and AI chips,
## Key Features of TF GraphDef Models
-TF GraphDef offers distinct features for streamlining model deployment and optimization.
+TF GraphDef offers distinct features for streamlining model deployment and optimization.
Here's a look at its key characteristics:
- - **Model Serialization**: TF GraphDef provides a way to serialize and store TensorFlow models in a platform-independent format. This serialized representation allows you to load and execute your models without the original Python codebase, making deployment easier.
+- **Model Serialization**: TF GraphDef provides a way to serialize and store TensorFlow models in a platform-independent format. This serialized representation allows you to load and execute your models without the original Python codebase, making deployment easier.
- - **Graph Optimization**: TF GraphDef enables the optimization of computational graphs. These optimizations can boost performance by streamlining execution flow, reducing redundancies, and tailoring operations to suit specific hardware.
+- **Graph Optimization**: TF GraphDef enables the optimization of computational graphs. These optimizations can boost performance by streamlining execution flow, reducing redundancies, and tailoring operations to suit specific hardware.
- - **Deployment Flexibility**: Models exported to the GraphDef format can be used in various environments, including resource-constrained devices, web browsers, and systems with specialized hardware. This opens up possibilities for wider deployment of your TensorFlow models.
+- **Deployment Flexibility**: Models exported to the GraphDef format can be used in various environments, including resource-constrained devices, web browsers, and systems with specialized hardware. This opens up possibilities for wider deployment of your TensorFlow models.
- - **Production Focus**: GraphDef is designed for production deployment. It supports efficient execution, serialization features, and optimizations that align with real-world use cases.
+- **Production Focus**: GraphDef is designed for production deployment. It supports efficient execution, serialization features, and optimizations that align with real-world use cases.
## Deployment Options with TF GraphDef
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ Here's how you can deploy with TF GraphDef efficiently across various platforms.
- **Web Browsers:** TensorFlow.js enables the deployment of TF GraphDef models directly within web browsers. It paves the way for real-time object detection applications running on the client side, using the capabilities of YOLOv8 through JavaScript.
-- **Specialized Hardware:** TF GraphDef's platform-agnostic nature allows it to target custom hardware, such as accelerators and TPUs (Tensor Processing Units). These devices can provide performance advantages for computationally intensive models.
+- **Specialized Hardware:** TF GraphDef's platform-agnostic nature allows it to target custom hardware, such as accelerators and TPUs (Tensor Processing Units). These devices can provide performance advantages for computationally intensive models.
## Exporting YOLOv8 Models to TF GraphDef
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/tf-savedmodel.md b/docs/en/integrations/tf-savedmodel.md
index 750357b6..50a4f228 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/tf-savedmodel.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/tf-savedmodel.md
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ Here are the key features that make TF SavedModel a great option for AI develope
## Deployment Options with TF SavedModel
-Before we dive into the process of exporting YOLOv8 models to the TF SavedModel format, let's explore some typical deployment scenarios where this format is used.
+Before we dive into the process of exporting YOLOv8 models to the TF SavedModel format, let's explore some typical deployment scenarios where this format is used.
TF SavedModel provides a range of options to deploy your machine learning models:
@@ -63,7 +63,6 @@ To install the required package, run:
For detailed instructions and best practices related to the installation process, check our [Ultralytics Installation guide](../quickstart.md). While installing the required packages for YOLOv8, if you encounter any difficulties, consult our [Common Issues guide](../guides/yolo-common-issues.md) for solutions and tips.
-
### Usage
Before diving into the usage instructions, it's important to note that while all [Ultralytics YOLOv8 models](../models/index.md) are available for exporting, you can ensure that the model you select supports export functionality [here](../modes/export.md).
diff --git a/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md b/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md
index f8d400e2..b87f2571 100644
--- a/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md
+++ b/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md
@@ -36,16 +36,16 @@ This section details the models available with their specific pre-trained weight
All the YOLOv8-World weights have been directly migrated from the official [YOLO-World](https://github.com/AILab-CVC/YOLO-World) repository, highlighting their excellent contributions.
-| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
-|-----------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------|-----------|------------|----------|--------|
-| YOLOv8s-world | [yolov8s-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8s-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
-| YOLOv8s-worldv2 | [yolov8s-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8s-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
-| YOLOv8m-world | [yolov8m-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8m-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
-| YOLOv8m-worldv2 | [yolov8m-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8m-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
-| YOLOv8l-world | [yolov8l-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8l-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
-| YOLOv8l-worldv2 | [yolov8l-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8l-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
-| YOLOv8x-world | [yolov8x-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8x-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
-| YOLOv8x-worldv2 | [yolov8x-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8x-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
+| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
+|-----------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------|-----------|------------|----------|--------|
+| YOLOv8s-world | [yolov8s-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8s-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
+| YOLOv8s-worldv2 | [yolov8s-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8s-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
+| YOLOv8m-world | [yolov8m-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8m-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
+| YOLOv8m-worldv2 | [yolov8m-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8m-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
+| YOLOv8l-world | [yolov8l-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8l-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
+| YOLOv8l-worldv2 | [yolov8l-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8l-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
+| YOLOv8x-world | [yolov8x-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8x-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
+| YOLOv8x-worldv2 | [yolov8x-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8x-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
## Zero-shot Transfer on COCO Dataset
diff --git a/docs/en/models/yolov9.md b/docs/en/models/yolov9.md
index 51ddfff8..da53ca2d 100644
--- a/docs/en/models/yolov9.md
+++ b/docs/en/models/yolov9.md
@@ -58,21 +58,37 @@ The performance of YOLOv9 on the [COCO dataset](../datasets/detect/coco.md) exem
**Table 1. Comparison of State-of-the-Art Real-Time Object Detectors**
-| Model | size
-Developed by Baidu, [PaddlePaddle](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/en) (**PA**rallel **D**istributed **D**eep **LE**arning) is China's first open-source deep learning platform. Unlike some frameworks built mainly for research, PaddlePaddle prioritizes ease of use and smooth integration across industries.
+Developed by Baidu, [PaddlePaddle](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/en) (**PA**rallel **D**istributed **D**eep **LE**arning) is China's first open-source deep learning platform. Unlike some frameworks built mainly for research, PaddlePaddle prioritizes ease of use and smooth integration across industries.
It offers tools and resources similar to popular frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch, making it accessible for developers of all experience levels. From farming and factories to service businesses, PaddlePaddle's large developer community of over 4.77 million is helping create and deploy AI applications.
@@ -26,11 +26,11 @@ By exporting your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to PaddlePaddle format, you can tap
PaddlePaddle models offer a range of key features that contribute to their flexibility, performance, and scalability across diverse deployment scenarios:
- - **Dynamic-to-Static Graph**: PaddlePaddle supports [dynamic-to-static compilation](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/en/guides/jit/index_en.html), where models can be translated into a static computational graph. This enables optimizations that reduce runtime overhead and boost inference performance.
+- **Dynamic-to-Static Graph**: PaddlePaddle supports [dynamic-to-static compilation](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/en/guides/jit/index_en.html), where models can be translated into a static computational graph. This enables optimizations that reduce runtime overhead and boost inference performance.
- - **Operator Fusion**: PaddlePaddle, like TensorRT, uses [operator fusion](https://developer.nvidia.com/gtc/2020/video/s21436-vid) to streamline computation and reduce overhead. The framework minimizes memory transfers and computational steps by merging compatible operations, resulting in faster inference.
+- **Operator Fusion**: PaddlePaddle, like TensorRT, uses [operator fusion](https://developer.nvidia.com/gtc/2020/video/s21436-vid) to streamline computation and reduce overhead. The framework minimizes memory transfers and computational steps by merging compatible operations, resulting in faster inference.
- - **Quantization**: PaddlePaddle supports [quantization techniques](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/en/api/paddle/quantization/PTQ_en.html), including post-training quantization and quantization-aware training. These techniques allow for the use of lower-precision data representations, effectively boosting performance and reducing model size.
+- **Quantization**: PaddlePaddle supports [quantization techniques](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/en/api/paddle/quantization/PTQ_en.html), including post-training quantization and quantization-aware training. These techniques allow for the use of lower-precision data representations, effectively boosting performance and reducing model size.
## Deployment Options in PaddlePaddle
@@ -103,7 +103,7 @@ For more details about supported export options, visit the [Ultralytics document
## Deploying Exported YOLOv8 PaddlePaddle Models
-After successfully exporting your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to PaddlePaddle format, you can now deploy them. The primary and recommended first step for running a PaddlePaddle model is to use the YOLO("./model_paddle_model") method, as outlined in the previous usage code snippet.
+After successfully exporting your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to PaddlePaddle format, you can now deploy them. The primary and recommended first step for running a PaddlePaddle model is to use the YOLO("./model_paddle_model") method, as outlined in the previous usage code snippet.
However, for in-depth instructions on deploying your PaddlePaddle models in various other settings, take a look at the following resources:
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/tf-graphdef.md b/docs/en/integrations/tf-graphdef.md
index cd167272..f7d3fdb6 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/tf-graphdef.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/tf-graphdef.md
@@ -20,17 +20,17 @@ GraphDef models can use hardware accelerators such as GPUs, TPUs, and AI chips,
## Key Features of TF GraphDef Models
-TF GraphDef offers distinct features for streamlining model deployment and optimization.
+TF GraphDef offers distinct features for streamlining model deployment and optimization.
Here's a look at its key characteristics:
- - **Model Serialization**: TF GraphDef provides a way to serialize and store TensorFlow models in a platform-independent format. This serialized representation allows you to load and execute your models without the original Python codebase, making deployment easier.
+- **Model Serialization**: TF GraphDef provides a way to serialize and store TensorFlow models in a platform-independent format. This serialized representation allows you to load and execute your models without the original Python codebase, making deployment easier.
- - **Graph Optimization**: TF GraphDef enables the optimization of computational graphs. These optimizations can boost performance by streamlining execution flow, reducing redundancies, and tailoring operations to suit specific hardware.
+- **Graph Optimization**: TF GraphDef enables the optimization of computational graphs. These optimizations can boost performance by streamlining execution flow, reducing redundancies, and tailoring operations to suit specific hardware.
- - **Deployment Flexibility**: Models exported to the GraphDef format can be used in various environments, including resource-constrained devices, web browsers, and systems with specialized hardware. This opens up possibilities for wider deployment of your TensorFlow models.
+- **Deployment Flexibility**: Models exported to the GraphDef format can be used in various environments, including resource-constrained devices, web browsers, and systems with specialized hardware. This opens up possibilities for wider deployment of your TensorFlow models.
- - **Production Focus**: GraphDef is designed for production deployment. It supports efficient execution, serialization features, and optimizations that align with real-world use cases.
+- **Production Focus**: GraphDef is designed for production deployment. It supports efficient execution, serialization features, and optimizations that align with real-world use cases.
## Deployment Options with TF GraphDef
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ Here's how you can deploy with TF GraphDef efficiently across various platforms.
- **Web Browsers:** TensorFlow.js enables the deployment of TF GraphDef models directly within web browsers. It paves the way for real-time object detection applications running on the client side, using the capabilities of YOLOv8 through JavaScript.
-- **Specialized Hardware:** TF GraphDef's platform-agnostic nature allows it to target custom hardware, such as accelerators and TPUs (Tensor Processing Units). These devices can provide performance advantages for computationally intensive models.
+- **Specialized Hardware:** TF GraphDef's platform-agnostic nature allows it to target custom hardware, such as accelerators and TPUs (Tensor Processing Units). These devices can provide performance advantages for computationally intensive models.
## Exporting YOLOv8 Models to TF GraphDef
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/tf-savedmodel.md b/docs/en/integrations/tf-savedmodel.md
index 750357b6..50a4f228 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/tf-savedmodel.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/tf-savedmodel.md
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ Here are the key features that make TF SavedModel a great option for AI develope
## Deployment Options with TF SavedModel
-Before we dive into the process of exporting YOLOv8 models to the TF SavedModel format, let's explore some typical deployment scenarios where this format is used.
+Before we dive into the process of exporting YOLOv8 models to the TF SavedModel format, let's explore some typical deployment scenarios where this format is used.
TF SavedModel provides a range of options to deploy your machine learning models:
@@ -63,7 +63,6 @@ To install the required package, run:
For detailed instructions and best practices related to the installation process, check our [Ultralytics Installation guide](../quickstart.md). While installing the required packages for YOLOv8, if you encounter any difficulties, consult our [Common Issues guide](../guides/yolo-common-issues.md) for solutions and tips.
-
### Usage
Before diving into the usage instructions, it's important to note that while all [Ultralytics YOLOv8 models](../models/index.md) are available for exporting, you can ensure that the model you select supports export functionality [here](../modes/export.md).
diff --git a/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md b/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md
index f8d400e2..b87f2571 100644
--- a/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md
+++ b/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md
@@ -36,16 +36,16 @@ This section details the models available with their specific pre-trained weight
All the YOLOv8-World weights have been directly migrated from the official [YOLO-World](https://github.com/AILab-CVC/YOLO-World) repository, highlighting their excellent contributions.
-| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
-|-----------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------|-----------|------------|----------|--------|
-| YOLOv8s-world | [yolov8s-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8s-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
-| YOLOv8s-worldv2 | [yolov8s-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8s-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
-| YOLOv8m-world | [yolov8m-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8m-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
-| YOLOv8m-worldv2 | [yolov8m-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8m-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
-| YOLOv8l-world | [yolov8l-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8l-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
-| YOLOv8l-worldv2 | [yolov8l-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8l-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
-| YOLOv8x-world | [yolov8x-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8x-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
-| YOLOv8x-worldv2 | [yolov8x-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8x-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
+| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
+|-----------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------|-----------|------------|----------|--------|
+| YOLOv8s-world | [yolov8s-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8s-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
+| YOLOv8s-worldv2 | [yolov8s-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8s-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
+| YOLOv8m-world | [yolov8m-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8m-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
+| YOLOv8m-worldv2 | [yolov8m-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8m-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
+| YOLOv8l-world | [yolov8l-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8l-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
+| YOLOv8l-worldv2 | [yolov8l-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8l-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
+| YOLOv8x-world | [yolov8x-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8x-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
+| YOLOv8x-worldv2 | [yolov8x-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8x-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
## Zero-shot Transfer on COCO Dataset
diff --git a/docs/en/models/yolov9.md b/docs/en/models/yolov9.md
index 51ddfff8..da53ca2d 100644
--- a/docs/en/models/yolov9.md
+++ b/docs/en/models/yolov9.md
@@ -58,21 +58,37 @@ The performance of YOLOv9 on the [COCO dataset](../datasets/detect/coco.md) exem
**Table 1. Comparison of State-of-the-Art Real-Time Object Detectors**
-| Model | size
(pixels) | APval
50-95 | APval
50 | APval
75 | params
(M) | FLOPs
(B) |
-|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------|---------------------|------------------|------------------|--------------------|-------------------|
-| YOLOv9-S | 640 | 46.8 | 63.4 | 50.7 | 7.2 | 26.7 |
-| YOLOv9-M | 640 | 51.4 | 68.1 | 56.1 | 20.1 | 76.8 |
-| [YOLOv9-C](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov9c.pt) | 640 | 53.0 | 70.2 | 57.8 | 25.5 | 102.8 |
-| [YOLOv9-E](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov9e.pt) | 640 | 55.6 | 72.8 | 60.6 | 58.1 | 192.5 |
+??? question "When will other model scales be available?"
-YOLOv9's iterations, ranging from the smaller S variant to the extensive E model, demonstrate improvements not only in accuracy (AP metrics) but also in efficiency with a reduced number of parameters and computational needs (FLOPs). This table underscores YOLOv9's ability to deliver high precision while maintaining or reducing the computational overhead compared to prior versions and competing models.
+ Despite all metrics shown for the various model scales in the table below, **only** the configurations for `YOLOv9c` and `YOLOv9e` have been published. The Ultralytics Team will work swiftly to add other configurations as they become available, so be sure to check back here regularly for updates.
+
+!!! tip "Performance"
+
+ === "Detection (COCO)"
+
+ | Model | size
(pixels) | mAPval
50-95 | mAPval
50 | params
(M) | FLOPs
(B) |
+ |---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------|----------------------|-------------------|--------------------|-------------------|
+ | YOLOv9t | 640 | 38.3 | 53.1 | 2.0 | 7.7 |
+ | YOLOv9s | 640 | 46.8 | 63.4 | 7.2 | 26.7 |
+ | YOLOv9m | 640 | 51.4 | 68.1 | 20.1 | 76.8 |
+ | [YOLOv9c](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov9c.pt) | 640 | 53.0 | 70.2 | 25.5 | 102.8 |
+ | [YOLOv9e](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov9e.pt) | 640 | 55.6 | 72.8 | 58.1 | 192.5 |
+
+ === "Segmentation (COCO)"
+
+ | Model | size
(pixels) | mAPbox
50-95 | mAPmask
50-95 | params
(M) | FLOPs
(B) |
+ |-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------|----------------------|-----------------------|--------------------|-------------------|
+ | [YOLOv9c-seg](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov9c-seg.pt) | 640 | 52.4 | 42.2 | 27.9 | 159.4 |
+ | [YOLOv9e-seg](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov9e-seg.pt) | 640 | 55.1 | 44.3 | 60.5 | 248.4 |
+
+YOLOv9's iterations, ranging from the tiny `t` variant to the extensive `e` model, demonstrate improvements not only in accuracy (mAP metrics) but also in efficiency with a reduced number of parameters and computational needs (FLOPs). This table underscores YOLOv9's ability to deliver high precision while maintaining or reducing the computational overhead compared to prior versions and competing models.
Comparatively, YOLOv9 exhibits remarkable gains:
-- **Lightweight Models**: YOLOv9-S surpasses the YOLO MS-S in parameter efficiency and computational load while achieving an improvement of 0.4∼0.6% in AP.
-- **Medium to Large Models**: YOLOv9-M and YOLOv9-E show notable advancements in balancing the trade-off between model complexity and detection performance, offering significant reductions in parameters and computations against the backdrop of improved accuracy.
+- **Lightweight Models**: YOLOv9s surpasses the YOLO MS-S in parameter efficiency and computational load while achieving an improvement of 0.4∼0.6% in AP.
+- **Medium to Large Models**: YOLOv9m and YOLOv9e show notable advancements in balancing the trade-off between model complexity and detection performance, offering significant reductions in parameters and computations against the backdrop of improved accuracy.
-The YOLOv9-C model, in particular, highlights the effectiveness of the architecture's optimizations. It operates with 42% fewer parameters and 21% less computational demand than YOLOv7 AF, yet it achieves comparable accuracy, demonstrating YOLOv9's significant efficiency improvements. Furthermore, the YOLOv9-E model sets a new standard for large models, with 15% fewer parameters and 25% less computational need than [YOLOv8x](yolov8.md), alongside a substantial 1.7% improvement in AP.
+The YOLOv9c model, in particular, highlights the effectiveness of the architecture's optimizations. It operates with 42% fewer parameters and 21% less computational demand than YOLOv7 AF, yet it achieves comparable accuracy, demonstrating YOLOv9's significant efficiency improvements. Furthermore, the YOLOv9e model sets a new standard for large models, with 15% fewer parameters and 25% less computational need than [YOLOv8x](yolov8.md), alongside a incremental 1.7% improvement in AP.
These results showcase YOLOv9's strategic advancements in model design, emphasizing its enhanced efficiency without compromising on the precision essential for real-time object detection tasks. The model not only pushes the boundaries of performance metrics but also emphasizes the importance of computational efficiency, making it a pivotal development in the field of computer vision.
@@ -125,13 +141,17 @@ This example provides simple YOLOv9 training and inference examples. For full do
The YOLOv9 series offers a range of models, each optimized for high-performance [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md). These models cater to varying computational needs and accuracy requirements, making them versatile for a wide array of applications.
-| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
-|------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------|-----------|------------|----------|--------|
-| YOLOv9-C | [yolov9c.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov9c.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
-| YOLOv9-E | [yolov9e.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov9e.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
+| Model | Filenames | Tasks | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
+|------------|-----------------------------------|----------------------------------------------|-----------|------------|----------|--------|
+| YOLOv9 | `yolov9c.pt` `yolov9e.pt` | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
+| YOLOv9-seg | `yolov9c-seg.pt` `yolov9e-seg.pt` | [Instance Segmentation](../tasks/segment.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
This table provides a detailed overview of the YOLOv9 model variants, highlighting their capabilities in object detection tasks and their compatibility with various operational modes such as [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md). This comprehensive support ensures that users can fully leverage the capabilities of YOLOv9 models in a broad range of object detection scenarios.
+!!! note
+
+ Training YOLOv9 models will require _more_ resources **and** take longer than the equivalent sized [YOLOv8 model](yolov8.md).
+
## Citations and Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the YOLOv9 authors for their significant contributions in the field of real-time object detection:
diff --git a/docs/en/modes/predict.md b/docs/en/modes/predict.md
index ea175b0b..7b36783e 100644
--- a/docs/en/modes/predict.md
+++ b/docs/en/modes/predict.md
@@ -364,7 +364,7 @@ Inference arguments:
|-----------------|----------------|------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| `source` | `str` | `'ultralytics/assets'` | Specifies the data source for inference. Can be an image path, video file, directory, URL, or device ID for live feeds. Supports a wide range of formats and sources, enabling flexible application across different types of input. |
| `conf` | `float` | `0.25` | Sets the minimum confidence threshold for detections. Objects detected with confidence below this threshold will be disregarded. Adjusting this value can help reduce false positives. |
-| `iou` | `float` | `0.7` | Intersection Over Union (IoU) threshold for Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS). Lower values result in fewer detections by eliminating overlapping boxes, useful for reducing duplicates. |
+| `iou` | `float` | `0.7` | Intersection Over Union (IoU) threshold for Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS). Lower values result in fewer detections by eliminating overlapping boxes, useful for reducing duplicates. |
| `imgsz` | `int or tuple` | `640` | Defines the image size for inference. Can be a single integer `640` for square resizing or a (height, width) tuple. Proper sizing can improve detection accuracy and processing speed. |
| `half` | `bool` | `False` | Enables half-precision (FP16) inference, which can speed up model inference on supported GPUs with minimal impact on accuracy. |
| `device` | `str` | `None` | Specifies the device for inference (e.g., `cpu`, `cuda:0` or `0`). Allows users to select between CPU, a specific GPU, or other compute devices for model execution. |
diff --git a/docs/en/reference/solutions/queue_management.md b/docs/en/reference/solutions/queue_management.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..14094a34
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/en/reference/solutions/queue_management.md
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
+---
+description: Discover Ultralytics YOLO's AI Queue Management for retail, using advanced machine learning to enhance customer experience with real-time queue analysis and wait time predictions.
+keywords: Ultralytics, YOLO, AI Queue Management, retail analytics, queue detection, wait time prediction, machine learning, YOLOv8, customer experience
+---
+
+# Reference for `ultralytics/solutions/queue_management.py`
+
+!!! Note
+
+ This file is available at [https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/solutions/queue_management.py](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/solutions/queue_management.py). If you spot a problem please help fix it by [contributing](https://docs.ultralytics.com/help/contributing/) a [Pull Request](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/edit/main/ultralytics/solutions/queue_management.py) 🛠️. Thank you 🙏!
+
+
+
+## ::: ultralytics.solutions.queue_management.QueueManager
+
+
diff --git a/docs/en/usage/simple-utilities.md b/docs/en/usage/simple-utilities.md
index c170f519..f4d43286 100644
--- a/docs/en/usage/simple-utilities.md
+++ b/docs/en/usage/simple-utilities.md
@@ -211,7 +211,8 @@ boxes.bboxes
See the [`Bboxes` reference section](../reference/utils/instance.md#ultralytics.utils.instance.Bboxes) for more attributes and methods available.
!!! tip
- Many of the following functions (and more) can be accessed using the [`Bboxes` class](#bounding-box-horizontal-instances) but if you prefer to work with the functions directly, see the next subsections on how to import these independently.
+
+ Many of the following functions (and more) can be accessed using the [`Bboxes` class](#bounding-box-horizontal-instances) but if you prefer to work with the functions directly, see the next subsections on how to import these independently.
### Scaling Boxes
@@ -258,7 +259,7 @@ new_boxes#(1)!
1. Bounding boxes scaled for the new image size
-### Bounding Box Format Conversions
+### Bounding Box Format Conversions
#### XYXY → XYWH
@@ -351,6 +352,7 @@ image_with_bboxes = ann.result()
1. Names can be used from `model.names` when [working with detection results](../modes/predict.md#working-with-results)
#### Oriented Bounding Boxes (OBB)
+
```python
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
@@ -387,7 +389,7 @@ image_with_obb = ann.result()
See the [`Annotator` Reference Page](../reference/utils/plotting.md#ultralytics.utils.plotting.Annotator) for additional insight.
-## Miscellaneous
+## Miscellaneous
### Code Profiling
diff --git a/docs/mkdocs_github_authors.yaml b/docs/mkdocs_github_authors.yaml
index 8c1c476a..2ac8014e 100644
--- a/docs/mkdocs_github_authors.yaml
+++ b/docs/mkdocs_github_authors.yaml
@@ -16,6 +16,7 @@ abirami.vina@gmail.com: abirami-vina
ayush.chaurarsia@gmail.com: AyushExel
chr043416@gmail.com: RizwanMunawar
glenn.jocher@ultralytics.com: glenn-jocher
+lakshanthad@yahoo.com: lakshanthad
muhammadrizwanmunawar123@gmail.com: RizwanMunawar
not.committed.yet: null
plashchynski@gmail.com: plashchynski
diff --git a/mkdocs.yml b/mkdocs.yml
index 594cc6a0..5984197f 100644
--- a/mkdocs.yml
+++ b/mkdocs.yml
@@ -300,7 +300,7 @@ nav:
- Conda Quickstart: guides/conda-quickstart.md
- Docker Quickstart: guides/docker-quickstart.md
- Raspberry Pi: guides/raspberry-pi.md
- - NVIDIA Jetson: guides/nvidia-jetson.md
+ - NVIDIA Jetson: guides/nvidia-jetson.md
- Triton Inference Server: guides/triton-inference-server.md
- Isolating Segmentation Objects: guides/isolating-segmentation-objects.md
- Edge TPU on Raspberry Pi: guides/coral-edge-tpu-on-raspberry-pi.md
@@ -512,6 +512,7 @@ nav:
- distance_calculation: reference/solutions/distance_calculation.md
- heatmap: reference/solutions/heatmap.md
- object_counter: reference/solutions/object_counter.md
+ - queue_management: reference/solutions/queue_management.md
- speed_estimation: reference/solutions/speed_estimation.md
- trackers:
- basetrack: reference/trackers/basetrack.md
diff --git a/ultralytics/__init__.py b/ultralytics/__init__.py
index 3155de0d..5b732067 100644
--- a/ultralytics/__init__.py
+++ b/ultralytics/__init__.py
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
-__version__ = "8.1.41"
+__version__ = "8.1.42"
from ultralytics.data.explorer.explorer import Explorer
from ultralytics.models import RTDETR, SAM, YOLO, YOLOWorld
diff --git a/ultralytics/cfg/models/v9/yolov9c-seg.yaml b/ultralytics/cfg/models/v9/yolov9c-seg.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f26ced8c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/ultralytics/cfg/models/v9/yolov9c-seg.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
+# YOLOv9c-seg
+# 654 layers, 27897120 parameters, 159.4 GFLOPs
+
+# parameters
+nc: 80 # number of classes
+
+# gelan backbone
+backbone:
+ - [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
+ - [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [256, 128, 64, 1]] # 2
+ - [-1, 1, ADown, [256]] # 3-P3/8
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 256, 128, 1]] # 4
+ - [-1, 1, ADown, [512]] # 5-P4/16
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]] # 6
+ - [-1, 1, ADown, [512]] # 7-P5/32
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]] # 8
+ - [-1, 1, SPPELAN, [512, 256]] # 9
+
+head:
+ - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
+ - [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]] # 12
+
+ - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
+ - [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [256, 256, 128, 1]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
+
+ - [-1, 1, ADown, [256]]
+ - [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
+
+ - [-1, 1, ADown, [512]]
+ - [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 1]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
+
+ - [[15, 18, 21], 1, Segment, [nc, 32, 256]] # Segment(P3, P4, P5)
diff --git a/ultralytics/cfg/models/v9/yolov9c.yaml b/ultralytics/cfg/models/v9/yolov9c.yaml
index 66c02d64..713477b6 100644
--- a/ultralytics/cfg/models/v9/yolov9c.yaml
+++ b/ultralytics/cfg/models/v9/yolov9c.yaml
@@ -1,4 +1,6 @@
-# YOLOv9
+# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
+# YOLOv9c
+# 618 layers, 25590912 parameters, 104.0 GFLOPs
# parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
diff --git a/ultralytics/cfg/models/v9/yolov9e-seg.yaml b/ultralytics/cfg/models/v9/yolov9e-seg.yaml
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..88ba2019
--- /dev/null
+++ b/ultralytics/cfg/models/v9/yolov9e-seg.yaml
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
+# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
+# YOLOv9c-seg
+# 1261 layers, 60512800 parameters, 248.4 GFLOPs
+
+# parameters
+nc: 80 # number of classes
+
+# gelan backbone
+backbone:
+ - [-1, 1, Silence, []]
+ - [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 1-P1/2
+ - [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 2-P2/4
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [256, 128, 64, 2]] # 3
+ - [-1, 1, ADown, [256]] # 4-P3/8
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 256, 128, 2]] # 5
+ - [-1, 1, ADown, [512]] # 6-P4/16
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [1024, 512, 256, 2]] # 7
+ - [-1, 1, ADown, [1024]] # 8-P5/32
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [1024, 512, 256, 2]] # 9
+
+ - [1, 1, CBLinear, [[64]]] # 10
+ - [3, 1, CBLinear, [[64, 128]]] # 11
+ - [5, 1, CBLinear, [[64, 128, 256]]] # 12
+ - [7, 1, CBLinear, [[64, 128, 256, 512]]] # 13
+ - [9, 1, CBLinear, [[64, 128, 256, 512, 1024]]] # 14
+
+ - [0, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 15-P1/2
+ - [[10, 11, 12, 13, 14, -1], 1, CBFuse, [[0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]] # 16
+ - [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 17-P2/4
+ - [[11, 12, 13, 14, -1], 1, CBFuse, [[1, 1, 1, 1]]] # 18
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [256, 128, 64, 2]] # 19
+ - [-1, 1, ADown, [256]] # 20-P3/8
+ - [[12, 13, 14, -1], 1, CBFuse, [[2, 2, 2]]] # 21
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 256, 128, 2]] # 22
+ - [-1, 1, ADown, [512]] # 23-P4/16
+ - [[13, 14, -1], 1, CBFuse, [[3, 3]]] # 24
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [1024, 512, 256, 2]] # 25
+ - [-1, 1, ADown, [1024]] # 26-P5/32
+ - [[14, -1], 1, CBFuse, [[4]]] # 27
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [1024, 512, 256, 2]] # 28
+ - [-1, 1, SPPELAN, [512, 256]] # 29
+
+# gelan head
+head:
+ - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
+ - [[-1, 25], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 2]] # 32
+
+ - [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
+ - [[-1, 22], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [256, 256, 128, 2]] # 35 (P3/8-small)
+
+ - [-1, 1, ADown, [256]]
+ - [[-1, 32], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 512, 256, 2]] # 38 (P4/16-medium)
+
+ - [-1, 1, ADown, [512]]
+ - [[-1, 29], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
+ - [-1, 1, RepNCSPELAN4, [512, 1024, 512, 2]] # 41 (P5/32-large)
+
+ # segment
+ - [[35, 38, 41], 1, Segment, [nc, 32, 256]] # Segment (P3, P4, P5)
diff --git a/ultralytics/cfg/models/v9/yolov9e.yaml b/ultralytics/cfg/models/v9/yolov9e.yaml
index 8e15a42b..df1cc0f0 100644
--- a/ultralytics/cfg/models/v9/yolov9e.yaml
+++ b/ultralytics/cfg/models/v9/yolov9e.yaml
@@ -1,4 +1,6 @@
-# YOLOv9
+# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
+# YOLOv9e
+# 1225 layers, 58206592 parameters, 193.0 GFLOPs
# parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
diff --git a/ultralytics/utils/plotting.py b/ultralytics/utils/plotting.py
index aed53b86..46539a46 100644
--- a/ultralytics/utils/plotting.py
+++ b/ultralytics/utils/plotting.py
@@ -364,6 +364,7 @@ class Annotator:
cv2.circle(self.im, (int(track[-1][0]), int(track[-1][1])), track_thickness * 2, color, -1)
def queue_counts_display(self, label, points=None, region_color=(255, 255, 255), txt_color=(0, 0, 0), fontsize=0.7):
+ """Displays queue counts on an image centered at the points with customizable font size and colors."""
x_values = [point[0] for point in points]
y_values = [point[1] for point in points]
center_x = sum(x_values) // len(points)
 -Developed by Baidu, [PaddlePaddle](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/en) (**PA**rallel **D**istributed **D**eep **LE**arning) is China's first open-source deep learning platform. Unlike some frameworks built mainly for research, PaddlePaddle prioritizes ease of use and smooth integration across industries.
+Developed by Baidu, [PaddlePaddle](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/en) (**PA**rallel **D**istributed **D**eep **LE**arning) is China's first open-source deep learning platform. Unlike some frameworks built mainly for research, PaddlePaddle prioritizes ease of use and smooth integration across industries.
It offers tools and resources similar to popular frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch, making it accessible for developers of all experience levels. From farming and factories to service businesses, PaddlePaddle's large developer community of over 4.77 million is helping create and deploy AI applications.
@@ -26,11 +26,11 @@ By exporting your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to PaddlePaddle format, you can tap
PaddlePaddle models offer a range of key features that contribute to their flexibility, performance, and scalability across diverse deployment scenarios:
- - **Dynamic-to-Static Graph**: PaddlePaddle supports [dynamic-to-static compilation](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/en/guides/jit/index_en.html), where models can be translated into a static computational graph. This enables optimizations that reduce runtime overhead and boost inference performance.
+- **Dynamic-to-Static Graph**: PaddlePaddle supports [dynamic-to-static compilation](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/en/guides/jit/index_en.html), where models can be translated into a static computational graph. This enables optimizations that reduce runtime overhead and boost inference performance.
- - **Operator Fusion**: PaddlePaddle, like TensorRT, uses [operator fusion](https://developer.nvidia.com/gtc/2020/video/s21436-vid) to streamline computation and reduce overhead. The framework minimizes memory transfers and computational steps by merging compatible operations, resulting in faster inference.
+- **Operator Fusion**: PaddlePaddle, like TensorRT, uses [operator fusion](https://developer.nvidia.com/gtc/2020/video/s21436-vid) to streamline computation and reduce overhead. The framework minimizes memory transfers and computational steps by merging compatible operations, resulting in faster inference.
- - **Quantization**: PaddlePaddle supports [quantization techniques](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/en/api/paddle/quantization/PTQ_en.html), including post-training quantization and quantization-aware training. These techniques allow for the use of lower-precision data representations, effectively boosting performance and reducing model size.
+- **Quantization**: PaddlePaddle supports [quantization techniques](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/en/api/paddle/quantization/PTQ_en.html), including post-training quantization and quantization-aware training. These techniques allow for the use of lower-precision data representations, effectively boosting performance and reducing model size.
## Deployment Options in PaddlePaddle
@@ -103,7 +103,7 @@ For more details about supported export options, visit the [Ultralytics document
## Deploying Exported YOLOv8 PaddlePaddle Models
-After successfully exporting your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to PaddlePaddle format, you can now deploy them. The primary and recommended first step for running a PaddlePaddle model is to use the YOLO("./model_paddle_model") method, as outlined in the previous usage code snippet.
+After successfully exporting your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to PaddlePaddle format, you can now deploy them. The primary and recommended first step for running a PaddlePaddle model is to use the YOLO("./model_paddle_model") method, as outlined in the previous usage code snippet.
However, for in-depth instructions on deploying your PaddlePaddle models in various other settings, take a look at the following resources:
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/tf-graphdef.md b/docs/en/integrations/tf-graphdef.md
index cd167272..f7d3fdb6 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/tf-graphdef.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/tf-graphdef.md
@@ -20,17 +20,17 @@ GraphDef models can use hardware accelerators such as GPUs, TPUs, and AI chips,
## Key Features of TF GraphDef Models
-TF GraphDef offers distinct features for streamlining model deployment and optimization.
+TF GraphDef offers distinct features for streamlining model deployment and optimization.
Here's a look at its key characteristics:
- - **Model Serialization**: TF GraphDef provides a way to serialize and store TensorFlow models in a platform-independent format. This serialized representation allows you to load and execute your models without the original Python codebase, making deployment easier.
+- **Model Serialization**: TF GraphDef provides a way to serialize and store TensorFlow models in a platform-independent format. This serialized representation allows you to load and execute your models without the original Python codebase, making deployment easier.
- - **Graph Optimization**: TF GraphDef enables the optimization of computational graphs. These optimizations can boost performance by streamlining execution flow, reducing redundancies, and tailoring operations to suit specific hardware.
+- **Graph Optimization**: TF GraphDef enables the optimization of computational graphs. These optimizations can boost performance by streamlining execution flow, reducing redundancies, and tailoring operations to suit specific hardware.
- - **Deployment Flexibility**: Models exported to the GraphDef format can be used in various environments, including resource-constrained devices, web browsers, and systems with specialized hardware. This opens up possibilities for wider deployment of your TensorFlow models.
+- **Deployment Flexibility**: Models exported to the GraphDef format can be used in various environments, including resource-constrained devices, web browsers, and systems with specialized hardware. This opens up possibilities for wider deployment of your TensorFlow models.
- - **Production Focus**: GraphDef is designed for production deployment. It supports efficient execution, serialization features, and optimizations that align with real-world use cases.
+- **Production Focus**: GraphDef is designed for production deployment. It supports efficient execution, serialization features, and optimizations that align with real-world use cases.
## Deployment Options with TF GraphDef
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ Here's how you can deploy with TF GraphDef efficiently across various platforms.
- **Web Browsers:** TensorFlow.js enables the deployment of TF GraphDef models directly within web browsers. It paves the way for real-time object detection applications running on the client side, using the capabilities of YOLOv8 through JavaScript.
-- **Specialized Hardware:** TF GraphDef's platform-agnostic nature allows it to target custom hardware, such as accelerators and TPUs (Tensor Processing Units). These devices can provide performance advantages for computationally intensive models.
+- **Specialized Hardware:** TF GraphDef's platform-agnostic nature allows it to target custom hardware, such as accelerators and TPUs (Tensor Processing Units). These devices can provide performance advantages for computationally intensive models.
## Exporting YOLOv8 Models to TF GraphDef
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/tf-savedmodel.md b/docs/en/integrations/tf-savedmodel.md
index 750357b6..50a4f228 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/tf-savedmodel.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/tf-savedmodel.md
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ Here are the key features that make TF SavedModel a great option for AI develope
## Deployment Options with TF SavedModel
-Before we dive into the process of exporting YOLOv8 models to the TF SavedModel format, let's explore some typical deployment scenarios where this format is used.
+Before we dive into the process of exporting YOLOv8 models to the TF SavedModel format, let's explore some typical deployment scenarios where this format is used.
TF SavedModel provides a range of options to deploy your machine learning models:
@@ -63,7 +63,6 @@ To install the required package, run:
For detailed instructions and best practices related to the installation process, check our [Ultralytics Installation guide](../quickstart.md). While installing the required packages for YOLOv8, if you encounter any difficulties, consult our [Common Issues guide](../guides/yolo-common-issues.md) for solutions and tips.
-
### Usage
Before diving into the usage instructions, it's important to note that while all [Ultralytics YOLOv8 models](../models/index.md) are available for exporting, you can ensure that the model you select supports export functionality [here](../modes/export.md).
diff --git a/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md b/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md
index f8d400e2..b87f2571 100644
--- a/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md
+++ b/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md
@@ -36,16 +36,16 @@ This section details the models available with their specific pre-trained weight
All the YOLOv8-World weights have been directly migrated from the official [YOLO-World](https://github.com/AILab-CVC/YOLO-World) repository, highlighting their excellent contributions.
-| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
-|-----------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------|-----------|------------|----------|--------|
-| YOLOv8s-world | [yolov8s-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8s-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
-| YOLOv8s-worldv2 | [yolov8s-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8s-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
-| YOLOv8m-world | [yolov8m-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8m-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
-| YOLOv8m-worldv2 | [yolov8m-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8m-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
-| YOLOv8l-world | [yolov8l-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8l-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
-| YOLOv8l-worldv2 | [yolov8l-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8l-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
-| YOLOv8x-world | [yolov8x-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8x-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
-| YOLOv8x-worldv2 | [yolov8x-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8x-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
+| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
+|-----------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------|-----------|------------|----------|--------|
+| YOLOv8s-world | [yolov8s-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8s-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
+| YOLOv8s-worldv2 | [yolov8s-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8s-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
+| YOLOv8m-world | [yolov8m-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8m-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
+| YOLOv8m-worldv2 | [yolov8m-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8m-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
+| YOLOv8l-world | [yolov8l-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8l-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
+| YOLOv8l-worldv2 | [yolov8l-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8l-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
+| YOLOv8x-world | [yolov8x-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8x-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
+| YOLOv8x-worldv2 | [yolov8x-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8x-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
## Zero-shot Transfer on COCO Dataset
diff --git a/docs/en/models/yolov9.md b/docs/en/models/yolov9.md
index 51ddfff8..da53ca2d 100644
--- a/docs/en/models/yolov9.md
+++ b/docs/en/models/yolov9.md
@@ -58,21 +58,37 @@ The performance of YOLOv9 on the [COCO dataset](../datasets/detect/coco.md) exem
**Table 1. Comparison of State-of-the-Art Real-Time Object Detectors**
-| Model | size
-Developed by Baidu, [PaddlePaddle](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/en) (**PA**rallel **D**istributed **D**eep **LE**arning) is China's first open-source deep learning platform. Unlike some frameworks built mainly for research, PaddlePaddle prioritizes ease of use and smooth integration across industries.
+Developed by Baidu, [PaddlePaddle](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/en) (**PA**rallel **D**istributed **D**eep **LE**arning) is China's first open-source deep learning platform. Unlike some frameworks built mainly for research, PaddlePaddle prioritizes ease of use and smooth integration across industries.
It offers tools and resources similar to popular frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch, making it accessible for developers of all experience levels. From farming and factories to service businesses, PaddlePaddle's large developer community of over 4.77 million is helping create and deploy AI applications.
@@ -26,11 +26,11 @@ By exporting your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to PaddlePaddle format, you can tap
PaddlePaddle models offer a range of key features that contribute to their flexibility, performance, and scalability across diverse deployment scenarios:
- - **Dynamic-to-Static Graph**: PaddlePaddle supports [dynamic-to-static compilation](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/en/guides/jit/index_en.html), where models can be translated into a static computational graph. This enables optimizations that reduce runtime overhead and boost inference performance.
+- **Dynamic-to-Static Graph**: PaddlePaddle supports [dynamic-to-static compilation](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/en/guides/jit/index_en.html), where models can be translated into a static computational graph. This enables optimizations that reduce runtime overhead and boost inference performance.
- - **Operator Fusion**: PaddlePaddle, like TensorRT, uses [operator fusion](https://developer.nvidia.com/gtc/2020/video/s21436-vid) to streamline computation and reduce overhead. The framework minimizes memory transfers and computational steps by merging compatible operations, resulting in faster inference.
+- **Operator Fusion**: PaddlePaddle, like TensorRT, uses [operator fusion](https://developer.nvidia.com/gtc/2020/video/s21436-vid) to streamline computation and reduce overhead. The framework minimizes memory transfers and computational steps by merging compatible operations, resulting in faster inference.
- - **Quantization**: PaddlePaddle supports [quantization techniques](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/en/api/paddle/quantization/PTQ_en.html), including post-training quantization and quantization-aware training. These techniques allow for the use of lower-precision data representations, effectively boosting performance and reducing model size.
+- **Quantization**: PaddlePaddle supports [quantization techniques](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/documentation/docs/en/api/paddle/quantization/PTQ_en.html), including post-training quantization and quantization-aware training. These techniques allow for the use of lower-precision data representations, effectively boosting performance and reducing model size.
## Deployment Options in PaddlePaddle
@@ -103,7 +103,7 @@ For more details about supported export options, visit the [Ultralytics document
## Deploying Exported YOLOv8 PaddlePaddle Models
-After successfully exporting your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to PaddlePaddle format, you can now deploy them. The primary and recommended first step for running a PaddlePaddle model is to use the YOLO("./model_paddle_model") method, as outlined in the previous usage code snippet.
+After successfully exporting your Ultralytics YOLOv8 models to PaddlePaddle format, you can now deploy them. The primary and recommended first step for running a PaddlePaddle model is to use the YOLO("./model_paddle_model") method, as outlined in the previous usage code snippet.
However, for in-depth instructions on deploying your PaddlePaddle models in various other settings, take a look at the following resources:
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/tf-graphdef.md b/docs/en/integrations/tf-graphdef.md
index cd167272..f7d3fdb6 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/tf-graphdef.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/tf-graphdef.md
@@ -20,17 +20,17 @@ GraphDef models can use hardware accelerators such as GPUs, TPUs, and AI chips,
## Key Features of TF GraphDef Models
-TF GraphDef offers distinct features for streamlining model deployment and optimization.
+TF GraphDef offers distinct features for streamlining model deployment and optimization.
Here's a look at its key characteristics:
- - **Model Serialization**: TF GraphDef provides a way to serialize and store TensorFlow models in a platform-independent format. This serialized representation allows you to load and execute your models without the original Python codebase, making deployment easier.
+- **Model Serialization**: TF GraphDef provides a way to serialize and store TensorFlow models in a platform-independent format. This serialized representation allows you to load and execute your models without the original Python codebase, making deployment easier.
- - **Graph Optimization**: TF GraphDef enables the optimization of computational graphs. These optimizations can boost performance by streamlining execution flow, reducing redundancies, and tailoring operations to suit specific hardware.
+- **Graph Optimization**: TF GraphDef enables the optimization of computational graphs. These optimizations can boost performance by streamlining execution flow, reducing redundancies, and tailoring operations to suit specific hardware.
- - **Deployment Flexibility**: Models exported to the GraphDef format can be used in various environments, including resource-constrained devices, web browsers, and systems with specialized hardware. This opens up possibilities for wider deployment of your TensorFlow models.
+- **Deployment Flexibility**: Models exported to the GraphDef format can be used in various environments, including resource-constrained devices, web browsers, and systems with specialized hardware. This opens up possibilities for wider deployment of your TensorFlow models.
- - **Production Focus**: GraphDef is designed for production deployment. It supports efficient execution, serialization features, and optimizations that align with real-world use cases.
+- **Production Focus**: GraphDef is designed for production deployment. It supports efficient execution, serialization features, and optimizations that align with real-world use cases.
## Deployment Options with TF GraphDef
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ Here's how you can deploy with TF GraphDef efficiently across various platforms.
- **Web Browsers:** TensorFlow.js enables the deployment of TF GraphDef models directly within web browsers. It paves the way for real-time object detection applications running on the client side, using the capabilities of YOLOv8 through JavaScript.
-- **Specialized Hardware:** TF GraphDef's platform-agnostic nature allows it to target custom hardware, such as accelerators and TPUs (Tensor Processing Units). These devices can provide performance advantages for computationally intensive models.
+- **Specialized Hardware:** TF GraphDef's platform-agnostic nature allows it to target custom hardware, such as accelerators and TPUs (Tensor Processing Units). These devices can provide performance advantages for computationally intensive models.
## Exporting YOLOv8 Models to TF GraphDef
diff --git a/docs/en/integrations/tf-savedmodel.md b/docs/en/integrations/tf-savedmodel.md
index 750357b6..50a4f228 100644
--- a/docs/en/integrations/tf-savedmodel.md
+++ b/docs/en/integrations/tf-savedmodel.md
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ Here are the key features that make TF SavedModel a great option for AI develope
## Deployment Options with TF SavedModel
-Before we dive into the process of exporting YOLOv8 models to the TF SavedModel format, let's explore some typical deployment scenarios where this format is used.
+Before we dive into the process of exporting YOLOv8 models to the TF SavedModel format, let's explore some typical deployment scenarios where this format is used.
TF SavedModel provides a range of options to deploy your machine learning models:
@@ -63,7 +63,6 @@ To install the required package, run:
For detailed instructions and best practices related to the installation process, check our [Ultralytics Installation guide](../quickstart.md). While installing the required packages for YOLOv8, if you encounter any difficulties, consult our [Common Issues guide](../guides/yolo-common-issues.md) for solutions and tips.
-
### Usage
Before diving into the usage instructions, it's important to note that while all [Ultralytics YOLOv8 models](../models/index.md) are available for exporting, you can ensure that the model you select supports export functionality [here](../modes/export.md).
diff --git a/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md b/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md
index f8d400e2..b87f2571 100644
--- a/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md
+++ b/docs/en/models/yolo-world.md
@@ -36,16 +36,16 @@ This section details the models available with their specific pre-trained weight
All the YOLOv8-World weights have been directly migrated from the official [YOLO-World](https://github.com/AILab-CVC/YOLO-World) repository, highlighting their excellent contributions.
-| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
-|-----------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------|-----------|------------|----------|--------|
-| YOLOv8s-world | [yolov8s-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8s-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
-| YOLOv8s-worldv2 | [yolov8s-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8s-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
-| YOLOv8m-world | [yolov8m-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8m-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
-| YOLOv8m-worldv2 | [yolov8m-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8m-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
-| YOLOv8l-world | [yolov8l-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8l-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
-| YOLOv8l-worldv2 | [yolov8l-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8l-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
-| YOLOv8x-world | [yolov8x-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8x-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
-| YOLOv8x-worldv2 | [yolov8x-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8x-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
+| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
+|-----------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------|-----------|------------|----------|--------|
+| YOLOv8s-world | [yolov8s-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8s-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
+| YOLOv8s-worldv2 | [yolov8s-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8s-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
+| YOLOv8m-world | [yolov8m-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8m-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
+| YOLOv8m-worldv2 | [yolov8m-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8m-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
+| YOLOv8l-world | [yolov8l-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8l-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
+| YOLOv8l-worldv2 | [yolov8l-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8l-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
+| YOLOv8x-world | [yolov8x-world.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8x-world.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
+| YOLOv8x-worldv2 | [yolov8x-worldv2.pt](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.1.0/yolov8x-worldv2.pt) | [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
## Zero-shot Transfer on COCO Dataset
diff --git a/docs/en/models/yolov9.md b/docs/en/models/yolov9.md
index 51ddfff8..da53ca2d 100644
--- a/docs/en/models/yolov9.md
+++ b/docs/en/models/yolov9.md
@@ -58,21 +58,37 @@ The performance of YOLOv9 on the [COCO dataset](../datasets/detect/coco.md) exem
**Table 1. Comparison of State-of-the-Art Real-Time Object Detectors**
-| Model | size